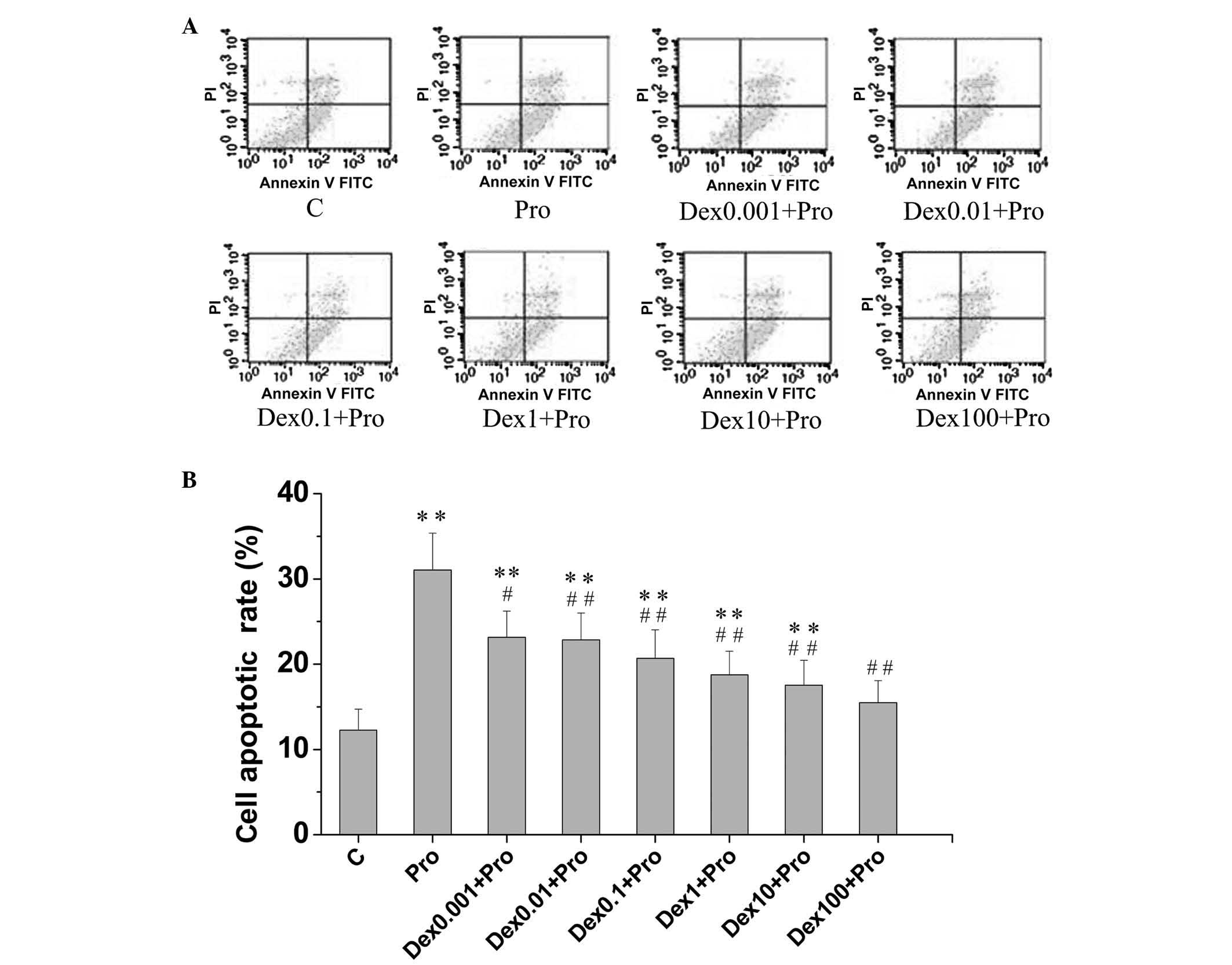
|
1
|
Sall JW, Stratmann G, Leong J, Woodward E
and Bickler PE: Propofol at clinically relevant concentrations
increases neuronal differentiation but is not toxic to hippocampal
neural precursor cells in vitro. Anesthesiology. 117:1080–1090.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kahraman S, Zup SL, McCarthy MM and Fiskum
G: GABAergic mechanism of propofol toxicity in immature neurons. J
Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 20:233–240. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Spahr-Schopfer I, Vutskits L, Toni N,
Buchs PA, Parisi L and Muller D: Differential neurotoxic effects of
propofol on dissociated cortical cells and organotypic hippocampal
cultures. Anesthesiology. 92:1408–1417. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cattano D, Young C, Straiko MM and Olney
JW: Subanesthetic doses of propofol induce neuroapoptosis in the
infant mouse brain. Anesth Analg. 106:1712–1714. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pesić V, Milanović D, Tanić N, Popić J,
Kanazir S, Jevtović-Todorović V and Ruzdijić S: Potential mechanism
of cell death in the developing rat brain induced by propofol
anesthesia. Int J Dev Neurosci. 27:279–287. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Creeley C, Dikranian K, Dissen G, Martin
L, Olney J and Brambrink A: Propofol-induced apoptosis of neurones
and oligodendrocytes in fetal and neonatal rhesus macaque brain. Br
J Anaesth. 110(Suppl 1): i29–i38. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Afonso J and Reis F: Dexmedetomidine:
Current role in anesthesia and intensive care. Rev Bras Anestesiol.
62:118–133. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Paris A, Mantz J, Tonner PH, Hein L, Brede
M and Gressens P: The effects of dexmedetomidine on perinatal
excitotoxic brain injury are mediated by the alpha2A-adrenoceptor
subtype. Anesth Analg. 102:456–461. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sanders RD, Xu J, Shu Y, Januszewski A,
Halder S, Fidalgo A, Sun P, Hossain M, Ma D and Maze M:
Dexmedetomidine attenuates isoflurane-induced neurocognitive
impairment in neonatal rats. Anesthesiology. 110:1077–1085. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li Y, Zeng M, Chen W, Liu C, Wang F, Han
