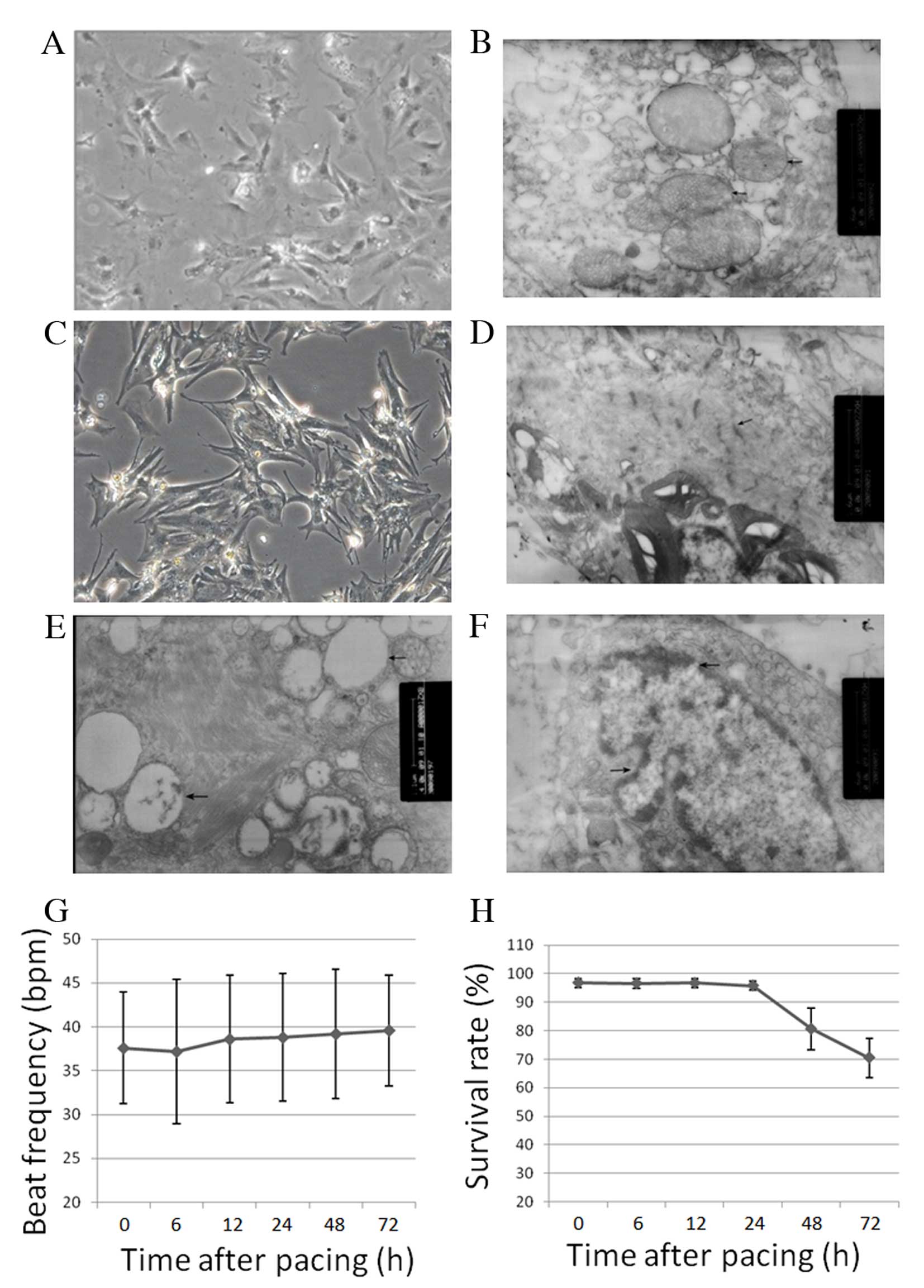
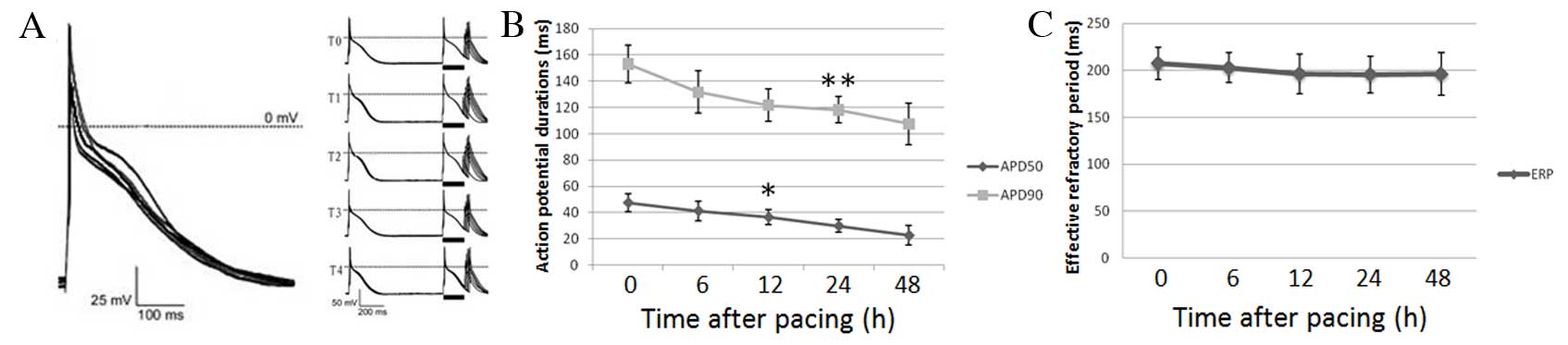
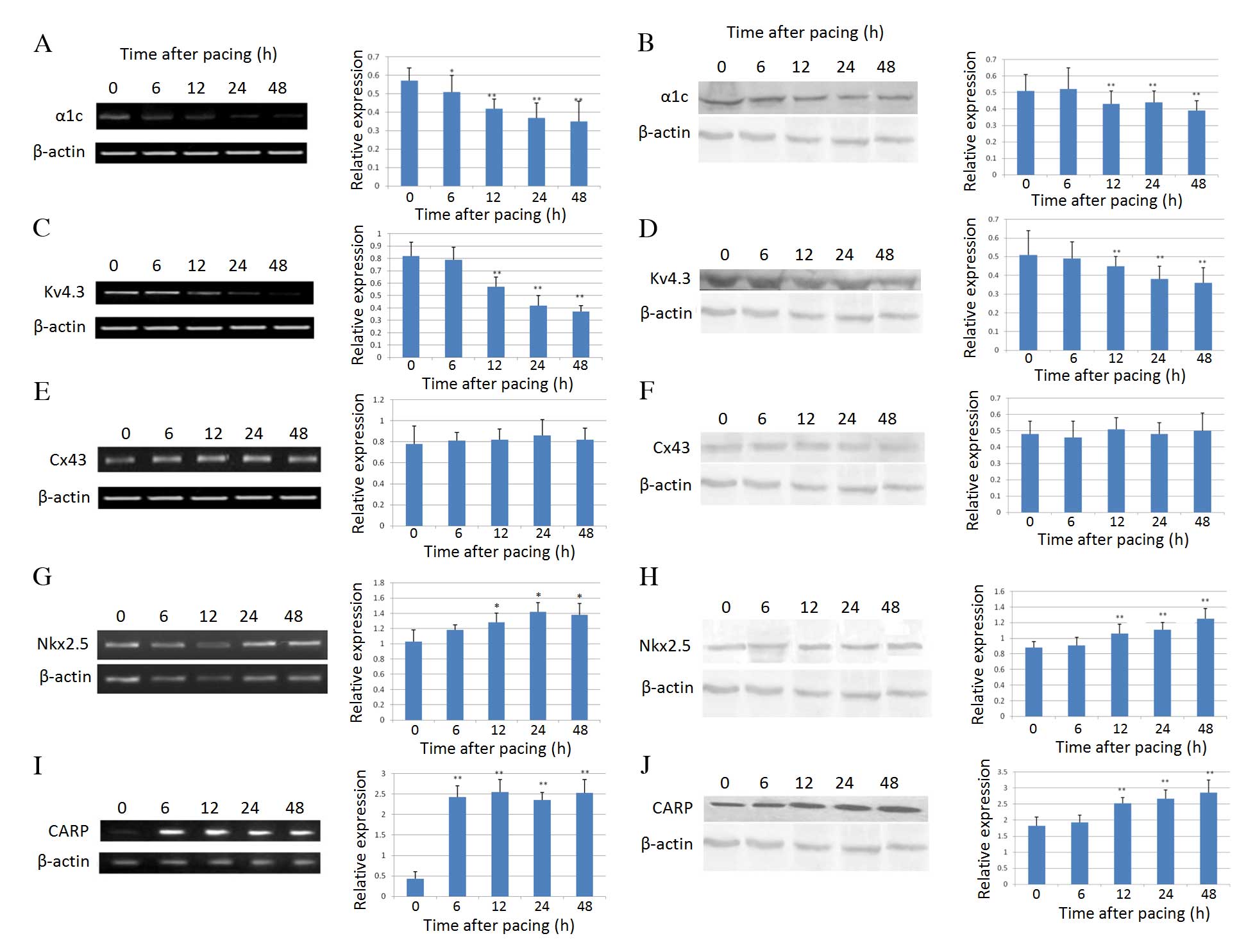
|
1
|
Wang XH, Huang CX, Wang Q, Li RG, Xu YJ,
Liu X, Fang WY and Yang YQ: A novel GATA5 loss-of-function mutation
underlies lone atrial fibrillation. Int J Mol Med. 31:43–50.
