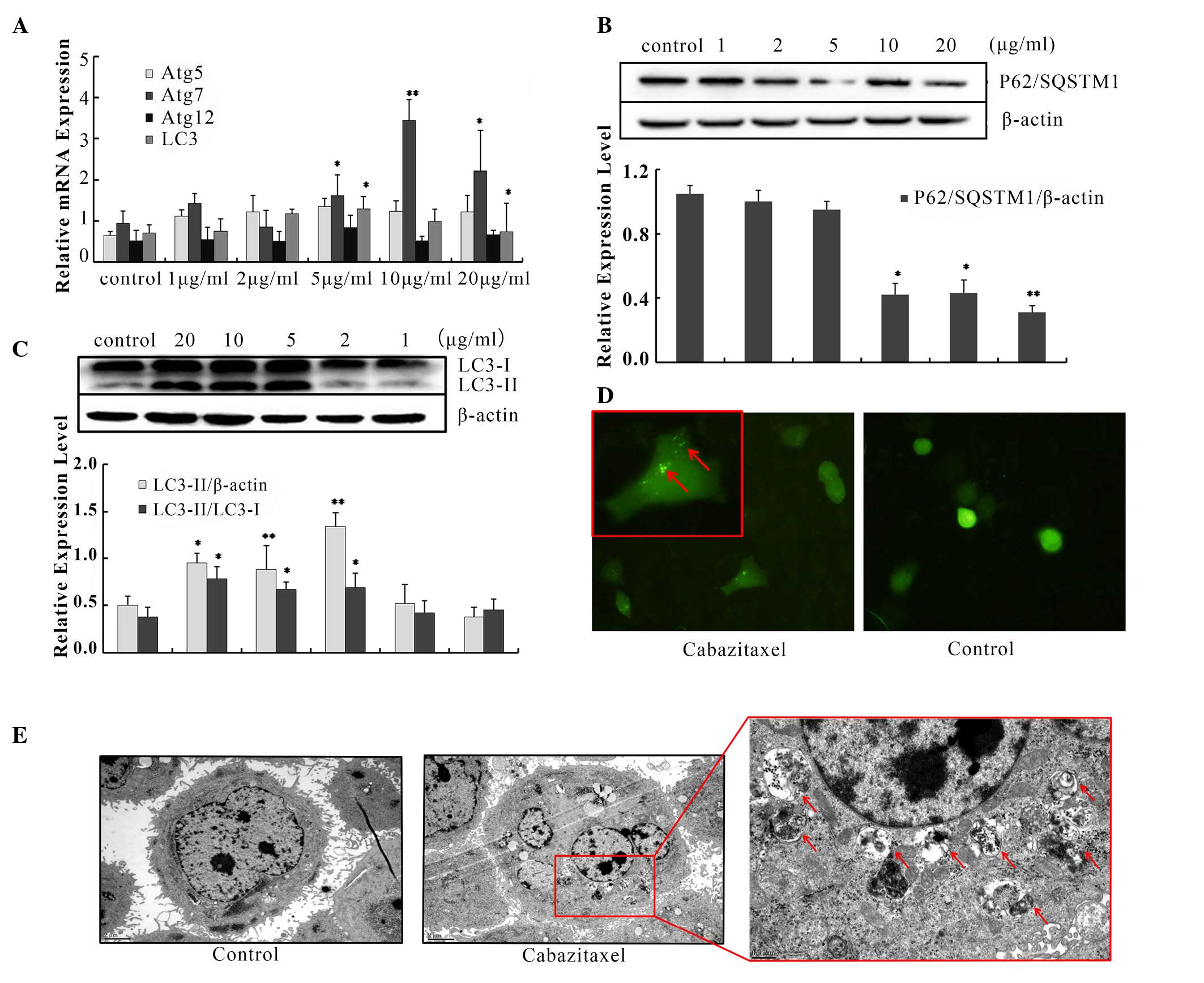
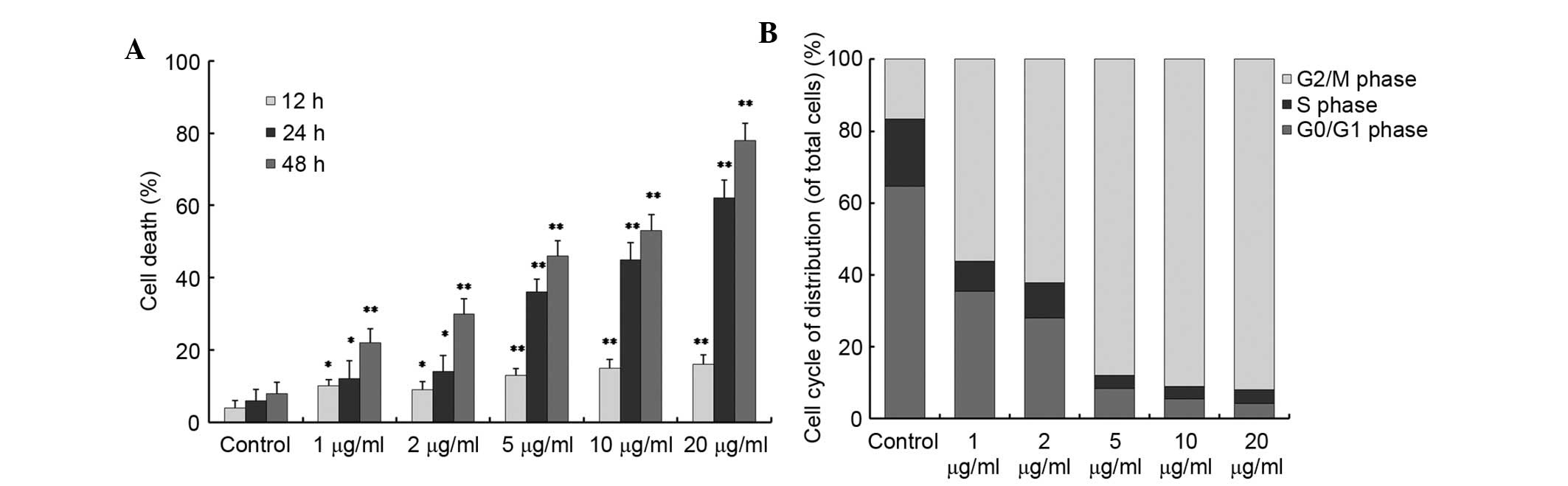
