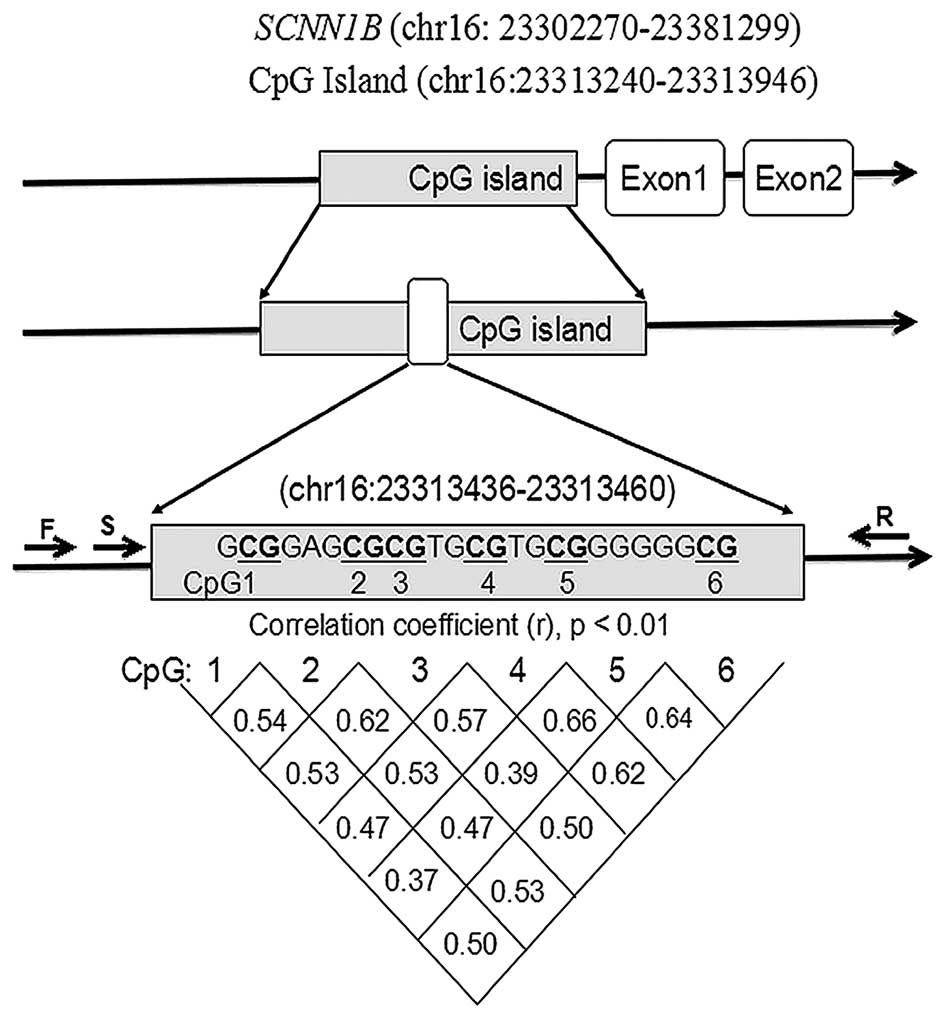
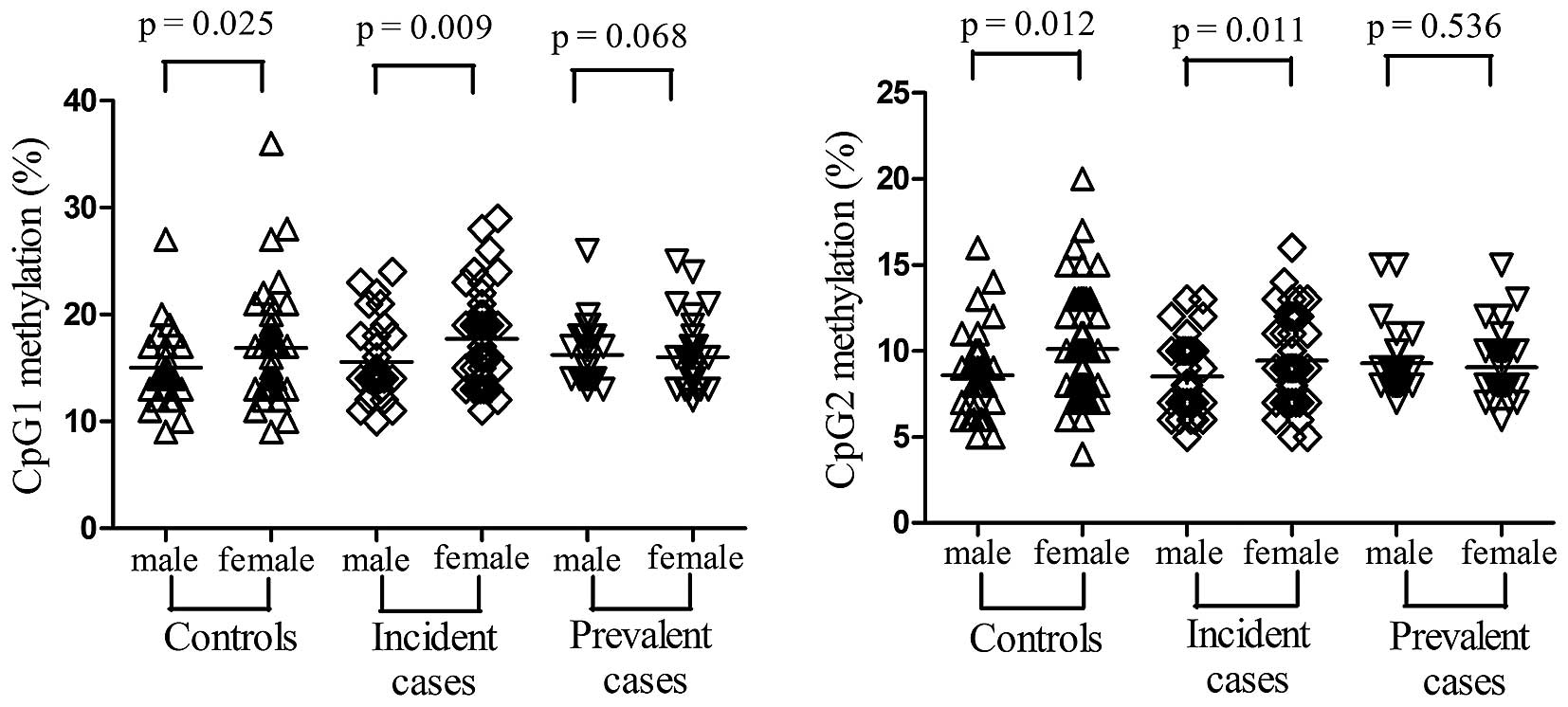
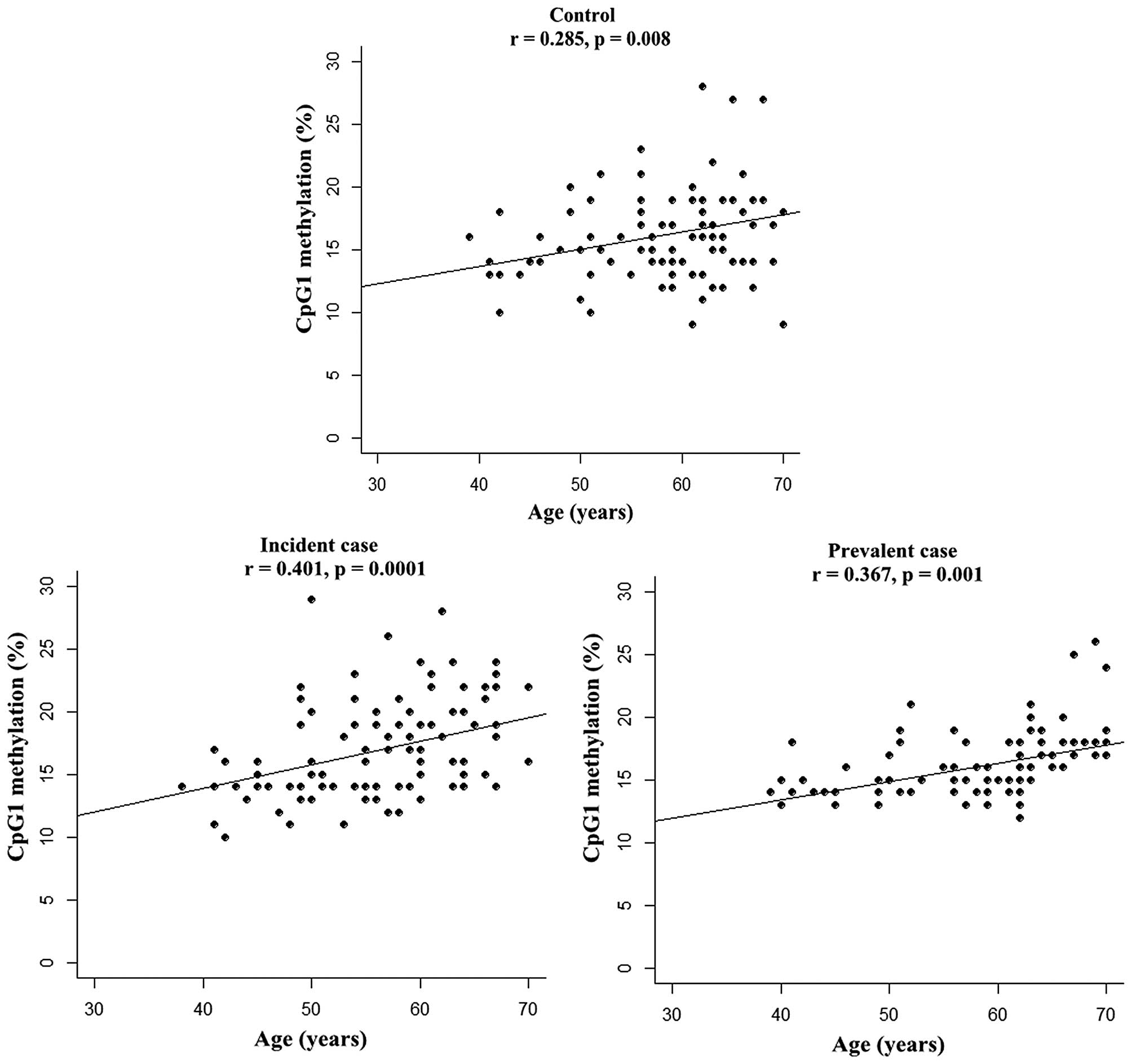
|
1
|
Pratt JH: Central role for ENaC in
development of hypertension. J Am Soc Nephrol. 16:3154–3159. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Garty H: Molecular properties of
epithelial, amiloride-blockable Na+ channels. FASEB J. 8:522–528.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Loffing J and Schild L: Functional domains
of the epithelial sodium channel. J Am Soc Nephrol. 16:3175–3181.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang LP, Gao LG, Zhou XL, Wu HY, Zhang L,
Wen D, Li YH, Liu YX, Tian T, Fan XH, et al: Genetic diagnosis of
liddle's syndrome by mutation analysis of SCNN1B and SCNN1G in a
Chinese family. Chin Med J (Engl). 125:1401–1404. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sawathiparnich P, Sumboonnanonda A,
