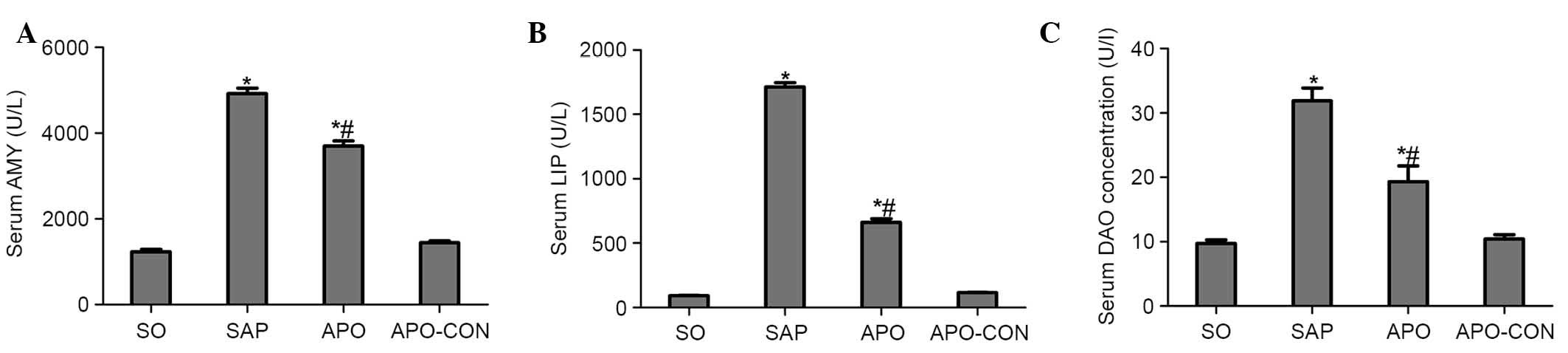
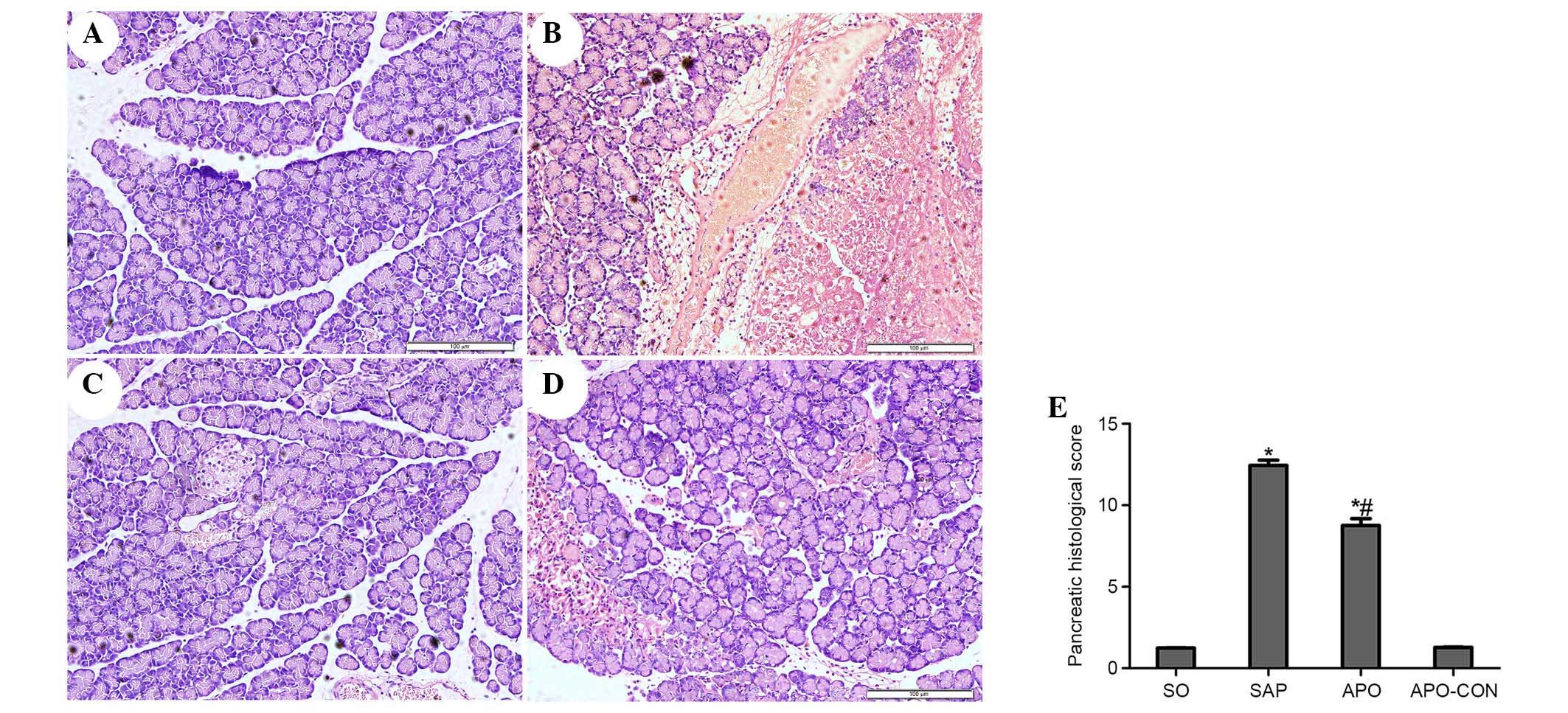
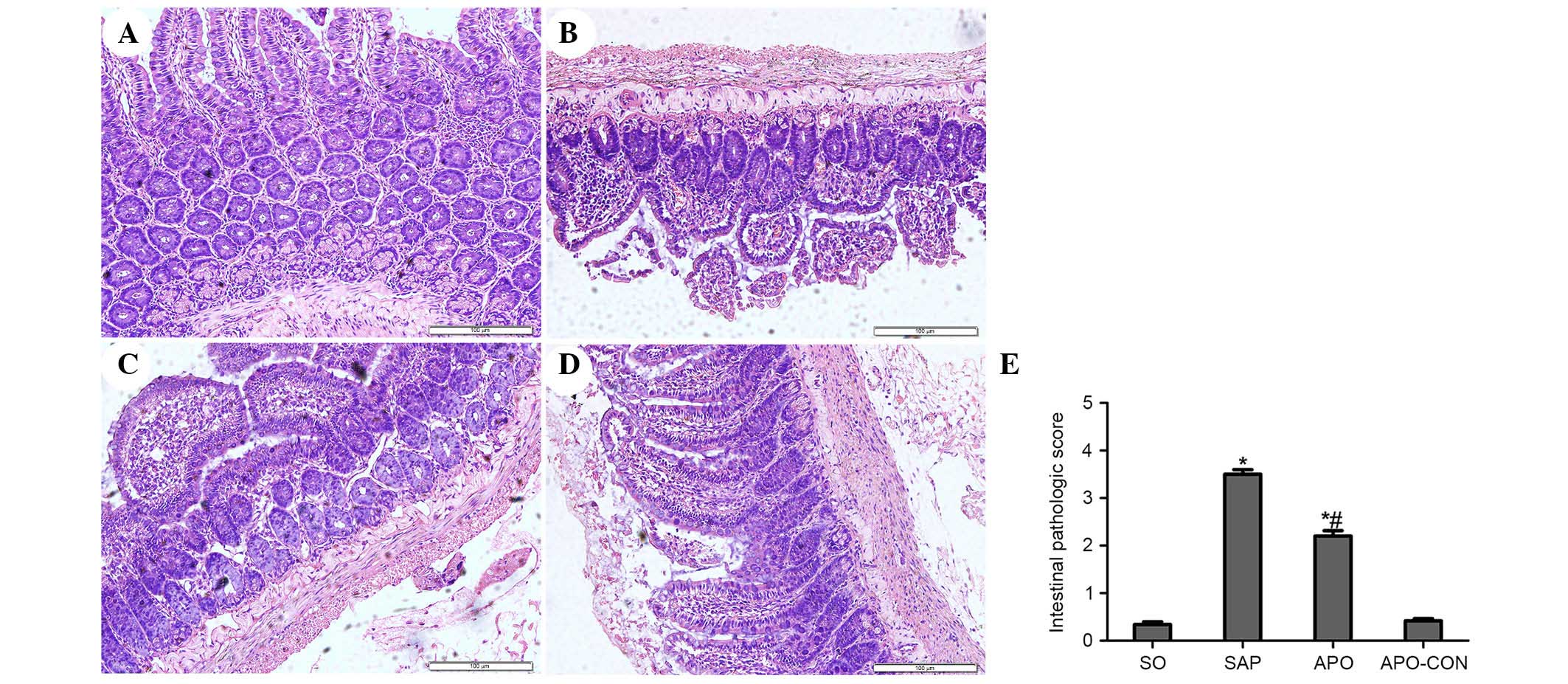
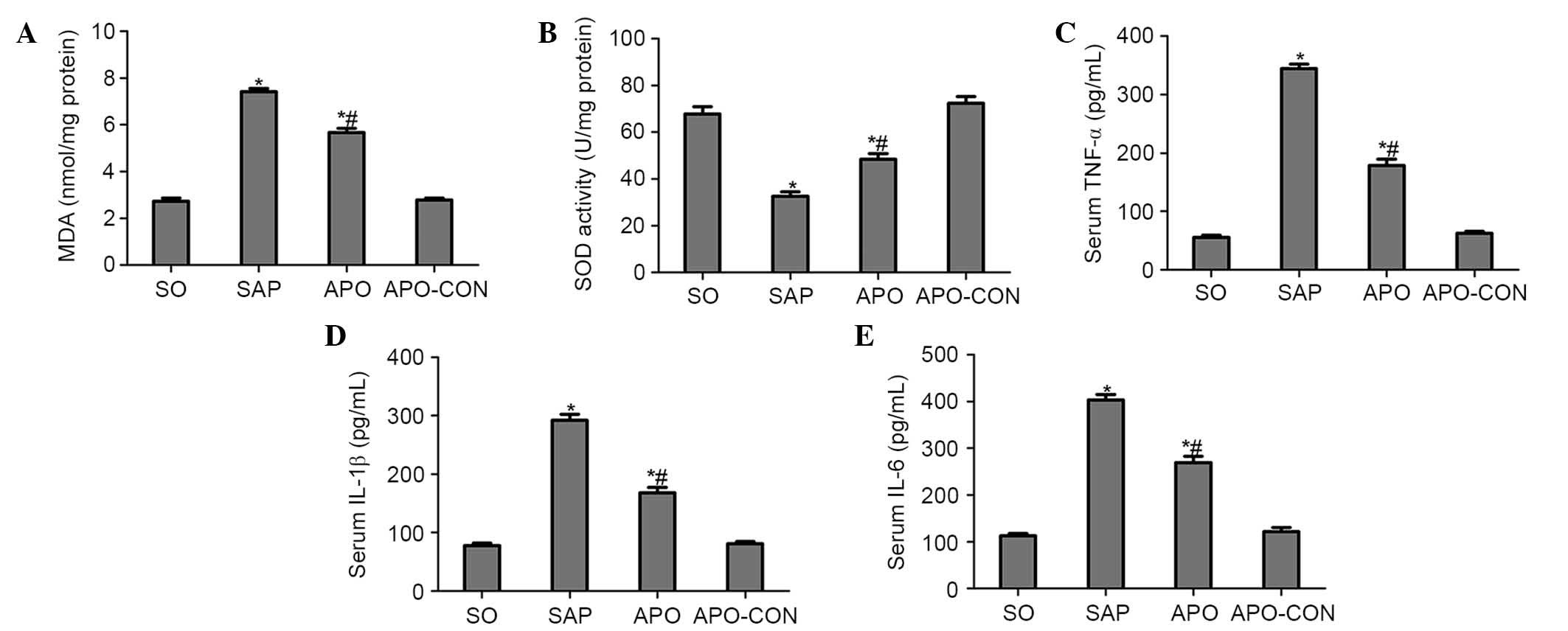
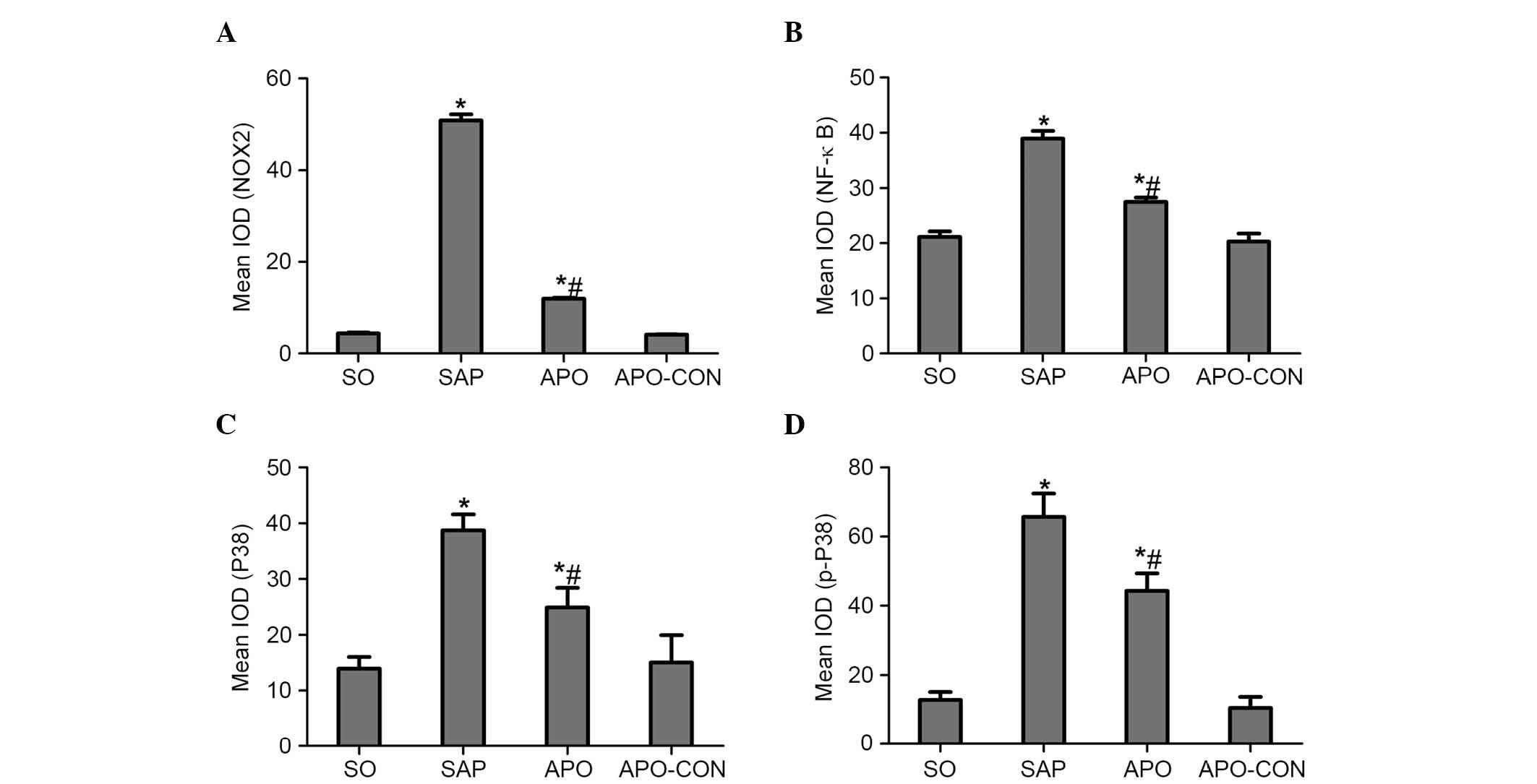
