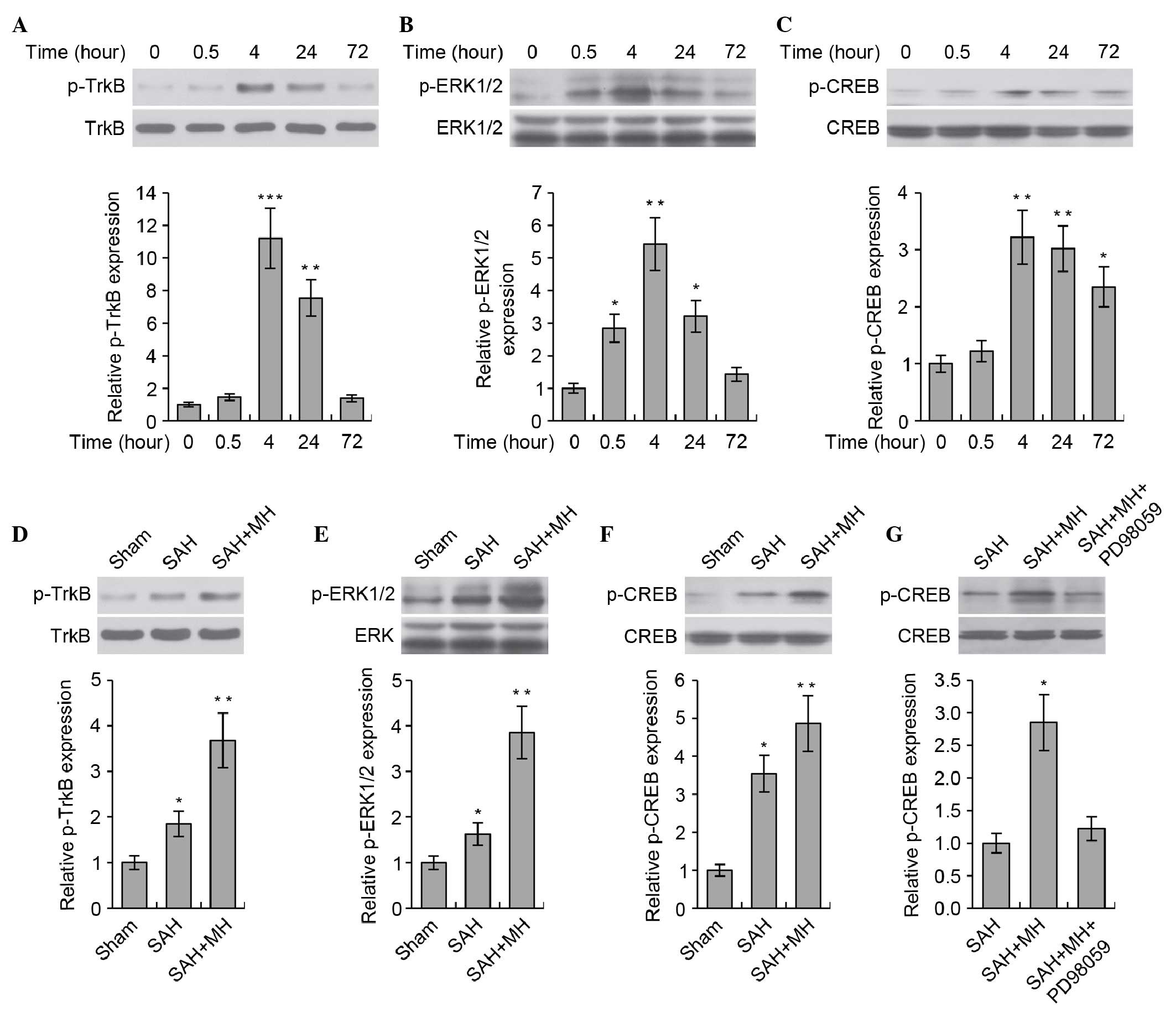
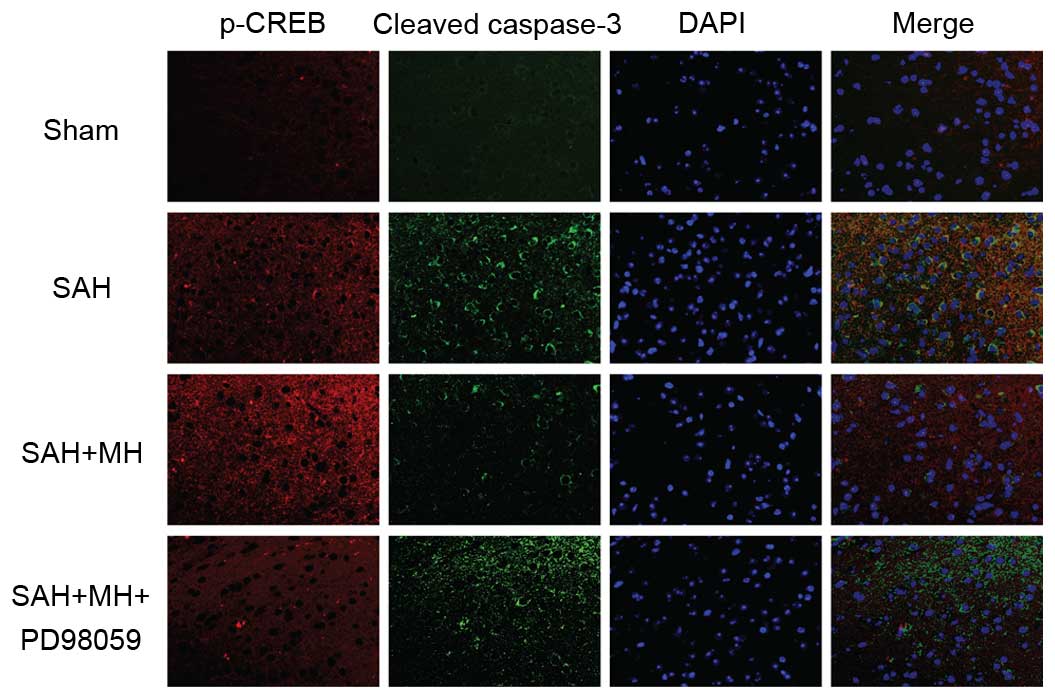
|
1
|
van Gijn J, Kerr RS and Rinkel GJ:
Subarachnoid haemorrhage. Lancet. 369:306–318. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ostrowski RP, Colohan AR and Zhang JH:
Molecular mechanisms of early brain injury after subarachnoid
hemorrhage. Neurol Res. 28:399–414. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bederson JB, Levy AL, Ding WH, Kahn R,
DiPerna CA, Jenkins AL III and Vallabhajosyula P: Acute
vasoconstriction after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery.
42:352–362. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Thome C, Schubert GA and Schilling L:
Hypothermia as a neuroprotective strategy in subarachnoid
hemorrhage: A pathophysiological review focusing on the acute
phase. Neurol Res. 27:229–237. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tissier R, Chenoune M, Pons S, Zini R,
Darbera L, Lidouren F, Ghaleh B, Berdeaux A and Morin D: Mild
hypothermia reduces per-ischemic reactive oxygen species production
and preserves mitochondrial respiratory complexes. Resuscitation.
84:249–255. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Lee SM, Zhao H, Maier CM and Steinberg GK:
The protective effect of early hypothermia on PTEN phosphorylation
correlates with free radical inhibition in rat stroke. J Cereb
Blood Flow Metab. 29:1589–1600. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Milde LN: Clinical use of mild hypothermia
for brain protection: A dream revisited. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol.