Weerakulwattana P and Limwongse C: A novel mutation in the
beta-subunit of the epithelial sodium channel gene (SCNN1B) in a
Thai family with liddle's syndrome. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab.
22:85–89. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang W, Zhou W, Jiang L, Cui B, Ye L, Su
T, Wang J, Li X and Ning G: Mutation analysis of SCNN1B in a family
with liddle's syndrome. Endocrine. 29:385–390. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Noda Y: Liddle's syndrome. Nihon Jinzo
Gakkai Shi. 53:160–162. 2011.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Choy MK, Movassagh M, Goh HG, Bennett MR,
Down TA and Foo RS: Genome-wide conserved consensus transcription
factor binding motifs are hyper-methylated. BMC Genomics.
11:5192010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang LN, Liu PP, Wang L, Yuan F, Xu L,
Xin Y, Fei LJ, Zhong QL, Huang Y, Xu L, et al: Lower ADD1 gene
promoter DNA methylation increases the risk of essential
hypertension. PLoS One. 8:e634552013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang X, Falkner B, Zhu H, Shi H, Su S, Xu
X, Sharma AK, Dong Y, Treiber F, Gutin B, et al: A genome-wide
methylation study on essential hypertension in young african
american males. PLoS One. 8:e539382013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xu L, Zheng D, Wang L, Jiang D, Liu H, Xu
L, Liao Q, Zhang L, Liu P, Shi X, et al: GCK gene-body
hypomethylation is associated with the risk of coronary heart
disease. Biomed Res Int. 2014:1517232014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jiang D, Zheng D, Wang L, Huang Y, Liu H,
Xu L, Liao Q, Liu P, Shi X, Wang Z, et al: Elevated PLA2G7 gene
promoter methylation as a gender-specific marker of aging increases
the risk of coronary heart disease in females. PLoS One.
