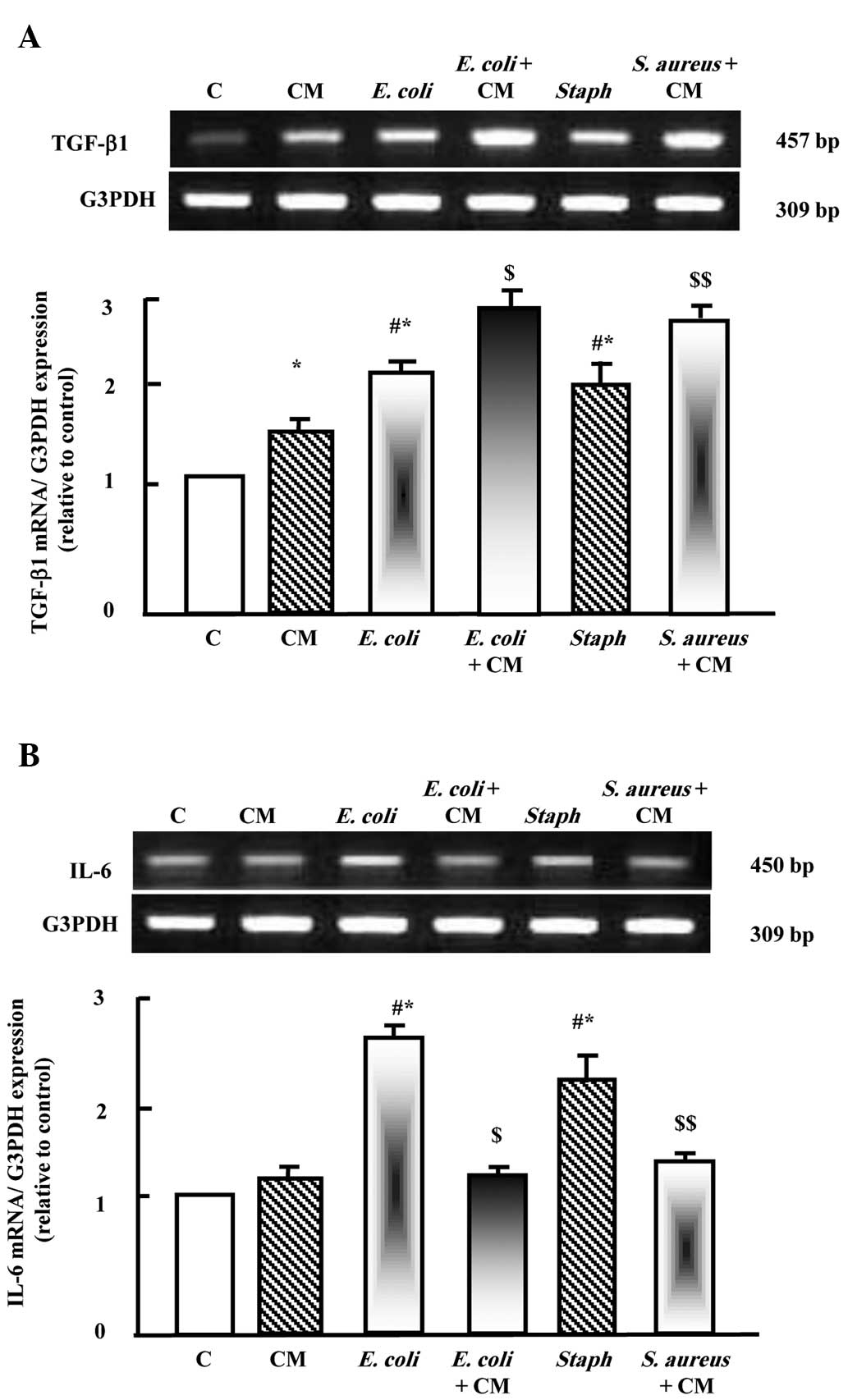
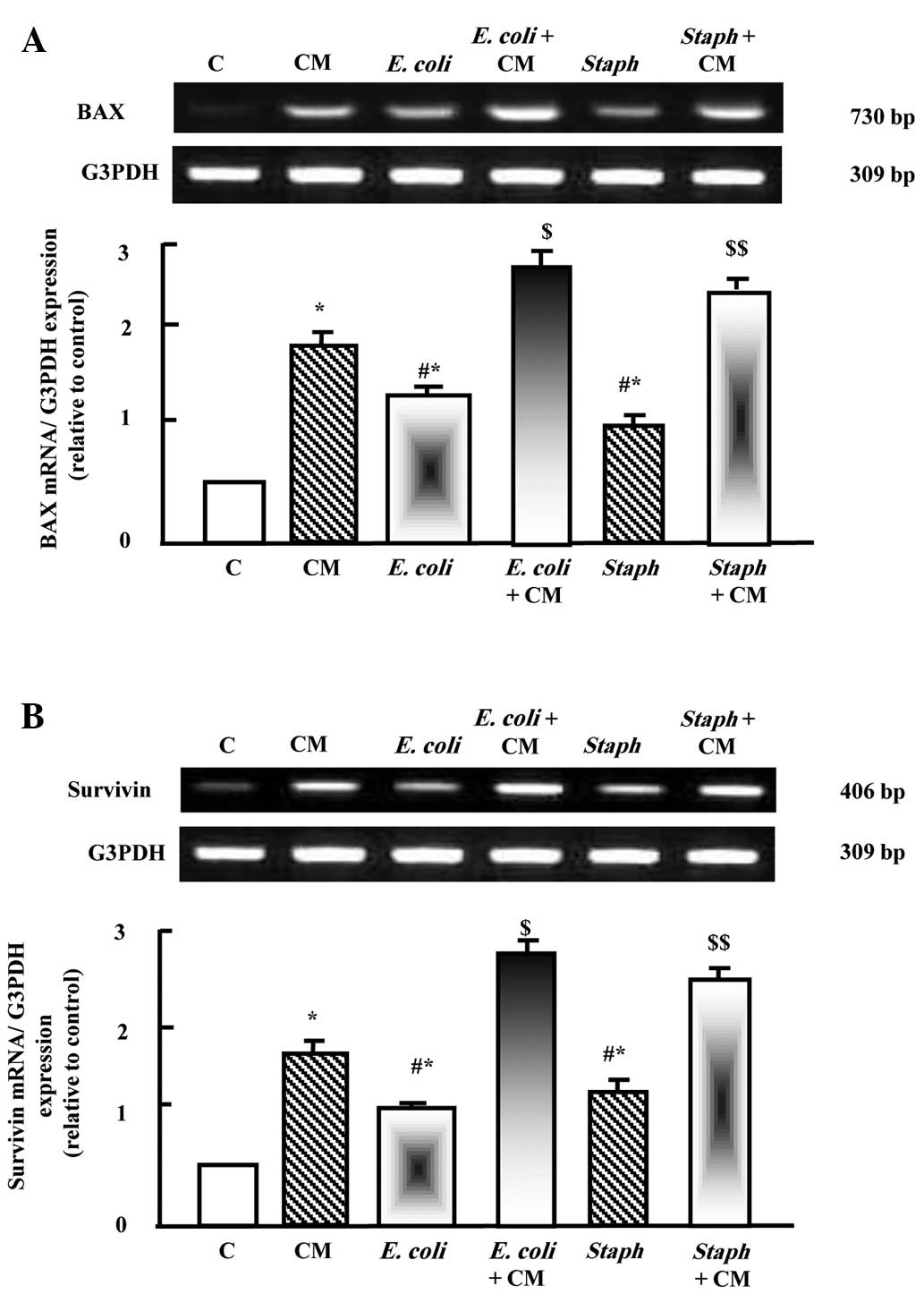
|
1
|
el Agamy EI, Ruppanner R, Ismail A,
Champagne CP and Assaf R: Antibacterial and antiviral activity of
camel milk protective proteins. J Dairy Res. 59:169–175. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kappeler S, Farah Z and Puhan Z:
Alternative splicing of lactophorin mRNA from lactating mammary
gland of the camel (Camelus dromedarius). J Dairy Sci.