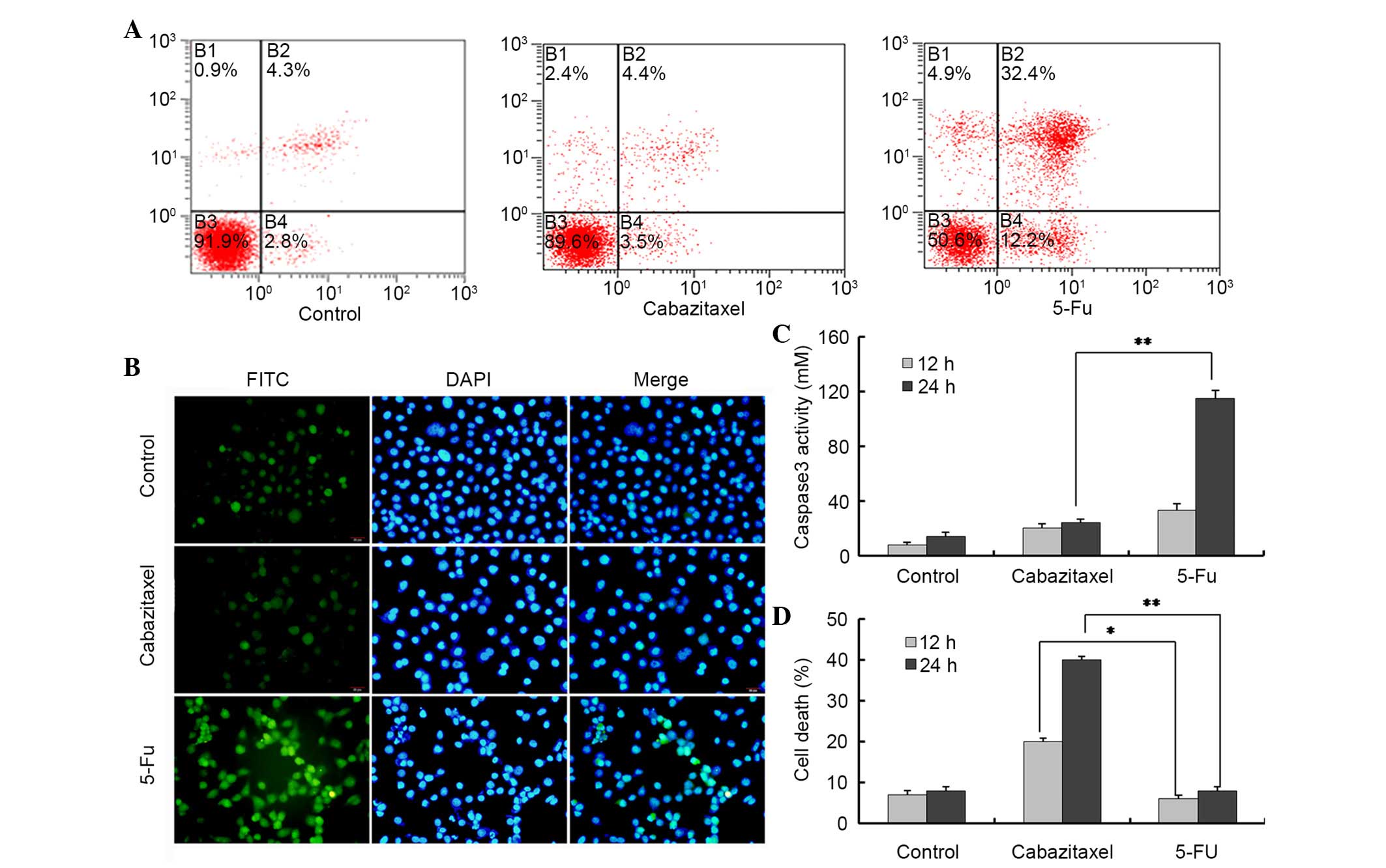
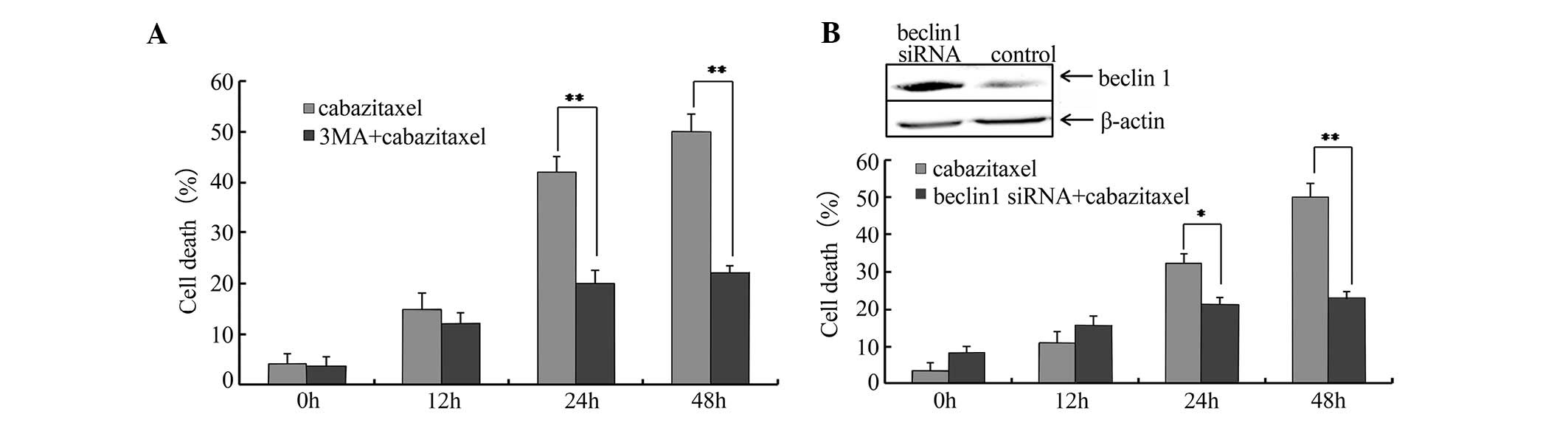
|
1
|
McLeod IX, Jia W and He YW: The
contribution of autophagy to lymphocyte survival and homeostasis.
