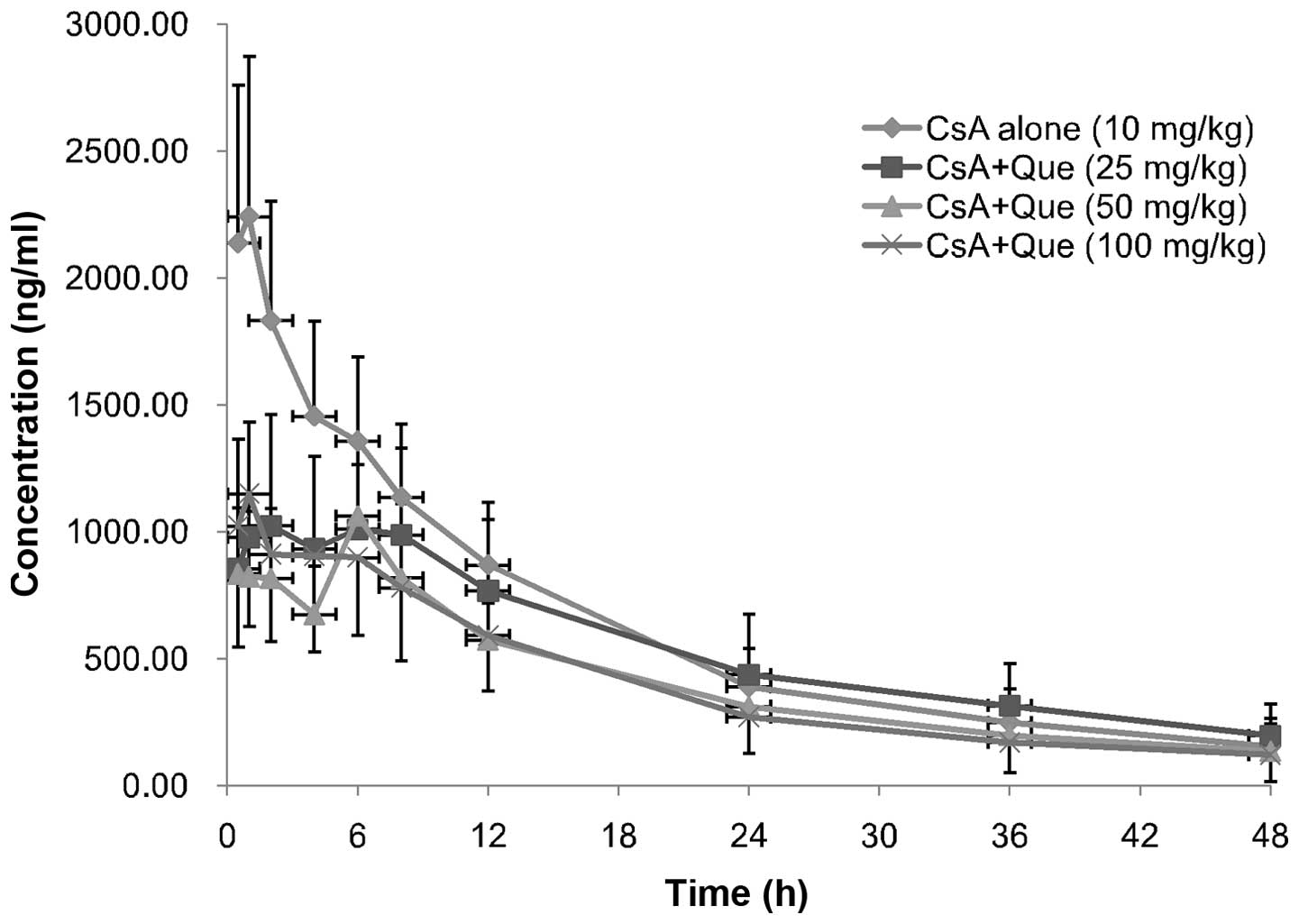
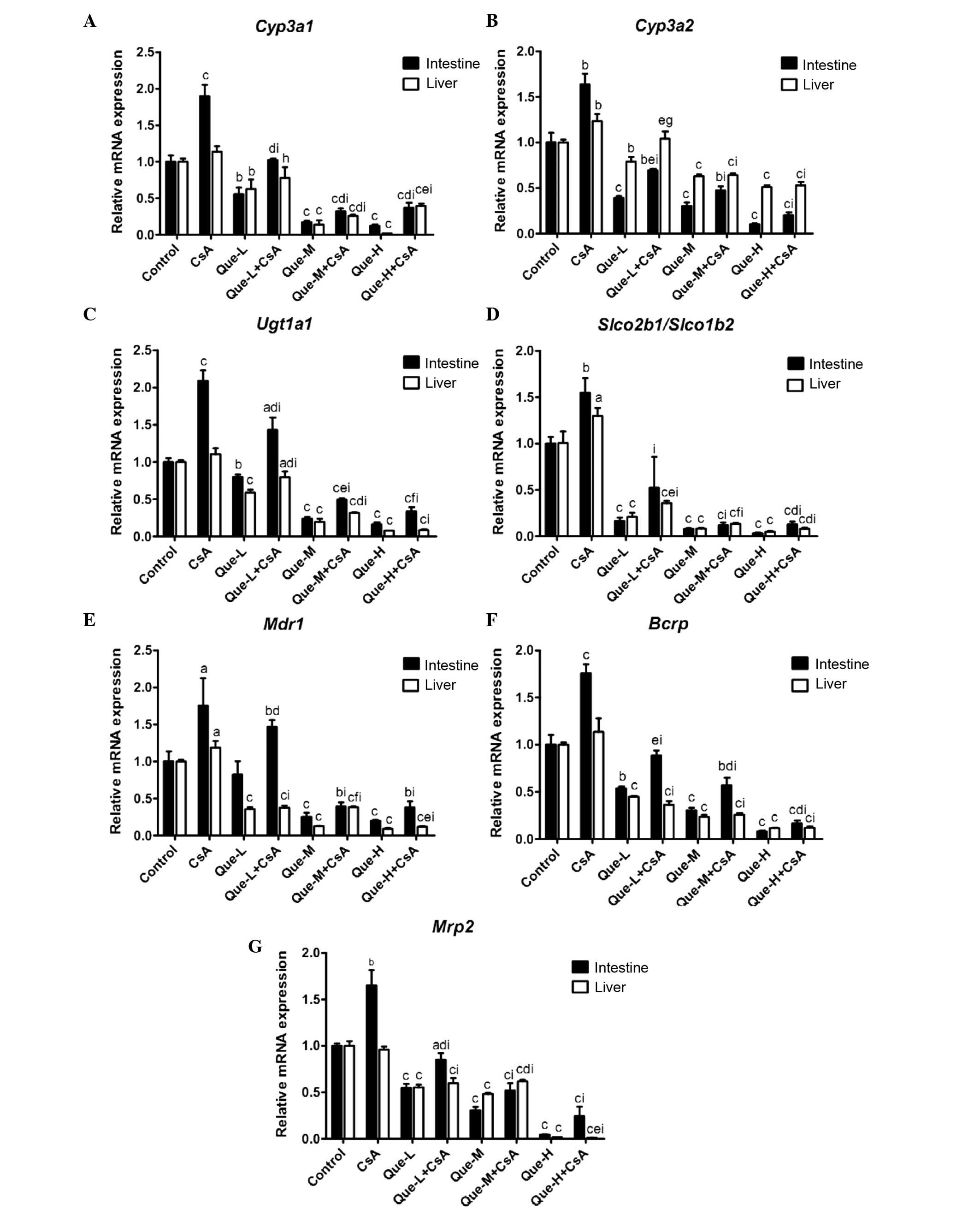
