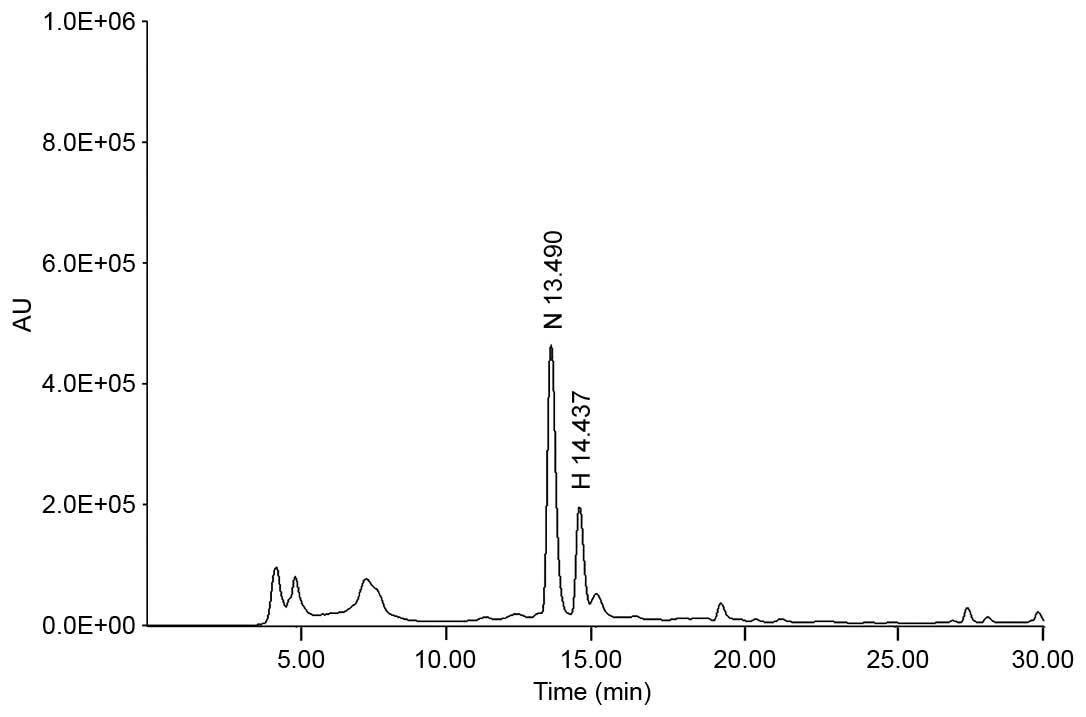
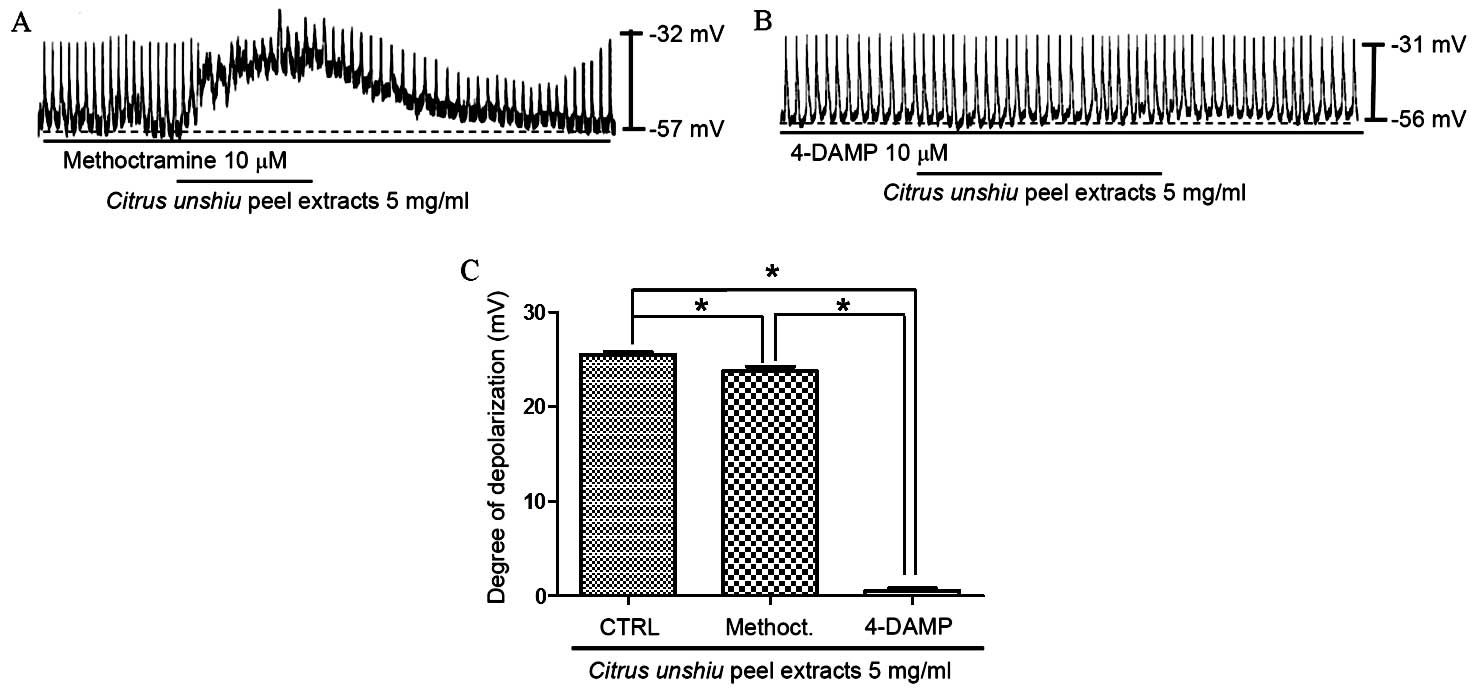
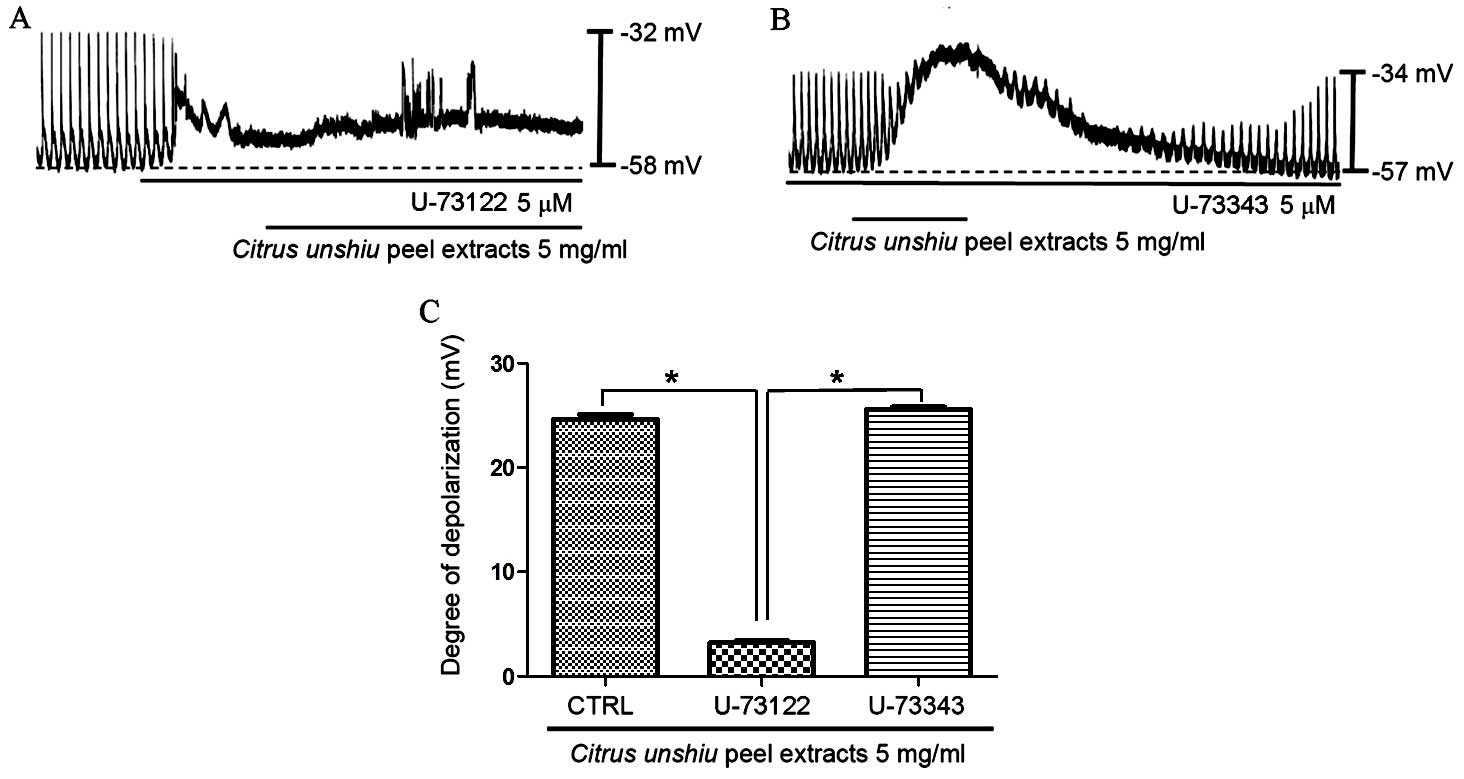
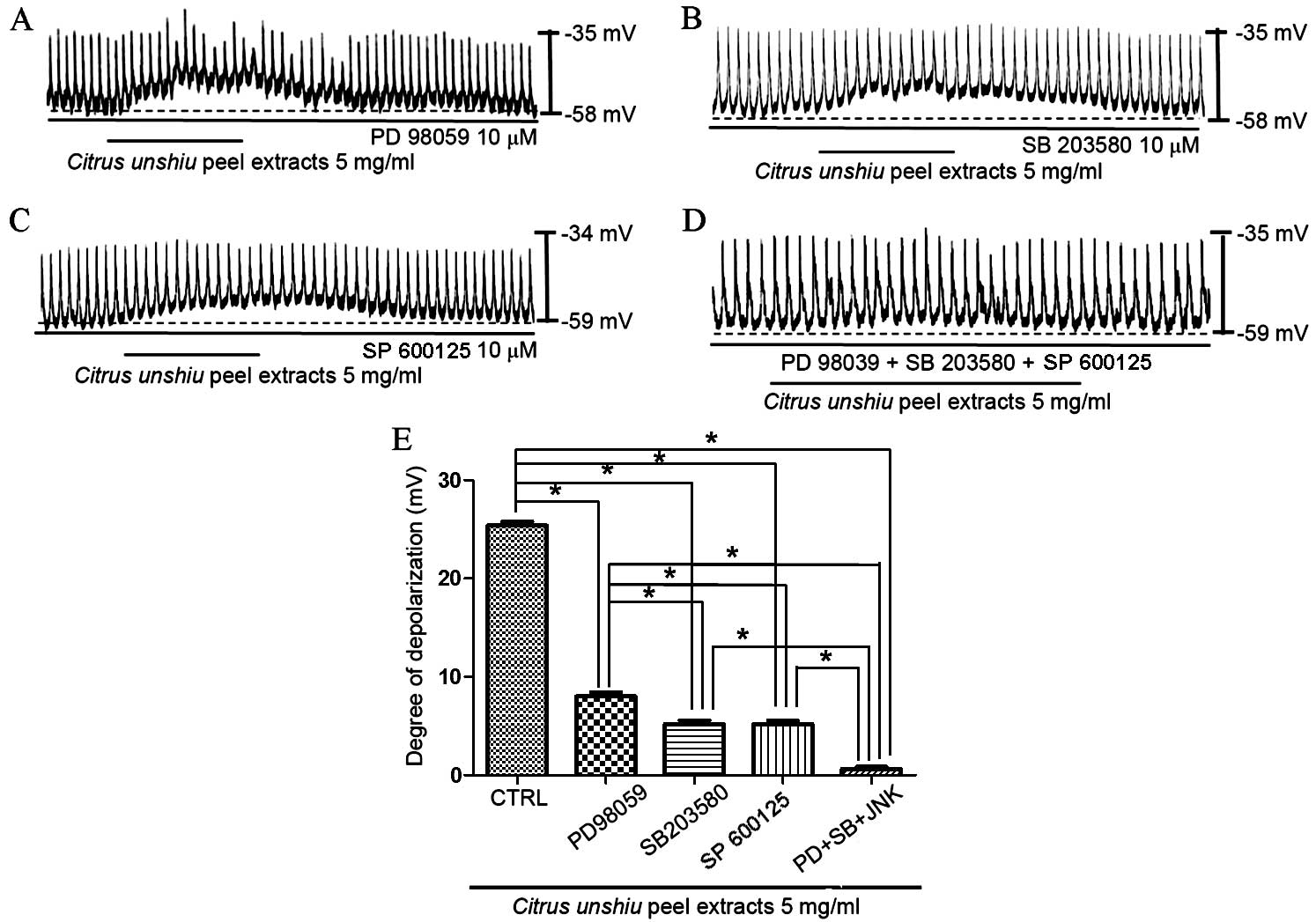
|
1
|
Bai D: Traditional Chinese medicines and
new drug development. Pure Appl Chem. 65:1103–1112. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Lim DW, Lee Y and Kim YT: Preventive
effects of Citrus unshiu peel extracts on bone and lipid metabolism
in OVX rats. Molecules. 19:783–794. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Choi IY, Kim SJ, Jeong HJ, Park SH, Song
