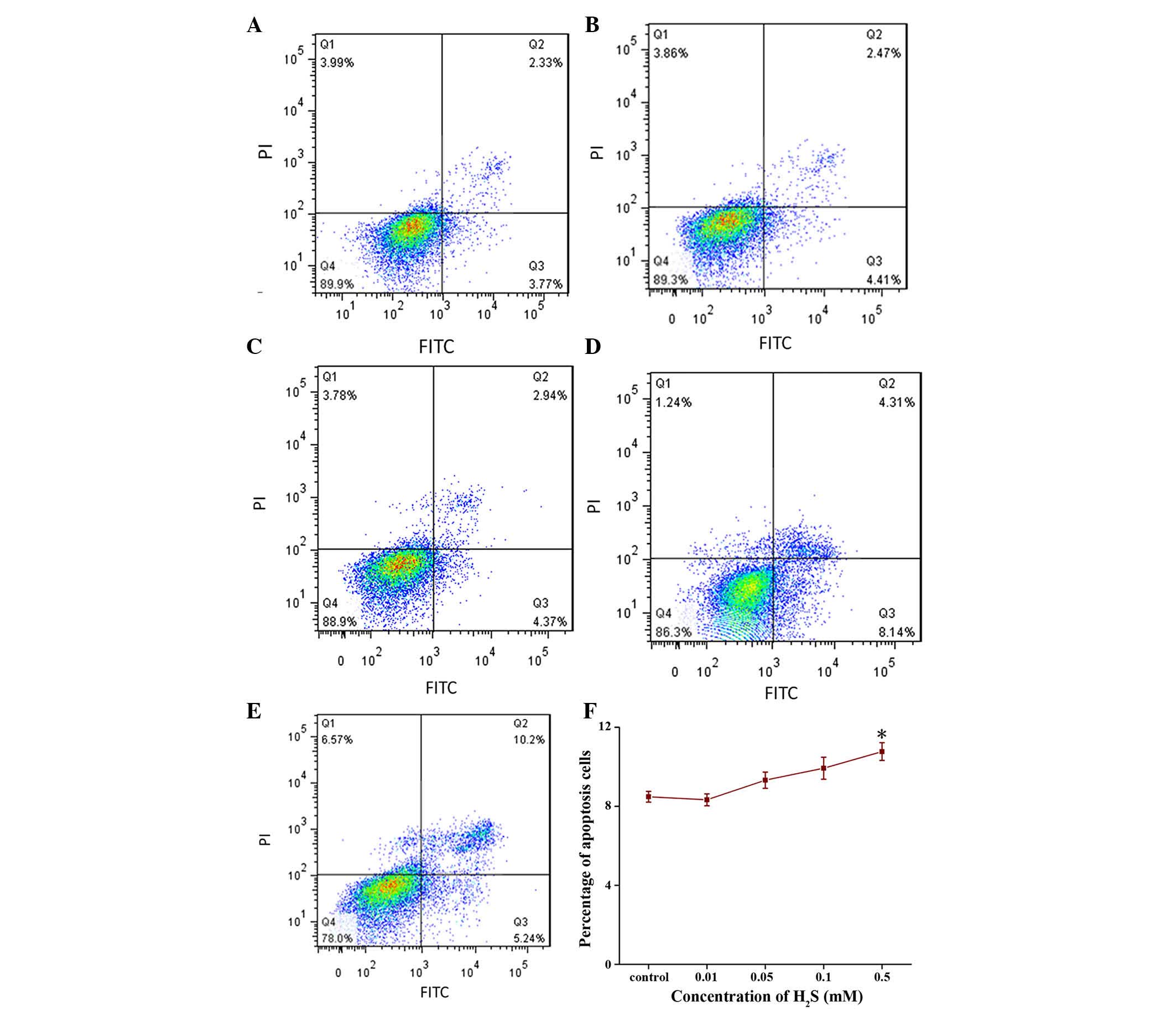
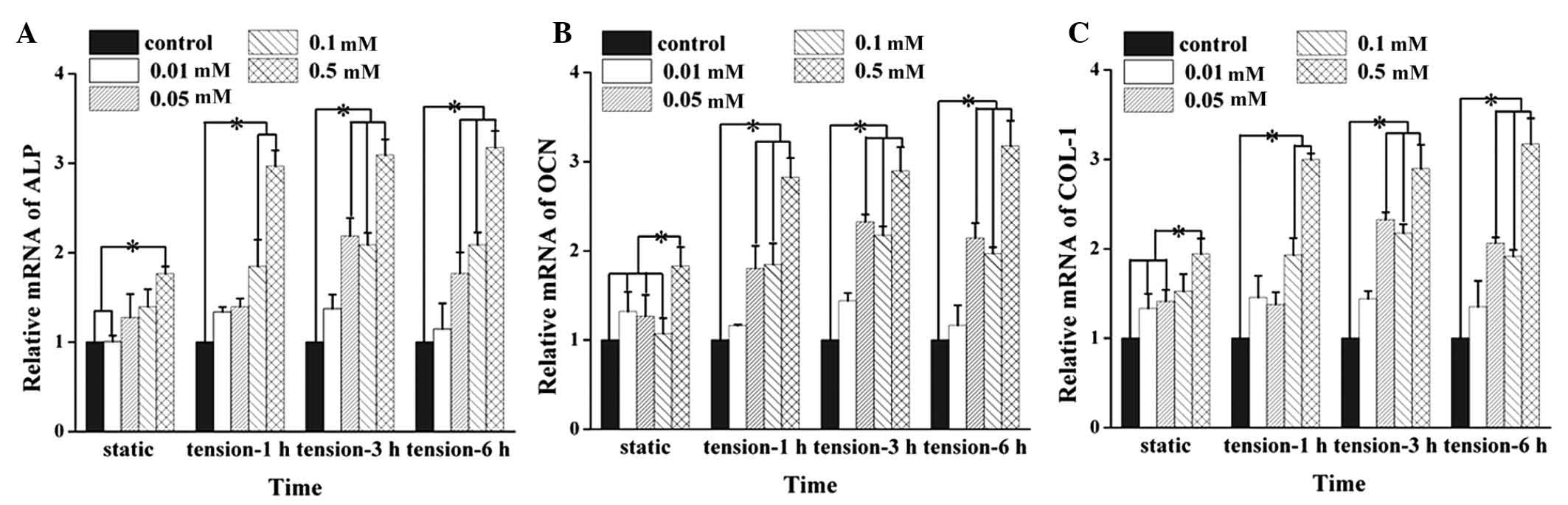
|
1
|
McCulloch CA, Lekic P and McKee MD: Role
of physical forces in regulating the form and function of the
periodontal ligament. Periodontol. 24:56–72. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Matsuda N, Morita N, Matsuda K and
Watanabe M: Proliferation and differentiation of human osteoblastic
cells associated with differential activation of MAP kinases in
response to epidermal growth factor, hypoxia, and mechanical stress
in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 249:350–354. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shimizu N, Ozawa Y, Yamaguchi M, Goseki T,
Ohzeki K and Abiko Y: Induction of COX-2 expression by mechanical
tension force in human periodontal ligament cells. J Periodontol.
69:670–677. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Myokai F, Oyama M, Nishimura F, Ohira T,
Yamamoto T, Arai H, Takashiba S and Murayama Y: Unique genes
induced by mechanical stress in periodontal ligament cells. J
Periodontal Res. 38:255–261. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu M, Dai J, Lin Y, Yang L, Dong H, Li Y,
Ding Y and Duan Y: Effect of the cyclic stretch on the expression
of osteogenesis genes in human periodontal ligament cells. Gene.
491:187–193. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
De Bernard B: Glycoproteins in the local
mechanism of calcification. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 233–244.
1982.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hauschka PV: Osteocalcin: The vitamin
K-dependent Ca2+-binding protein of bone matrix. Haemostasis.
