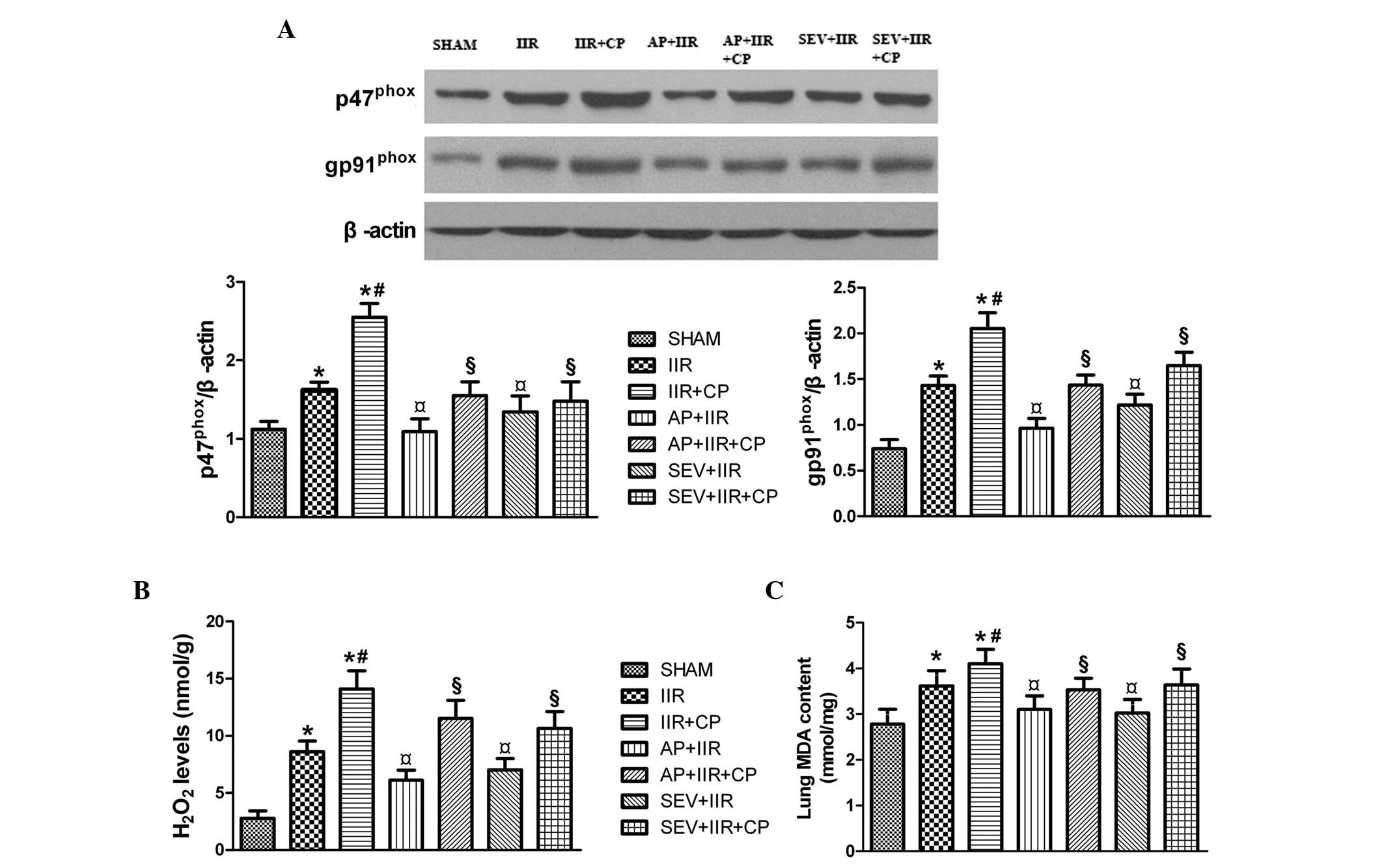
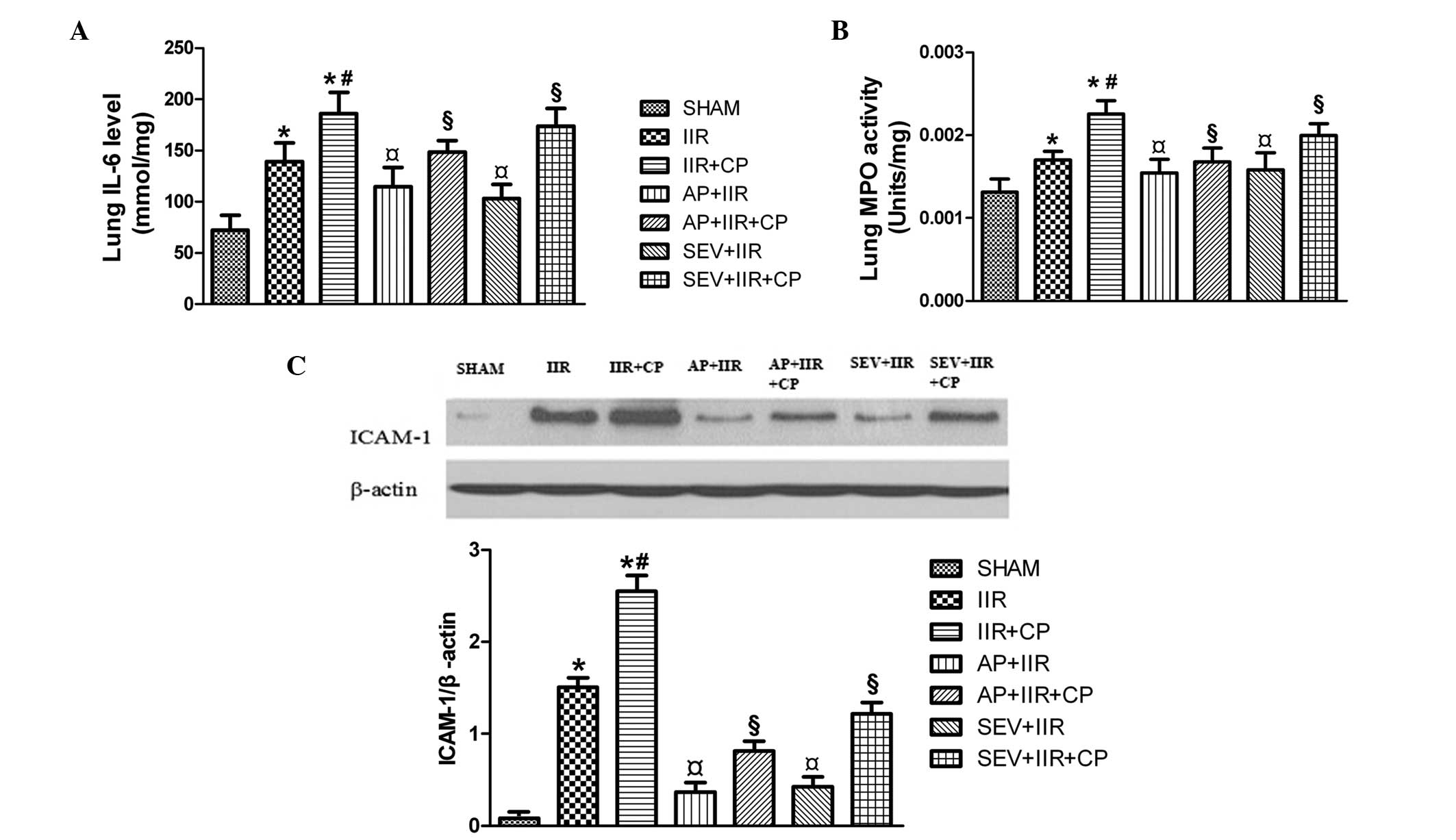
|
1
|
Douzinas EE, Orfanos SE, Livaditi O, et
al: Hypoxemic resuscitation prevents pulmonary capillary
endothelial dysfunction induced by normoxemic resuscitation from
hemorrhagic shock. Crit Care Med. 37:869–875. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Haglund U and Bergqvist D: Intestinal
ischemia-the basics. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 384:233–238. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mallick IH, Yang W, Winslet MC and
Seifalian AM: Ischemia-reperfusion injury of the intestine and
protective strategies against injury. Dig Dis Sci. 49:1359–1377.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kosieradzki M, Lisik W, Rowiński W and
Małkowski P: Progress in abdominal organ transplantation. Med Sci
Monit. 17:RA282–291. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Frutos-Vivar F, Ferguson ND and Esteban A:
Epidemiology of acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress
syndrome. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 27:327–336. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ben DF, Yu XY, Ji GY, et al: TLR4 mediates
lung injury and inflammation in intestinal ischemia-reperfusion. J
Surg Res. 174:326–333. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Guzel A, Kanter M, Pergel A and Erboga M:
Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of infliximab on acute
lung injury in a rat model of intestinal ischemia/reperfusion. J
Mol Histol. 43:361–369. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chabot F, Mitchell JA, Gutteridge JM and
Evans TW: Reactive oxygen species in acute lung injury. Eur Respir
J. 11:745–757. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tasoulis MK, Livaditi O, Stamatakos M, et
al: High concentrations of reactive oxygen species in the BAL fluid
are correlated with lung injury in rabbits after hemorrhagic shock
and resuscitation. Tohoku J Exp Med. 219:193–199. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee JH, Jo YH, Kim K, et al: Effect of
N-acetylcysteine (NAC) on acute lung injury and acute kidney injury
in hemorrhagic shock. Resuscitation. 84:121–127. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Gan X, Su G, Zhao W, Huang P, Luo G and
Hei Z: The mechanism of sevoflurane preconditioning-induced
protections against small intestinal ischemia reperfusion injury is
independent of mast cell in rats. Mediators Inflamm.