YS, Lee JH, Kang TH, Park JH, Hwang GS, Lee EJ, et al: Hesperidin
inhibits expression of hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha and
inflammatory cytokine production from mast cells. Mol Cell Biochem.
305:153–161. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yang G, Lee J, Jung ED, Ham I and Choi HY:
Lipid lowering activity of Citri unshii pericarpium in hyperlipemic
rats. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 30:783–791. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Braddock RJ: Byproducts of citrus fruits.
Food Technol. 49:74–77. 1995.
|
|
6
|
Giannuzzo AN, Boggetti HJ, Nazareno MA and
Mishima HT: Supercritical fluid extraction of naringin from the
peel of Citrus paradisi. Phytochem Anal. 14:221–223. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jeong SM, Kim SY, Kim DR, Jo SC, Nam KC,
Ahn DU and Lee SC: Effect of heat treatment on the antioxidant
activity of extracts from citrus peels. J Agric Food Chem.
52:3389–3393. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim DK, Lee KT, Eun JS, Zee OP, Lim JP,
Eum SS, Kim SH and Shin TY: Anti-allergic components from the peels
of Citrus unshiu. Arch Pharm Res. 22:642–645. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Park SH, Park EK and Kim DH: Passive
cutaneous anaphylaxis-inhibitory activity of flavanones from Citrus
unshiu and Poncirus trifoliata. Planta Med. 71:24–27. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jo CR, Park BJ, Chung SH, Kim CB, Cha BS
and Byun MW: Antibacterial and anti-fungal activity of citrus
(Citrus unshiu) essential oil extracted from peel by-products. Food
Sci Biotechnol. 13:384–386. 2004.