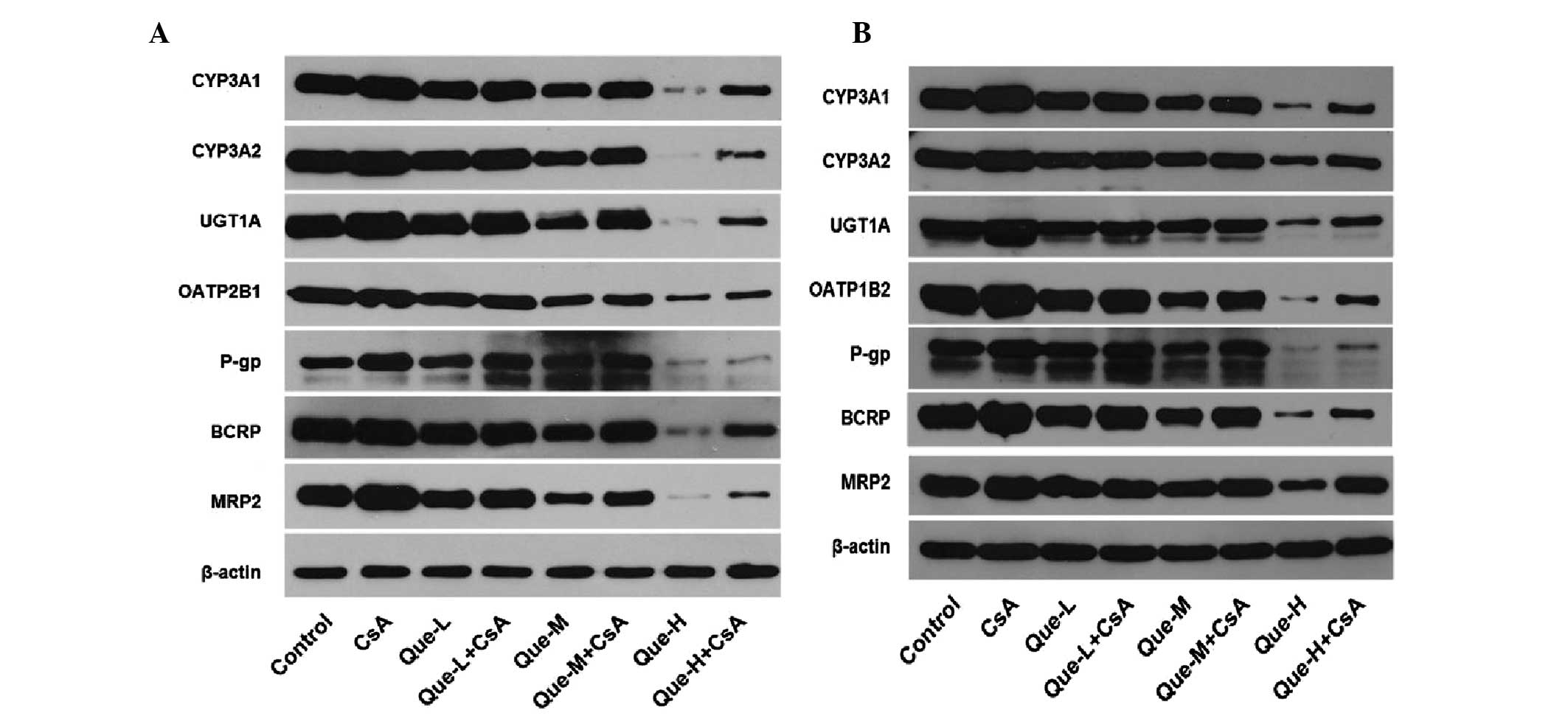