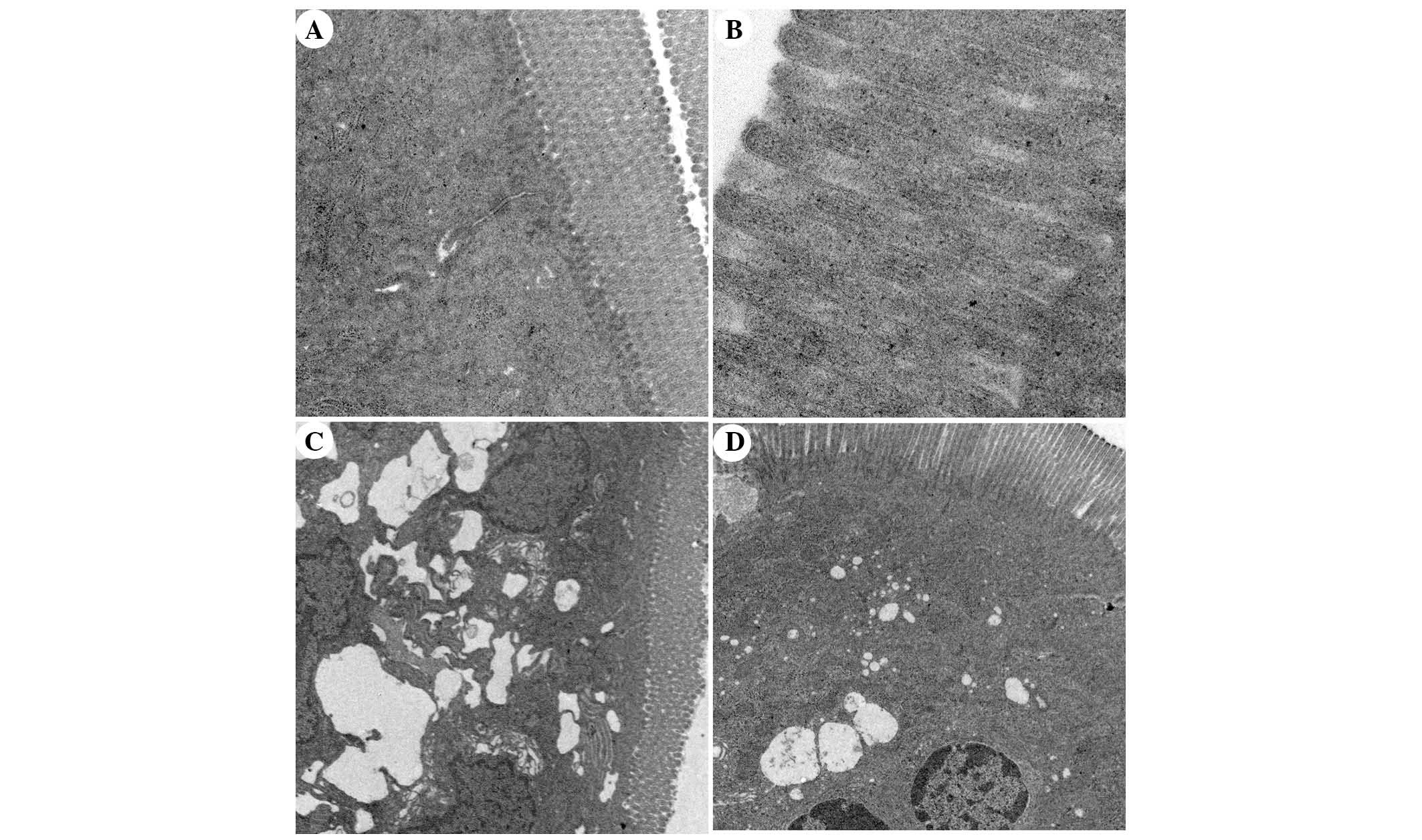
|
1
|
Lankisch PG, Apte M and Banks PA: Acute
pancreatitis. Lancet. 386:85–96. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ammori BJ: Role of the gut in the course
of severe acute pancreatitis. Pancreas. 26:122–129. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rahman SH, Ammori BJ, Holmfield J, Larvin
M and McMahon MJ: Intestinal hypoperfusion contributes to gut
barrier failure in severe acute pancreatitis. J Gastrointest Surg.
7:26–35; discussion 35–36. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Capurso G, Zerboni G, Signoretti M,
Valente R, Stigliano S, Piciucchi M and Delle Fave G: Role of the
gut barrier in acute pancreatitis. J Clin Gastroenterol.
