|
1
|
Gomceli I, Demiriz B and Tez M: Gastric
carcinogenesis. World J Gastroenterol. 18:5164–5170.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Brenner B, Hoshen MB, Purim O, David MB,
Ashkenazi K, Marshak G, Kundel Y, Brenner R, Morgenstern S, Halpern
M, et al: MicroRNAs as a potential prognostic factor in gastric
cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 17:3976–3985. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yu Z, Pestell TG, Lisanti MP and Pestell
RG: Cancer stem cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 44:2144–2151. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xu G, Shen J, Ou Yang X, Sasahara M and Su
X: Cancer stem cells: The 'heartbeat' of gastric cancer. J
Gastroenterol. 48:781–797. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Visvader JE and Lindeman GJ: Cancer stem
cells: Current status and evolving complexities. Cell Stem Cell.
10:717–728. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Conley SJ, Gheordunescu E, Kakarala P,
Newman B, Korkaya H, Heath AN, Clouthier SG and Wicha MS:
Antiangiogenic agents increase breast cancer stem cells via the
generation of tumor hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:2784–2789.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yan K, Wu Q, Yan DH, Lee CH, Rahim N,
Tritschler I, DeVecchio J, Kalady MF, Hjelmeland AB and Rich JN:
Glioma cancer stem cells secrete Gremlin1 to promote their
maintenance within the tumor hierarchy. Genes Dev. 28:1085–1100.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Visvader JE and Lindeman GJ: Cancer stem
cells in solid tumours: Accumulating evidence and unresolved
questions. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:755–768. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Que T, Song Y, Liu Z, Zheng S, Long H, Li
Z, Liu Y, Wang G, Liu Y, Zhou J, et al: Decreased miRNA-637 is an
unfavorable prognosis marker and promotes glioma cell growth,
migration and invasion via direct targeting Akt1. Oncogene.
34:4952–4963. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
McGirt LY, Adams CM, Baerenwald DA,
Zwerner JP, Zic JA and Eischen CM: miR-223 regulates cell growth
and targets proto-oncogenes in mycosis fungoides/cutaneous T-cell
lymphoma. J Invest Dermatol. 134:1101–1107. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
Chen PS, Su JL and Hung MC: Dysregulation
of microRNAs in cancer. J Biomed Sci. 19:902012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Croce CM and Calin GA: miRNAs, cancer, and
stem cell division. Cell. 122:6–7. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Okada N, Lin CP, Ribeiro MC, Biton A, Lai
G, He X, Bu P, Vogel H, Jablons DM, Keller AC, et al: A positive
feedback between p53 and miR-34 miRNAs mediates tumor suppression.
Genes Dev. 28:438–450. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bao B, Wang Z, Ali S, Ahmad A, Azmi AS,
Sarkar SH, Banerjee S, Kong D, Li Y, Thakur S and Sarkar FH:
Metformin inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion by
attenuating CSC function mediated by deregulating miRNAs in
pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 5:355–364. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Liu C, Kelnar K, Vlassov AV, Brown D, Wang
J and Tang DG: Distinct microRNA expression profiles in prostate
cancer stem/progenitor cells and tumor-suppressive functions of
let-7. Cancer Res. 72:3393–3404. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chabre O, Libé R, Assié G, Barreau O,
Bertherat J, Bertagna X, Feige JJ and Cherradi N: Serum miR-483-5p
and miR-195 are predictive of recurrence risk in adrenocortical
cancer patients. Endocr Relat Cancer. 20:579–594. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang Z, Ge S, Wang X, Yuan Q, Yan Q, Ye