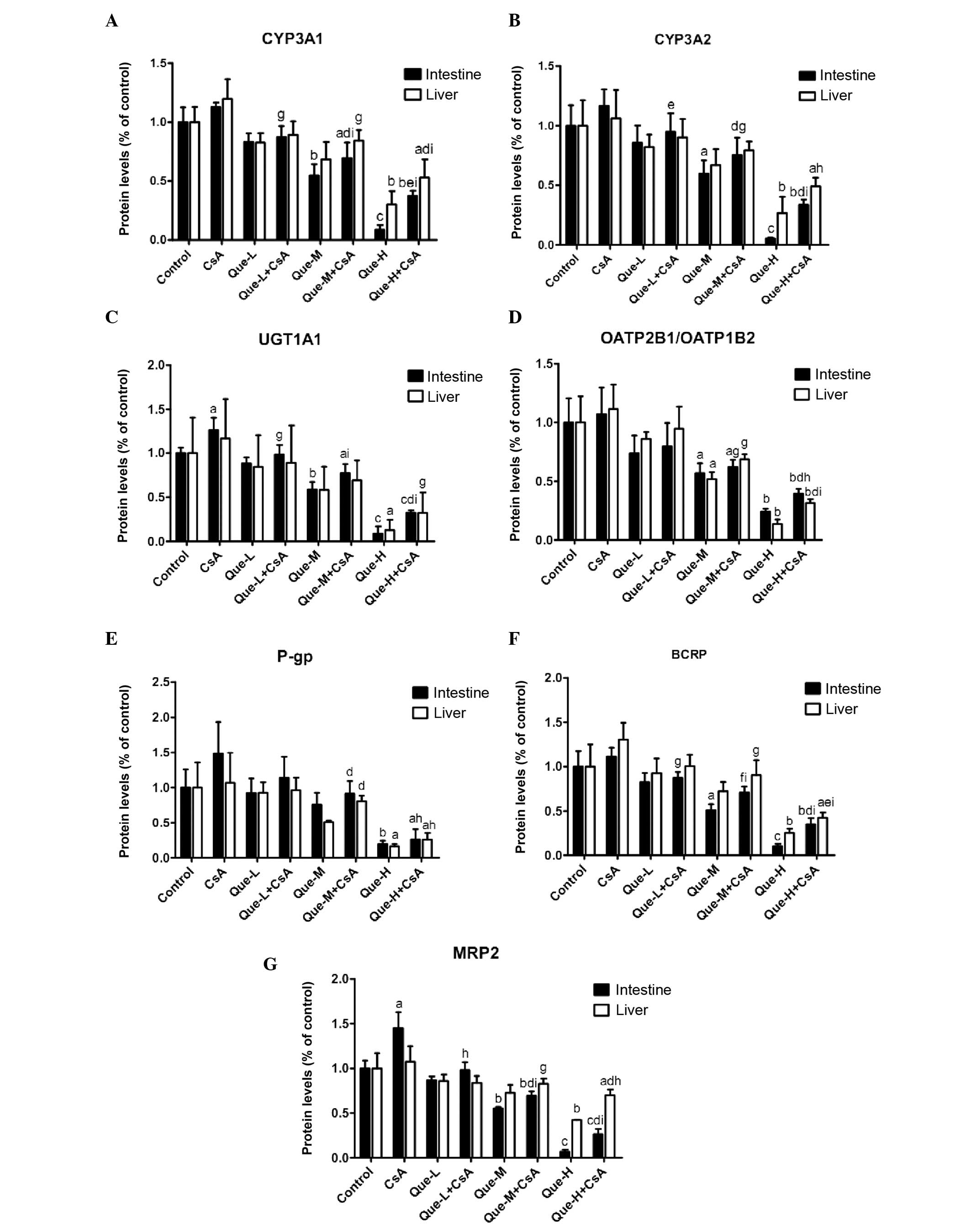
|
1
|
Ma Y, Zeng M, Sun R and Hu M: Disposition
of flavonoids impacts their efficacy and safety. Curr Drug Metab.