16:258–272. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Neugebauer BM, Moore MA, Broess M,
Gerstenfeld LC and Hauschka PV: Characterization of structural
sequences in the chicken osteocalcin gene: Expression of
osteocalcin by maturing osteoblasts and by hypertrophic
chondrocytes in vitro. J Bone Miner Res. 10:157–163. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Huang YH, Ohsaki Y and Kurisu K:
Distribution of type I and type III collagen in the developing
periodontal ligament of mice. Matrix. 11:25–35. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mariotti A: The extracellular matrix of
the periodontium: Dynamic and interactive tissues. Periodontol
2000. 3:39–63. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Beauchamp RO Jr, Bus JS, Popp JA, Boreiko
CJ and Andjelkovich DA: A critical-review of the literature on
hydrogen-sulfide toxicity. Crit Rev Toxicol. 13:25–97. 1984.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zanardo RC, Brancaleone V, Distrutti E,
Fiorucci S, Cirino G and Wallace JL: Hydrogen sulfide is an
endogenous modulator of leukocyte-mediated inflammation. FASEB J.
20:2118–2120. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ma HB, Huang S, Yin XR, Zhang Y and Di ZL:
Apoptotic pathway induced by diallyl trisulfide in pancreatic
cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol. 20:193–203. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee ZW, Teo XY, Tay EY, Tan CH, Hagen T,
Moore PK and Deng LW: Utilizing hydrogen sulfide as a novel
anti-cancer agent by targeting cancer glycolysis and pH imbalance.
Br J Pharmacol. 171:4322–4336. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tay AS, Hu LF, Lu M, Wong PT and Bian JS:
Hydrogen sulfide protects neurons against hypoxic injury via
stimulation of ATP-sensitive potassium channel/protein kinase
C/extracellular signal-regulated kinase/heat shock protein 90
pathway. J Neuroscience. 167:277–286. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Baskar R and Bian J: Hydrogen sulfide gas
has cell growth regulatory role. Eur J Pharmacol. 656:5–9. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liao C and Hua Y: Effect of hydrogen
sulphide on the expression of osteoprotegerin and receptor
activator of NF-kB ligand in human periodontal ligament cells
induced by tension-force stimulation. Arch Oral Biol. 58:1784–1790.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wu Y, Liu F, Zhang X and Shu L: Insulin
modulates cytokines expression in human periodontal ligament cells.
Arch Oral Biol. 59:1301–1306. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hughes MN, Centelles MN and Moore KP:
Making and working with hydrogen sulfide: The chemistry and
generation of hydrogen sulfide in vitro and its measurement in
vivo: A review. Free Radical Bio Med. 47:1346–1353. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Dong-Xu L, Hong-Ning W, Chun-Ling W, Hong
L, Ping S and Xiao Y: Modulus of elasticity of human periodontal
ligament by optical measurement and numerical simulation. Angle
Orthod. 81:229–236. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ito M, Suga T, Akiyoshi K, Nukuzuma S,
Kon-no M, Umegaki Y, Kohdera U and Ihara T: Detection of measles
virus RNA on SYBR green real-time reverse transcription-polymerase
chain reaction. Pediatr Int. 52:611–615. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kimura H, Nagai Y, Umemura K and Kimura Y:
Physiological roles of hydrogen sulfide: Synaptic modulation,
neuroprotection, and smooth muscle relaxation. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 7:795–803. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Piper HM, Meuter K and Schäfer C: Cellular
mechanisms of ischemia-reperfusion injury. Ann Thorac Surg.
75:S644–S648. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Abe K and Kimura H: The possible role of
hydrogen sulfide as an endogenous neuromodulator. J Neurosci.
16:1066–1071. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wei HJ, Li X and Tang XQ: Therapeutic
benefits of H2S in Alzheimer's disease. J Clin Neurosci.
21:1665–1669. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tang XQ, Yang CT, Chen J, Yin WL, Tian SW,
Hu B, Feng JQ and Li YJ: Effect of hydrogen sulphide on
beta-amyloid-induced damage in PC12 cells. Clin Exp Pharmacol
Physiol. 35:180–186. 2008.
|
|
27
|
Tang XQ, Ren YK, Zhou CF, Yang CT, Gu HF,
He JQ, Chen RQ, Zhuang YY, Fang HR and Wang CY: Hydrogen sulfide
prevents formaldehyde-induced neurotoxicity to PC12 cells by
attenuation of mitochondrial dysfunction and pro-apoptotic
potential. Neurochem Int. 61:16–24. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Eghbal MA, Pennefather PS and O'Brien PJ:
H2S cytotoxicity mechanism involves reactive oxygen
species formation and mitochondrial depolarization. Toxicology.