H, Che Y, Lin Y, Zhang J and Liu P: Serum miR-483-5p as a potential
biomarker to detect hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Int.
7:199–207. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Song Q, Xu Y, Yang C, Chen Z, Jia C, Chen
J, Zhang Y, Lai P, Fan X, Zhou X, et al: miR-483-5p promotes
invasion and metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma by targeting RhoGDI1
and ALCAM. Cancer Res. 74:3031–3042. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
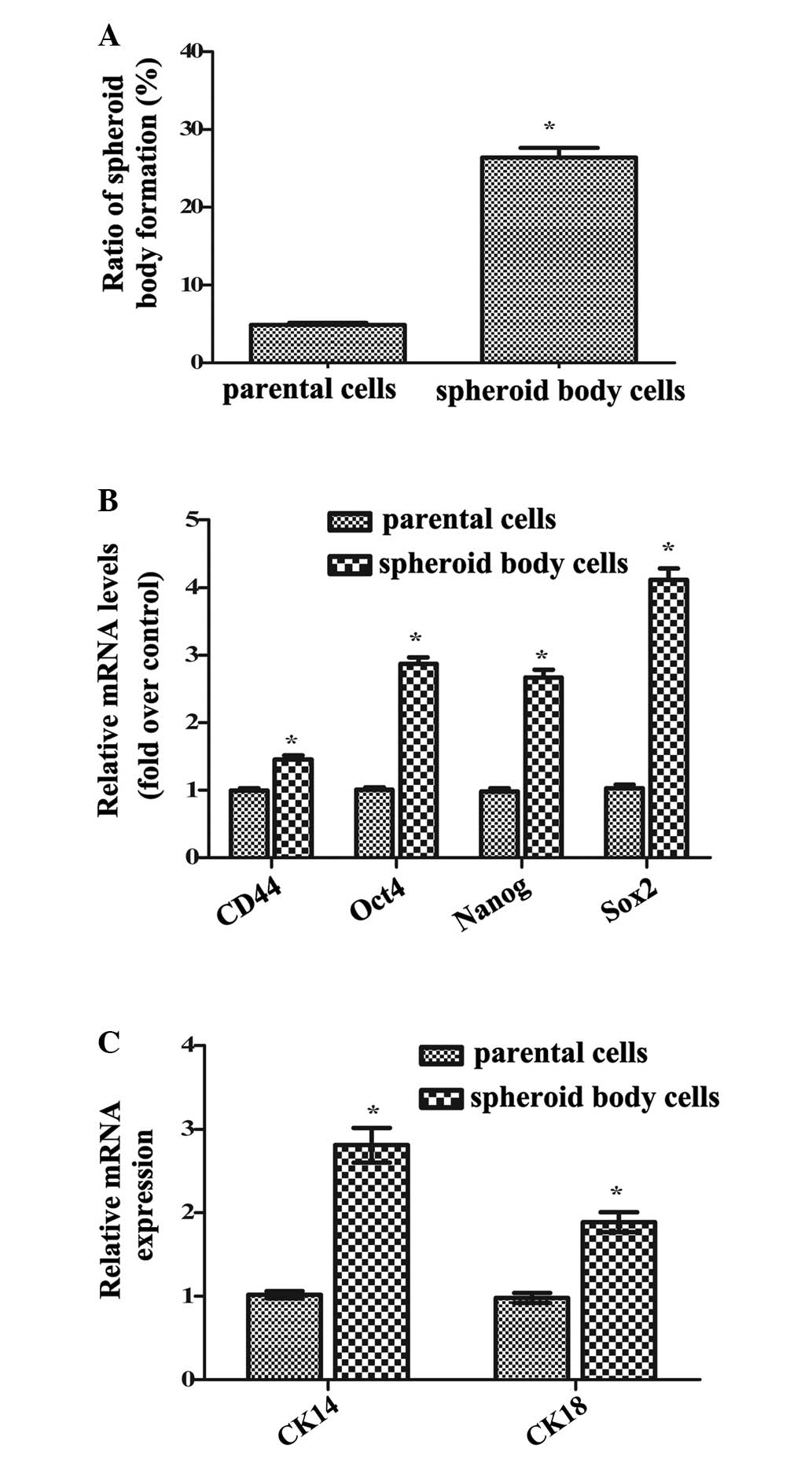
Liu J, Ma L, Xu J, Liu C, Zhang J, Liu J,
Chen R and Zhou Y: Spheroid body-forming cells in the human gastric
cancer cell line MKN-45 possess cancer stem cell properties. Int J
Oncol. 42:453–459. 2013.
|
|
21
|
Wang L, Shi M, Hou S, Ding B, Liu L, Ji X,
Zhang J and Deng Y: MiR-483-5p suppresses the proliferation of
glioma cells via directly targeting ERK1. FEBS Lett. 586:1312–1317.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-timequantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wu H, Echt CS, Popp MP and Davis JM:
Molecular cloning, structure and expression of an
elicitor-inducible chitinase gene from pine trees. Plant Mol Biol.
33:979–987. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
White BD, Chien AJ and Dawson DW:
Dysregulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in gastrointestinal
cancers. Gastroenterology. 142:219–232. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Yu T, Liu K, Wu Y, Fan J, Chen J, Li C,
Yang Q and Wang Z: MicroRNA-9 inhibits the proliferation of oral
squamous cell carcinoma cells by suppressing expression of CXCR4
via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncogene. 33:5017–5027.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Brower JV, Clark PA, Lyon W and Kuo JS:
MicroRNAs in cancer: Glioblastoma and glioblastoma cancer stem
cells. Neurochem Int. 77:68–77. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jiang J, Zhang Y, Chuai S, Wang Z, Zheng
D, Xu F, Li C, Liang Y and Chen Z: Trastuzumab (herceptin) targets
gastric cancer stem cells characterized by CD90 phenotype.
Oncogene. 31:671–682. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Templeton AK, Miyamoto S, Babu A, Munshi A
and Ramesh R: Cancer stem cells: Progress and challenges in lung
cancer. Stem Cell Investigation. 1:92014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Qu X, Zhao M, Wu S, Yu W, Xu J, Xu J, Li J
and Chen L: Circulating microRNA 483-5p as a novel biomarker for
diagnosis survival prediction in multiple myeloma. Med Oncol.
31:2192014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Arensman M, Lay AR, Kulikauskas RM, Chien
AJ and Dawson DW: Wnt/β-catenin transcriptional activation promotes
tumorigenesis and predicts survival in pancreatic cancer. Cancer
Res. 73:40112013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Holland JD, Klaus A, Garratt AN and
Birchmeier W: Wnt signaling in stem and cancer stem cells. Curr
Opin Cell Biol. 25:254–264. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cai C and Zhu X: The Wnt/β-catenin pathway
regulates self-renewal of cancer stem-like cells in human gastric
cancer. Mol Med Rep. 5:1191–1196. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li J and Zhou BP: Activation of β-catenin
and Akt pathways by Twist are critical for the maintenance of EMT
associated cancer stem cell-like characters. BMC Cancer. 11:492011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kim HY, Park JH, Won HY, Lee JY and Kong
G: CBX7 inhibits breast tumorigenicity through DKK-1-mediated
suppression of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. FASEB J. 29:300–313.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|