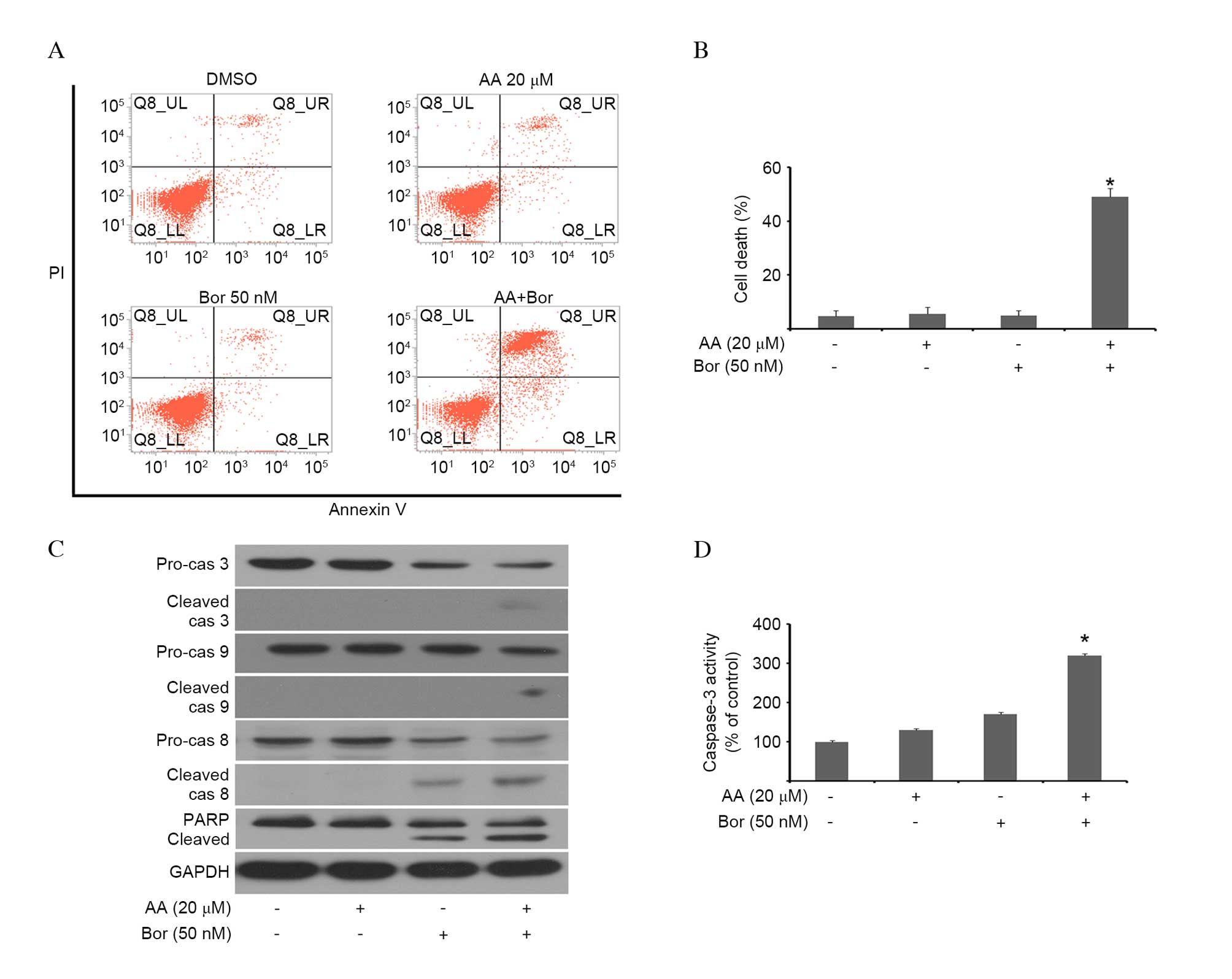
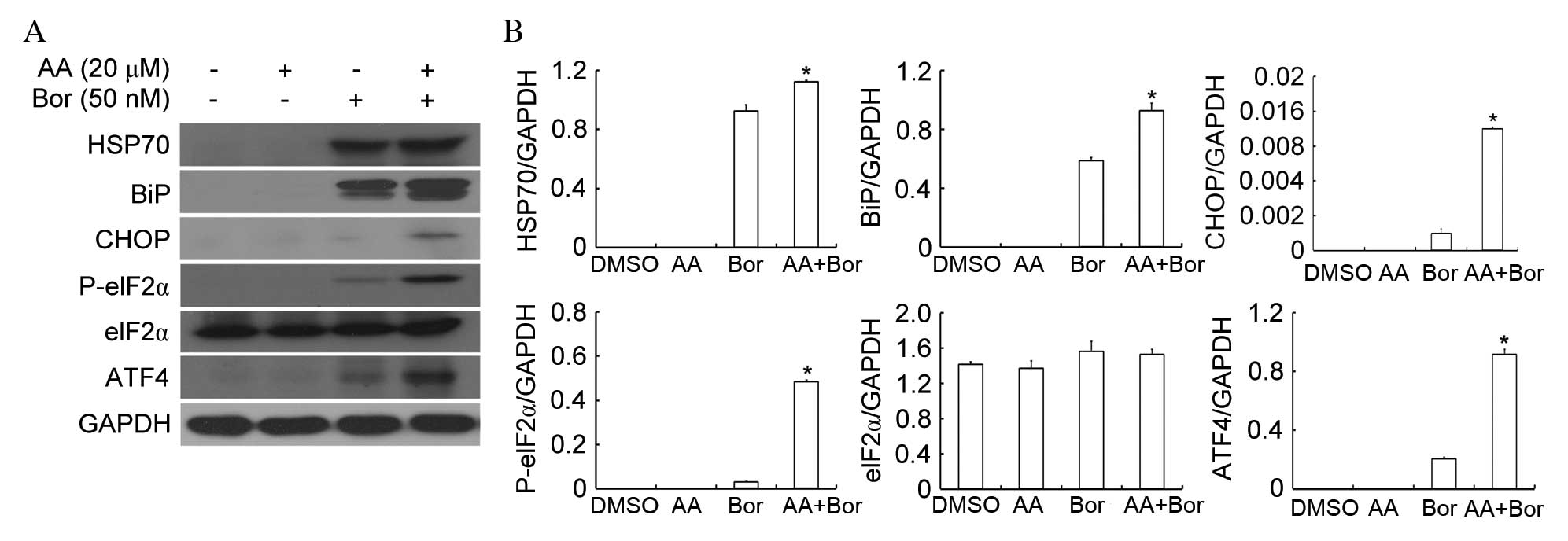
|
1
|
Sultan S, Irfan SM, Parveen S, Ali H and
Basharat M: Multiple Myeloma: A retrospective analysis of 61
patients from a tertiary care center. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
17:1833–1835. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liu JD, Sun CY, Tang L, Wu YY, Wang QY, Hu
B and Hu Y: Efficacy and safety of panobinostat in relapsed or/and
refractory multiple myeloma: Meta analyses of clinical trials and
systematic review. Sci Rep. 6:273612016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hershko A and Ciechanover A: The ubiquitin
system. Annu Rev Biochem. 67:425–479. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Adams J: The development of proteasome
inhibitors as anticancer drugs. Cancer Cell. 5:417–421. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Adams J, Palombella VJ, Sausville EA,
Johnson J, Destree A, Lazarus DD, Maas J, Pien CS, Prakash S and
Elliott PJ: Proteasome inhibitors: A novel class of potent and
effective antitumor agents. Cancer Res. 59:2615–2622.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Orlowski RZ and Dees EC: The role of the
ubiquiti-nation-proteasome pathway in breast cancer: Applying drugs
that affect the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway to the therapy of
breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 5:1–7. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Jagannathan S, Abdel-Malek MA, Malek E,
Vad N, Latif T, Anderson KC and Driscoll JJ: Pharmacologic screens
reveal metformin that suppresses GRP78-dependent autophagy to
enhance the anti-myeloma effect of bortezomib. Leukemia.