46:S46–S51. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang XP, Zhang J, Song QL and Chen HQ:
Mechanism of acute pancreatitis complicated with injury of
intestinal mucosa barrier. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 8:888–895. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Tian R, Tan JT, Wang RL, Xie H, Qian YB
and Yu KL: The role of intestinal mucosa oxidative stress in gut
barrier dysfunction of severe acute pancreatitis. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 17:349–355. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Masamune A, Watanabe T, Kikuta K, Satoh K
and Shimosegawa T: NADPH oxidase plays a crucial role in the
activation of pancreatic stellate cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest
Liver Physiol. 294:G99–G108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lambeth JD: NOX enzymes and the biology of
reactive oxygen. Nat Rev Immunol. 4:181–189. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hancock JT, Desikan R and Neill SJ:
Hydrogen peroxide and nitric oxide in plant defence: Revealing
potential targets for oxidative stress tolerance? Biofactors.
15:99–101. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Yu JH, Lim JW, Kim H and Kim KH: NADPH
oxidase mediates interleukin-6 expression in cerulein-stimulated
pancreatic acinar cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 37:1458–1469.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gukovskaya AS, Vaquero E, Zaninovic V,
Gorelick FS, Lusis AJ, Brennan ML, Holland S and Pandol SJ:
Neutrophils and NADPH oxidase mediate intrapancreatic trypsin
activation in murine experimental acute pancreatitis.
Gastroenterology. 122:974–984. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Uysal A, Sahna E, Ozguler IM, Burma O and
Ilhan N: Effects of apocynin, an NADPH oxidase inhibitor, on levels
of ADMA, MPO, iNOS and TLR4 induced by myocardial ischemia
reperfusion. Perfusion. 30:472–477. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zhang YS, He L, Liu B, Li NS, Luo XJ, Hu
CP, Ma QL, Zhang GG, Li YJ and Peng J: A novel pathway of NADPH
oxidase/vascular peroxidase 1 in mediating oxidative injury
following ischemia-reperfusion. Basic Res Cardiol. 107:2662012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Schmidt J, Rattner DW, Lewandrowski K,
Compton CC, Mandavilli U, Knoefel WT and Warshaw AL: A better model
of acute pancreatitis for evaluating therapy. Ann Surg. 215:44–56.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chiu CJ, McArdle AH, Brown R, Scott HJ and
Gurd FN: Intestinal mucosal lesion in low-flow states. I. A
morphological, hemodynamic, and metabolic reappraisal. Arch Surg.
101:478–483. 1970. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mohammed AM, Syeda K, Hadden T and Kowluru
A: Upregulation of phagocyte-like NADPH oxidase by cytokines in
pancreatic beta-cells: Attenuation of oxidative and nitrosative
stress by 2-bromopalmitate. Biochem Pharmacol. 85:109–114. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Rebelato E, Mares-Guia TR, Graciano MF,
Labriola L, Britto LR, Garay-Malpartida HM, Curi R, Sogayar MC and
Carpinelli AR: Expression of NADPH oxidase in human pancreatic
islets. Life Sci. 91:244–249. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hu R, Wang YL, Edderkaoui M, Lugea A, Apte
MV and Pandol SJ: Ethanol augments PDGF-induced NADPH oxidase
activity and proliferation in rat pancreatic stellate cells.
Pancreatology. 7:332–340. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cao WL, Xiang XH, Chen K, Xu W and Xia SH:
Potential role of NADPH oxidase in pathogenesis of pancreatitis.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 5:169–177. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Impellizzeri D, Esposito E, Mazzon E,
Paterniti I, Di Paola R, Bramanti P and Cuzzocrea S: Effect of
apocynin, a NADPH oxidase inhibitor, on acute lung inflammation.
