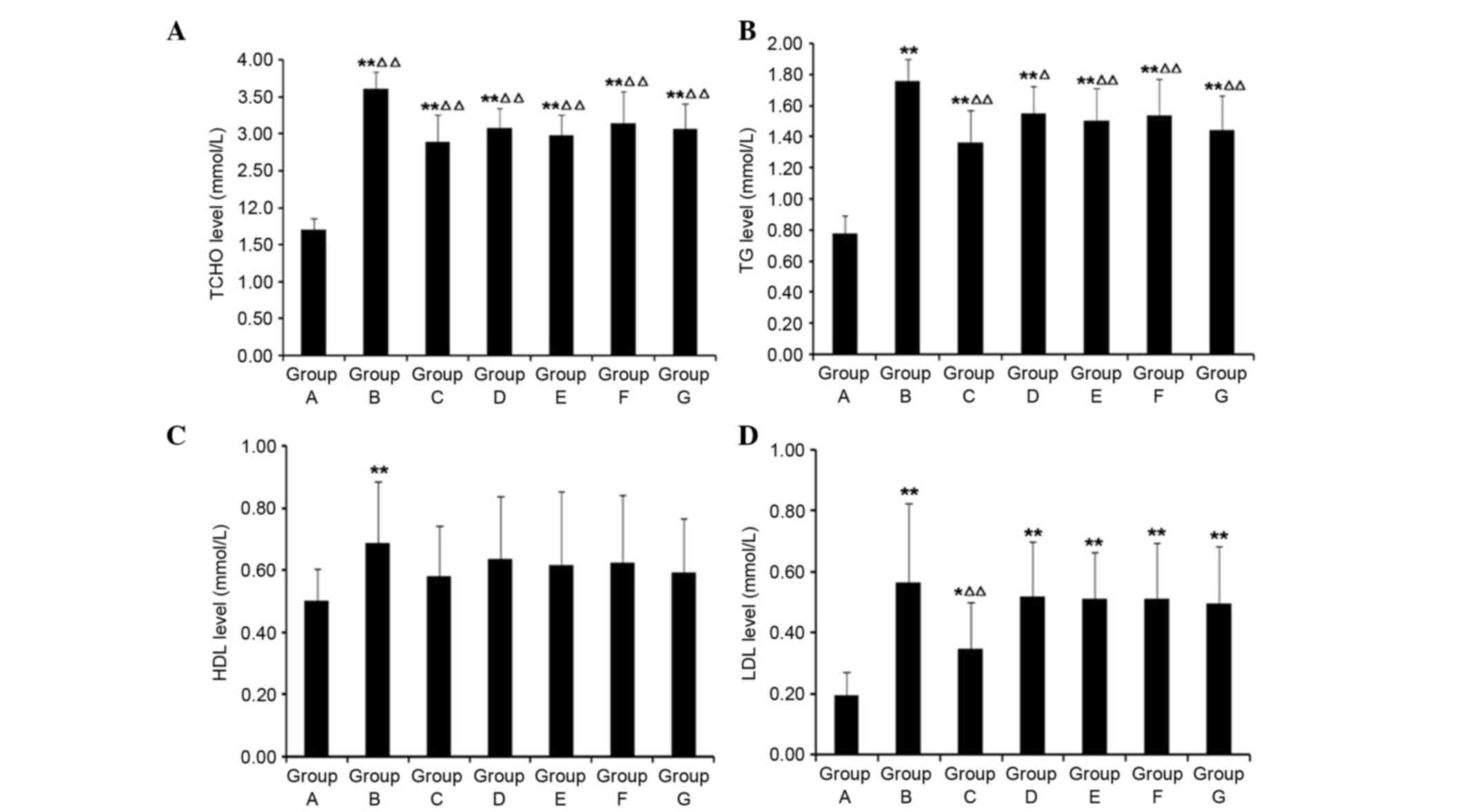
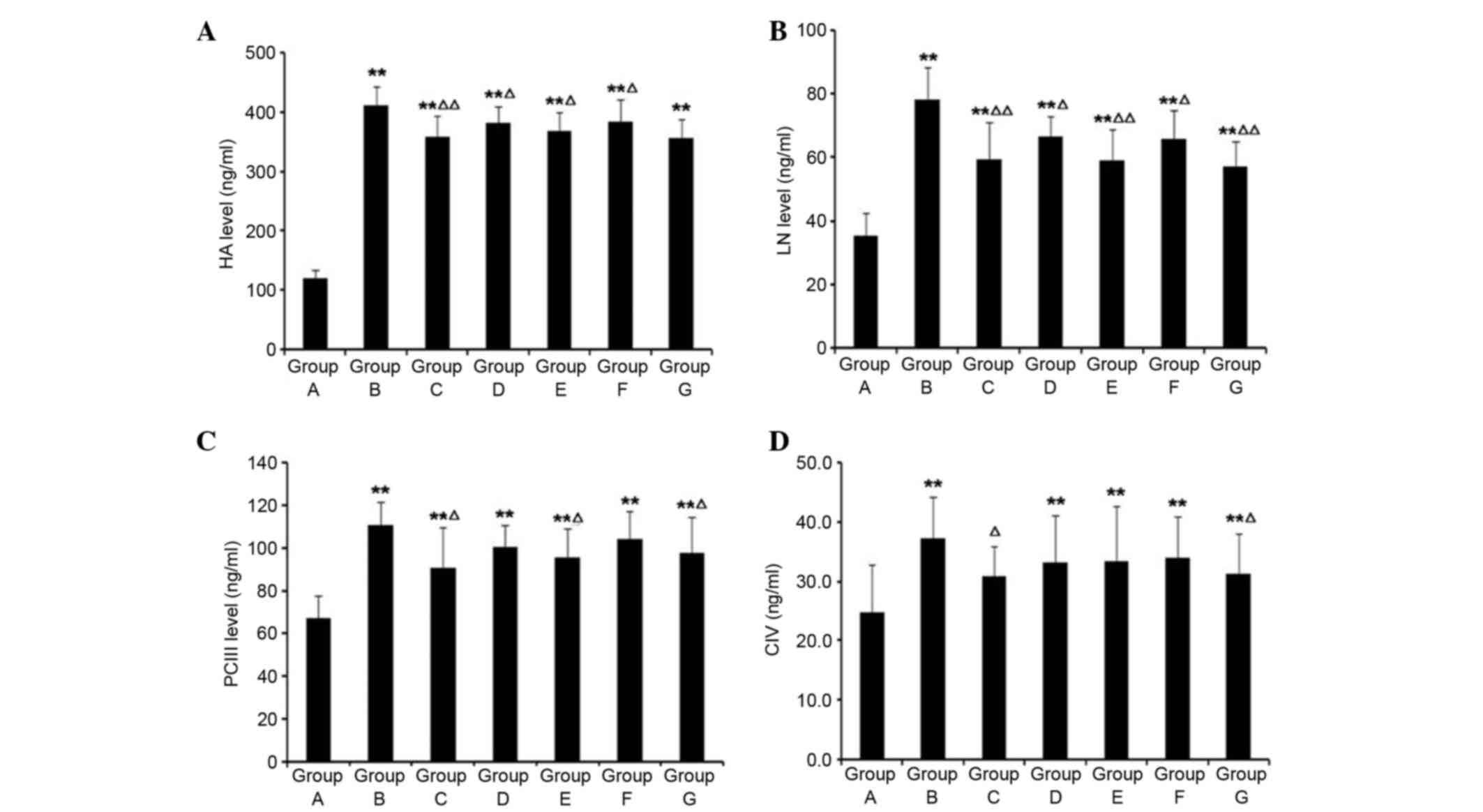
|
1
|
Zois C, Baltayiannis G, Karayiannis P and
Tsianos EV: Systematic review: Hepatic fibrosis-regression with
therapy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 28:1175–1187. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bralet MP: Image in pathology. Congenital
hepatic fibrosis. Ann Pathol. 24:2842004.(In French). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cogliati B, Da Silva TC, Aloia TP, Chaible
LM, Real-Lima MA, Sanches DS, Matsuzaki P, Hernandez-Blazquez FJ
and Dagli ML: Morphological and molecular pathology of
CCL4-induced hepatic fibrosis in connexin43-deficient
mice. Microsc Res Tech. 74:421–429. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang L, Cheng D, Wang H, Di L, Zhou X, Xu
T, Yang X and Liu Y: The hepatoprotective and antifibrotic effects
of Saururus chinensis against carbon tetrachloride induced hepatic
fibrosis in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 126:487–491. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu P, Hu YY, Liu C, Xu LM, Liu CH, Sun
KW, Hu DC, Yin YK, Zhou XQ, Wan MB, et al: Multicentre clinical
study On Fuzhenghuayu capsule against liver fibrosis due to chronic
hepatitis B. World J Gastroenterol. 11:2892–2899. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ru QJ, Tang ZM, Zhang ZE and Zhu Q:
Clinical observation on effect of xuefu zhuyu decoction in treating
patients with liver fibrosis caused by chronic hepatitis B. Chin J
Integr Trad Western Med. 24:983–985. 2004.
|
|
7
|
Lu C, Shen Q, Yang J, Wang B and Song C:
The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Safflower (Carthamus
tinctorius L.). Mitochondrial DNA A DNA Mapp Seq Anal.