|
|
11
|
Min KY, Kim HJ, Lee KA, Kim KT and Paik
HD: Antimicrobial activity of acid-hydrolyzed Citrus unshiu peel
extract in milk. J Dairy Sci. 97:1955–1960. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee S, Ra J, Song JY, Gwak C, Kwon HJ, Yim
SV, Hong SP, Kim J, Lee KH, Cho JJ, et al: Extracts from Citrus
unshiu promote immune mediated inhibition of tumor growth in a
murine renal cell carcinoma model. J Ethnopharmacol. 133:973–979.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Park HJ, Jung UJ, Cho SJ, Jung HK, Shim S
and Choi MS: Citrus unshiu peel extract ameliorates hyperglycemia
and hepatic steatosis by altering inflammation and hepatic glucose-
and lipid-regulating enzymes in db/db mice. J Nutr Biochem.
24:419–427. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Lee YH, Kim YS, Song M, Lee M, Park J and
Kim H: A herbal formula HT048, Citrus unshiu and Crataegus
pinnatifida, prevents obesity by inhibiting adipogenesis and
lipogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes and HFD-induced obese rats.
Molecules. 20:9656–9670. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim KS, Rhee HI, Park EK, Jung K, Jeon HJ,
Kim JH, Yoo H, Han CK, Cho YB, Ryu CJ, et al: Anti-inflammatory
effects of Radix Gentianae Macrophyllae (Qinjiao), Rhizoma Coptidis
(Huanglian) and Citri Unshiu Pericarpium (Wenzhou migan) in animal
models. Chin Med. 3:102008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Oh YC, Cho WK, Jeong YH, Im GY, Yang MC,
Hwang YH and Ma JY: Anti-inflammatory effect of Citrus unshiu peel
in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. Am J Chin Med.
40:611–629. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bocco A, Cuvelier ME, Richard H and Berset
C: Antioxidant activity and phenolic composition of citrus peel and
seed extracts. J Agri Food Chem. 46:2123–2129. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Jeong SM, Kim SY, Kim DR, Jo SC, Nam KC,
Ahn DU and Lee SC: Effect of heat treatment on the antioxidant
activity of extracts from Citrus peels. J Agri Food Chem.
52:3389–3393. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yang X, Kang SM, Jeon BT, Kim YD, Ha JH,
Kim YT and Jeon YJ: Isolation and identification of an antioxidant
flavonoid compound from citrus-processing byproduct. J Sci Food
Agric. 91:1925–1927. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Suzuki M, Sasaki K, Yoshizaki F, Oguchi K,
Fujisawa M and Cyong JC: Anti-hepatitis C virus effect of Citrus
unshiu peel and its active ingredient nobiletin. Am J Chin Med.
33:87–94. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim CM, Shin MK, Ahn DG and Lee KS:
Chungyak Daesajun. Jungdam; Seoul: 8. pp. 4026–4030. 1997
|
|
22
|
Lyu JH and Lee HT: Effects of dried Citrus
unshiu peels on gastrointestinal motility in rodents. Arch Pharm
Res. 36:641–648. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ward SM, Burns AJ, Torihashi S and Sanders
KM: Mutation of the proto-oncogene c-kit blocks development of
interstitial cells and electrical rhythmicity in murine intestine.
J Physiol. 480:91–97. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huizinga JD, Thuneberg L, Klüppel M,
Malysz J, Mikkelsen HB and Bernstein A: W/kit gene required for
interstitial cells of Cajal and for intestinal pacemaker activity.
