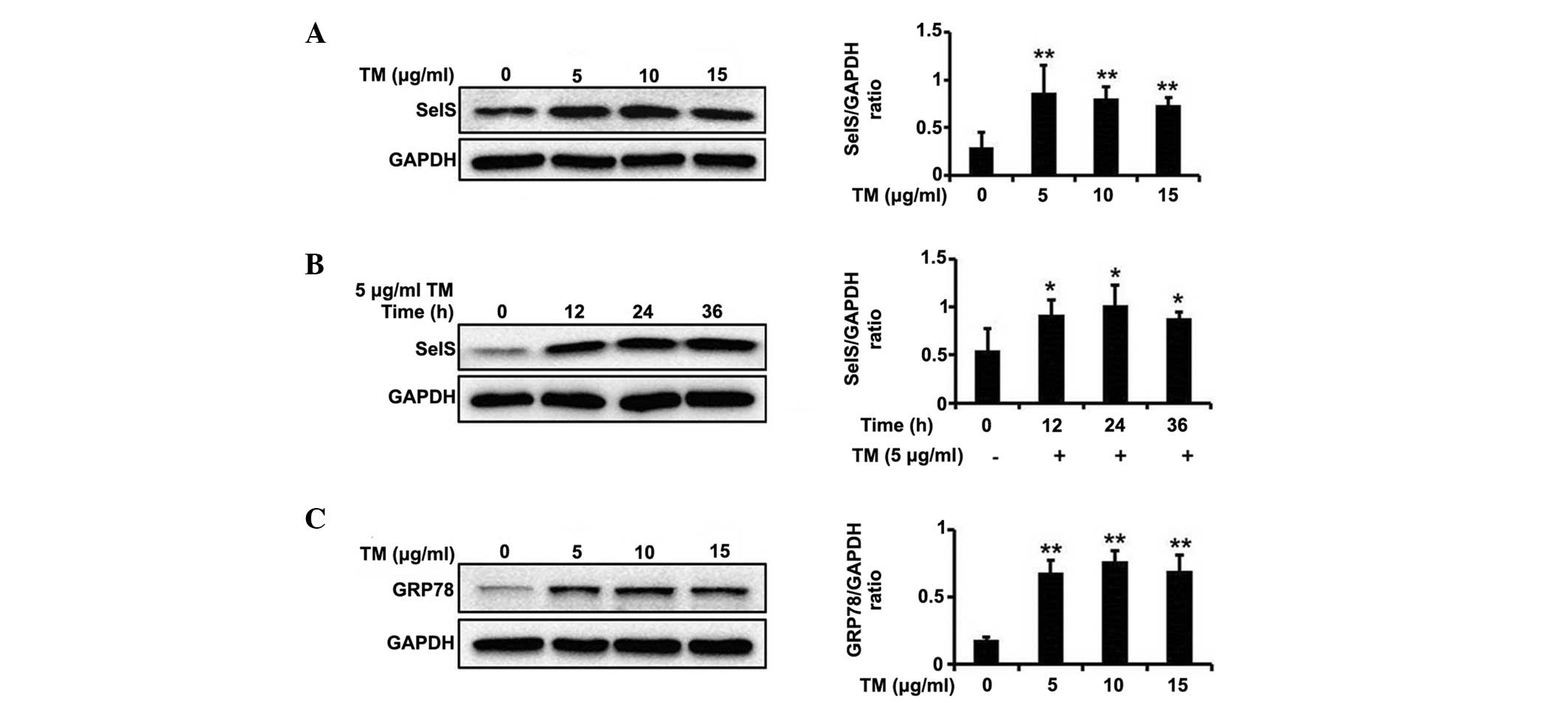
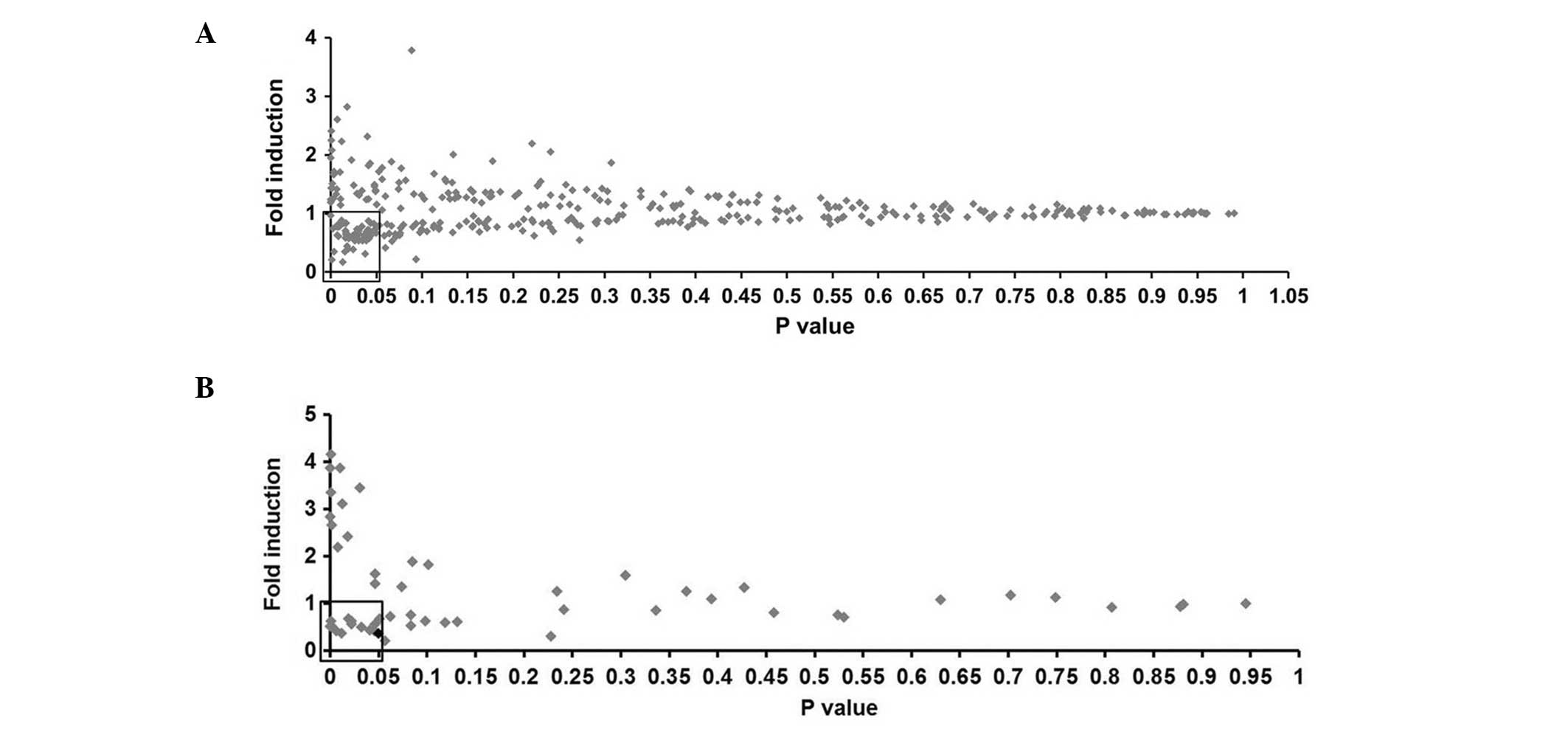
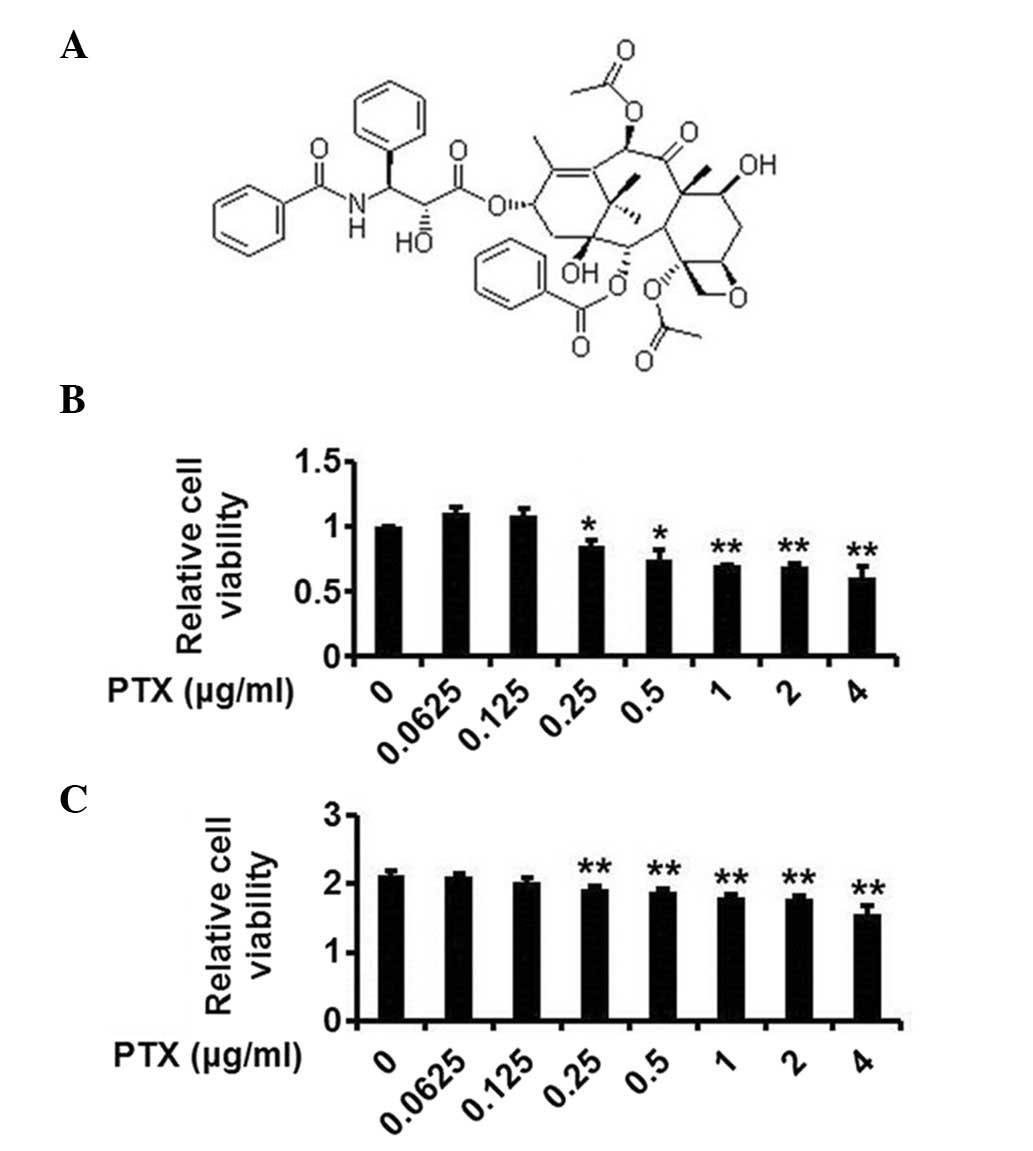
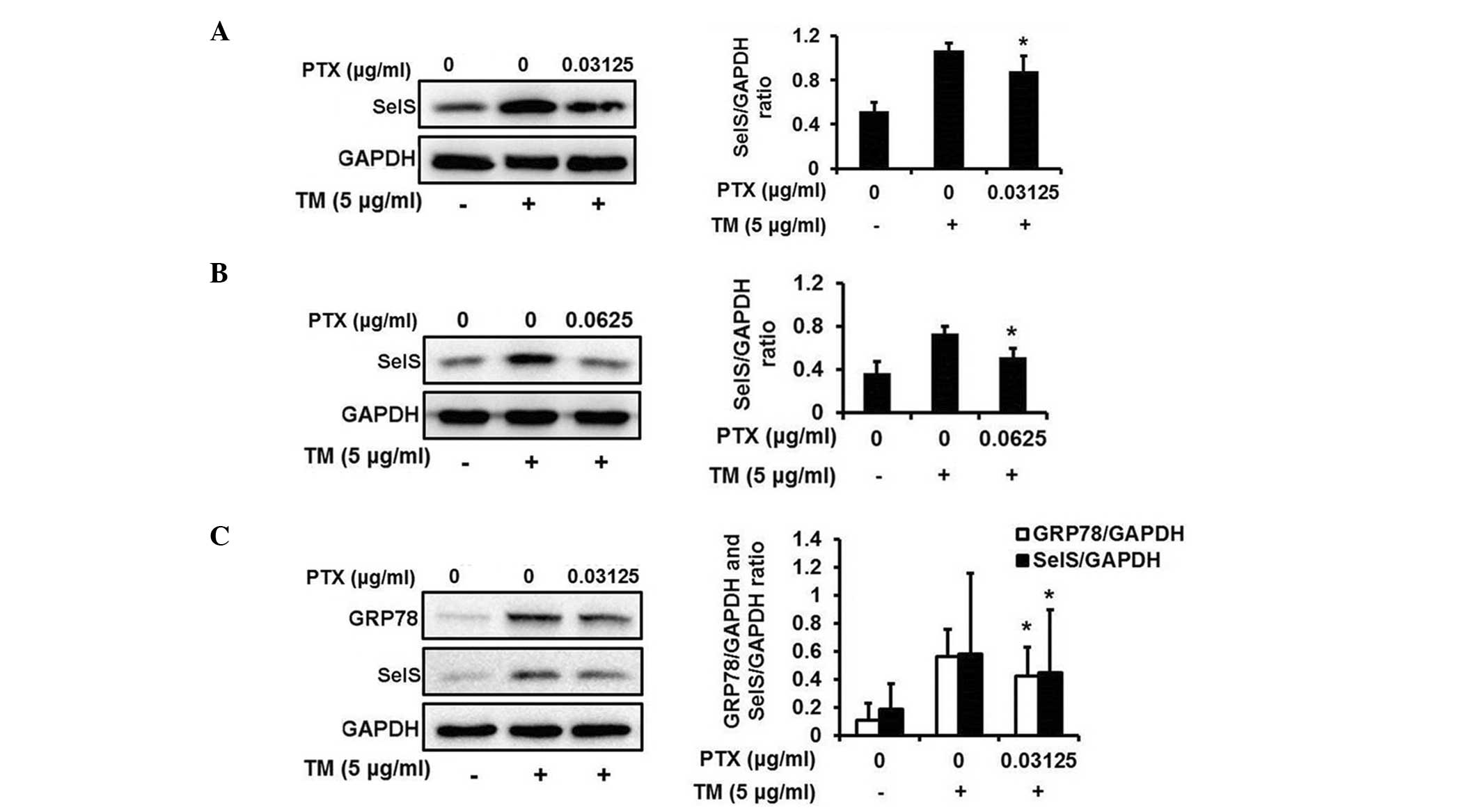
|
1
|
Gentile CL, Frye M and Pagliassotti MJ:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the unfolded protein response in
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Antioxid Redox Signal.
15:505–521. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
2
|
Marciniak SJ and Ron D: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress signaling in disease. Physiol Rev. 86:1133–1149.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Meusser B, Hirsch C, Jarosch E and Sommer
T: ERAD: The long road to destruction. Nat Cell Biol. 7:766–772.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sozen E, Karademir B and Ozer NK: Basic
mechanisms in endoplasmic reticulum stress and relation to
cardiovascular diseases. Free Radic Biol Med. 78:30–41. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zhao L and Ackerman SL: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress in health and disease. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
18:444–452. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Halliday M and Mallucci GR: Targeting the
unfolded protein response in neurodegeneration: A new approach to
therapy. Neuropharmacology. 76:169–174. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Imai Y, Soda M, Inoue H, Hattori N, Mizuno
Y and Takahashi R: An unfolded putative transmembrane polypeptide,
which can lead to endoplasmic reticulum stress, is a substrate of
Parkin. Cell. 105:891–902. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kaufman RJ: Orchestrating the unfolded
protein response in health and disease. J Clin Invest.
110:1389–1398. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Minamino T and Kitakaze M: ER stress in
cardiovascular disease. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 48:1105–1110. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Sulaiman RS, Basavarajappa HD and Corson
TW: Natural product inhibitors of ocular angiogenesis. Exp Eye Res.