15:841–864. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Shi S and Klotz U: Drug interactions with
herbal medicines. Clin Pharmacokinet. 51:77–104. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Morris ME and Zhang S: Flavonoid-drug
interactions: Effects of flavonoids on ABC transporters. Life Sci.
78:2116–2130. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Egert S, Wolffram S, Bosy-Westphal A,
Boesch-Saadatmandi C, Wagner AE, Frank J, Rimbach G and Mueller MJ:
Daily quercetin supplementation dose-dependently increases plasma
quercetin concentrations in healthy humans. J Nutr. 138:1615–1621.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Russo M, Spagnuolo C, Tedesco I, Bilotto S
and Russo GL: The flavonoid quercetin in disease prevention and
therapy: Facts and fancies. Biochem Pharmacol. 83:6–15. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Cai X, Fang Z, Dou J, Yu A and Zhai G:
Bioavailability of quercetin: Problems and promises. Curr Med Chem.
20:2572–2582. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dajas F: Life or death: Neuroprotective
and anticancer effects of quercetin. J Ethnopharmacol. 143:383–396.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zal F, Mostafavi-Pour Z and Vessal M:
Comparison of the effects of vitamin E and/or quercetin in
attenuating chronic cyclosporine A-induced nephrotoxicity in male
rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 34:720–724. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mostafavi-Pour Z, Zal F, Monabati A and
Vessal M: Protective effects of a combination of quercetin and
vitamin E against cyclosporine A-induced oxidative stress and
hepatotoxicity in rats. Hepatol Res. 38:385–392. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Dodda D, Chhajed R and Mishra J:
Protective effect of quercetin against acetic acid induced
inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) like symptoms in rats: Possible
morphological and biochemical alterations. Pharmacol Rep.
66:169–173. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dodda D, Chhajed R, Mishra J and Padhy M:
Targeting oxidative stress attenuates trinitrobenzene sulphonic
acid induced inflammatory bowel disease like symptoms in rats: Role
of quercetin. Indian J Pharmacol. 46:286–291. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Abarikwu SO, Pant AB and Farombi EO: The
protective effects of quercetin on the cytotoxicity of atrazine on
rat Sertoli-germ cell co-culture. Int J Androl. 35:590–600. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Abarikwu SO, Pant AB and Farombi EO:
Quercetin decreases steroidogenic enzyme activity, NF-κB
expression, and oxidative stress in cultured Leydig cells exposed
to atrazine. Mol Cell Biochem. 373:19–28. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Tang Y, Gao C, Xing M, Li Y, Zhu L, Wang
D, Yang X, Liu L and Yao P: Quercetin prevents ethanol-induced
dyslipidemia and mitochondrial oxidative damage. Food Chem Toxicol.
50:1194–1200. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Qu L, Liang X, Gu B and Liu W: Quercetin
alleviates high glucose-induced Schwann cell damage by autophagy.
Neural Regen Res. 9:1195–1203. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jiang W and Hu M: Mutual interactions
between flavonoids and enzymatic and transporter elements
responsible for flavonoid disposition via phase II metabolic
pathways. RSC Adv. 2:7948–7963. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Duan KM, Wang SY, Ouyang W, Mao YM and
Yang LJ: Effect of quercetin on CYP3A activity in Chinese healthy
participants. J Clin Pharmacol. 52:940–946. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Priyadarsini RV and Nagini S: Quercetin
suppresses cytochrome P450 mediated ROS generation and NFκB
activation to inhibit the development of
7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene (DMBA) induced hamster buccal pouch
carcinomas. Free Radic Res. 46:41–49. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Chen Y, Xiao P, Ou-Yang DS, Fan L, Guo D,
Wang YN, Han Y, Tu JH, Zhou G, Huang YF and Zhou HH: Simultaneous
action of the flavonoid quercetin on cytochrome P450 (CYP) 1A2,
CYP2A6, N-acetyltransferase and xanthine oxidase activity in
healthy volunteers. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 36:828–833. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rastogi H and Jana S: Evaluation of
inhibitory effects of caffeic acid and quercetin on human liver
cytochrome p450 activities. Phytother Res. 28:1873–1878. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Brand W, Schutte ME, Williamson G, van
Zanden JJ, Cnubben NH, Groten JP, van Bladeren PJ and Rietjens IM:
Flavonoid-mediated inhibition of intestinal ABC transporters may
affect the oral bioavailability of drugs, food-borne toxic
compounds and bioactive ingredients. Biomed Pharmacother.