Nature. 373:347–349. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kim BJ, Kwon YK, Kim E and So I: Effects
of histamine on cultured interstitial cells of cajal in murine
small intestine. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 17:149–156. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kim BJ, Lim HH, Yang DK, Jun JY, Chang IY,
Park CS, So I, Stanfield PR and Kim KW: Melastatin-type transient
receptor potential channel 7 is required for intestinal pacemaking
activity. Gastroenterology. 129:1504–1517. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ahn DK: Illustrated guide to clinical
medical herbs. Hyeonamsa Publ. Corp.; Seoul: pp. 147–148. 2012
|
|
28
|
Goto K, Matsuoka S and Noma A: Two types
of spontaneous depolarizations in the interstitial cells freshly
prepared from the murine small intestine. J Physiol. 559:411–422.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Huizinga JD, Chang G, Diamant NE and
El-Sharkawy TY: Electrophysiological basis of excitation of canine
colonic circular muscle by cholinergic agents and substance P. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 231:692–699. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Inoue R and Chen S: Physiology of
muscarinic receptor operated nonselective cation channels in
guinea-pig ileal smooth muscle. EXS. 66:261–268. 1993.
|
|
31
|
Epperson A, Hatton WJ, Callaghan B,
Doherty P, Walker RL, Sanders KM, Ward SM and Horowitz B: Molecular
markers expressed in cultured and freshly isolated interstitial
cells of Cajal. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 279:C529–C539.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Komori S, Kawai M, Takewaki T and Ohashi
H: GTP-binding protein involvement in membrane currents evoked by
carbachol and histamine in guinea-pig ileal muscle. J Physiol.
450:105–126. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ogata R, Inoue Y, Nakano H, Ito Y and
Kitamura K: Oestradiol-induced relaxation of rabbit basilar artery
by inhibition of voltage-dependent Ca channels through GTP-binding
protein. Br J Pharmacol. 117:351–359. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sakamoto T, Unno T, Matsuyama H, Uchiyama
M, Hat tori M, Nishimura M and Komori S: Characterization of
muscarinic receptor-mediated cationic currents in longitudinal
smooth muscle cells of mouse small intestine. J Pharmacol Sci.
100:215–226. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Slack BE: The M3 muscarinic acetylcholine
receptor is coupled to mitogen-activated protein kinase via protein
kinase C and epidermal growth factor receptor kinase. Biochem J.
348:381–387. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tanizawa H, Ohkawa Y, Takino Y, Miyase T,
Ueno A, Kageyama T and Hara S: Studies on natural antioxidants in
citrus species. I Determination of antioxidative activities of
citrus fruits. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 40:1940–1942. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Kawaii S, Tomono Y, Katase E, Ogawa K and
Yano M: Quantitation of flavonoid constituents in citrus fruits. J
Agric Food Chem. 47:3565–3571. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kimura T, But PPH, Guo JX and Sung CK:
International collation of traditional and folk medicine: Northeast
Asia. River Edge: World Scientific Publishing Co; 1996, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Jung UJ, Lee MK, Park YB, Kang MA and Choi
MS: Effect of citrus flavonoids on lipid metabolism and
glucose-regulating enzyme mRNA levels in type-2 diabetic mice. Int
J Biochem Cell Biol. 38:1134–1145. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Abeysinghe DC, Li X, Sun C, Zhang W, Zhou
C and Chen K: Bioactive compounds and antioxidant capacities in
different edible tissues of citrus fruit of four species. Food
Chem. 104:1338–1344. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Funaguchi N, Ohno Y, La BL, Asai T,
Yuhgetsu H, Sawada M, Takemura G, Minatoguchi S, Fujiwara T and
Fujiwara H: Narirutin inhibits airway inflammation in an allergic
mouse model. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 34:766–770. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lu Y, Zhang C, Bucheli P and Wei D: Citrus
flavonoids in fruit and traditional Chinese medicinal food
ingredients in China. Plant Food Hum Nutr. 61:57–65. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Ma YQ, Ye XQ, Fang ZX, Chen JC, Xu GH and
Liu DH: Phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of extracts
from ultrasonic treatment of Satsuma Mandarin (Citrus unshiu Marc)
peels. J Agri Food Chem. 56:5682–5690. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Wu MJ, Kee KH, Na J, Kim SW, Bae Y, Shin