4:211–215. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Erecinska M, Thoresen M and Silver IA:
Effects of hypothermia on energy metabolism in Mammalian central
nervous system. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 23:513–530. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Smith SL and Hall ED: Mild pre- and
posttraumatic hypothermia attenuates blood-brain barrier damage
following controlled cortical impact injury in the rat. J
Neurotrauma. 13:1–9. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Karibe H, Zarow GJ, Graham SH and
Weinstein PR: Mild intraischemic hypothermia reduces postischemic
hyperperfusion, delayed postischemic hypoperfusion, blood-brain
barrier disruption, brain edema, and neuronal damage volume after
temporary focal cerebral ischemia in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow
Metab. 14:620–627. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Maeda T, Katayama Y, Kawamata T and
Yamamoto T: Mechanisms of excitatory amino acid release in contused
brain tissue: Effects of hypothermia and in situ administration of
Co2+ on extracellular levels of glutamate. J Neurotrauma.
15:655–664. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mori K, Maeda M, Miyazaki M and Iwase H:
Effects of mild and moderate hypothermia on cerebral metabolism and
glutamate in an experimental head injury. Acta Neurochir Suppl.
71:222–224. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chatzipanteli K, Yanagawa Y, Marcillo AE,
Kraydieh S, Yezierski RP and Dietrich WD: Posttraumatic hypothermia
reduces polymorphonuclear leukocyte accumulation following spinal
cord injury in rats. J Neurotrauma. 17:321–332. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Busto R, Globus MY, Dietrich WD, Martinez
E, Valdes I and Ginsberg MD: Effect of mild hypothermia on
ischemia-induced release of neurotransmitters and free fatty acids
in rat brain. Stroke. 20:904–910. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gasser S, Khan N, Yonekawa Y, Imhof HG and
Keller E: Long-term hypothermia in patients with severe brain edema
after poor-grade subarachnoid hemorrhage: Feasibility and intensive
care complications. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 15:240–248. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Thome C, Schubert G, Piepgras A, Elste V,
Schilling L and Schmiedek P: Hypothermia reduces acute vasospasm
following SAH in rats. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 77:255–258.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bishop CC, Powell S, Rutt D and Browse NL:
Transcranial Doppler measurement of middle cerebral artery blood
flow velocity: A validation study. Stroke. 17:913–915. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hasegawa Y, Suzuki H, Altay O and Zhang
JH: Preservation of tropomyosin-related kinase B (TrkB) signaling
by sodium orthovanadate attenuates early brain injury after
subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Stroke. 42:477–483. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
He Q, Wang S, Liu X, Guo H, Yang H, Zhang
L, Zhuang P, Zhang Y, Ye Z and Hu L: Salvianolate lyophilized
injection promotes post-stroke functional recovery via the
activation of VEGF and BDNF-TrkB-CREB signaling pathway. Int J Clin
Exp Med. 8:108–122. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Doczi T, Laszlo FA, Szerdahelyi P and Joo
F: Involvement of vasopressin in brain edema formation: Further
evidence obtained from the brattleboro diabetes insipidus rat with
experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery. 14:436–441.
1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Piepgras A, Elste V, Frietsch T, Schmiedek
P, Reith W and Schilling L: Effect of moderate hypothermia on
experimental severe subarachnoid hemorrhage, as evaluated by
apparent diffusion coefficient changes. Neurosurgery. 48:1128–1135.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sun BL, Zhang SM, Xia ZL, Yang MF, Yuan H,
Zhang J and Xiu RJ: The effects of nimodipine on regional cerebral
blood flow, brain water and electrolyte contents in rats with
subarachnoid hemorrhage. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 29:337–344.