29:2184–2191. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Eriksson E, Wickström M, Perup LS, Johnsen
JI, Eksborg S, Kogner P and Sävendahl L: Protective role of humanin
on bortezomib-induced bone growth impairment in anticancer
treatment. J Natl Cancer Inst. 106:djt4592014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Huang WC, Lin YS, Chen CL, Wang CY, Chiu
WH and Lin CF: Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta mediates endoplasmic
reticulum stress-induced lysosomal apoptosis in leukemia. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 329:524–531. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jiang C, Zhang S, Liu H, Zeng Q, Xia T,
Chen Y, Kuang G, Zhao G, Wu X, Zhang X, et al: The role of the IRE1
pathway in PBDE-47-induced toxicity in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y
cells in vitro. Toxicol Lett. 211:325–333. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ron D and Walter P: Signal integration in
the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 8:519–529. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sano R and Reed JC: ER stress-induced cell
death mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1833:3460–3470. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu C, Bailly-Maitre B and Reed JC:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress: Cell life and death decisions. J Clin
Invest. 115:2656–2664. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Armstrong JL, Flockhart R, Veal GJ, Lovat
PE and Redfern CP: Regulation of endoplasmic reticulum
stress-induced cell death by ATF4 in neuroectodermal tumor cells. J
Biol Chem. 285:6091–6100. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Jiang HY and Wek RC: Phosphorylation of
the alpha-subunit of the eukaryotic initiation factor-2 (eIF2alpha)
reduces protein synthesis and enhances apoptosis in response to
proteasome inhibition. J Biol Chem. 280:14189–14202. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Qing G, Li B, Vu A, Skuli N, Walton ZE,
Liu X, Mayes PA, Wise DR, Thompson CB, Maris JM, et al: ATF4
regulates MYC-mediated neuroblastoma cell death upon glutamine
deprivation. Cancer Cell. 22:631–644. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jung J, Kim J, Roh SH, Jun I, Sampson RD,
Gee HY, Choi JY and Lee MG: The HSP70 co-chaperone DNAJC14 targets
misfolded pendrin for unconventional protein secretion. Nat Commun.
7:113862016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wu Y, He L, Zhang L, Chen J, Yi Z, Zhang
J, Liu M and Pang X: Anacardic acid (6-pentadecylsalicylic acid)
inhibits tumor angiogenesis by targeting Src/FAK/Rho GTPases
signaling pathway. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 339:403–411. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Seong YA, Shin PG and Kim GD: Anacardic
acid induces mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis in the A549 human
lung adenocarcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 42:1045–1051.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Seong YA, Shin PG, Yoon JS, Yadunandam AK
and Kim GD: Induction of the endoplasmic reticulum stress and
autophagy in human lung carcinoma A549 cells by anacardic acid.
Cell Biochem Biophys. 68:369–377. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Huang H, Hua X, Liu N, Li X, Liu S, Chen
X, Zhao C, Lan X, Yang C, Dou QP, et al: Anacardic acid induces
cell apoptosis associated with induction of ATF4-dependent
endoplasmic reticulum stress. Toxicol Lett. 228:170–178. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hill DS, Martin S, Armstrong JL, Flockhart
R, Tonison JJ, Simpson DG, Birch-Machin MA, Redfern CP and Lovat
PE: Combining the endoplasmic reticulum stress-inducing agents
bortezomib and fenretinide as a novel therapeutic strategy for
metastatic melanoma. Clin Cancer Res. 15:1192–1198. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Huang H, Liu N, Guo H, Liao S, Li X, Yang
C, Liu S, Song W, Liu C, Guan L, et al: L-carnitine is an
endogenous HDAC inhibitor selectively inhibiting cancer cell growth
in vivo and in vitro. PLoS One. 7:e490622012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huang H, Zhang X, Li S, Liu N, Lian W,
McDowell E, Zhou P, Zhao C, Guo H, Zhang C, et al: Physiological
levels of ATP negatively regulate proteasome function. Cell Res.