8:e597522013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cheng J, Tang L, Hong Q, Ye H, Xu X, Xu L,
Bu S, Wang Q, Dai D, Jiang D and Duan S: Investigation into the
promoter DNA methylation of three genes (CAMK1D, CRY2 and CALM2) in
the peripheral blood of patients with type 2 diabetes. Exp Ther
Med. 8:579–584. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tang L, Wang L, Ye H, Xu X, Hong Q, Wang
H, Xu L, Bu S, Zhang L, Cheng J, et al: BCL11A gene DNA methylation
contributes to the risk of type 2 diabetes in males. Exp Ther Med.
8:459–463. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tang L, Ye H, Hong Q, Wang L, Wang Q, Wang
H, Xu L, Bu S, Zhang L, Cheng J, et al: Elevated CpG island
methylation of GCK gene predicts the risk of type 2 diabetes in
chinese males. Gene. 547:329–333. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tang LL, Liu Q, Bu SZ, Xu LT, Wang QW, Mai
YF and Duan SW: The effect of environmental factors and DNA
methylation on type 2 diabetes mellitus. Yi Chuan. 35:1143–1152.
2013.(In Chinese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Holliday R: The inheritance of epigenetic
defects. Science. 238:163–170. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cheng J, Wang Y, Zhou K, Wang L, Li J,
Zhuang Q, Xu X, Xu L, Zhang K and Dai D: Male-specific association
between dopamine receptor D4 gene methylation and schizophrenia.
PLoS One. 9:e891282014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
European Society of Hypertension-European
Society of Cardiology Guidelines Committee, . 2003 European society
of hypertension-european society of cardiology guidelines for the
management of arterial hypertension. J Hypertens. 21:1011–1053.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dai D, Cheng J, Zhou K, Lv Y, Zhuang Q,
Zheng R, Zhang K, Jiang D, Gao S and Duan S: Significant
association between DRD3 gene body methylation and schizophrenia.
Psychiatry Res. 220:772–777. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Altobelli E, Petrocelli R, Maccarone M,
Altomare G, Argenziano G, Giannetti A, Peserico A, Vena GA, Tiberti
S, Chimenti S and Peris K: Risk factors of hypertension, diabetes
and obesity in italian psoriasis patients: A survey on
socio-demographic characteristics, smoking habits and alcohol
consumption. Eur J Dermatol. 19:252–256. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mathers JC: Nutritional modulation of
ageing: Genomic and epigenetic approaches. Mech Ageing Dev.
127:584–589. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hughes T, Ture-Ozdemir F, Alibaz-Oner F,
Coit P, Direskeneli H and Sawalha AH: Epigenome-wide scan
identifies a treatment-responsive pattern of altered DNA
methylation among cytoskeletal remodeling genes in monocytes and
CD4+ T cells from patients with behcet's disease.
Arthritis Rheumatol. 66:1648–1658. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Polidoro S, Broccoletti R, Campanella G,
Di Gaetano C, Menegatti E, Scoletta M, Lerda E, Matullo G, Vineis
P, Berardi D, et al: Effects of bisphosphonate treatment on DNA
methylation in osteonecrosis of the jaw. Mutat Res. 757:104–113.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Laytragoon-Lewin N, Rutqvist LE and Lewin
F: DNA methylation in tumour and normal mucosal tissue of head and
neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) patients: New diagnostic
approaches and treatment. Med Oncol. 30:6542013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Crudo A, Petropoulos S, Moisiadis VG,
Iqbal M, Kostaki A, Machnes Z, Szyf M and Matthews SG: Prenatal
synthetic glucocorticoid treatment changes DNA methylation states
in male organ systems: Multigenerational effects. Endocrinology.
153:3269–3283. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Guay SP, Brisson D, Lamarche B, Biron S,
Lescelleur O, Biertho L, Marceau S, Vohl MC, Gaudet D and Bouchard
L: ADRB3 gene promoter DNA methylation in blood and visceral
adipose tissue is associated with metabolic disturbances in men.
