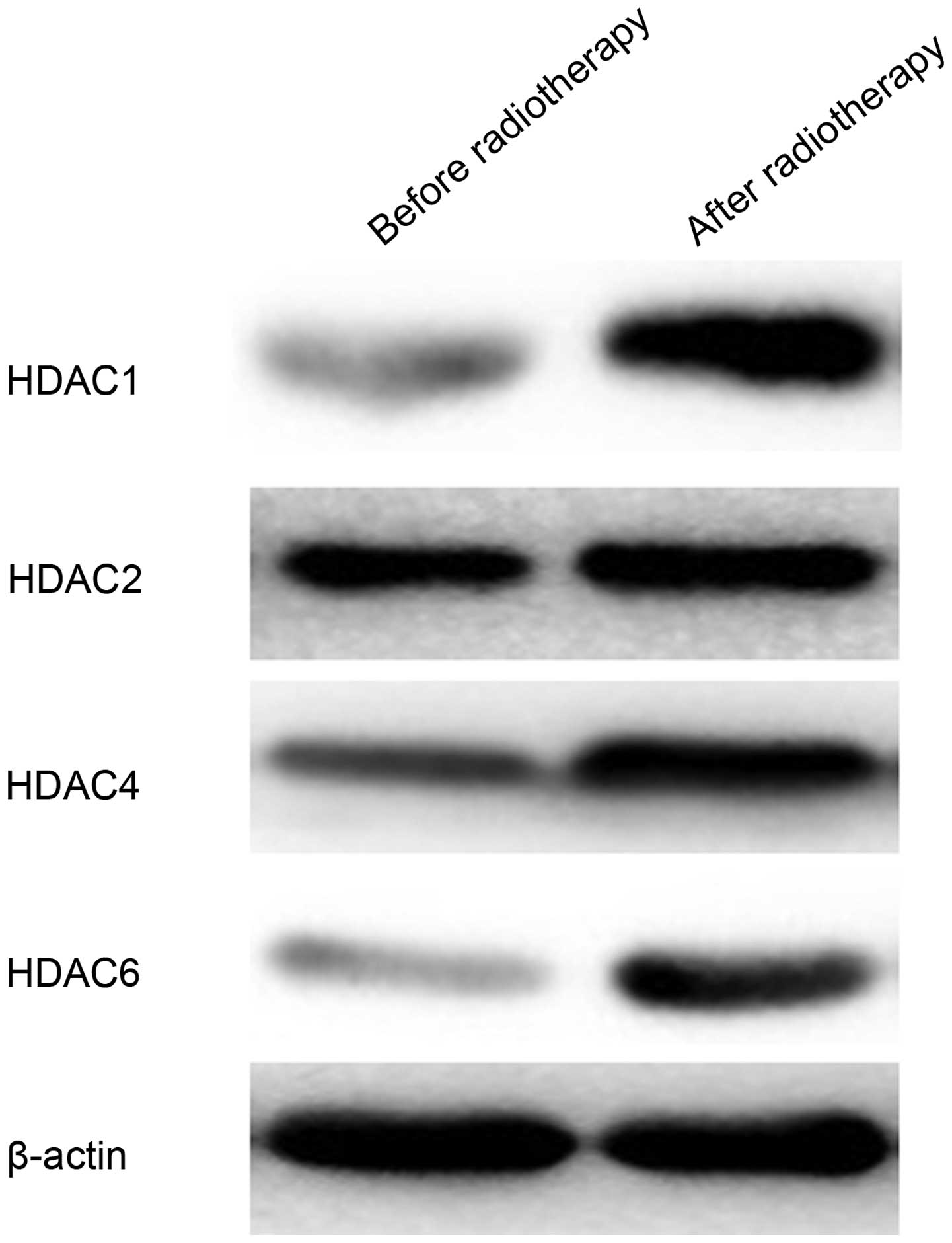
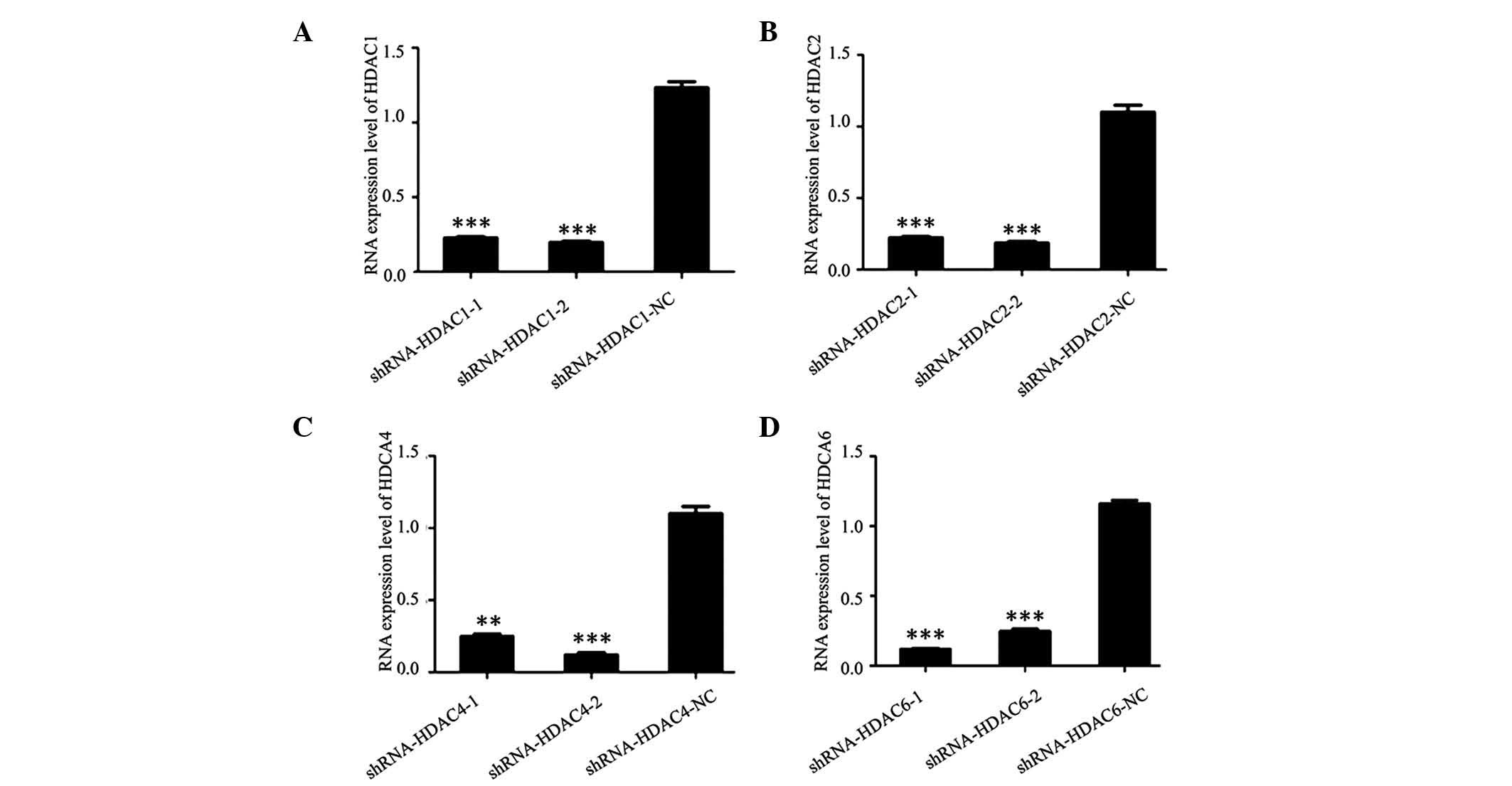
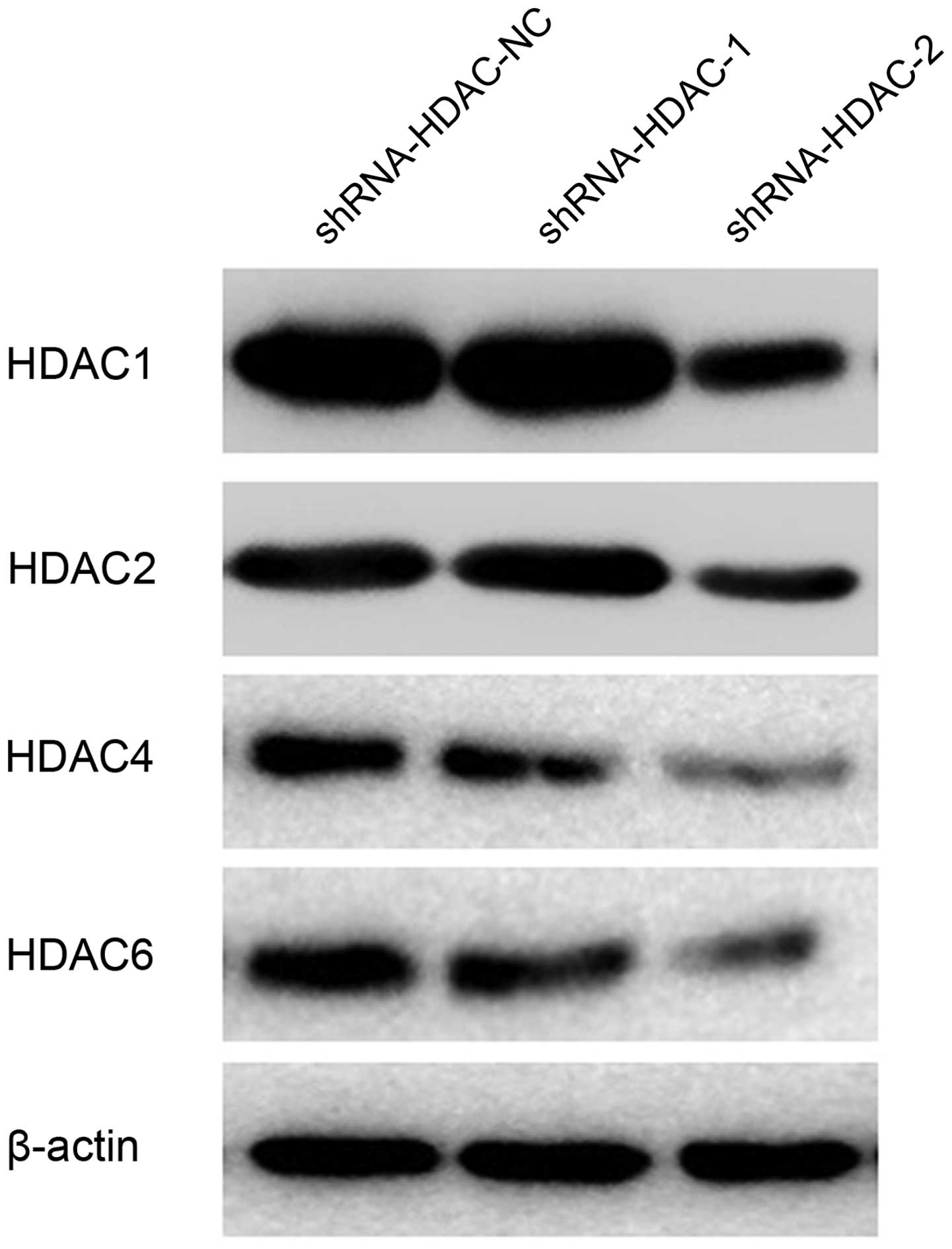
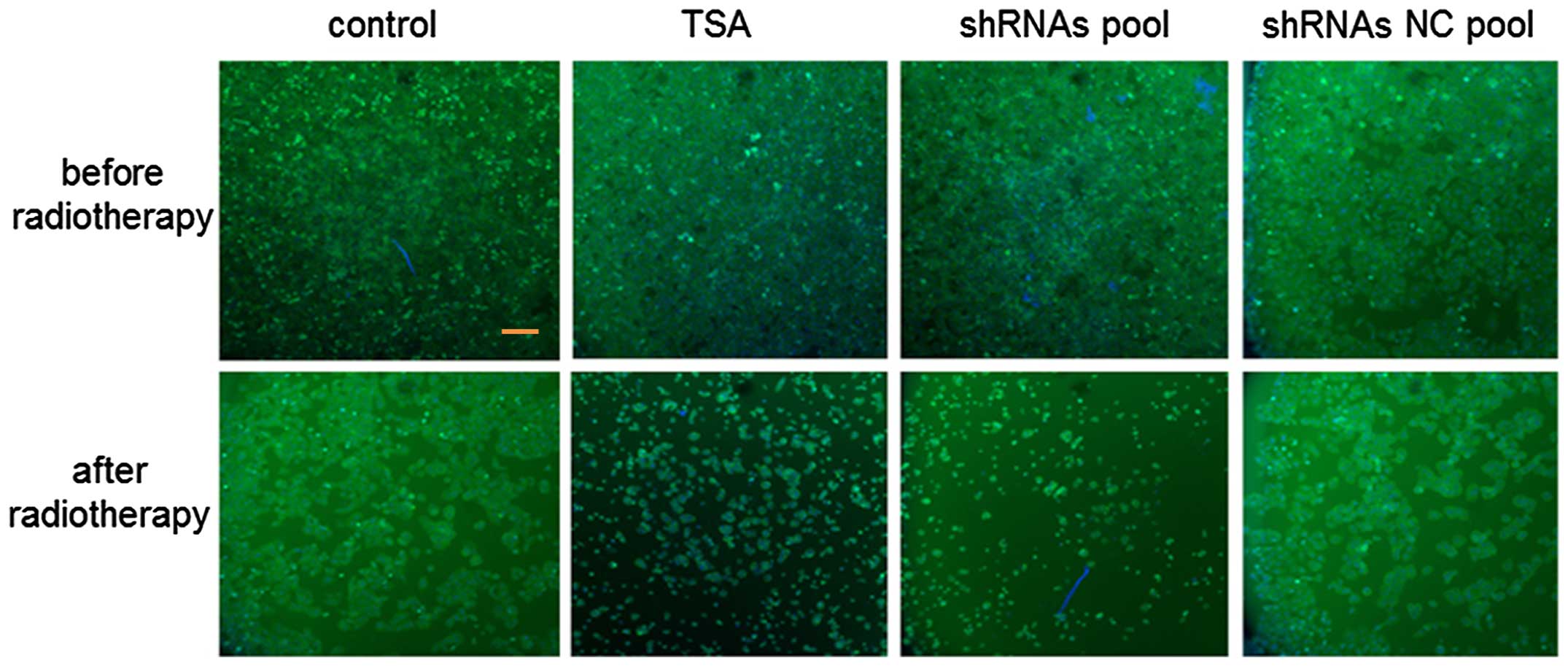
|
1
|
Mitsiades CS, Poulaki V, McMullan C, Negri
J, Fanourakis G, Goudopoulou A, Richon VM, Marks PA and Mitsiades
N: Novel histone deacetylase inhibitors in the treatment of thyroid
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 11:3958–3965. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Abu-Amero KK, Alzahrani AS, Zou M and Shi
Y: High frequency of somatic mitochondrial DNA mutations in human
thyroid carcinomas and complex I respiratory defect in thyroid