Biochem Pharmacol. 81:636–648. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kono H, Rusyn I, Uesugi T, Yamashina S,
Connor HD, Dikalova A, Mason RP and Thurman RG: Diphenyleneiodonium
sulfate, an NADPH oxidase inhibitor, prevents early alcohol-induced
liver injury in the rat. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
280:G1005–G1012. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dodd-O JM and Pearse DB: Effect of the
NADPH oxidase inhibitor apocynin on ischemia-reperfusion lung
injury. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 279:H303–H312.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Joshi S, Peck AB and Khan SR: NADPH
oxidase as a therapeutic target for oxalate induced injury in
kidneys. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013:4623612013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ferreira AP, Rodrigues FS, Della-Pace ID,
Mota BC, Oliveira SM, Velho Gewehr Cde C, Bobinski F, de Oliveira
CV, Brum JS, Oliveira MS, et al: The effect of NADPH-oxidase
inhibitor apocynin on cognitive impairment induced by moderate
lateral fluid percussion injury: Role of inflammatory and oxidative
brain damage. Neurochem Int. 63:583–593. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Genovese T, Mazzon E, Paterniti I,
Esposito E, Bramanti P and Cuzzocrea S: Modulation of NADPH oxidase
activation in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Brain
Res. 1372:92–102. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Liu PG, He SQ, Zhang YH and Wu J:
Protective effects of apocynin and allopurinol on
ischemia/reperfusion-induced liver injury in mice. World J
Gastroenterol. 14:2832–2837. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Leveau P, Wang X, Sun Z, Börjesson A,
Andersson E and Andersson R: Severity of pancreatitis-associated
gut barrier dysfunction is reduced following treatment with the PAF
inhibitor lexipafant. Biochem Pharmacol. 69:1325–1331. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang JW, Zhang GX, Chen HL, Liu GL, Owusu
L, Wang YX, Wang GY and Xu CM: Therapeutic effect of Qingyi
decoction in severe acute pancreatitis-induced intestinal barrier
injury. World J Gastroenterol. 21:3537–3546. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sun JJ, Chu ZJ, Liu WF, Qi SF, Yang YH, Ge
PL, Zhang XH, Li WS, Yang C and Zhang YM: Perirenal space blocking
restores gastrointestinal function in patients with severe acute
pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 19:8752–8757. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
Yue C, Wang W, Tian WL, Huang Q, Zhao RS,
Zhao YZ, Li QR and Li JS: Lipopolysaccharide-induced failure of the
gut barrier is site-specific and inhibitable by growth hormone.
Inflamm Res. 62:407–415. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Leung PS and Chan YC: Role of oxidative
stress in pancreatic inflammation. Antioxid Redox Signal.
11:135–165. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Ju KD, Lim JW, Kim KH and Kim H: Potential
role of NADPH oxidase-mediated activation of Jak2/Stat3 and
mitogen-activated protein kinases and expression of TGF-β1 in the
pathophysiology of acute pancreatitis. Inflamm Res. 60:791–800.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kim H: Cerulein pancreatitis: Oxidative
stress, inflammation, and apoptosis. Gut Liver. 2:74–80. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Williard DE, Twait E, Yuan Z, Carter AB
and Samuel I: Nuclear factor kappa B-dependent gene transcription
in cholecystokinin- and tumor necrosis factor-alpha-stimulated
isolated acinar cells is regulated by p38 mitogen-activated protein
kinase. Am J Surg. 200:283–290. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yang Y, Kim SC, Yu T, Yi YS, Rhee MH, Sung
GH, Yoo BC and Cho JY: Functional roles of p38 mitogen-activated
protein kinase in macrophage-mediated inflammatory responses.
Mediators Inflamm. 2014:3523712014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cao MH, Xu J, Cai HD, Lv ZW, Feng YJ, Li
K, Chen CQ and Li YY: p38 MAPK inhibition alleviates experimental
acute pancreatitis in mice. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int.
14:101–106. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Papachristou DJ, Papadakou E, Basdra EK,
Baltopoulos P, Panagiotopoulos E and Papavassiliou AG: Involvement
of the p38 MAPK-NF-kappaB signal transduction pathway and COX-2 in
the pathobiology of meniscus degeneration in humans. Mol Med.
14:160–166. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhu L, Song S, Pi Y, Yu Y, She W, Ye H, Su
Y and Hu Q: Cumulated Ca2+ spike duration underlies
Ca2+ oscillation frequency-regulated NFκB
transcriptional activity. J Cell Sci. 124:2591–2601. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tudhope SJ, Finney-Hayward TK, Nicholson
AG, Mayer RJ, Barnette MS, Barnes PJ and Donnelly LE: Different
mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent cytokine responses in
cells of the monocyte lineage. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 324:306–312.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|