20:1372–1385. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu N, Li X, Huang H, Zhao C, Liao S, Yang
C, Liu S, Song W, Lu X, Lan X, et al: Clinically used antirheumatic
agent auranofin is a proteasomal deubiquitinase inhibitor and
inhibits tumor growth. Oncotarget. 5:5453–5471. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Huang H, Chen D, Li S, Li X, Liu N, Lu X,
Liu S, Zhao K, Zhao C, Guo H, et al: Gambogic acid enhances
proteasome inhibitor-induced anticancer activity. Cancer Lett.
301:221–228. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chou TC and Talalay P: Quantitative
analysis of dose-effect relationships: The combined effects of
multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv Enzyme Regul. 22:27–55.
1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang Q, Li J, Gu J, Huang B, Zhao Y, Zheng
D, Ding Y and Zeng L: Potentiation of
(−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate-induced apoptosis by bortezomib in
multiple myeloma cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai).
41:1018–1026. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ma C, Mandrekar SJ, Alberts SR, Croghan
GA, Jatoi A, Reid JM, Hanson LJ, Bruzek L, Tan AD, Pitot HC, et al:
A phase I and pharmacologic study of sequences of the proteasome
inhibitor, bortezomib (PS-341, Velcade), in combination with
paclitaxel and carboplatin in patients with advanced malignancies.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 59:207–215. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Fribley A, Zeng Q and Wang CY: Proteasome
inhibitor PS-341 induces apoptosis through induction of endoplasmic
reticulum stress-reactive oxygen species in head and neck squamous
cell carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 24:9695–9704. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nawrocki ST, Carew JS, Dunner K Jr, Boise
LH, Chiao PJ, Huang P, Abbruzzese JL and McConkey DJ: Bortezomib
inhibits PKR-like endoplasmic reticulum (ER) kinase and induces
apoptosis via ER stress in human pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer
Res. 65:11510–11519. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhao X, Qiu W, Kung J, Zhao X, Peng X,
Yegappan M, Yen-Lieberman B and Hsi ED: Bortezomib induces
caspase-dependent apoptosis in Hodgkin lymphoma cell lines and is
associated with reduced c-FLIP expression: A gene expression
profiling study with implications for potential combination
therapies. Leuk Res. 32:275–285. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Shringarpure R, Catley L, Bhole D, Burger
R, Podar K, Tai YT, Kessler B, Galardy P, Ploegh H, Tassone P, et
al: Gene expression analysis of B-lymphoma cells resistant and
sensitive to bortezomib. Br J Haematol. 134:145–156. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Calvaruso G, Giuliano M, Portanova P,
Pellerito O, Vento R and Tesoriere G: Hsp72 controls
bortezomib-induced HepG2 cell death via interaction with
pro-apoptotic factors. Oncol Rep. 18:447–450. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Qi W, White MC, Choi W, Guo C, Dinney C,
McConkey DJ and Siefker-Radtke A: Inhibition of inducible heat
shock protein-70 (hsp72) enhances bortezomib-induced cell death in
human bladder cancer cells. PLoS One. 8:e695092013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Beck D, Niessner H, Smalley KS, Flaherty
K, Paraiso KH, Busch C, Sinnberg T, Vasseur S, Iovanna JL, Driessen
S, et al: Vemurafenib potently induces endoplasmic reticulum
stress-mediated apoptosis in BRAFV600E melanoma cells. Sci Signal.
6:ra72013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|