2013.
|
|
2
|
Zhou YM, Zheng PX, Yang YQ, Ge ZM and Kang
WQ: A novel PITX2c loss-of-function mutation underlies lone atrial
fibrillation. Int J Mol Med. 32:827–834. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yoon N, Cho JG, Kim KH, Park KH, Sim DS,
Yoon HJ, Hong YJ, Park HW, Kim JH, Ahn Y, et al: Beneficial effects
of an angiotensin-II receptor blocker on structural atrial
reverse-remodeling in a rat model of ischemic heart failure. Exp
Ther Med. 5:1009–1016. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Qiu XB, Xu YJ, Li RG, Xu L, Liu X, Fang
WY, Yang YQ and Qu XK: PITX2C loss-of-function mutations
responsible for idiopathic atrial fibrillation. Clinics (Sao
Paulo). 69:15–22. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Gan TY, Qiao W, Xu GJ, Zhou XH, Tang BP,
Song JG, Li YD, Zhang J, Li FP, Mao T and Jiang T: Aging-associated
changes in L-type calcium channels in the left atria of dogs. Exp
Ther Med. 6:919–924. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xu GJ, Gan TY, Tang BP, Chen ZH, Mahemuti
A, Jiang T, Song JG, Guo X, Li YD, Zhou XH, et al: Alterations in
the expression of atrial calpains in electrical and structural
remodeling during aging and atrial fibrillation. Mol Med Rep.
8:1343–1352. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fu G, Cao Y, Lu J, Li J, Liu L, Wang H, Su
F and Zheng Q: Programmed cell death-1 deficiency results in atrial
remodeling in C57BL/6 mice. Int J Mol Med. 31:423–429. 2013.
|
|
8
|
Heijman J and Dobrev D: Systems approaches
to post-operative atrial fibrillation-do they help us to better
understand the ionic basis of the arrhythmogenic substrate? J Mol
Cell Cardio. 53:320–322. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Nattel S and Dobrev D: The
multidimensional role of calcium in atrial fibrillation
pathophysiology: Mechanistic insights and therapeutic
opportunities. Eur Heart J. 33:1870–1877. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ren Y, Zhang M, Zhang T and Huang R:
Effect of ouabain on myocardial remodeling in rats. Exp Ther Med.
6:65–70. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Huo R, Sheng Y, Guo WT and Dong DL: The
potential role of Kv4.3 K+ channel in heart hypertrophy. Channels
(Austin). 8:203–209. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yue L, Xie J and Nattel S: Molecular
determinants of cardiac fibroblast electrical function and
therapeutic implications for atrial fibrillation. Cardiovasc Res.
89:744–753. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Huang RT, Xue S, Xu YJ, Zhou M and Yang
YQ: A novel NKX2.5 loss-of-function mutation responsible for
familial atrial fibrillation. Int J Mol Med. 31:1119–1126.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yuan F, Qiu XB, Li RG, Qu XK, Wang J, Xu
YJ, Liu X, Fang WY, Yang YQ and Liao DN: A novel NKX2-5
loss-of-function mutation predisposes to familial dilated
cardiomyopathy and arrhythmias. Int J Mol Med. 35:478–486.
2015.
|
|
15
|
Wang J, Zhang DF, Sun YM, Li RG, Qiu XB,
Qu XK, Liu X, Fang WY and Yang YQ: NKX2-6 mutation predisposes to
familial atrial fibrillation. Int J Mol Med. 34:1581–1590.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yu H, Xu JH, Song HM, Zhao L, Xu WJ, Wang
J, Li RG, Xu L, Jiang WF, Qiu XB, et al: Mutational spectrum of the
NKX2-5 gene in patients with lone atrial fibrillation. Int J Med
Sci. 11:554–563. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang Y, Rath N, Hannenhalli S, Wang Z,
Cappola T, Kimura S, Atochina-Vasserman E, Lu MM, Beers MF and
Morrisey EE: GATA and Nkx factors synergistically regulate
tissue-specific gene expression and development in vivo.