Immunol Rev. 249:195–204. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang Y and Qin ZH: Coordination of
autophagy with other cellular activities. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
34:585–594. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Janku F, McConkey DJ, Hong DS and Kurzrock
R: Autophagy as a target for anticancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin
Oncol. 8:528–539. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Deretic V: Autophagy in infection. Curr
Opin Cell Biol. 22:252–262. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jiang S, Dupont N, Castillo EF and Deretic
V: Secretory versus degradative autophagy: Unconventional secretion
of inflammatory mediators. J Innate Immun. 5:471–479. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Janda E, Isidoro C, Carresi C and Mollace
V: Defective autophagy in Parkinson's disease: Role of oxidative
stress. Mol Neurobiol. 46:639–661. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ren SY and Xu X: Role of autophagy in
metabolic syndrome-associated heart disease. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1852:225–231. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
White E and DiPaola RS: The double-edged
sword of autophagy modulation in cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
15:5308–5316. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Galluzzi L, Vicencio JM, Kepp O, Tasdemir
E, Maiuri MC and Kroemer G: To die or not to die: That is the
autophagic question. Curr Mol Med. 8:78–91. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shen S, Kepp O and Kroemer G: The end of
autophagic cell death? Autophagy. 8:1–3. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kaminskyy V, Abdi A and Zhivotovsky B: A
quantitative assay for the monitoring of autophagosome accumulation
in different phases of the cell cycle. Autophagy. 7:83–90. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Jiang P and Mizushima N: LC3- and
p62-based biochemical methods for the analysis of autophagy
progression in mammalian cells. Methods. 75:13–18. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Torrisi R, Balduzzi A, Ghisini R, Rocca A,
Bottiglieri L, Giovanardi F, Veronesi P, Luini A, Orlando L, Viale
G, et al: Tailored preoperative treatment of locally advanced
triple negative (hormone receptor negative and HER2 negative)
breast cancer with epirubicin, cisplatin, and infusional
fluorouracil followed by weekly paclitaxel. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 62:667–672. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kaufmann SH and Earnshaw WC: Induction of
apoptosis by cancer chemotherapy. Exp Cell Res. 256:42–49. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang ZJ, Chee CE, Huang S and Sinicrope
FA: The role of autophagy in cancer: Therapeutic implications. Mol
Cancer Ther. 10:1533–1541. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Guo WJ, Zhang YM, Zhang L, Huang B, Tao
FF, Chen W, Guo ZJ, Xu Q and Sun Y: Novel monofunctional platinum
(II) complex Mono-Pt induces apoptosis-independent autophagic cell
death in human ovarian carcinoma cells, distinct from cisplatin.
Autophagy. 9:996–1008. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu XW, Cai TY, Zhu H, Cao J, Su Y, Hu YZ,
He QJ and Yang B: Q6, a novel hypoxia-targeted drug, regulates
hypoxia-inducible factor signaling via an autophagy-dependent
mechanism in hepatocellular carcinoma. Autophagy. 10:111–122. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Dragowska WH, Weppler SA, Wang JC, Wong
LY, Kapanen AI, Rawji JS, Warburton C, Qadir MA, Donohue E, Roberge
M, et al: Induction of autophagy is an early response to gefitinib
and a potential therapeutic target in breast cancer. PLoS One.