DH, Choi S, Jun JY, Jeong HS and Park JS: Pituitary adenylate
cyclase-activating polypeptide inhibits pacemaker activity of
colonic interstitial cells of cajal. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
19:435–440. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lee S, Gim H, Shim JH, Jung Kim H, Lee JR,
Kim SC, Kwon YK, Ha KT, So I and Kim BJ: The traditional herbal
medicine, Ge-Gen-Tang, inhibits pacemaker potentials by nitric
oxide/cGMP dependent ATP-sensitive K(+) channels in cultured
interstitial cells of Cajal from mouse small intestine. J
Ethnopharmacol. 170:201–209. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ehlert FJ, Pak KJ and Griffin MT:
Muscarinic agonists and antagonists: Effects on gastrointestinal
function. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 208:343–374. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
So KY, Kim SH, Sohn HM, Choi SJ, Parajuli
SP, Choi S, Yeum CH, Yoon PJ and Jun JY: Carbachol regulates
pacemaker activities in cultured interstitial cells of Cajal from
the mouse small intestine. Mol Cells. 27:525–531. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Garrington TP and Johnson GL: Organization
and regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling
pathways. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 11:211–218. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lukacs NW, Strieter RM, Chensue SW, Widmer
M and Kunkel SL: TNF-alpha mediates recruitment of neutrophils and
eosinophils during airway inflammation. J Immunol. 154:5411–5417.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Cook AK, Carty M, Singer CA, Yamboliev IA
and Gerthoffer WT: Coupling of M(2) muscarinic receptors to ERK MAP
kinases and caldesmon phosphorylation in colonic smooth muscle. Am
J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 278:G429–G437.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Budd DC, Willars GB, McDonald JE and Tobin
AB: Phosphorylation of the Gq/11-coupled M3-muscarinic receptor is
involved in receptor activation of the ERK-1/2 mitogen-activated
protein kinase pathway. J Biol Chem. 276:4581–4587. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Matthiesen S, Bahulayan A, Kempkens S,
Haag S, Fuhrmann R, Stichnote C, Juergens UR and Racké K:
Muscarinic receptors mediate stimulation of human lung fibroblast.
Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 35:621–627. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Luttrell LM: Activation and targeting of
mitogen-activated protein kinases by G-protein-coupled receptors.
Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 80:375–382. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Gu J and Iyer VR: PI3K signaling and mRNA
expression during the response of quiescent human fibroblasts to
distinct proliferative stimuli. Genome Biol. 7:R422006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Frucht H, Jensen RT, Dexter D, Yang WL and
Xiao Y: Human colon cancer cell proliferation mediated by the M3
muscarinic cholinergic receptor. Clin Cancer Res. 5:2532–2539.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Cheng K, Zimniak P and Raufman JP:
Transactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor mediates
cholinergic agonist-induced proliferation of H508 human colon
cancer cells. Cancer Res. 63:6744–6750. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ukegawa JI, Takeuchi Y, Kusayanagi S and
Mitamura K: Growth-promoting effect of muscarinic acetylcholine
receptors in colon cancer cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
129:272–278. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Guizzetti M and Costa LG: Activation of
phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase by muscarinic receptors in
astrocytoma cells. Neuroreport. 12:1639–1642. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Jimenez E and Montiel M: Activation of MAP
kinase by muscarinic cholinergic receptors induces cell
proliferation and protein synthesis in human breast cancer cells. J
Cell Physiol. 204:678–686. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Oppitz M, Möbus V, Brock S and Drews U:
Muscarinic receptors in cell lines from ovarian carcinoma: Negative
correlation with survival of patients. Gynecol Oncol. 85:159–164.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Song P, Sekhon HS, Lu A, Arredondo J,
Sauer D, Gravett C, Mark GP, Grando SA and Spindel ER: M3
muscarinic receptor antagonists inhibit small cell lung carcinoma
growth and mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylation induced
by acetylcholine secretion. Cancer Res. 67:3936–3944. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|