27:3351–3353. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhao JF, Liu J, Guo Y, Liu Q, Dai Z, Ma SC
and Lin RC: Chemical constituents from safflower injection and
their bioactivity. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 39:3102–3106.
2014.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li Y, Chen Y, Wang L, Chen X, Liu X, Sun C
and Yan W: Research on technological process of two-pot
countercurrent extraction of hydroxysafflor yellow A. Zhongguo
Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 34:2743–2747. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bie XD, Han J and Dai HB: Effects of
hydroxysafflor yellow A on the experimental traumatic brain injury
in rats. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 12:239–247. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu SX, Zhang Y, Wang YF, Li XC, Xiang MX,
Bian C and Chen P: Upregulation of heme oxygenase-1 expression by
hydroxysafflor yellow A conferring protection from
anoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis in H9c2 cardiomyocytes. Int
J Cardiol. 160:95–101. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhu HJ, Wang LJ, Wang XQ, Pan H, Li NS,
Yang HB, Jin M, Zang BX and Gong FY: Hormone-sensitive lipase is
involved in the action of hydroxysafflor yellow A (HYSA) inhibiting
adipogenesis of 3T3-L1cells. Fitoterapia. 93:182–188. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang C, Huang Q, Wang C, Zhu X, Duan Y,
Yuan S and Bai X: Hydroxysafflor yellow A suppresses oleic
acid-induced acute lung injury via protein kinase A. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 272:895–904. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chobert MN, Couchie D, Fourcot A, Zafrani
ES, Laperche Y, Mavier P and Brouillet A: Liver precursor cells
increase hepatic fibrosis induced by chronic carbon tetrachloride
intoxication in rats. Lab Invest. 92:135–150. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang XH, Lu XF, Liu CY, Hu SJ, Kang XX and
Yang J: Diagnostics (8th). People's Health Publishing House.
3522015.(In Chinese).
|
|
16
|
Friedman SL: Hepatic fibrosis-overview.
Toxicology. 254:120–129. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Guo J and Friedman SL: Hepatic
fibmgenesis. Semin Liver Dis. 27:413–426. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Spengler U: Hepatic microcirculation: A
critical but neglected factor for the outcome of viral hepatitis. J
Hcpatol. 50:631–633. 2009.
|
|
19
|
Liu C, Wang G, Chen G, Mu Y, Zhang L, Hu
X, Sun M, Liu C and Liu P: Huangqi decoction inhibils apoptosis and
fibrosis, but promotes Kupffer cell activation in
dimefhyllnitrosamine-induced rat liver fibrosis. BMC Complement
Altern Med. 12:512012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang Q, Wen R, Lin Q, Wang N, Lu P and Zhu
X: Wogonoside shows antifibrotic effects in an experimental
regression model of hepatic fibrosis. Dig Dis Sci. 60:3329–3339.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang F, Li J, Zhu J, Wang D, Chen S and
Bai X: Hydroxysafflor yellow A inhibits angiogenesis of
hepatocellular carcinoma via blocking ERK/MAPK and NF-κB signaling
pathway in H22 tumor-bearing mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 754:105–114.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu C, Wang G, Chen G, Mu Y, Zhang L, Hu
X, Sun M, Liu C and Liu P: Huangqi decoction inhibits apoptosis and
fibrosis, but promotes Kupffer cell activation in
dimethylnitrosamine-induced rat liver fibrosis. BMC Complement
Altern Med. 12:512012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang XH, Wang DD and Zhu Y: Recent
research progress on hydroxysafflor yellow A. J Trad Chin Med Univ
Hunan. 33:102–106. 2013.(In Chinese).
|
|
24
|
Liu SY, Zhang YQ, Liu YL, Guo P and Zhou
CM: Intervention of chronic hepatitis B liver fibrosis patients in
different stages by syndrome typing and different activating blood
removing stasis methods: A clinical study. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie
He Za Zhi. 33:1457–1461. 2013.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shi XF, Xu M and Liu Q: The effects of
total saponins of panax notoginseng on I, III-type collage and TGF
in liver of cirrhosis rats. Zhongyao Yaoli Yu Linchuang. 17:7–8.
2001.
|
|
26
|
Wynn TA: Cellular and molecular mechanisms
on fibrosis. J Pathl. 214:199–210. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Friedman SL, Rockey DC and Bissell DM:
Hepatic fibrosis 2006: Report of the third SSALD single topic
conference. Hepatology. 45:242–249. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Krählenbühl S, Reichen J, Zimmermann A,
Gehr P and Stucki J: Mitochondrial structure and function in
CCl4-induced cirrhosis in the rat. Hepatology.