2013:3787032013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Campos R, Shimizu MH, Volpini RA, et al:
N-acetylcysteine prevents pulmonary edema and acute kidney injury
in rats with sepsis submitted to mechanical ventilation. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 302:L640–L650. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang P, Liu D, Gan X, et al: Mast cells
activation contribute to small intestinal ischemia reperfusion
induced acute lung injury in rats. Injury. 43:1250–1256. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
van den Elsen LW, Nusse Y, Balvers M, et
al: n-3 Long-chain PUFA reduce allergy-related mediator release by
human mast cells in vitro via inhibition of reactive oxygen
species. Br J Nutr. 109:1821–1831. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Sawaguchi M, Tanaka S, Nakatani Y, et al:
Role of mast cells and basophils in IgE responses and in allergic
airway hyperrespon-siveness. J Immunol. 188:1809–1818. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xia YC, Harris T, Stewart AG and Mackay
GA: Secreted factors from human mast cells trigger inflammatory
cytokine production by human airway smooth muscle cells. Int Arch
Allergy Immunol. 160:75–85. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Chandler JR, Myers D, Mehta D, et al:
Emergence delirium in children: a randomized trial to compare total
intravenous anesthesia with propofol and remifentanil to
inhalational sevoflurane anesthesia. Paediatr Anaesth. 23:309–315.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bi SS, Deng CH, Zhou TY, et al:
Remifentanil-sevoflurane interaction models of circulatory response
to laryngoscopy and circulatory depression. Br J Anaesth.
110:729–740. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Casanova J, Garutti I, Simon C, et al: The
effects of anesthetic preconditioning with sevoflurane in an
experimental lung auto-transplant model in pigs. Anesth Analg.
113:742–748. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hu X, Zhang Y, Li W, Liu J and Li Y:
Preconditioning with sevoflurane ameliorates spatial learning and
memory deficit after focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in rats.
Int J Dev Neurosci. 31:328–333. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bedirli N, Demirtas CY, Akkaya T, et al:
Volatile anesthetic preconditioning attenuated sepsis induced lung
inflammation. J Surg Res. 178:e17–23. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xiong XQ, Lin LN, Wang LR and Jin LD:
Sevoflurane attenuates pulmonary inflammation and
ventilator-induced lung injury by upregulation of HO-1 mRNA
expression in mice. Int J Nanomedicine. 6:1075–1081. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Song SY, Zhou B, Yang SM, Liu GZ, Tian JM
and Yue XQ: Preventive effects of sevoflurane treatment on lung
inflammation in rats. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 6:53–56. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ye R, Yang Q, Kong X, et al: Sevoflurane
preconditioning improves mitochondrial function and long-term
neurologic sequelae after transient cerebral ischemia: role of
mitochondrial permeability transition. Crit Care Med. 40:2685–2693.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Paterniti I, Galuppo M, Mazzon E, et al:
Protective effects of apocynin, an inhibitor of NADPH oxidase
activity, in splanchnic artery occlusion and reperfusion. J Leukoc
Biol. 88:993–1003. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gan X, Liu D, Huang P, Gao W, Chen X and
Hei Z: Mast-cell-releasing tryptase triggers acute lung injury
induced by small intestinal ischemia-reperfusion by activating
PAR-2 in rats. Inflammation. 35:1144–1153. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Hofbauer B, Saluja AK, Bhatia M, et al:
Effect of recombinant platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase on
two models of experimental acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology.
115:1238–1247. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mirzahosseini A, Dalmadi B and Csutora P:
Histamine receptor H4 regulates mast cell degranulation and IgE
induced FcεRI upregulation in murine bone marrow-derived mast
cells. Cell Immunol. 283:38–44. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Neveu WA, Allard JL, Raymond DM, et al:
Elevation of IL-6 in the allergic asthmatic airway is independent
of inflammation but associates with loss of central airway
function. Respir Res. 11:282010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mullane KM, Kraemer R and Smith B:
Myeloperoxidase activity as a quantitative assessment of neutrophil
infiltration into ischemic myocardium. J Pharmacol Methods.
14:157–167. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Grek CL, Newton DA, Spyropoulos DD and
Baatz JE: Hypoxia up-regulates expression of hemoglobin in alveolar
epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 44:439–447. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Frieri M, Patel R and Celestin J: Mast
cell activation syndrome: a review. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep.
