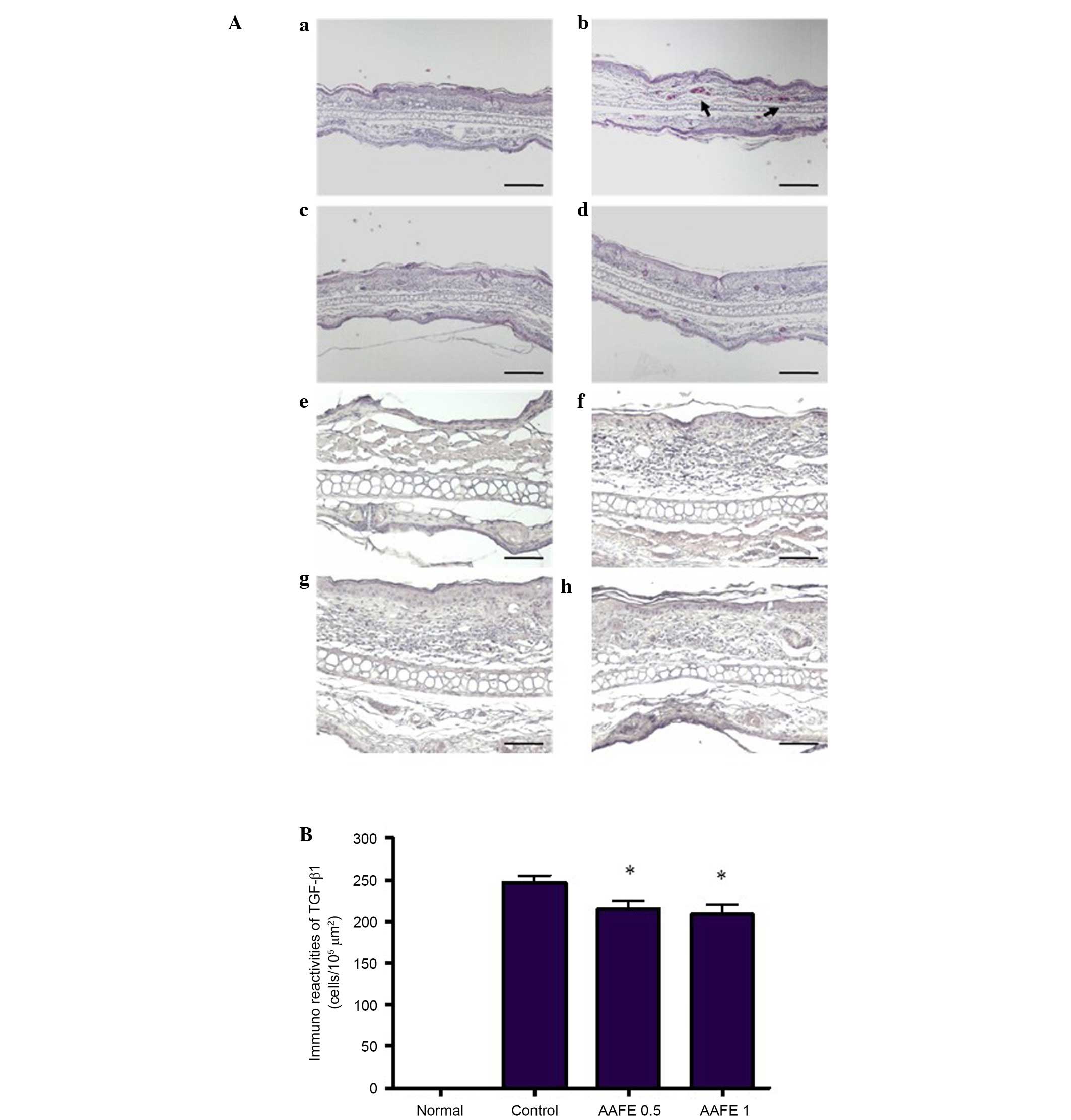
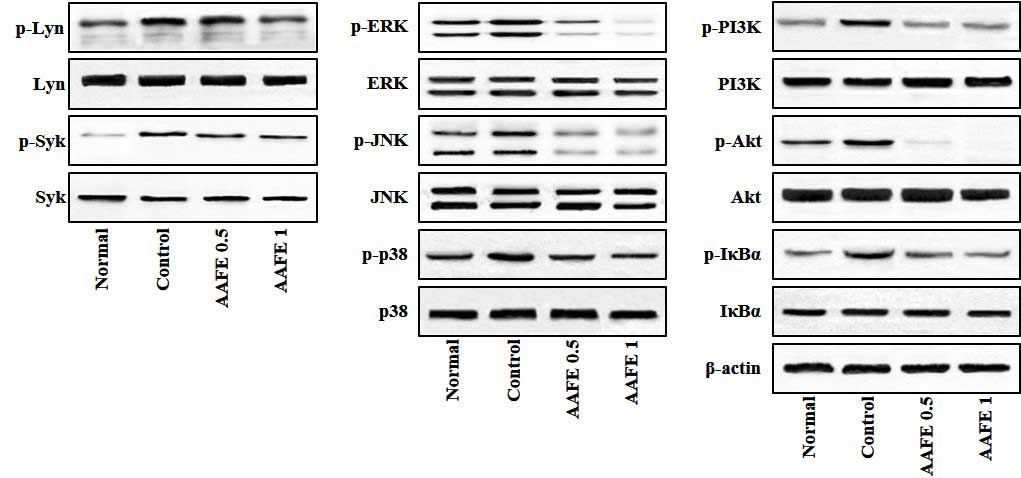
|
1
|
Ren X, Yao C, Wu F, Li Z, Xing J and Zhang
H: Effectiveness of moxibustion treatment in quality of life in
patients with knee osteoarthritis: A randomized, double-blinded,
placebo-controlled trial. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2015:5695232015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen R, Chen M, Xiong J, Chi Z, Zhang B,
Tian N, Xu Z, Zhang T, Li W, Zhang W, et al: Curative effect of
heat-sensitive moxibustion on chronic persistent asthma: A
multicenter randomized controlled trial. J Tradit Chin Med.
33:584–591. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Park JW, Lee BH and Lee H: Moxibustion in
the management of irritable bowel syndrome: Systematic review and
meta-analysis. BMC Complement Altern Med. 13:2472013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yang J, Yu S, Lao L, Yang M, Chen J, Luo
X, Wang Y, Chen X, Li J, Zhu L, et al: Use of moxibustion to treat
primary dysmenorrhea at two interventional times: Study protocol
for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. 16:352015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Guo J, Wang LP, Liu CZ, Zhang J, Wang GL,
Yi JH and Cheng JL: Efficacy of acupuncture for primary insomnia: A
randomized controlled clinical trial. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2013:1638502013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jeong MA, Lee KW, Yoon DY and Lee HJ:
Jaceosidin, a pharmacologically active flavone derived from
Artemisia argyi, inhibits phorbolester-induced upregulation of
COX-2 and MMP-9 by blocking phosphorylation of ERK-1 and -2 in
cultured human mammary epithelial cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1095:458–466. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee SH, Bae EA, Park EK, Shin YW, Baek NI,
Han EJ, Chung HG and Kim DH: Inhibitory effect of eupatilin and
jaceosidin isolated from Artemisia princeps in IgE-induced
hypersensitivity. Int Immunopharmacol. 7:1678–1684. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim MJ, Han JM, Jin YY, Baek NI, Bang MH,
Chung HG, Choi MS, Lee KT, Sok DE and Jeong TS: In vitro
antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of Jaceosidin from
Artemisia princeps Pampanini cv. Sajabal. Arch Pharm Res.
31:429–437. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Min SW, Kim NJ, Baek NI and Kim DH:
Inhibitory effect of eupatilin and jaceosidin isolated from
Artemisia princeps on carrageenan-induced inflammation in mice. J
Ethnopharmacol. 125:497–500. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yin Y, Sun Y, Gu L, Zheng W, Gong F, Wu X,
Shen Y and Xu Q: Jaceosidin inhibits contact hypersensitivity in
mice via down-regulating IFN-γ/STAT1/T-bet signaling in T cells.