cancer cell lines. Oncogene. 24:1455–1460. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Roomi MW, Bhanap B, Niedzwiecki A and Rath
M: Inhibitory effects of a novel nutrient mixture on MMP secretion
and invasion on human thyroid cancer cell line SW 579. JANA.
12:26–34. 2009.
|
|
4
|
McTiernan A, Weiss NS and Daling JR:
Incidence of thyroid cancer in women in relation to known or
suspected risk factors for breast cancer. Cancer Res. 47:292–295.
1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pasieka JL: Anaplastic thyroid cancer.
Curr Opin Oncol. 15:78–83. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
O'Doherty MJ and Coakley AJ: Drug therapy
alternatives in the treatment of thyroid cancer. Drugs. 55:801–812.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rosenbluth BD, Serrano V, Happersett L,
Shaha AR, Tuttle RM, Narayana A, Wolden SL, Rosenzweig KE, Chong LM
and Lee NY: Intensity-modulated radiation therapy for the treatment
of nonanaplastic thyroid cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
63:1419–1426. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang Y, Tsang R, Asa S, Dickson B,
Arenovich T and Brierley J: Clinical outcome of anaplastic thyroid
carcinoma treated with radiotherapy of once-and twice-daily
fractionation regimens. Cancer. 107:1786–1792. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chow SM, Law SC, Mendenhall WM, Au SK,
Chan PT, Leung TW, Tong CC, Wong IS and Lau WH: Papillary thyroid
carcinoma: Prognostic factors and the role of radioiodine and
external radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 52:784–795.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Choy H and Milas L: Enhancing radiotherapy
with cyclooxygenase-2 enzyme inhibitors: A rational advance? J Natl
Cancer Inst. 95:1440–1452. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Williams KJ, Telfer BA, Shannon AM, Babur
M, Stratford IJ and Wedge SR: Combining radiotherapy with AZD2171,
a potent inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor signaling:
pathophysiologic effects and therapeutic benefit. Mol Cancer Ther.