X, Zuo Z and Peng S: Dexmedetomidine reduces isoflurane-induced
neuroapoptosis partly by preserving PI3K/Akt pathway in the
hippocampus of neonatal rats. PloS One. 9:e936392014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lu LX, Yon JH, Carter LB and
Jevtovic-Todorovic V: General anesthesia activates BDNF-dependent
neuroapoptosis in the developing rat brain. Apoptosis.
11:1603–1615. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hwang L, Choi IY, Kim SE, Ko IG, Shin MS,
Kim CJ, Kim SH, Jin JJ, Chung JY and Yi JW: Dexmedetomidine
ameliorates intracerebral hemorrhage-induced memory impairment by
inhibiting apoptosis and enhancing brain-derived neurotrophic
factor expression in the rat hippocampus. Int J Mol Med.
31:1047–1056. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yan M, Dai H, Ding T, Dai A, Zhang F, Yu
L, Chen G and Chen Z: Effects of dexmedetomidine on the release of
glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor from rat astrocyte
cells. Neurochem Int. 58:549–557. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bell MT, Puskas F, Bennett DT, Herson PS,
Quillinan N, Fullerton DA and Reece TB: Dexmedetomidine, an α-2a
adrenergic agonist, promotes ischemic tolerance in a murine model
of spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.
147:500–506. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Lesuisse C, Qiu D, Böse CM, Nakaso K and
Rupp F: Regulation of agrin expression in hippocampal neurons by
cell contact and electrical activity. Brain Res Mol Brain Res.
81:92–100. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bercker S, Bert B, Bittigau P,
Felderhoff-Müser U, Bührer C, Ikonomidou C, Weise M, Kaisers UX and
Kerner T: Neurodegeneration in newborn rats following propofol and
sevoflurane anesthesia. Neurotox Res. 16:140–147. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Brambrink AM, Evers AS, Avidan MS, Farber
NB, Smith DJ, Zhang X, Dissen GA, Creeley CE and Olney JW:
Isoflurane-induced neuroapoptosis in the neonatal rhesus macaque
brain. Anesthesiology. 112:834–841. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Young C, Jevtovic-Todorovic V, Qin YQ,
Tenkova T, Wang H, Labruyere J and Olney JW: Potential of ketamine
and midazolam, individually or in combination, to induce apoptotic
neurodegeneration in the infant mouse brain. Br J Pharmacol.