Development. 134:189–198. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wang J, Zhang DF, Sun YM and Yang YQ: A
novel PITX2c loss-of-function mutation associated with familial
atrial fibrillation. Eur J Med Genet. 57:25–31. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Shi HF, Yang JF, Wang Q, Li RG, Xu YJ, Qu
XK, Fang WY, Liu X and Yang YQ: Prevalence and spectrum of GJA5
mutations associated with lone atrial fibrillation. Mol Med Rep.
7:767–774. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Iwasaki YK, Nishida K, Kato T and Nattel
S: Atrial fibrillation pathophysiology: Implications for
management. Circulation. 124:2264–2274. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee HL, Chang PC, Chou CC, Wo HT, Chu Y,
Wen MS, Yeh SJ and Wu D: Blunted proarrhythmic effect of nicorandil
in a Langendorff-perfused phase-2 myocardial infarction rabbit
model. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 36:142–151. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Shaw RM and Rudy Y: Electrophysiologic
effects of acute myocardial ischemia: A theoretical study of
altered cell excitability and action potential duration. Cardiovasc
Res. 35:256–272. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang X, Wang X, Gu Y, Wang T and Huang C:
Wenxin Keli attenuates ischemia-induced ventricular arrhythmias in
rats: Involvement of L-type calcium and transient outward potassium
currents. Mol Med Rep. 7:519–524. 2013.
|
|
24
|
Zhang H, Wu S, Huang C and Li X: Long-term
treatment of spontaneously hypertensive rats with losartan and
molecular basis of modulating Ito of ventricular myocytes. Mol Med
Rep. 9:1959–1967. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nattel S, Burstein B and Dobrev D: Atrial
remodeling and atrial fibrillation: Mechanisms and implications.
Circ Arrhythm Electrophysio. 1:62–73. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Shi S, Liu T, Li Y, Qin M, Tang Y, Shen
JY, Liang J, Yang B and Huang C: Chronic N-methyl-D-aspartate
receptor activation induces cardiac electrical remodeling and
increases susceptibility to ventricular arrhythmias. Pacing Clin
Electrophysiol. 37:1367–1377. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang Q, Deng C, Rao F, Modi RM, Zhu J,
Liu X, Mai L, Tan H, Yu X, Lin Q, et al: Silencing of desmoplakin
decreases connexin43/Nav1.5 expression and sodium current in HL-1
cardiomyocytes. Mol Med Rep. 8:780–786. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yan Y, Huang J, Ding F, Mei J, Zhu J, Liu
H and Sun K: Aquaporin 1 plays an important role in myocardial
edema caused by cardiopulmonary bypass surgery in goat. Int J Mol
Med. 31:637–643. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Valderrábano M: Influence of anisotropic
conduction properties in the propagation of the cardiac action
potential. Prog Biophys MolBiol. 94:144–168. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Mommersteeg MT, Christoffels VM, Anderson
RH and Moorman AF: Atrial fibrillation: A developmental point of
view. Heart Rhythm. 6:1818–1824. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hong K and Xiong Q: Genetic basis of
atrial fibrillation. Curr Opin Cardiol. 29:220–226. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Searcy RD, Vincent EB, Liberatore CM and
Yutzey KE: A GATA-dependent nkx-2.5 regulatory element activates
early cardiac gene expression in transgenic mice. Development.
125:4461–4470. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mahida S: Transcription factors and atrial
fibrillation. Cardiovasc Res. 101:194–202. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Gutierrez-Roelens I, De Roy L, Ovaert C,
Sluysmans T, Devriendt K, Brunner HG and Vikkula M: A novel
CSX/NKX2-5 mutation causes autosomal-dominant AV block: Are atrial
fibrillation and syncopes part of the phenotype? Eur J Hum Genet.
14:1313–1316. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Moskowitz IP, Kim JB, Moore ML, Wolf CM,
Peterson MA, Shendure J, Nobrega MA, Yokota Y, Berul C, Izumo S, et
al: A molecular pathway including Id2, Tbx5, and Nkx2-5 required
for cardiac conduction system development. Cell. 129:1365–1376.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chen B, Zhong L, Roush SF, Pentassuglia L,
Peng X, Samaras S, Davidson JM, Sawyer DB and Lim CC: Disruption of
a GATA4/Ankrd1 signaling axis in cardiomyocytes leads to sarcomere
disarray: Implications for anthracycline cardiomyopathy. PLoS One.
7:e357432012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|