129:161–171. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Corson TW and Crews CM: Molecular
understanding and modern application of traditional medicines:
Triumphs and trials. Cell. 130:769–774. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hou P, Li Y, Zhang X, Liu C, Guan J, Li H,
Zhao T, Ye J, Yang W, Liu K, et al: Pluripotent stem cells induced
from mouse somatic cells by small-molecule compounds. Science.
341:651–654. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Walder K, Kantham L, McMillan JS,
Trevaskis J, Kerr L, De Silva A, Sunderland T, Godde N, Gao Y,
Bishara N, et al: Tanis: A link between type 2 diabetes and
inflammation? Diabetes. 51:1859–1866. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ye Y, Shibata Y, Yun C, Ron D and Rapoport
TA: A membrane protein complex mediates retro-translocation from
the ER lumen into the cytosol. Nature. 429:841–847. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Du S, Liu H and Huang K: Influence of SelS
gene silence on beta-Mercaptoethanol-mediated endoplasmic reticulum
stress and cell apoptosis in HepG2 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1800:511–517. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kim KH, Gao Y, Walder K, Collier GR,
Skelton J and Kissebah AH: SEPS1 protects RAW264.7 cells from
pharmacological ER stress agent-induced apoptosis. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 354:127–132. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gao Y, Feng HC, Walder K, Bolton K,
Sunderland T, Bishara N, Quick M, Kantham L and Collier GR:
Regulation of the seleno-protein SelS by glucose deprivation and
endoplasmic reticulum stress-SelS is a novel glucose-regulated
protein. FEBS Lett. 563:185–190. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang Y, Bao YL, Wu Y, Yu CL, Sun Y and Li
YX: Identification and characterization of the human SLC5A8 gene
promoter. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 196:124–132. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lee AS: The glucose-regulated proteins:
Stress induction and clinical applications. Trends Biochem Sci.
26:504–510. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Iwasa K, Nambu Y, Motozaki Y, Furukawa Y,
Yoshikawa H and Yamada M: Increased skeletal muscle expression of
the endoplasmic reticulum chaperone GRP78 in patients with
myasthenia gravis. J Neuroimmunol. 273:72–76. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ma KX, Chen GW, Shi CY, Cheng FF, Dou H,
Feng CC and Liu DZ: Molecular characterization of the
glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78) gene in planarian Dugesia
japonica. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 171:12–17. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dara L, Ji C and Kaplowitz N: The
contribution of endoplasmic reticulum stress to liver diseases.
Hepatology. 53:1752–1763. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu H, Cao MM, Wang Y, Li LC, Zhu LB, Xie
GY and Li YB: Endoplasmic reticulum stress is involved in the
connection between inflammation and autophagy in type 2 diabetes.
Gen Comp Endocrinol. 210:124–129. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Luo T, Kim JK, Chen B, Abdel-Latif A,
Kitakaze M and Yan L: Attenuation of ER stress prevents
post-infarction-induced cardiac rupture and remodeling by
modulating both cardiac apoptosis and fibrosis. Chem Biol Interact.
225:90–98. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Torres M, Matamala JM, Duran-Aniotz C,
Cornejo VH, Foley A and Hetz C: ER stress signaling and
neurodegeneration: At the intersection between Alzheimer's disease
and Prion-related disorders. Virus Res. 207:69–75. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gao Y, Hannan NR, Wanyonyi S,
Konstantopolous N, Pagnon J, Feng HC, Jowett JB, Kim KH, Walder K
and Collier GR: Activation of the selenoprotein SEPS1 gene
expression by pro-inflammatory cytokines in HepG2 cells. Cytokine.
33:246–251. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Speckmann B, Gerloff K, Simms L, Oancea I,
Shi W, McGuckin MA, Radford-Smith G and Khanna KK: Selenoprotein S
is a marker but not a regulator of endoplasmic reticulum stress in
intestinal epithelial cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 67:265–277. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Malhi H and Kaufman RJ: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress in liver disease. J Hepatol. 54:795–809. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Taniguchi M and Yoshida H: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress in kidney function and disease. Curr Opin Nephrol
Hypertens. 24:345–350. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cnop M, Foufelle F and Velloso LA:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress, obesity and diabetes. Trends Mol Med.
18:59–68. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|