6:599–606. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Coucke P: A phase I trial on LBH 589
(panobinostat), a histone deacetylase inhibitor (HDAC) in
combination with external radiotherapy for the treatment of
prostate cancer, esophageal cancer and head and neck cancer. BJMO.
3:117–123. 2009.
|
|
13
|
Minucci S and Pelicci PG: Histone
deacetylase inhibitors and the promise of epigenetic (and more)
treatments for cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:38–51. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Borbone E, Berlingieri MT, De Bellis F,
Nebbioso A, Chiappetta G, Mai A, Altucci L and Fusco A: Histone
deacetylase inhibitors induce thyroid cancer-specific apoptosis
through proteasome-dependent inhibition of TRAIL degradation.
Oncogene. 29:105–116. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Thurn KT, Thomas S, Moore A and Munster
PN: Rational therapeutic combinations with histone deacetylase
inhibitors for the treatment of cancer. Future Oncol. 7:263–283.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gallinari P, Di Marco S, Jones P, Pallaoro
M and Steinkühler C: HDACs, histone deacetylation and gene
transcription: From molecular biology to cancer therapeutics. Cell
Res. 17:195–211. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Giaginis C, Alexandrou P, Delladetsima I,
Giannopoulou I, Patsouris E and Theocharis S: Clinical significance
of histone deacetylase (HDAC)-1, HDAC-2, HDAC-4 and HDAC-6
expression in human malignant and benign thyroid lesions. Tumour
Biol. 35:61–71. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Shen L, Orillion A and Pili R: Histone
deacetylase inhibitors as immunomodulators in cancer therapeutics.
Epigenomics. 8:415–428. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang L, Bao X, Yang J, Li H, Zhou Q, Jiang
X, Li M, Liu X, Yuan X, Sun Y, et al: Novel cinnamohydroxamic acid
derivatives as HDAC inhibitors with anticancer activity in vitro
and in vivo. Chem Biol Interact. 249:64–70. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Platta CS, Greenblatt DY, Kunnimalaiyaan M
and Chen H: The HDAC inhibitor trichostatin A inhibits growth of
small cell lung cancer cells. J Surg Res. 142:219–226. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Clarke C, Burbridge E and Smyth P: Can
deacetylation promote radioiodide uptake in thyroid cancer?
Endocrine Abstracts. 9:1542005.
|
|
22
|
Sui G, Soohoo C, Affar el B, Gay F and Shi
Y, Forrester WC and Shi Y: A DNA vector-based RNAi technology to
suppress gene expression in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 99:5515–5520. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Seibler J, Küter-Luks B, Kern H, Streu S,
Plum L, Mauer J, Kühn R, Brüning JC and Schwenk F: Single copy
shRNA configuration for ubiquitous gene knockdown in mice. Nucleic
Acids Res. 33:e672005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wu G, Ma Z, Qian J and Liu B: PP4R1
accelerates cell growth and proliferation in HepG2 hepatocellular
carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 8:2067–2074. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Spitzner M, Emons G, Kramer F, Gaedcke J,
Rave-Fränk M, Scharf JG, Burfeind P, Becker H, Beissbarth T,
Ghadimi BM, et al: A gene expression signature for
chemoradiosensitivity of colorectal cancer cells. Int J Radiat
Oncol Biol Phys. 78:1184–1192. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Elashoff M, Matveyenko AV, Gier B,
Elashoff R and Butler PC: Pancreatitis, pancreatic and thyroid
cancer with glucagon-like peptide-1-based therapies.