203:69–76. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nyman S, Gottlow J, Karring T and Lindhe
J: The regenerative potential of the periodontal ligament. An
experimental study in the monkey. J Clin Periodontol. 9:257–265.
1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nyman S, Lindhe J, Karring T and Rylander
H: New attachment following surgical treatment of human periodontal
disease. J Clin Periodontol. 9:290–296. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nyman S, Gottlow J, Lindhe J, Karring T
and Wennstrom J: New attachment formation by guided tissue
regeneration. J Periodont Res. 22:252–254. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Somerman MJ, Archer SY, Imm GR and Foster
RA: A comparative study of human periodontal ligament cells and
gingival fibroblasts in vitro. J Dent Res. 67:66–70. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liang L, Yu JF, Wang Y, Wang G and Ding Y:
Effect of estrogen receptor beta on the osteoblastic
differentiation function of human periodontal ligament cells. Arch
Oral Biol. 53:553–557. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kawarizadeh A, Bourauel C, Götz W and
Jäger A: Early responses of periodontal ligament cells to
mechanical stimulus in vivo. J Dent Res. 84:902–906. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Roberts WE, Mozsary PG and Klingler E:
Nuclear size as a cell-kinetic marker for osteoblast
differentiation. Am J Anat. 165:373–384. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wada N, Maeda H, Tanabe K, Tsuda E, Yano
K, Nakamuta H and Akamine A: Periodontal ligament cells secrete the
factor that inhibits osteoclastic differentiation and function: The
factor is osteoprotegerin/osteoclastogenesis inhibitory factor. J
Periodontal Res. 36:56–63. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kobawashi M, Takiguchi T, Suzuki R,
Yamaguchi A, Deguchi K, Shionome M, Miyazawa Y, Nishihara T, Nagumo
M and Hasegawa K: Recombinant human bone morphogenic protein-2
stimulates osteoblastic differentiation in cells isolated from
human periodontal ligament. J Dent Res. 78:1624–1633. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Verna C, Zaffe D and Siciliani G:
Histomorphometric study of bone reactions during orthodontic tooth
movement in rats. Bone. 24:371–379. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Groeneveld MC, Everts V and Beertsen W:
Alkaline phosphatase activity in the periodontal ligament and
gingiva of the rat molar: Its relation to cementum formation. J
Dent Res. 74:1374–1381. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Okamoto T, Yatsuyzuka N, Tanaka Y, Kan M,
Yamanaka T, Sakamoto A, Takata T, Akagawa Y, Sato GH, Sato JD and
Takada K: Growth and differentiation of periodontal
ligament-derived cells in serum-free defined culture. In Vitro Cell
Dev Biol Anim. 33:302–309. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Von den Hoff JW: Effects of mechanical
tension on matrix degradation by human periodontal ligament cells
cultured in collagen gels. J Periodont Res. 38:449–457. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wescott DC, Pinkerton MN, Gaffey BJ, Beggs
KT, Milne TJ and Meikle MC: Osteogenic gene expression by human
periodontal ligament cells under cyclic tension. J Dent Res.
86:1212–1216. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Peverali FA, Basdra EK and Papavassiliou
AG: Stretch-mediated activation of selective MAPK subtypes and
potentiation of AP-1 binding in human osteoblastic cells. Mol Med.
7:68–78. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chiba M and Mitani H: Cytoskeletal changes
and the system of regulation of alkaline phosphatase activity in
human periodontal ligament cells induced by mechanical stress. Cell
Biochem Funct. 22:249–256. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Jacobs C, Grimm S, Ziebart T, Walter C and
Wehrbein H: Osteogenic differentiation of periodontal fibroblasts
is dependent on the strength of mechanical strain. Arch Oral Biol.
58:896–904. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yamaguchi N, Chiba M and Mitani H: The
induction of c-fos mRNA expression by mechanical stress in human
periodontal ligament cells. Arch Oral Biol. 47:465–471. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Molina T, Kabsch K, Alonso A, Kohl A,
Komposch G and Tomakidi P: Topographic changes of focal adhesion
components and modulation of p125FAK activation in stretched human
periodontal ligament fibroblasts. J Dent Res. 80:1984–1989. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|