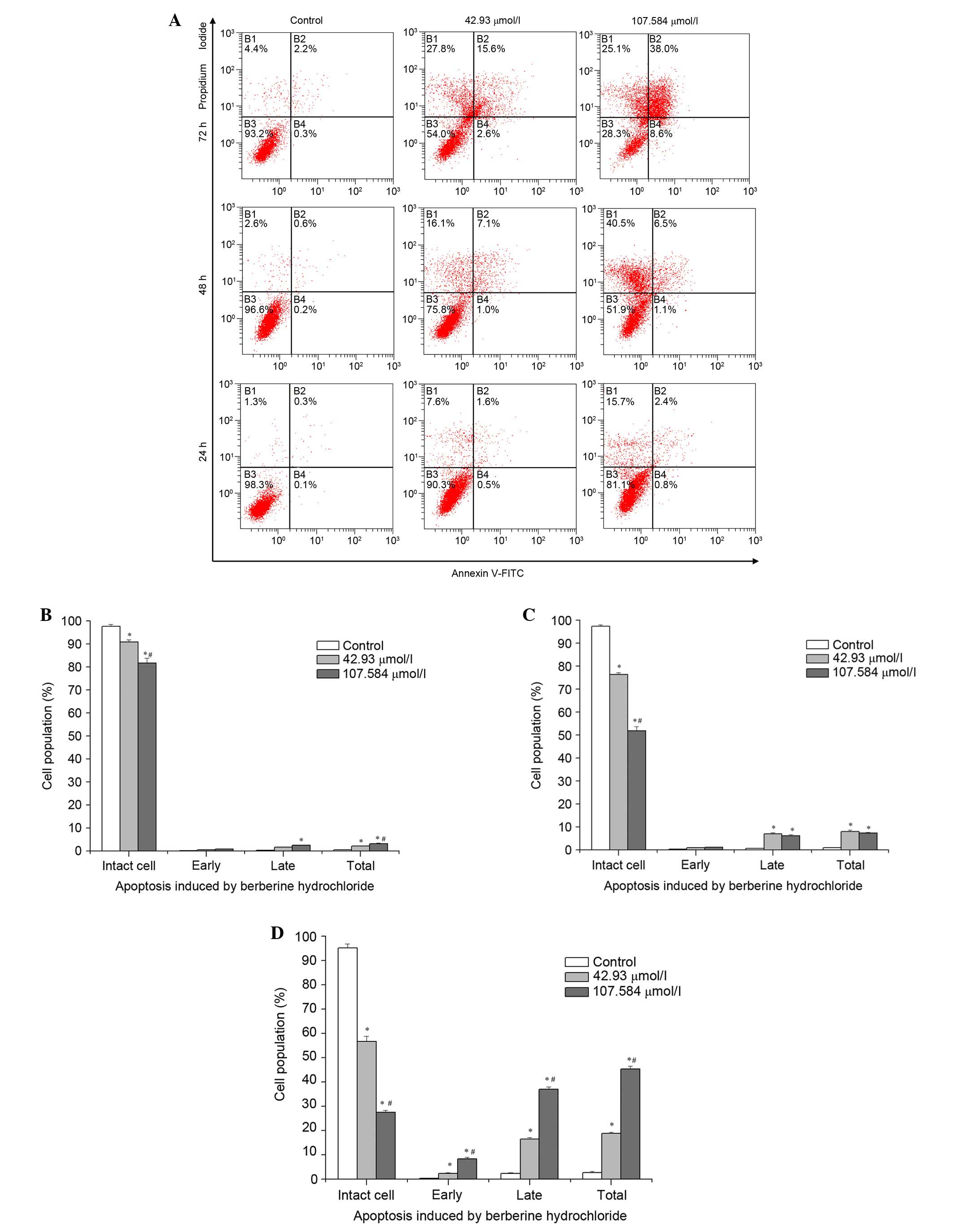
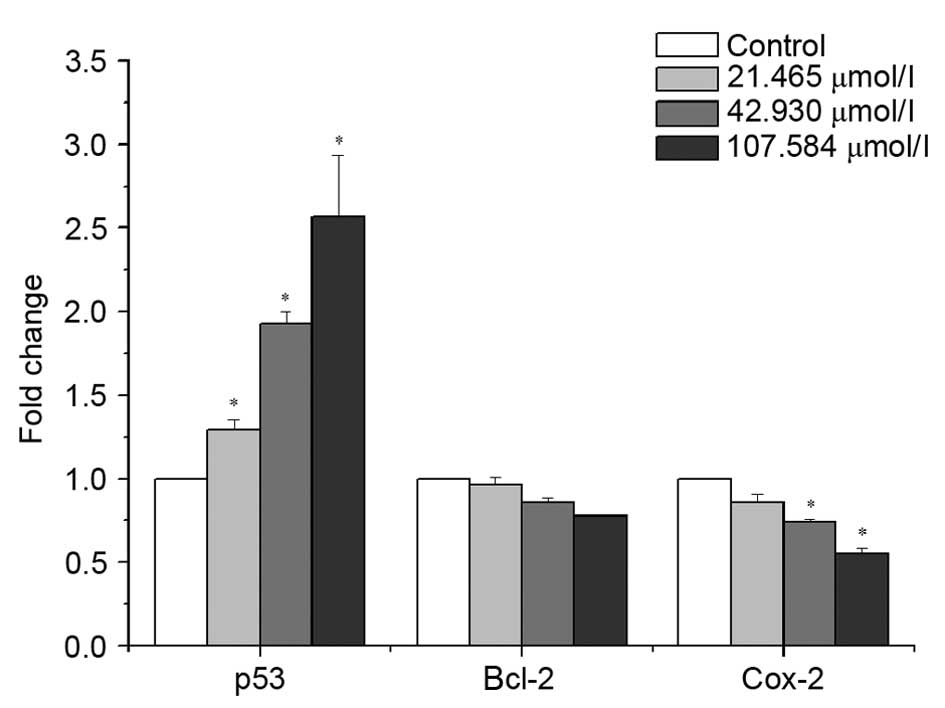
|
1
|
Xie J, Xu Y, Huang X, Chen Y, Fu J, Xi M
and Wang L: Berberine-induced apoptosis in human breast cancer
cells is mediated by reactive oxygen species generation and
mitochondrial-related apoptotic pathway. Tumour Biol. 36:1279–1288.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Parkin DM: The global health burden of
infection-associated cancers in the year 2002. Int J Cancer.
118:3030–3044. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Engel N, Oppermann C, Falodun A and Kragl
U: Proliferative effects of five traditional Nigerian medicinal
plant extracts on human breast and bone cancer cell lines. J
Ethnopharmacol. 137:1003–1010. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sun Y, Xun K, Wang Y and Chen X: A
systematic review of the anticancer properties of berberine, a
natural product from Chinese herbs. Anticancer Drugs. 20:757–769.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li X, Zhao SJ, Shi HL, Qiu SP, Xie JQ, Wu
H, Zhang BB, Wang ZT, Yuan JY and Wu XJ: Berberine hydrochloride
IL-8 dependently inhibits invasion and IL-8-independently promotes
cell apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 cells. Oncol Rep. 32:2777–2788.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xi S, Chuang K, Fang K, Lee Y, Chung J and
Chuang Y: Effect of berberine on activity and mRNA expression of
N-acetyltransferase in human lung cancer cell line A549. J Tradit
Chin Med. 34:302–308. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Guamán Ortiz LM, Tillhon M, Parks M, Dutto
I, Prosperi E, Savio M, Arcamone AG, Buzzetti F, Lombardi P and
Scovassi AI: Multiple effects of berberine derivatives on colon
cancer cells. Biomed Res Int. 2014:9245852014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wu HL, Chuang TY, Al-Hendy A, Diamond MP,
Azziz R and Chen YH: Berberine inhibits the proliferation of human
uterine leiomyoma cells. Fertil Steril. 103:1098–1106. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Qing Y, Hu H, Liu Y, Feng T, Meng W, Jiang
L, Sun Y and Yao Y: Berberine induces apoptosis in human multiple
myeloma cell line U266 through hypomethylation of p53 promoter.