146:189–197. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fredriksson A, Pontén E, Gordh T and
Eriksson P: Neonatal exposure to a combination of
N-methyl-D-aspartate and gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor
anesthetic agents potentiates apoptotic neurodegeneration and
persistent behavioral deficits. Anesthesiology. 107:427–436. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Honegger P and Matthieu JM: Selective
toxicity of the general anesthetic propofol for GABAergic neurons
in rat brain cell cultures. J Neurosci Res. 45:631–636. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vutskits L, Gascon E, Tassonyi E and Kiss
JZ: Clinically relevant concentrations of propofol but not
midazolam alter in vitro dendritic development of isolated
gamma-aminobutyric acid-positive interneurons. Anesthesiology.
102:970–976. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sanders RD, Sun P, Patel S, Li M, Maze M
and Ma D: Dexmedetomidine provides cortical neuroprotection: Impact
on anaesthetic-induced neuroapoptosis in the rat developing brain.
Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 54:710–716. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Duan X, Li Y, Zhou C, Huang L and Dong Z:
Dexmedetomidine provides neuroprotection: Impact on
ketamine-induced neuroapoptosis in the developing rat brain. Acta
Anaesthesiol Scand. 58:1121–1126. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dahmani S, Rouelle D, Gressens P and Mantz
J: Characterization of the postconditioning effect of
dexmedetomidine in mouse organotypic hippocampal slice cultures
exposed to oxygen and glucose deprivation. Anesthesiology.
112:373–383. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Laudenbach V, Mantz J, Lagercrantz H,
Desmonts JM, Evrard P and Gressens P: Effects of
alpha(2)-adrenoceptor agonists on perinatal excitotoxic brain
injury: Comparison of clonidine and dexmedetomidine.
Anesthesiology. 96:134–141. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Liao Z, Cao D, Han X, Liu C, Peng J, Zuo
Z, Wang F and Li Y: Both JNK and P38 MAPK pathways participate in
the protection by dexmedetomidine against isoflurane-induced
neuroapoptosis in the hippocampus of neonatal rats. Brain Res Bull.
107:69–78. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhu YM, Wang CC, Chen L, Qian LB, Ma LL,
Yu J, Zhu MH, Wen CY, Yu LN and Yan M: Both PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2
pathways participate in the protection by dexmedetomidine against
transient focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Brain
Res. 1494:1–8. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Lonze BE and Ginty DD: Function and
regulation of CREB family transcription factors in the nervous
system. Neuron. 35:605–623. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Impey S, McCorkle SR, Cha-Molstad H, Dwyer
JM, Yochum GS, Boss JM, McWeeney S, Dunn JJ, Mandel G and Goodman
RH: Defining the CREB regulon: A genome-wide analysis of
transcription factor regulatory regions. Cell. 119:1041–1054.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kandel ER: The molecular biology of memory
storage: A dialogue between genes and synapses. Science.
294:1030–1038. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang L, Zhao H, Zhang X, Chen L, Zhao X,
Bai X and Zhang J: Nobiletin protects against cerebral ischemia via
activating the p-Akt, p-CREB, BDNF and Bcl-2 pathway and
ameliorating BBB permeability in rat. Brain Res Bull. 96:45–53.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Huang W, Cao J, Liu X, Meng F, Li M, Chen
B and Zhang J: AMPK plays a dual role in regulation of CREB/BDNF
pathway in mouse primary hippocampal cells. J Mol Neurosci.
56:782–788. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cory S, Huang DC and Adams JM: The Bcl-2
family: Roles in cell survival and oncogenesis. Oncogene.
22:8590–8607. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Koo E, Oshodi T, Meschter C, Ebrahimnejad
A and Dong G: Neurotoxic effects of dexmedetomidine in fetal
cynomolgus monkey brains. J Toxicol Sci. 39:251–262. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|