Epigenomics. 6:33–43. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bellavia A, Urch B, Speck M, Brook RD,
Scott JA, Albetti B, Behbod B, North M, Valeri L, Bertazzi PA, et
al: DNA hypomethylation, ambient particulate matter and increased
blood pressure: Findings from controlled human exposure
experiments. J Am Heart Assoc. 2:e0002122013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Alexeeff SE, Baccarelli AA, Halonen J,
Coull BA, Wright RO, Tarantini L, Bollati V, Sparrow D, Vokonas P
and Schwartz J: Association between blood pressure and DNA
methylation of retrotransposons and pro-inflammatory genes. Int J
Epidemiol. 42:270–280. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bell JT, Tsai PC, Yang TP, Pidsley R,
Nisbet J, Glass D, Mangino M, Zhai G, Zhang F, Valdes A, et al:
Epigenome-wide scans identify differentially methylated regions for
age and age-related phenotypes in a healthy ageing population. PLoS
Genet. 8:e10026292012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Teschendorff AE, Menon U, Gentry-Maharaj
A, Ramus SJ, Weisenberger DJ, Shen H, Campan M, Noushmehr H, Bell
CG, Maxwell AP, et al: Age-dependent DNA methylation of genes that
are suppressed in stem cells is a hallmark of cancer. Genome Res.
20:440–446. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Maegawa S, Hinkal G, Kim HS, Shen L, Zhang
L, Zhang J, Zhang N, Liang S, Donehower LA and Issa JP: Widespread
and tissue specific age-related DNA methylation changes in mice.
Genome Res. 20:332–340. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Issa JP, Ottaviano YL, Celano P, Hamilton
SR, Davidson NE and Baylin SB: Methylation of the oestrogen
receptor CpG island links ageing and neoplasia in human colon. Nat
Genet. 7:536–540. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wilson VL and Jones PA: DNA methylation
decreases in aging but not in immortal cells. Science. 220:1055–75.
1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Khattar RS, Swales JD, Dore C, Senior R
and Lahiri A: Effect of aging on the prognostic significance of
ambulatory systolic, diastolic and pulse pressure in essential
hypertension. Circulation. 104:783–789. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Grodzicki T, Michalewicz L and Messerli
FH: Aging and essential hypertension: Effect of left ventricular
hypertrophy on cardiac function. Am J Hypertens. 11:425–429. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kaz AM, Wong CJ, Dzieciatkowski S, Luo Y,
Schoen RE and Grady WM: Patterns of DNA methylation in the normal
colon vary by anatomical location, gender, and age. Epigenetics.
9:492–502. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tapp HS, Commane DM, Bradburn DM,
Arasaradnam R, Mathers JC, Johnson IT and Belshaw NJ: Nutritional
factors and gender influence age-related DNA methylation in the
human rectal mucosa. Aging Cell. 12:148–155. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Burghardt KJ, Pilsner JR, Bly MJ and
Ellingrod VL: DNA methylation in schizophrenia subjects: Gender and
MTHFR 677C/T genotype differences. Epigenomics. 4:261–268. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang FF, Cardarelli R, Carroll J, Fulda
KG, Kaur M, Gonzalez K, Vishwanatha JK, Santella RM and Morabia A:
Significant differences in global genomic DNA methylation by gender
and race/ethnicity in peripheral blood. Epigenetics. 6:623–629.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hao Y, Huang W, Nielsen DA and Kosten TA:
Litter gender composition and sex affect maternal behavior and DNA
methylation levels of the oprm1 gene in rat offspring. Front
Psychiatry. 2:212011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Boks MP, Derks EM, Weisenberger DJ,
Strengman E, Janson E, Sommer IE, Kahn RS and Ophoff RA: The
relationship of DNA methylation with age, gender and genotype in
twins and healthy controls. PLoS One. 4:e67672009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Vaissiere T, Hung RJ, Zaridze D, Moukeria
A, Cuenin C, Fasolo V, Ferro G, Paliwal A, Hainaut P, Brennan P, et
al: Quantitative analysis of DNA methylation profiles in lung
cancer identifies aberrant DNA methylation of specific genes and
its association with gender and cancer risk factors. Cancer Res.
69:243–252. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
El-Maarri O, Becker T, Junen J, Manzoor
SS, Diaz-Lacava A, Schwaab R, Wienker T and Oldenburg J: Gender
specific differences in levels of DNA methylation at selected loci
from human total blood: A tendency toward higher methylation levels
in males. Hum Genet. 122:505–514. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|