Cell Biol Int. 38:563–570. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhu Y, Ma N, Li HX, Tian L, Ba YF and Hao
B: Berberine induces apoptosis and DNA damage in MG-63 human
osteosarcoma cells. Mol Med Rep. 10:1734–1738. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang Q, Zhang C, Yang X, Yang B, Wang J,
Kang Y, Wang Z, Li D, Huang G, Ma Z, et al: Berberine inhibits the
expression of hypoxia induction factor-1alpha and increases the
radiosensitivity of prostate cancer. Diagn Pathol. 9:982014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang LY, Wu YL, Gao XH and Guo F:
Mitochondrial protein cyclophilin-D-mediated programmed necrosis
attributes to berberine-induced cytotoxicity in cultured prostate
cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 450:697–703. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chu SC, Yu CC, Hsu LS, Chen KS, Su MY and
Chen PN: Berberine reverses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
and inhibits metastasis and tumor-induced angiogenesis in human
cervical cancer cells. Mol Pharmacol. 86:609–623. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lu B, Hu M, Liu K and Peng J: Cytotoxicity
of berberine on human cervical carcinoma HeLa cells through
mitochondria, death receptor and MAPK pathways, and in-silico
drug-target prediction. Toxicol In Vitro. 24:1482–1490. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li CH, Wu DF, Ding H, Zhao Y, Zhou KY and
Xu DF: Berberine hydrochloride impact on physiological processes
and modulation of twist levels in nasopharyngeal carcinoma CNE-1
cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:1851–1857. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang C, Yang X, Zhang Q, Yang B, Xu L,
Qin Q, Zhu H, Liu J, Cai J, Tao G, et al: Berberine radiosensitizes
human nasopharyngeal carcinoma by suppressing hypoxia-inducible
factor-1α expression. Acta Otolaryngol. 134:185–192. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wang N, Zhu M, Wang X, Tan HY, Tsao SW and
Feng Y: Berberine-induced tumor suppressor p53 up-regulation gets
involved in the regulatory network of MIR-23a in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1839:849–857. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang L, Wei D, Han X, Zhang W, Fan C,
Zhang J, Mo C, Yang M, Li J, Wang Z, et al: The combinational
effect of vincristine and berberine on growth inhibition and
apoptosis induction in hepatoma cells. J Cell Biochem. 115:721–730.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Guo N, Yan A, Gao X, Chen Y, He X, Hu Z,
Mi M, Tang X and Gou X: Berberine sensitizes rapamycin-mediated
human hepatoma cell death in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 10:3132–3138.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang XZ, Wang L, Liu DW, Tang GY and
Zhang HY: Synergistic inhibitory effect of berberine and d-limonene
on human gastric carcinoma cell line MGC803. J Med Food.
17:955–962. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mittal A, Tabasum S and Singh RP:
Berberine in combination with doxorubicin suppresses growth of
murine melanoma B16F10 cells in culture and xenograft.
Phytomedicine. 21:340–347. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Mahata S, Bharti AC, Shukla S, Tyagi A,
Husain SA and Das BC: Berberine modulates AP-1 activity to suppress
HPV transcription and downstream signaling to induce growth arrest
and apoptosis in cervical cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 10:392011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lin JP, Yang JS, Chang NW, Chiu TH, Su CC,
Lu KW, Ho YT, Yeh CC, Mei-Dueyang, Lin HJ and Chung JG: GADD153
mediates berberine-induced apoptosis in human cervical cancer Ca
ski cells. Anticancer Res. 27:3379–3386. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Abu Bakar MF, Mohamad M, Rahmat A, Burr SA
and Fry JR: Cytotoxicity, cell cycle arrest, and apoptosis in
breast cancer cell lines exposed to an extract of the seed kernel
of Mangifera pajang (bambangan). Food Chem Toxicol. 48:1688–1697.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tian Z, An N, Zhou B, Xiao P, Kohane IS
and Wu E: Cytotoxic diarylheptanoid induces cell cycle arrest and
apoptosis via increasing ATF3 and stabilizing p53 in SH-SY5Y cells.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 63:1131–1139. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Itoh M, Murata T, Suzuki T, Shindoh M,
Nakajima K, Imai K and Yoshida K: Requirement of STAT3 activation
for maximal collagenase-1 (MMP-1) induction by epidermal growth
factor and malignant characteristics in T24 bladder cancer cells.
Oncogene. 25:1195–1204. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Jiang N, Zhou LQ and Zhang XY:
Downregulation of the nucleosome-binding protein 1 (NSBP1) gene can
inhibit the in vitro and in vivo proliferation of prostate cancer
cells. Asian J Androl. 12:709–717. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhou A, Scoggin S, Gaynor RB and Williams
NS: Identification of NF-kappa B-regulated genes induced by
TNFalpha utilizing expression profiling and RNA interference.
Oncogene. 22:2054–2064. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lapillonne H, Konopleva M, Tsao T, Gold D,
McQueen T, Sutherland RL, Madden T and Andreeff M: Activation of
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma by a novel
synthetic triterpenoid 2-cyano-3, 12-dioxooleana-1, 9-dien-28-oic
acid induces growth arrest and apoptosis in breast cancer cells.
