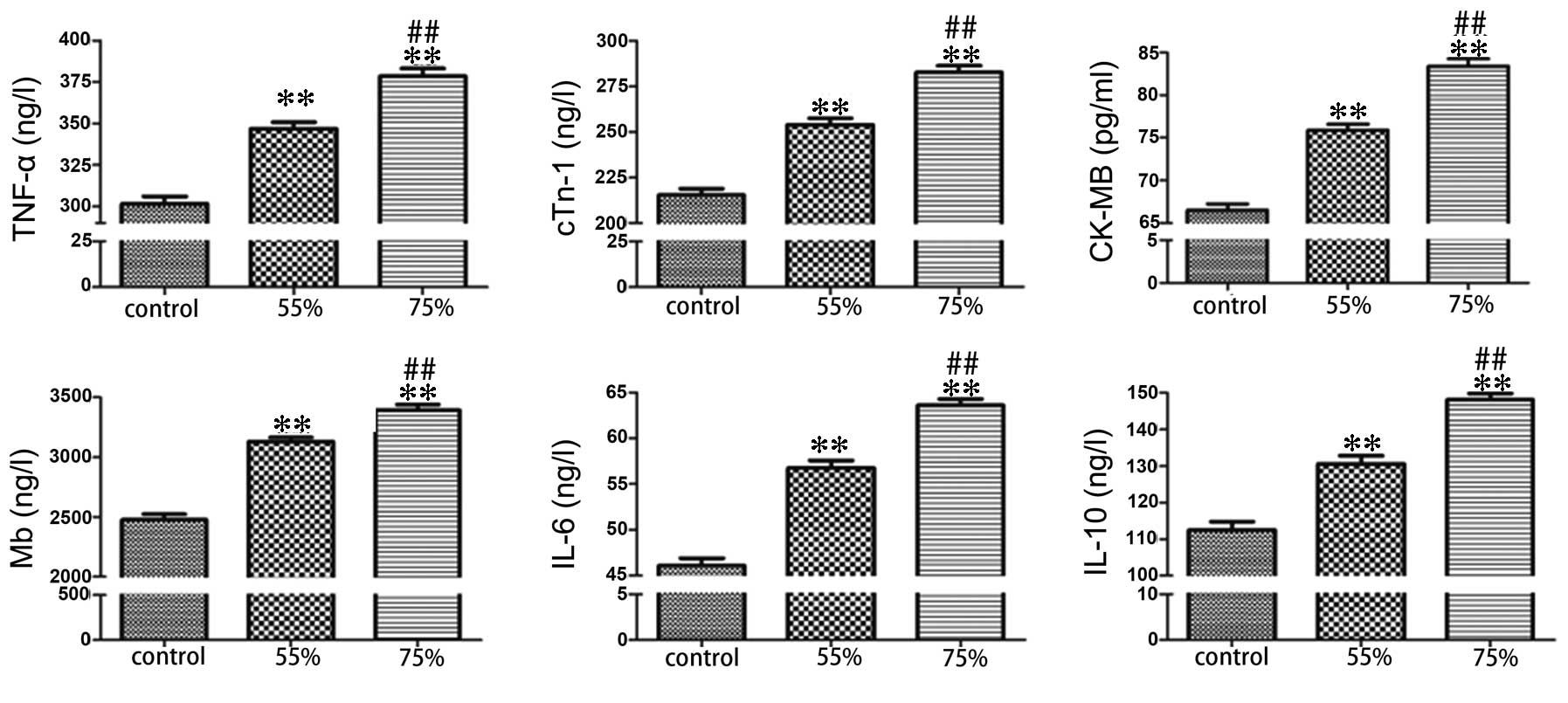
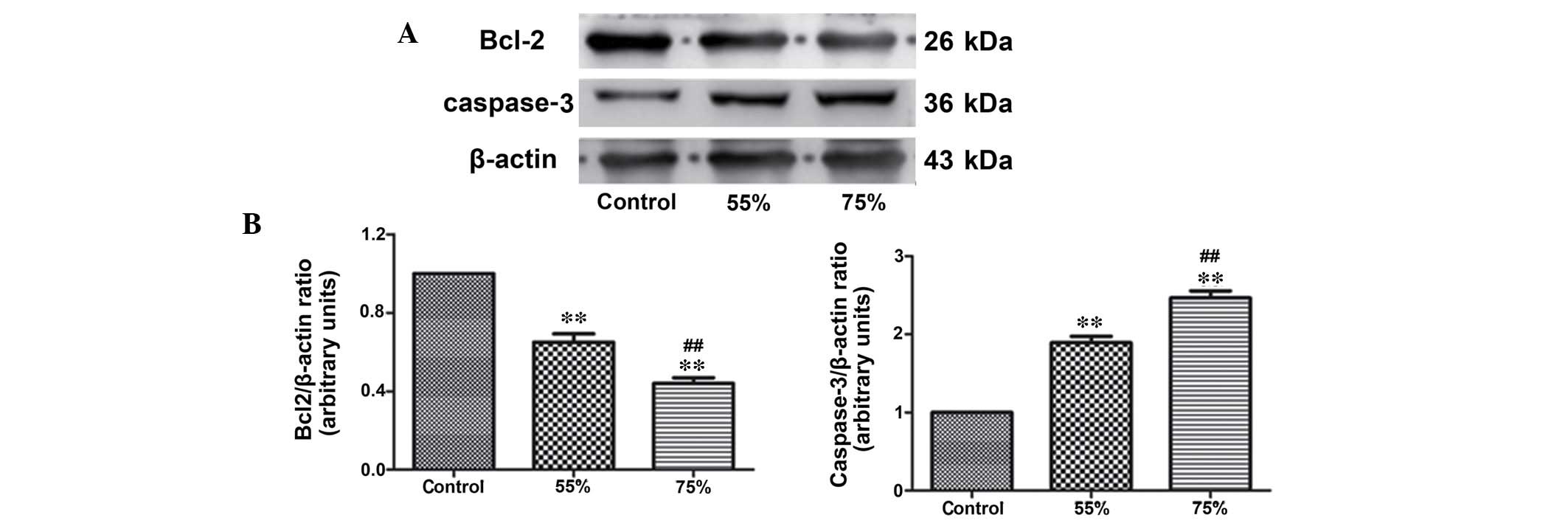
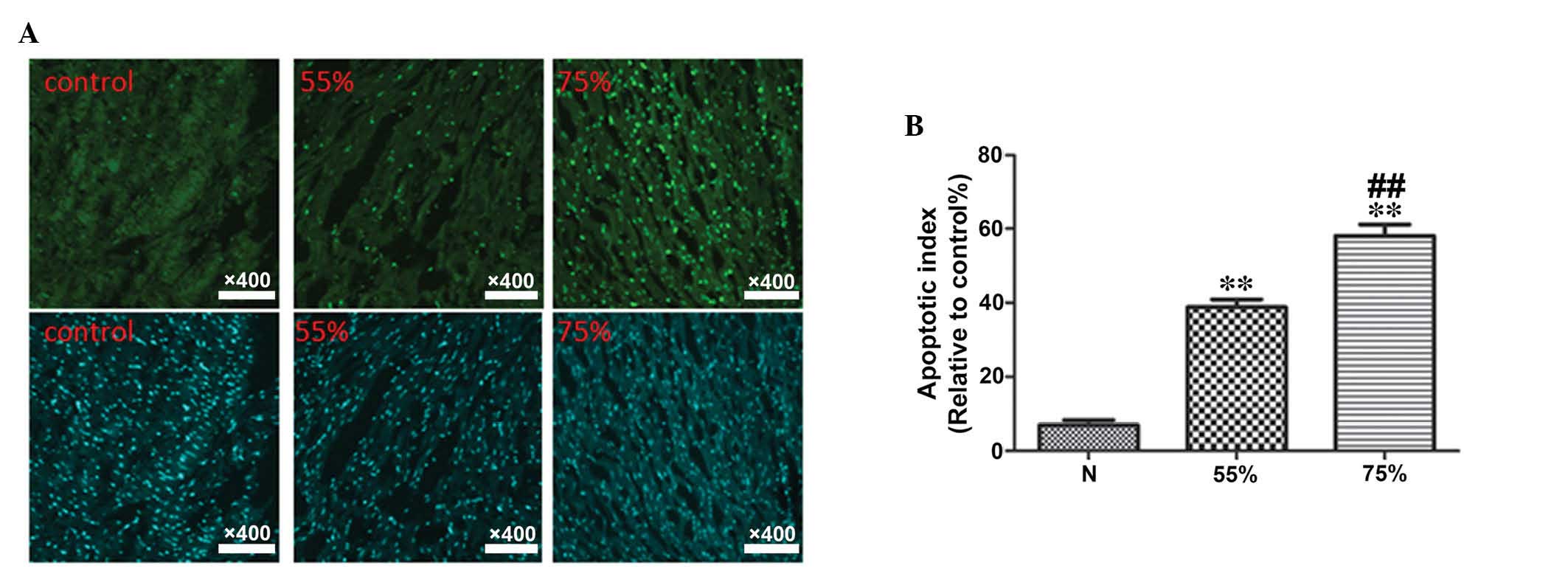
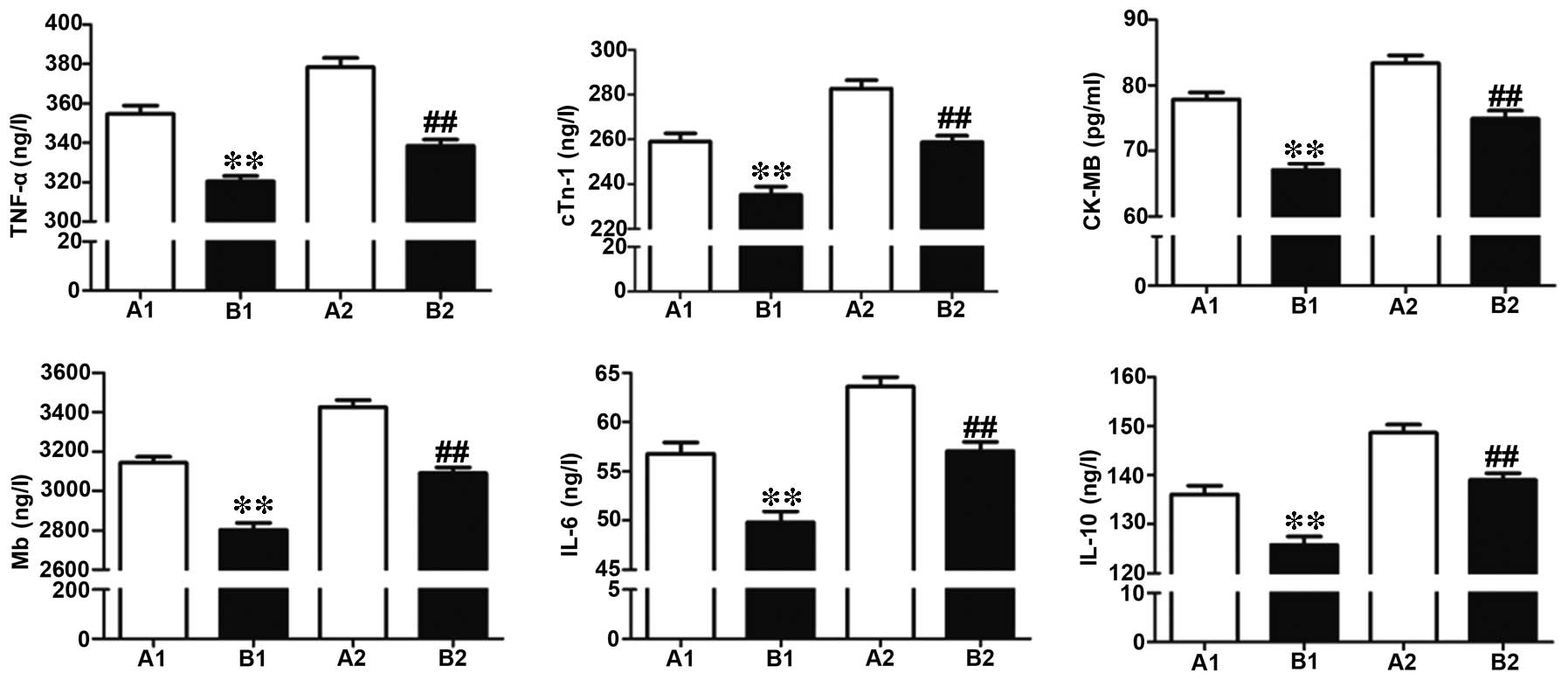
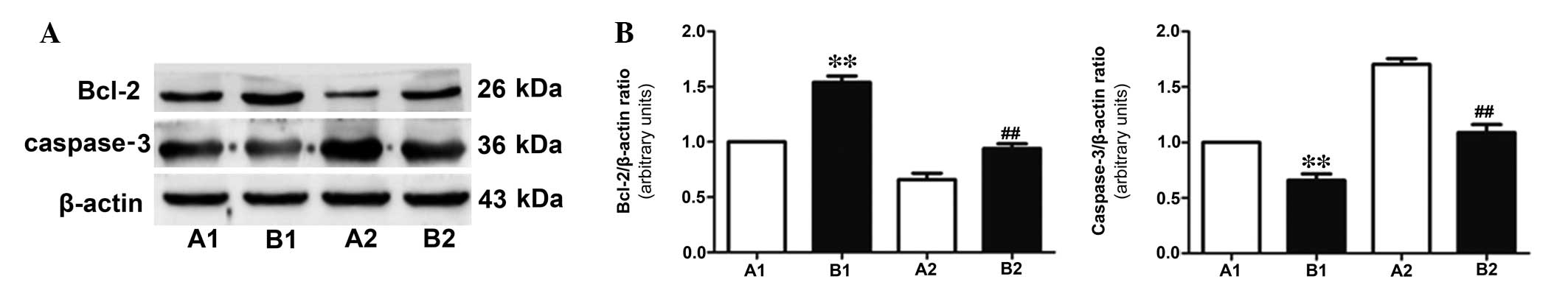
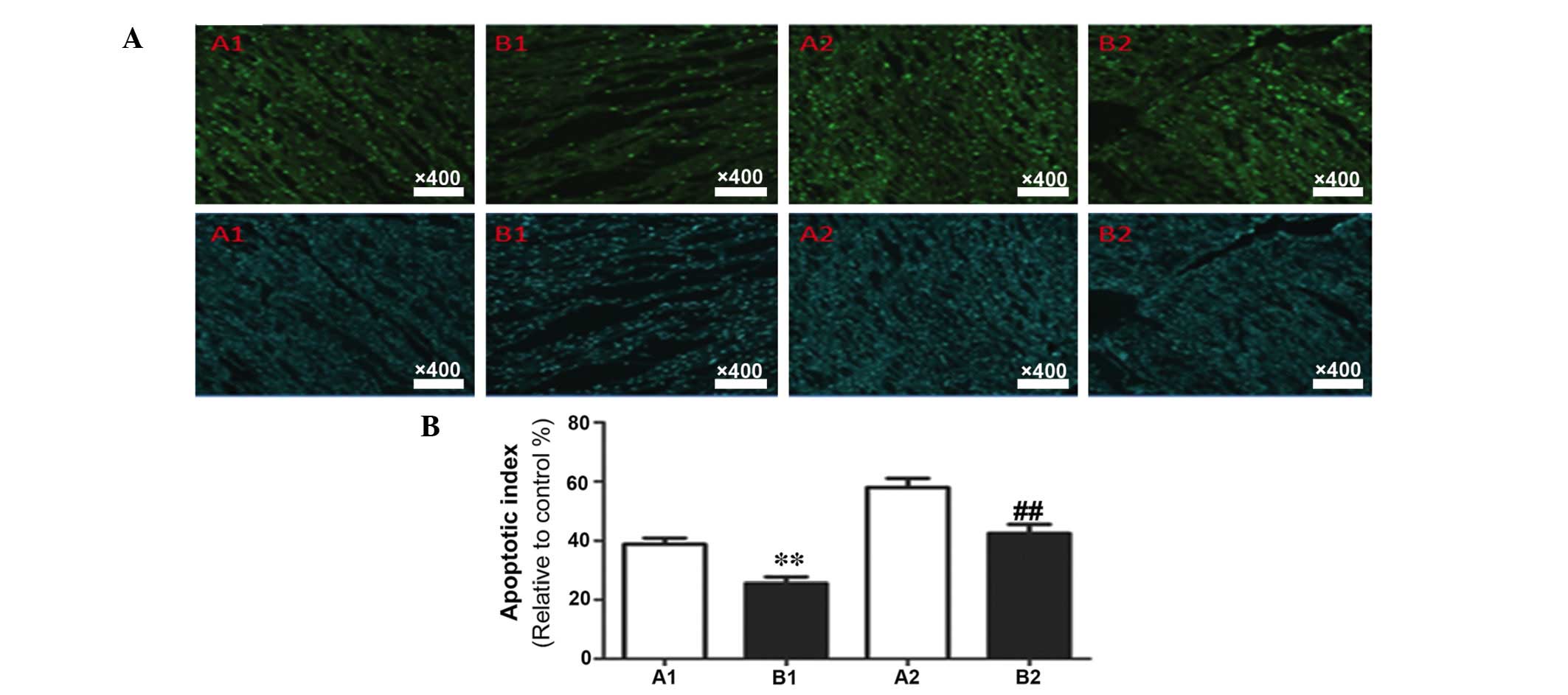
|
1
|
Al Shammeri O, Stafford RS, Alzenaidi A,
Al-Hutaly B and Abdulmonem A: Quality of medical management in
coronary artery disease. Ann Saudi Med. 34:488–493. 2014.
|
|
2
|
Bashinskaya B, Nahed BV, Walcott BP,
Coumans JV and Onuma OK: Socioeconomic status correlates with the
prevalence of advanced coronary artery disease in the United
States. PLoS One. 7:e463142012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu Y, Zhou X, Jiang H, Gao M, Wang L, Shi
Y and Gao J: Percutaneous coronary intervention strategies and
prognosis for graft lesions following coronary artery bypass
grafting. Exp Ther Med. 9:1656–1664. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Deja MA and Malinowski M: Conditioning the
heart in cardiac surgery. Kardiol Pol. 69(Suppl 3): S80–S84.
2011.In Polish.
|
|
5
|
Gorenoi V, Dintsios CM, Schonermark MP and
Hagen A: Drug-eluting stents vs. coronary artery bypass-grafting in
coronary heart disease. GMS Health Technol Assess. 4:c132008.