13:27–32. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Kleniewska P, Piechota A, Skibska B and
Gorąca A: The NADPH oxidase family and its inhibitors. Arch Immunol
Ther Exp (Warsz). 60:277–294. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Shen A, Yang J, Gu Y, et al:
Lipopolysaccharide-evoked activation of p38 and JNK leads to an
increase in ICAM-1 expression in Schwann cells of sciatic nerves.
FEBS J. 275:4343–4353. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Elnakish MT, Hassanain HH, Janssen PM,
Angelos MG and Khan M: Emerging role of oxidative stress in
metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular diseases: important role of
Rac/NADPH oxidase. J Pathol. 231:290–300. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang J, Qiao L, Li S and Yang G:
Protective effect of ginsenoside Rb1 against lung injury induced by
intestinal ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Molecules. 18:1214–1226.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mao YF, Zheng XF, Cai JM, et al:
Hydrogen-rich saline reduces lung injury induced by intestinal
ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
381:602–605. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Rossman JE, Caty MG, Zheng S, et al:
Mucosal protection from intestinal ischemia-reperfusion reduces
oxidant injury to the lung. J Surg Res. 73:41–46. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Ramos L, Peña G, Cai B, Deitch EA and
Ulloa L: Mast cell stabilization improves survival by preventing
apoptosis in sepsis. J Immunol. 185:709–716. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fishman JE, Sheth SU, Levy G, et al:
Intraluminal nonbacterial intestinal components control gut and
lung injury after trauma hemorrhagic shock. Ann Surg.
260:1112–1120. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhao W, Gan X, Su G, et al: The
interaction between oxidative stress and mast cell activation plays
a role in acute lung injuries induced by intestinal
ischemia-reperfusion. J Surg Res. 187:542–552. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Wingard CJ, Walters DM, Cathey BL, et al:
Mast cells contribute to altered vascular reactivity and
ischemia-reper-fusion injury following cerium oxide nanoparticle
instillation. Nanotoxicology. 5:531–545. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
43
|
Mukundan C, Gurish MF, Austen KF, Hechtman
HB and Friend DS: Mast cell mediation of muscle and pulmonary
injury following hindlimb ischemia-reperfusion. J Histochem
Cytochem. 49:1055–1056. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Han W, Lu X, Jia X, Zhou T and Guo C:
Soluble mediators released from PI-IBS patients’ colon induced
alteration of mast cell: involvement of reactive oxygen species.
Dig Dis Sci. 57:311–319. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Zhao J, Wang F, Zhang Y, et al:
Sevoflurane preconditioning attenuates myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury via caveolin-3-dependent
cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition. Circulation. 128(11 Suppl 1): 121–129.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Zhou SP, Liao WT, Yang LK and Sun L:
Effects of sevoflurane pretreatment on renal Src and FAK expression
in diabetic rats after renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Mol Cell
Biochem. 384:203–211. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Liu R, Ishibe Y and Ueda M:
Isoflurane-sevoflurane admin-stration before ischemia attenuates
ischemia-reperfusion-induced injury in isolated rat lungs.
Anesthesiology. 92:833–840. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kong HY, Zhu SM, Wang LQ, He Y, Xie HY and
Zheng SS: Sevoflurane protects against acute kidney injury in a
small-size liver transplantation model. Am J Nephrol. 32:347–355.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yang Q, Dong H, Deng J, et al: Sevoflurane
preconditioning induces neuroprotection through reactive oxygen
species-mediated up-regulation of antioxidant enzymes in rats.
Anesth Analg. 112:931–937. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Breithaupt-Faloppa AC, Fantozzi ET, de
Assis-Ramos MM, et al: Protective effect of estradiol on acute lung
inflammation induced by an intestinal ischemic insult is dependent
on nitric oxide. Shock. 40:203–209. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Guido BC, Zanatelli M, Tavares-de-Lima W,
Oliani SM and Damazo AS: Annexin-A1 peptide down-regulates the
leukocyte recruitment and up-regulates interleukin-10 release into
lung after intestinal ischemia-reperfusion in mice. J Inflamm
(Lond). 10:102013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Neri M, Fineschi V, Di Paolo M, et al:
Cardiac Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Cytokines Response After
Myocardial Infarction. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2013.
|
|
53
|
Thiyagarajan R, Subramanian SK, Sampath N,
et al: Association between cardiac autonomic function, oxidative
stress and inflammatory response in impaired fasting glucose
subjects: cross-sectional study. PLoS One. 7:e418892012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Könczöl M, Weiß A, Gminski R, Merfort I
and Mersch-Sundermann V: Oxidative stress and inflammatory response
to printer toner particles in human epithelial A549 lung cells.
Toxicol Lett. 216:171–180. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Lloberas N, Torras J, Herrero-Fresneda I,
et al: Postischemic renal oxidative stress induces inflammatory
response through PAF and oxidized phospholipids. Prevention by
antioxidant treatment FASEB J. 16:908–910. 2002.
|