Cancer Res. 63:5926–5939. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chidambara Murthy KN, Jayaprakasha GK and
Patil BS: The natural alkaloid berberine targets multiple pathways
to induce cell death in cultured human colon cancer cells. Eur J
Pharmacol. 688:14–21. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hur JM, Hyun MS, Lim SY, Lee WY and Kim D:
The combination of berberine and irradiation enhances anti-cancer
effects via activation of p38 MAPK pathway and ROS generation in
human hepatoma cells. J Cell Biochem. 107:955–964. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim JB, Yu JH, Ko E, Lee KW, Song AK, Park
SY, Shin I, Han W and Noh DY: The alkaloid Berberine inhibits the
growth of Anoikis-resistant MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell
lines by inducing cell cycle arrest. Phytomedicine. 17:436–440.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wang J, Liu Q and Yang Q:
Radiosensitization effects of berberine on human breast cancer
cells. Int J Mol Med. 30:1166–1172. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chou HC, Lu YC, Cheng CS, Chen YW, Lyu PC,
Lin CW, Timms JF and Chan HL: Proteomic and redox-proteomic
analysis of berberine-induced cytotoxicity in breast cancer cells.
J Proteomics. 75:3158–3176. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zheng F, Tang Q, Wu J, Zhao S, Liang Z, Li
L, Wu W and Hann S: p38α MAPK-mediated induction and interaction of
FOXO3a and p53 contribute to the inhibited-growth and
induced-apoptosis of human lung adenocarcinoma cells by berberine.
J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 33:362014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Ma X, Zhou J, Zhang CX, Li XY, Li N, Ju
RJ, Shi JF, Sun MG, Zhao WY, Mu LM, et al: Modulation of
drug-resistant membrane and apoptosis proteins of breast cancer
stem cells by targeting berberine liposomes. Biomaterials.
34:4452–4465. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Qi HW, Xin LY, Xu X, Ji XX and Fan LH:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition markers to predict response of
Berberine in suppressing lung cancer invasion and metastasis. J
Transl Med. 12:222014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Scordino A, Campisi A, Grasso R, Bonfanti
R, Gulino M, Iauk L, Parenti R and Musumeci F: Delayed luminescence
to monitor programmed cell death induced by berberine on thyroid
cancer cells. J Biomed Opt. 19:1170052014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Weyhenmeyer B, Murphy AC, Prehn JH and
Murphy BM: Targeting the anti-apoptotic bcl-2 family members for
the treatment of cancer. Exp Oncol. 34:192–199. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Green DR: Apoptotic pathways: Paper wraps
stone blunts scissors. Cell. 102:1–4. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Žegura B, Gajski G, Štraser A and
Garaj-Vrhovac V: Cylindrospermopsin induced DNA damage and
alteration in the expression of genes involved in the response to
DNA damage, apoptosis and oxidative stress. Toxicon. 58:471–479.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Vogelstein B, Lane D and Levine AJ:
Surfing the p53 network. Nature. 408:307–310. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Certo M, Del Gaizo Moore V, Nishino M, Wei
G, Korsmeyer S, Armstrong SA and Letai A: Mitochondria primed by
death signals determine cellular addiction to antiapoptotic BCL-2
family members. Cancer Cell. 9:351–365. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kim R, Tanabe K, Uchida Y, Emi M, Inoue H
and Toge T: Current status of the molecular mechanisms of
anticancer drug-induced apoptosis. The contribution of
molecular-level analysis to cancer chemotherapy. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 50:343–352. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhang C, Yan W, Li B, Xu B, Gong Y, Chu F,
Zhang Y, Yao Q, Wang P and Lei H: A New Ligustrazine
Derivative-Selective Cytotoxicity by Suppression of NF-kB/p65 and
COX-2 expression on human hepatoma cells. Part 3. Int J Mol Sci.
16:16401–16413. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Breinig M, Schirmacher P and Kern MA:
Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2)-a therapeutic target in liver cancer? Curr
Pharm Des. 13:3305–3315. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Tang TC, Poon RT, Lau CP, Xie D and Fan
ST: Tumor cyclooxygenase-2 levels correlate with tumor invasiveness
in human hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol.
11:1896–1902. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhong B, Cai X, Chennamaneni S, Yi X, Liu
L, Pink JJ, Dowlati A, Xu Y, Zhou A and Su B: From COX-2 inhibitor
nimesulide to potent anti-cancer agent: Synthesis, in vitro, in
vivo, and pharmacokinetic evaluation. Eur J Med Chem. 47:432–444.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Mazhar D, Gillmore R and Waxman J: COX and
cancer. QJM. 98:711–718. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|