Gastroenterology. 141:150–156. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kelly WK, O'Connor OA, Krug LM, Chiao JH,
Heaney M, Curley T, MacGregore-Cortelli B, Tong W, Secrist JP,
Schwartz L, et al: Phase I study of an oral histone deacetylase
inhibitor, suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, in patients with
advanced cancer. J Clin Oncol. 23:3923–3931. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Luong QT, O'Kelly J, Braunstein GD,
Hershman JM and Koeffler HP: Antitumor activity of suberoylanilide
hydroxamic acid against thyroid cancer cell lines in vitro and in
vivo. Clin Cancer Res. 12:5570–5577. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jones PA and Baylin SB: The fundamental
role of epigenetic events in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 3:415–428.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Khochbin S, Verdel A, Lemercier C and
Seigneurin-Berny D: Functional significance of histone deacetylase
diversity. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 11:162–166. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim JH, Choi YK, Kwon HJ, Yang HK, Choi JH
and Kim DY: Downregulation of gelsolin and retinoic acid receptor
beta expression in gastric cancer tissues through histone
deacetylase 1. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 19:218–224. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Giannini R and Cavallini A: Expression
analysis of a subset of coregulators and three nuclear receptors in
human colorectal carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 25:4287–4292.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Krusche CA, Wülfing P, Kersting C, Vloet
A, Böcker W, Kiesel L, Beier HM and Alfer J: Histone deacetylase-1
and-3 protein expression in human breast cancer: A tissue
microarray analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 90:15–23. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sasaki H, Moriyama S, Nakashima Y,
Kobayashi Y, Kiriyama M, Fukai I, Yamakawa Y and Fujii Y: Histone
deacetylase 1 mRNA expression in lung cancer. Lung Cancer.
46:171–178. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Woyach JA, Kloos RT, Ringel MD, Arbogast
D, Collamore M, Zwiebel JA, Grever M, Villalona-Calero M and Shah
MH: Lack of therapeutic effect of the histone deacetylase inhibitor
vorinostat in patients with metastatic radioiodine-refractory
thyroid carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 94:164–170. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
37
|
Furuya F, Shimura H, Suzuki H, Taki K,
Ohta K, Haraguchi K, Onaya T, Endo T and Kobayashi T: Histone
deacetylase inhibitors restore radioiodide uptake and retention in
poorly differentiated and anaplastic thyroid cancer cells by
expression of the sodium/iodide symporter thyroperoxidase and
thyroglobulin. Endocrinology. 145:2865–2875. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zarnegar R, Brunaud L, Kanauchi H, Wong M,
Fung M, Ginzinger D, Duh QY and Clark OH: Increasing the
effectiveness of radioactive iodine therapy in the treatment of
thyroid cancer using Trichostatin A, a histone deacetylase
inhibitor. Surgery. 132:984–990. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kumar KS, Sonnemann J, Hong le TT, Buurman
C, Adler F, Maass M, Völker U and Beck JF: Histone deacetylase
inhibitors, but not vincristine, cooperate with radiotherapy to
induce cell death in medulloblastoma. Anticancer Res. 27:465–470.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang J, Mi P, Lin G, Wang YX, Liu G and
Chen X: Imaging-guided delivery of RNAi for anticancer treatment.
Adv Drug Deliv Rev. Jan 22–2016.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Bennasser Y, Yeung ML and Jeang KT: RNAi
therapy for HIV infection principles and practicalities. BioDrugs.
21:17–22. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Harper SQ: Progress and challenges in RNA
interference therapy for Huntington disease. Arch Neurol.
66:933–938. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Boudreau RL and Davidson BL: RNAi therapy
for neurodegenerative diseases. Curr Top Dev Biol. 75:73–92. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Cheng YJ, Ding H, Du HQ, Yan H, Zhao JB,
Zhang WB, Zou YJ, Liu HY and Xiao H: Downregulation of
phosphoglycerate kinase 1 by shRNA sensitizes U251 xenografts to
radiotherapy. Oncol Rep. 32:1513–1520. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wang HR, Li XM and Lu XY: Silencing of
signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 gene expression
using RNAi enhances the efficacy of radiotherapy for laryngeal
carcinoma in vivo. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi.
44:591–596. 2009.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Li Y, Han N, Yin T, Huang L, Liu S, Liu D,
Xie C and Zhang M: Lentivirus-mediated Nox4 shRNA invasion and
angiogenesis and enhances radiosensitivity in human glioblastoma.
Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014:5817322014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kendziorra E, Ahlborn K, Spitzner M,
Rave-Fränk M, Emons G, Gaedcke J, Kramer F, Wolff HA, Becker H,
Beissbarth T, et al: Silencing of the Wnt transcription factor TCF4
sensitizes colorectal cancer cells to (chemo-) radiotherapy.
Carcinogenesis. 32:1824–1831. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|