2003.
|
|
23
|
Wojcicka G, Jamroz-Wisniewska A, Widomska
S, Ksiazek M and Bełtowski J: Role of extracellular
signal-regulated kinases (ERK) in leptin-induced hypertension. Life
Sci. 82:402–412. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cahill J, Calvert JW and Zhang JH:
Mechanisms of early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 26:1341–1353. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Niizuma K, Endo H and Chan PH: Oxidative
stress and mitochondrial dysfunction as determinants of ischemic
neuronal death and survival. J Neurochem. 109(Suppl 1): S133–S138.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
D'Cruz BJ, Fertig KC, Filiano AJ, Hicks
SD, DeFranco DB and Callaway CW: Hypothermic reperfusion after
cardiac arrest augments brain-derived neurotrophic factor
activation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 22:843–851. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Boris-Moller F, Kamme F and Wieloch T: The
effect of hypothermia on the expression of neurotrophin mRNA in the
hippocampus following transient cerebral ischemia in the rat. Brain
Res Mol Brain Res. 63:163–173. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
McGirt MJ, Garces Ambrossi GL, Huang J and
Tamargo RJ: Simvastatin for the prevention of symptomatic cerebral
vasospasm following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A
single-institution prospective cohort study. J Neurosurg.
110:968–974. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Vajkoczy P, Meyer B, Weidauer S, Raabe A,
Thome C, Ringel F, Breu V and Schmiedek P: Clazosentan
(AXV-034343), a selective endothelin A receptor antagonist, in the
prevention of cerebral vasospasm following severe aneurysmal
subarachnoid hemorrhage: Results of a randomized, double-blind,
placebo-controlled, multicenter phase IIa study. J Neurosurg.
103:9–17. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Broderick JP, Brott TG, Duldner JE,
Tomsick T and Leach A: Initial and recurrent bleeding are the major
causes of death following subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke.
25:1342–1347. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Le Roux PD and Winn HR: Management of the
ruptured aneurysm. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 9:525–540. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Abe Y, Sakairi T, Kajiyama H, Shrivastav
S, Beeson C and Kopp JB: Bioenergetic characterization of mouse
podocytes. Am J Physiol. 299:464–476. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Germanò A, d'Avella D, Imperatore C,
Caruso G and Tomasello F: Time-course of blood-brain barrier
permeability changes after experimental subarachnoid haemorrhage.
Acta Neurochir (Wien). 142:575–581. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Zhou C, Yamaguchi M, Colohan AR and Zhang
JH: Role of p53 and apoptosis in cerebral vasospasm after
experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
25:572–582. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kirkman MA and Smith M: Intracranial
pressure monitoring, cerebral perfusion pressure estimation, and
ICP/CPP-guided therapy: A standard of care or optional extra after
brain injury? Br J Anaesth. 112:35–46. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Haddad SH and Arabi YM: Critical care
management of severe traumatic brain injury in adults. Scand J
Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 20:122012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Numakawa T, Suzuki S, Kumamaru E, Adachi
N, Richards M and Kunugi H: BDNF function and intracellular
signaling in neurons. Histol Histopathol. 25:237–258. 2010.
|
|
38
|
Tian X, Guo J, Zhu M, Li M, Wu G and Xia
Y: δ-Opioid receptor activation rescues the functional TrkB
receptor and protects the brain from ischemia-reperfusion injury in
the rat. PLoS One. 8:e692522013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Xu L, Yenari MA, Steinberg GK and Giffard
RG: Mild hypothermia reduces apoptosis of mouse neurons in vitro
early in the cascade. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 22:21–28. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fujioka A, Terai K, Itoh RE, Aoki K,
Nakamura T, Kuroda S, Nishida E and Matsuda M: Dynamics of the
Ras/ERK MAPK cascade as monitored by fluorescent probes. J Biol
Chem. 281:8917–8926. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yang T, Massa SM and Longo FM: LAR protein
tyrosine phosphatase receptor associates with TrkB and modulates
neurotrophic signaling pathways. J Neurobiol. 66:1420–1436. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sánchez-Huertas C and Rico B:
CREB-dependent regulation of GAD65 transcription by BDNF/TrkB in
cortical interneurons. Cereb Cortex. 21:777–788. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|