Eur J Pharmacol. 651:205–211. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Bao X, Yuan H, Wang C, Liu J and Lan M:
Antitumor and immunomodulatory activities of a polysaccharide from
Artemisia argyi. Carbohydr Polym. 98:1236–1243. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang S, Li J, Sun J, Zeng KW, Cui JR,
Jiang Y and Tu PF: NO inhibitory guaianolide-derived terpenoids
from Artemisia argyi. Fitoterapia. 85:169–175. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Nam Y, Choi M, Hwang H, Lee MG, Kwon BM,
Lee WH and Suk K: Natural flavone jaceosidin is a neuroinflammation
inhibitor. Phytother Res. 27:404–411. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zeng KW, Wang S, Dong X, Jiang Y and Tu
PF: Sesquiterpene dimer (DSF-52) from Artemisia argyi inhibits
microglia-mediated neuroinflammation via suppression of NF-κB,
JNK/p38 MAPKs and Jak2/Stat3 signaling pathways. Phytomedicine.
21:298–306. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Spergel JM and Paller AS: Atopic
dermatitis and the atopic march. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 112(Suppl
6): S118–S127. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Akdis CA, Akdis M, Trautmann A and Blaser
K: Immune regulation in atopic dermatitis. Curr Opin Immunol.
12:641–646. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Peng W and Novak N: Pathogenesis of atopic
dermatitis. Clin Exp Allergy. 45:566–574. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen L, Martinez O, Overbergh L, Mathieu
C, Prabhakar BS and Chan LS: Early up-regulation of Th2 cytokines
and late surge of Th1 cytokines in an atopic dermatitis model. Clin
Exp Immunol. 138:375–387. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dickinson RJ and Keyse SM: Diverse
physiological functions for dual-specificity MAP kinase
phosphatases. J Cell Sci. 119:4607–4615. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sabio G and Davis RJ: TNF and MAP kinase
signalling pathways. Semin Immunol. 26:237–245. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fruman DA and Bismuth G: Fine tuning the
immune response with PI3K. Immunol Rev. 228:253–272. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wullaert A, Bonnet MC and Pasparakis M:
NF-κB in the regulation of epithelial homeostasis and inflammation.
Cell Res. 21:146–158. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals: Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 8th.
National Academies Press (US); Washington (DC), USA: 2011
|
|
24
|
Shore PA, Burkhalter A and Cohn VH Jr: A
method for the fluorometric assay of histamine in tissues. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 127:182–186. 1959.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sanderson MP, Wex E, Kono T, Uto K and
Schnapp A: Syk and Lyn mediate distinct Syk phosphorylation events
in Fcε RI-signal transduction: Implications for regulation of
IgE-mediated degranulation. Mol Immunol. 48:171–178. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Siraganian RP, de Castro RO, Barbu EA and
Zhang J: Mast cell signaling: The role of protein tyrosine kinase
Syk, its activation and screening methods for new pathway
participants. FEBS Lett. 584:4933–4940. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lee KS, Park SJ, Kim SR, Min KH, Lee KY,
Choe YH, Hong SH, Lee YR, Kim JS, Hong SJ, et al: Inhibition of
VEGF blocks TGF-beta1 production through a PI3K/Akt signalling
pathway. Eur Respir J. 31:523–531. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Gilfillan AM and Beaven MA: Regulation of
mast cell responses in health and disease. Crit Rev Immunol.
31:475–529. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Kalesnikoff J and Galli SJ: New
developments in mast cell biology. Nat Immunol. 9:1215–1223. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Leung DY, Boguniewicz M, Howell MD, Nomura
I and Hamid QA: New insights into atopic dermatitis. J Clin Invest.
113:651–657. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Schuepbach-Mallepell S, Philippe V,
Brüggen MC, Watanabe H, Roques S, Baldeschi C and Gaide O:
Antagonistic effect of the inflammasome on thymic stromal
lymphopoietin expression in the skin. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
132:1348–1357. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Peti W and Page R: Molecular basis of MAP
kinase regulation. Protein Sci. 22:1698–1710. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kim MS, Rådinger M and Gilfillan AM: The
multiple roles of phosphoinositide 3-kinase in mast cell biology.
Trends Immunol. 29:493–501. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|