82:2084–2093. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yagil R, Saran A and Etzion Z: Camel's
milk: For drinking only? Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol.
78:263–266. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Korhonen H and Pihlanto A: Food-derived
bioactive peptides-opportunities for designing future foods. Curr
Pharm Des. 9:1297–1308. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Omer RH and Eltinay AH: Changes in
chemical composition of Camel's raw milk during storage. Pak J
Nutr. 8:607–610. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Rao MB, Gupta RC and Dastur NN: Camel milk
and milk products. Indian J Dairy Sci. 23:71–78. 1970.
|
|
7
|
Al-Hashem F: Camel milk protects against
aluminium chloride-induced toxicity in the liver and kidney of
white albino rats. Am J Biochem Biotechnol. 5:98–108. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Dallak MA, Bin-Jaliah I, Al-Khateeb MA,
Nwoye LO, Shatoor AS, Soliman HS and Al-Hashem FH: In vivo acute
effects of orally administered hydro-ethanol extract of Catha
edulis on blood glucose levels in normal, glucose-fed hyperglycemic
and alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Saudi Med J. 31:627–633.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Khan AA and Alzohairy M: Hepatoprotective
effects of camel milk against CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity in Rats.
Asian J Biochem. 6:171–180. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Aff MEM: Effect of camel's milk on
cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in swiss albino mice. Am J Biochem
Biotechnol. 6:1472010.
|
|
11
|
Al-Fartosi KG, Khuon OS and Al-Tae HI:
Protective role of camel's milk against paracetamol induced
hepatotoxicity in male rats. Int J Res Pharmaceut Biomed Sci.
2:1795–1799. 2011.
|
|
12
|
Kappeler SR, Heuberger C, Farah Z and
Puhan Z: Expression of the peptidoglycan recognition protein, PGRP,
in the lactating mammary gland. J Dairy Sci. 87:2660–2668. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Velioglu Ogünç A, Manukyan M, Cingi A,
Eksioglu-Demiralp E, Ozdemir Aktan A and Süha Yalçin A: Dietary
whey supplementation in experimental models of wound healing. Int J
Vitam Nutr Res. 78:70–73. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Korashy HM, Maayah ZH, Abd-Allah AR,
El-Kadi AO and Alhaider AA: Camel milk triggers apoptotic signaling
pathways in human hepatoma HepG2 and breast cancer MCF7 cell lines
through transcriptional mechanism. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2012:5931952012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cenci-Goga BT, Karama M, Rossitto PV,
Morgante RA and Cullor JS: Enterotoxin production by Staphylococcus
aureus isolated from mastitic cows. J Food Prot. 66:1693–1696.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cimolai N: MRSA and the environment:
Implications for comprehensive control measures. Eur J Clin
Microbiol Infect Dis. 27:481–493. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Curran JP and Al-Salihi FL: Neonatal
staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome: Massive outbreak due to an
unusual phage type. Pediatrics. 66:285–290. 1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Noreddine B, Majda M, Nargisse B and Kamal
H: Antimicrobial activity of camel's milk against pathogenic
strains of Escherichia coli and Listeria monocytogenes. Int J Dairy
Infect. 5:39–43. 2004.
|
|
19
|
Althnaian T, Albokhadaim I and El-Bahr SM:
Biochemical and histopathological study in rats intoxicated with
carbontetrachloride and treated with camel milk. SpringerPlus.