|
|
6
|
Alexander JH and Smith PK: Coronary-artery
bypass grafting. N Engl J Med. 374:1954–1964. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Luo T and Ni Y: Short-term and long-term
postoperative safety of off-pump versus on-pump coronary artery
bypass grafting for coronary heart disease: A meta-analysis for
randomized controlled trials. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 63:319–327.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wu S, Wan F, Zhang Z, Zhao H, Cui ZQ and
Xie JY: Redo coronary artery bypass grafting: On-pump and off-pump
coronary artery bypass grafting revascularization techniques. Chin
Med Sci J. 30:28–33. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gomez-Lara J, Roura G, Blasco-Lucas A,
Ortiz D, Sbraga F, Romaguera R, Ferreiro JL, Teruel L,
Sanchez-Elvira G, Homs S, et al: Global risk score for choosing the
best revascularization strategy in patients with unprotected left
main stenosis. J Invasive Cardiol. 25:650–658. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Vallely MP and Ross DE: Intracoronary
shunts and off-pump surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 90:700–701. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Guizilini S, Viceconte M, Esperanca GT,
Bolzan DW, Vidotto M, Moreira RS, Câncio AA and Gomes WJ: Pleural
subxyphoid drain confers better pulmonary function and clinical
outcomes in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease after off-pump
coronary artery bypass grafting: A randomized controlled trial. Rev
Bras Cir Cardiovasc. 29:588–594. 2014.
|
|
12
|
Wagner R, Piler P, Gabbasov Z, Maruyama J,
Maruyama K, Nicovsky J and Kruzliak P: Adjuvant cardioprotection in
cardiac surgery: Update. BioMed Res Int. 2014:8080962014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Goncu MT, Sezen M, Toktas F, Ari H, Gunes
M, Tiryakioglu O and Yavuz S: Effect of antegrade graft
cardioplegia combined with passive graft perfusion in on-pump
coronary artery bypass grafting. J Int Med Res. 38:1333–1342. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Teoh LK, Grant R, Hulf JA, Pugsley WB and
Yellon DM: The effect of preconditioning (ischemic and
pharmacological) on myocardial necrosis following coronary artery
bypass graft surgery. Cardiovasc Res. 53:175–180. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Aarsaether E, Rydningen M, Einar Engstad R
and Busund R: Cardioprotective effect of pretreatment with
beta-glucan in coronary artery bypass grafting. Scand Cardiovasc J.
40:298–304. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tritapepe L, De Santis V, Vitale D,
Santulli M, Morelli A, Nofroni I, Puddu PE, Singer M and
Pietropaoli P: Preconditioning effects of levosimendan in coronary
artery bypass grafting-a pilot study. Br J Anaesth. 96:694–700.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yogaratnam JZ, Laden G, Guvendik L, Cowen
M, Cale A and Griffin S: Pharmacological preconditioning with
hyperbaric oxygen: Can this therapy attenuate myocardial ischemic
reper-fusion injury and induce myocardial protection via nitric
oxide? J Surg Res. 149:155–164. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Jeysen ZY, Gerard L, Levant G, Cowen M,
Cale A and Griffin S: Research report: The effects of hyperbaric
oxygen preconditioning on myocardial biomarkers of cardioprotection
in patients having coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Undersea
Hyperb Med. 38:175–185. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sezai A, Hata M, Wakui S, Niino T,
Takayama T, Hirayama A, Saito S and Minami K: Efficacy of
continuous low-dose hANP administration in patients undergoing
emergent coronary artery bypass grafting for acute coronary
syndrome. Circ J. 71:1401–1407. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fattouch K, Bianco G, Speziale G,
Sampognaro R, Lavalle C, Guccione F, Dioguardi P and Ruvolo G:
Beneficial effects of C1 esterase inhibitor in ST-elevation
myocardial infarction in patients who underwent surgical
reperfusion: A randomised double-blind study. Eur J Cardiothorac
Surg. 32:326–332. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sidorenko GI, Gelis LG, Medvedeva EA,
Ostrovskiĭ IuP, Lazareva IV, Sevruk TV, Shibeko NA and Petrov IuP:
Pharmacological protection of the myocardium with reamberin in
coronary artery bypass grafting in patients with postinfarction
angina. Ter Arkh. 83:35–40. 2011.In Russian.
|
|
22
|
Michelis KC, Boehm M and Kovacic JC: New
vessel formation in the context of cardiomyocyte regeneration - the
role and importance of an adequate perfusing vasculature. Stem Cell
Res. 13(3 Pt B): 666–682. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|