8:e765032013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou J, Hu H, Long J, Wan F, Li L, Zhang
S, Shi YE and Chen Y: Vitexin 6, a novel lignan, induces autophagy
and apoptosis by activating the Jun N-terminal kinase pathway.
Anticancer Drugs. 24:928–936. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Vrignaud P, Sémiond D, Lejeune P, Bouchard
H, Calvet L, Combeau C, Riou JF, Commerçon A, Lavelle F and Bissery
MC: Preclinical antitumor activity of cabazitaxel, a semisynthetic
taxane active in taxane-resistant tumors. Clin Cancer Res.
19:2973–2983. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Azarenko O, Smiyun G, Mah J, Wilson L and
Jordan MA: Antiproliferative mechanism of action of the novel
taxane cabazitaxel as compared with the parent compound docetaxel
in MCF7 breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 13:2092–2103. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu F, Liu D, Yang Y and Zhao S: Effect of
autophagy inhibition on chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in A549 lung
cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 5:1261–1265. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yu D, Makkar G, Dong T, Strickland DK,
Sarkar R and Monahan TS: MARCKS signaling differentially regulates
vascular smooth muscle and endothelial cell proliferation through a
KIS-, p27kip1- dependent mechanism. PLoS One. 10:e01413972015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)). Method Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Sharma K, Le N, Alotaibi M and Gewirtz DA:
Cytotoxic autophagy in cancer therapy. Int J Mol Sci.
15:10034–10051. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kung CP, Budina A, Balaburski G,
Bergenstock MK and Murphy M: Autophagy in tumor suppression and
cancer therapy. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 21:71–100. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shen HM and Codogno P: Autophagic cell
death: Loch Ness monster or endangered species? Autophagy.
7:457–465. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Choi KS: Autophagy and cancer. Exp Mol
Med. 44:109–120. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mihaylova MM and Shaw RJ: The AMPK
signalling pathway coordinates cell growth, autophagy and
metabolism. Nat Cell Biol. 13:1016–1023. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Høyer-Hansen M and Jäättelä M:
AMP-activated protein kinase: A universal regulator of autophagy?
Autophagy. 3:381–383. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shi WY, Xiao D, Wang L, Dong LH, Yan ZX,
Shen ZX, Chen SJ, Chen Y and Zhao WL: Therapeutic metformin/AMPK
activation blocked lymphoma cell growth via inhibition of mTOR
pathway and induction of autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 3:e2752012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Corcelle E, Djerbi N, Mari M, Nebout M,
Fiorini C, Fénichel P, Hofman P, Poujeol P and Mograbi B: Control
of the autophagy maturation step by the MAPK ERK and p38: Lessons
from environmental carcinogens. Autophagy. 3:57–59. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Li Y, Zhang P, Qiu F, Chen L, Miao C, Li
J, Xiao W and Ma E: Inactivation of PI3K/Akt signaling mediates
proliferation inhibition and G2/M phase arrest induced by
andrographolide in human glioblastoma cells. Life Sci. 90:962–967.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Takeuchi H, Kondo Y, Fujiwara K, Kanzawa
T, Aoki H, Mills GB and Kondo S: Synergistic augmentation of
rapamycin-induced autophagy in malignant glioma cells by
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B inhibitors. Cancer
Res. 65:3336–3346. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Paglin S, Lee NY, Nakar C, Fitzgerald M,
Plotkin J, Deuel B, Hackett N, McMahill M, Sphicas E, Lampen N and
Yahalom J: Rapamycin-sensitive pathway regulates mitochondrial
membrane potential, autophagy, and survival in irradiated MCF-7
cells. Cancer Res. 65:11061–11070. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Fumarola C, Bonelli MA, Petronini PG and
Alfieri RR: Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in non small cell lung
cancer. Biochem Pharmacol. 90:197–207. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|