60:508–519. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Alvarez AI, Real R, Pérez M, Mendoza G,
Prieto JG and Merino G: Modulation of the activity of ABC
transporters (P-glycoprotein, MRP2, BCRP) by flavonoids and drug
response. J Pharm Sci. 99:598–617. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
van Zanden JJ, Wortelboer HM, Bijlsma S,
Punt A, Usta M, Bladeren PJ, Rietjens IM and Cnubben NH:
Quantitative structure activity relationship studies on the
flavonoid mediated inhibition of multidrug resistance proteins 1
and 2. Biochem Pharmacol. 69:699–708. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Odenthal J, van Heumen BW, Roelofs HM, te
Morsche RH, Marian B, Nagengast FM and Peters WH: The influence of
curcumin, quercetin, and eicosapentaenoic acid on the expression of
phase II detoxification enzymes in the intestinal cell lines HT-29,
Caco-2, HuTu 80, and LT97. Nutr Cancer. 64:856–863. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang SY, Duan KM, Li Y, Mei Y, Sheng H,
Liu H, Mei X, Ouyang W, Zhou HH and Liu ZQ: Effect of quercetin on
P-glycoprotein transport ability in Chinese healthy subjects. Eur J
Clin Nutr. 67:390–394. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wu LX, Guo CX, Chen WQ, Yu J, Qu Q, Chen
Y, Tan ZR, Wang G, Fan L, Li Q, et al: Inhibition of the organic
anion-transporting polypeptide 1B1 by quercetin: An in vitro and in
vivo assessment. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 73:750–757. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Tedesco D and Haragsim L: Cyclosporine: A
review. J Transplant. 2012:2303862012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dupuis R, Yuen A and Innocenti F: The
influence of UGT polymorphisms as biomarkers in solid organ
transplantation. Clin Chim Acta. 413:1318–1325. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kato R, Nishide M, Kozu C, Iwamoto A,
Urashima K, Suzuki K, Ijiri Y, Hayashi T and Tanaka K: Is
cyclosporine A transport inhibited by pravastatin via multidrug
resistant protein 2? Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 66:153–158. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Fu J, Tjandra M, Becker C, Bednarczyk D,
Capparelli M, Elling R, Hanna I, Fujimoto R, Furegati M, Karur S,
et al: Potent nonimmunosuppressive cyclophilin inhibitors with
improved pharmaceutical properties and decreased transporter
inhibition. J Med Chem. 57:8503–8516. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li L, Yao QQ, Xu SY, Hu HH, Shen Q, Tian
Y, Pan LY, Zhou H, Jiang HD, Lu C, et al: Cyclosporin A affects the
bioavailability of ginkgolic acids via inhibition of P-gp and BCRP.
Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 88:759–767. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yu CP, Wu PP, Hou YC, Lin SP, Tsai SY,
Chen CT and Chao PD: Quercetin and rutin reduced the
bioavailability of cyclosporine from Neoral, animmunosuppressant,
through activating P-glycoprotein and CYP 3A4. J Agric Food Chem.
59:4644–4648. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Choi JS, Choi BC and Choi KE: Effect of
quercetin on the pharmacokinetics of oral cyclosporine. Am J Health
Syst Pharm. 61:2406–2409. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yang CY, Chao PD, Hou YC, Tsai SY, Wen KC
and Hsiu SL: Marked decrease of cyclosporin bioavailability caused
by coadministration of ginkgo and onion in rats. Food Chem Toxicol.