2:572013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cirioni O, Giacometti A, Ghiselli R,
Bergnach C, Orlando F, Silvestri C, Mocchegiani F, Licci A,
Skerlavaj B, Rocchi M, et al: LL-37 protects rats against lethal
sepsis caused by gram-negative bacteria. Antimicrob Agents
Chemother. 50:1672–1679. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hari Prasad O, Navya A, Vasu D and
Chiranjeevi T: Protective effects of Prosopis juliflora against
Staphylococcus aureus induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Int J Pharm
Biomed Res. 2:172–178. 2011.
|
|
22
|
Soliman MM, Baiyoumi AA and Yassin MH:
Molecular and histopathological study on the ameliorative effects
of curcumin against lead acetate-induced hepatotoxicity and
nephrototoxicity in wistar rats. Biol Trace Elem Res. 167:91–102.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Herr I and Debatin KM: Cellular stress
response and apoptosis in cancer therapy. Blood. 98:2603–2614.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tsang WP, Chau SP, Kong SK, Fung KP and
Kwok TT: Reactive oxygen species mediate doxorubicin induced
p53-independent apoptosis. Life Sci. 73:2047–2058. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Vecchione A and Croce CM: Apoptomirs:
Small molecules have gained the license to kill. Endocr Relat
Cancer. 17:F37–F50. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Lowe SW and Lin AW: Apoptosis in cancer.
Carcinogenesis. 21:485–495. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Feghali CA and Wright TM: Cytokines in
acute and chronic inflammation. Front Biosci. 2:d12–d26.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Arend WP and Gabay C: Cytokines in the
rheumatic diseases. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 30:41–67. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Frieboes RM, Murck H, Maier P, Schier T,
Holsboer F and Steiger A: Growth hormone-releasing peptide-6
stimulates sleep, growth hormone, ACTH and cortisol release in
normal man. Neuroendocrinology. 61:584–589. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Itoh H, Pratt RE and Dzau VJ: Atrial
natriuretic polypeptide inhibits hypertrophy of vascular smooth
muscle cells. J Clin Invest. 86:1690–1697. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Aoki H, Ohnishi H, Hama K, Ishijima T,
Satoh Y, Hanatsuka K, Ohashi A, Wada S, Miyata T, Kita H, et al:
Autocrine loop between TGF-beta1 and IL-1beta through Smad3- and
ERK-dependent pathways in rat pancreatic stellate cells. Am J
Physiol Cell Physiol. 290:C1100–C1108. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Distler JH, Hirth A, Kurowska-Stolarska M,
Gay RE, Gay S and Distler O: Angiogenic and angiostatic factors in
the molecular control of angiogenesis. Q J Nucl Med. 47:149–161.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Werner S, Krieg T and Smola H:
Keratinocyte-fibroblast interactions in wound healing. J Invest
Dermatol. 127:998–1008. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Conesa C, Sánchez L, Rota C, Pérez MD,
Calvo M, Farnaud S and Evans RW: Isolation of lactoferrin from milk
of different species: Calorimetric and antimicrobial studies. Comp
Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 150:131–139. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Henry-Mowatt J, Dive C, Martinou JC and
James D: Role of mitochondrial membrane permeabilization in
apoptosis and cancer. Oncogene. 23:2850–2860. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Karst AM and Li G: BH3-only proteins in
tumorigenesis and malignant melanoma. Cell Mol Life Sci.
64:318–330. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Lavrik IN, Golks A and Krammer PH:
Caspases: Pharmacological manipulation of cell death. J Clin
Invest. 115:2665–2672. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Reed JC: Bcl-2 family proteins. Oncogene.
17:3225–3236. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Brentnall M, Rodriguez-Menocal L, De
Guevara RL, Cepero E and Boise LH: Caspase-9, caspase-3 and
caspase-7 have distinct roles during intrinsic apoptosis. BMC Cell
Biol. 14:322013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sah NK, Khan Z, Khan GJ and Bisen PS:
Structural, functional and therapeutic biology of survivin. Cancer
Lett. 244:164–171. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|