44:1572–1578. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hsiu SL, Hou YC, Wang YH, Tsao CW, Su SF
and Chao PD: Quercetin significantly decreased cyclosporin oral
bioavailability in pigs and rats. Life Sci. 72:227–235. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hsu PW, Shia CS, Lin SP, Chao PD, Juang SH
and Hou YC: Potential risk of mulberry-drug interaction: Modulation
on P-glycoprotein and cytochrome P450 3A. J Agric Food Chem.
61:4464–4469. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Colombo D, Lunardon L and Bellia G:
Cyclosporine and herbal supplement interactions. J Toxicol.
2014:1453252014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shi S and Li Y: Interplay of
Drug-Metabolizing enzymes and transporters in drug absorption and
disposition. Curr Drug Metab. 15:915–941. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Wu B: Pharmacokinetic interplay of phase
II metabolism and transport: A theoretical study. J Pharm Sci.
101:381–393. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Lei H, Luo J, Tong L, Peng LQ, Qi Y, Jia
ZG and Wei Q: Quercetin binds to calcineurin at a similar region to
cyclosporin A and tacrolimus. Food Chem. 127:1169–1174. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Barbas CF III, Burton DR, Scott JK and
Silverman GJ: Quantitation of DNA and RNA. CSH Protoc.
2007:pdb.ip472007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–428. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Kim KA, Park PW and Park JY: Short-term
effect of quercetin on the pharmacokinetics of fexofenadine, a
substrate of P-glycoprotein, in healthy volunteers. Eur J Clin
Pharmacol. 65:609–614. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kim KA, Park PW, Kim HK, Ha JM and Park
JY: Effect of quercetin on the pharmacokinetics of rosiglitazone, a
CYP2C8 substrate, in healthy subjects. J Clin Pharmacol.
45:941–946. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Choi JS, Jo BW and Kim YC: Enhanced
paclitaxel bioavailability after oral administration of paclitaxel
or prodrug to rats pretreated with quercetin. Eur J Pharm Biopharm.
57:313–318. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Challa VR, Babu PR, Challa SR, Johnson B
and Maheswari C: Pharmacokinetic interaction study between
quercetin and valsartan in rats and in vitro models. Drug Dev Ind
Pharm. 39:865–872. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Babu PR, Babu KN, Peter PL, Rajesh K and
Babu PJ: Influence of quercetin on the pharmacokinetics of
ranolazine in rats and in vitro models. Drug Dev Ind Pharm.
39:873–879. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Shin SC, Choi JS and Li X: Enhanced
bioavailability of tamoxifen after oral administration of tamoxifen
with quercetin in rats. Int J Pharm. 313:144–149. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Choi JS, Piao YJ and Kang KW: Effects of
quercetin on the bioavailability of doxorubicin in rats: Role of
CYP3A4 and P-gp inhibition by quercetin. Arch Pharm Res.
34:607–613. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wang YH, Chao PD, Hsiu SL, Wen KC and Hou
YC: Lethal quercetin-digoxin interaction in pigs. Life Sci.
74:1191–1197. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Nguyen MA, Staubach P, Wolffram S and
Langguth P: Effect of single-dose and short-term administration of
quercetin on the pharmacokinetics of talinolol in
humans-Implications for the evaluation of transporter-mediated
flavonoid-drug interactions. Eur J Pharm Sci. 61:54–60. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Challa SR, Challa VR and Ragam SK:
Quercetin declines plasma exposure of metoprolol tartrate in the
rat model. J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 5:185–190. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Cermak R, Wein S, Wolffram S and Langguth
P: Effects of the flavonol quercetin on the bioavailability of
simvastatin in pigs. Eur J Pharm Sci. 38:519–524. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Burke JF Jr, Pirsch JD, Ramos EL, Salomon
DR, Stablein DM, Van Buren DH and West JC: Long-term efficacy and
safety of cyclosporine in renal-transplant recipients. N Engl J
Med. 331:358–363. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kronbach T, Fischer V and Meyer UA:
Cyclosporine metabolism in human liver: Identification of a
cytochrome P-450III gene family as the major
cyclosporine-metabolizing enzyme explains interactions of
cyclosporine with other drugs. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 43:630–635.
1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Elens L, Bouamar R, Shuker N, Hesselink
DA, van Gelder T and van Schaik RH: Clinical implementation of
pharmacogenetics in kidney transplantation: Calcineurin inhibitors
in the starting blocks. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 77:715–728. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
57
|
Yu ES, Min HJ, An SY, Won HY, Hong JH and
Hwang ES: Regulatory mechanisms of IL-2 and IFNgamma suppression by
quercetin in T helper cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 76:70–78. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
van der Logt EM, Roelofs HM, Nagengast FM
and Peters WH: Induction of rat hepatic and intestinal
UDP-glucuronosyltransferases by naturally occurring dietary
anticarcinogens. Carcinogenesis. 24:1651–1656. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Mitsunaga Y, Takanaga H, Matsuo H, Naito
M, Tsuruo T, Ohtani H and Sawada Y: Effect of bioflavonoids on
vincristine transport across blood-brain barrier. Eur J Pharmacol.
395:193–201. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
van Zanden JJ, van der Woude H, Vaessen J,
Usta M, Wortelboer HM, Cnubben NH and Rietjens IM: The effect of
quercetin phase II metabolism on its MRP1 and MRP2 inhibiting
potential. Biochem Pharmacol. 74:345–351. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Ebert B, Seidel A and Lampen A:
Phytochemicals induce breast cancer resistance protein in Caco-2
cells and enhance the transport of benzo[a]pyrene-3-sulfate.
Toxicol Sci. 96:227–236. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Benet LZ: The drug transporter-metabolism
alliance: Uncovering and defining the interplay. Mol Pharm.
6:1631–1643. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Gan LS, Moseley MA, Khosla B, Augustijns
PF, Bradshaw TP, Hendren RW and Thakker DR: CYP3A-like cytochrome
P450-mediated metabolism and polarized efflux of cyclosporin A in
Caco-2 cells. Drug Metab Dispos. 24:344–349. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Li Y, Zhou J, Ramsden D, Taub ME, O'Brien
D, Xu J, Busacca CA, Gonnella N and Tweedie DJ: Enzyme-transporter
interplay in the formation and clearance of abundant metabolites of
faldaprevir found inexcreta but not in circulation. Drug Metab
Dispos. 42:384–393. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Chen X, Yin OQ, Zuo Z and Chow MS:
Pharmacokinetics and modeling of quercetin and metabolites. Pharm
Res. 22:892–901. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Ishizawa K, Yoshizumi M, Kawai Y, Terao J,
Kihira Y, Ikeda Y, Tomita S, Minakuchi K, Tsuchiya K and Tamaki T:
Pharmacology in health food: Metabolism of quercetin in vivo and
its protective effect against arteriosclerosis. J Pharmacol Sci.
115:466–470. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Yokoyama A, Sakakibara H, Crozier A, Kawai
Y, Matsui A, Terao J, Kumazawa S and Shimoi K: Quercetin
metabolites and protection against peroxynitrite-induced oxidative
hepatic injury in rats. Free Radic Res. 43:913–921. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Wong CC, Botting NP, Orfila C, Al-Maharik
N and Williamson G: Flavonoid conjugates interact with organic
anion transporters (OATs) and attenuate cytotoxicity of adefovir
mediated by organic anion transporter 1 (OAT1/SLC22A6). Biochem
Pharmacol. 81:942–949. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|