12:526–532. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Domitrović R, Rashed K, Cvijanović O,
Vladimir-Knežević S, Škoda M and Višnić A: Myricitrin exhibits
antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic activity in carbon
tetrachloride-intoxicated mice. Chem Biol Interact. 230:21–29.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang ZB, Huang ZM, Wang JJ, Wu JM, Chen
XR, Wu JS and Zhang QY: Inducing rat liver cirrhosis by adjusting
the dosage of CCl4 according to body weight changes.
Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 16:234–235. 2008.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gonzalez M, Sealls W, Jesch ED, Brosnan
MJ, Ladunga I, Ding X, Black PN and DiRusso CC: Defining a
relationship between dietary fatty acids and the cytochrome P450
system in a mouse model of fatty liver disease. Physiol Genomics.
43:121–135. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang CC, Lim LY, Deubner H, Tapia K, Lau
AW, Manansala J, Krows M, Shuhart MC and Kowdley KV: Factors
predictive of significant hepatic fibrosis in adults with chronic
hepatitis B and normal serum ALT. J Clin Gastroenterol. 42:820–826.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Park JH, Park CK, Kim ES, Park SY, Jo CM,
Tak WY, Kweon YO, Kim SK and Choi YW: The diagnostic value of serum
hyaluronic acid, 7S domain of type IV collagen and AST/ALT ratio as
markers of hepatic fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B and cirrhosis
patients. Taehan Kan Hakhoe Chi. 9:79–88. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li CH, Piao DM, Xu WX, Yin ZR, Jin JS and
Shen ZS: Morphological and serum hyaluronic acid, laminin and type
IV collagen changes in dimethylnitrosamine-induced hepatic fibrosis
of rats. World J Gastroenterol. 11:7620–7624. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Khan JA, Khan FA, Dilawar M, Ijaz A, Khan
NA and Mehmood T: Serum hyaluronic acid as a marker of hepatic
fibrosis. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 17:323–326. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Geramizadeh B, Janfeshan K and
Saberfiroozi M: Serum hyaluronic acid as a noninvasive marker of
hepatic fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B. Saudi J Gastroenterol.
14:174–177. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Huang Z, Li Q and Wang Z: Observation on
dynamic changes of serum procollagen III, hyaluronic acid and
laminin in rats with hepatic fibrosis treated with Hujin pill.
Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 20:447–449. 2000.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tsutsumi M, Takase S, Urashima S, Ueshima
Y, Kawahara H and Takada A: Serum markers for hepatic fibrosis in
alcoholic liver disease: Which is the best marker, type III
procollagen, type IV collagen, laminin, tissue inhibitor of
metalloproteinase, or prolyl hydroxylase? Alcohol Clin Exp Res.
20:1512–1517. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Iushchuk ND, Znoĭko OO, Safiullina NKh,
Dudina KR, Kelli EI, Klimova EA, Kashirin VI, Braginskiĭ DM,
Kushlinskiĭ NE, Liubimova NV, et al: Diagnostic significance of
type IV collagen and hyaluronic acid in the serum of patients with
chronic hepatitis C for staging hepatic fibrosis. Ter Arkh.
77:50–55. 2005.(In Russian).
|
|
40
|
Toyoki Y, Sasaki M, Narumi S, Yoshihara S,
Morita T and Konn M: Semiquantitative evaluation of hepatic
fibrosis by measuring tissue hydroxyproline.
Hepatogastroenterology. 45:2261–2264. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu J, Tan H, Sun Y, Zhou S, Cao J and
Wang F: The preventive effects of heparin-superoxide dismutase on
carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver failure and hepatic
fibrosis in mice. Mol Cell Biochem. 327:219–228. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Huang Q, Li Y, Zhang S, Huang R, Zheng L,
Wei L, He M, Liao M, Li L, Zhuo L and Lin X: Effect and mechanism
of methyl helicterate isolated from Helicteres angustifolia
(Sterculiaceae) on hepatic fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride
in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 143:889–895. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kanno K, Tazuma S and Chayama K:
AT1A-deficient mice show less severe progression of liver fibrosis
induced by CCl(4). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 308:177–183. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Smyth R, Munday MR, York MJ, Clarke CJ,
Dare T and Turton JA: Comprehensive characterization of serum
clinical chemistry parameters and the identification of urinary
superoxide dismutase in a carbon tetrachloride-induced model of
hepatic fibrosis in the female Hanover Wistar rat. Int J Exp
Pathol. 88:361–376. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yu J, Wang Y, Qian H, Zhao Y, Liu B and Fu
C: Polyprenols from Taxus chinensis var. mairei prevent the
development of CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in rats. J
Ethnopharmacol. 142:151–160. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Liu J, Tan H, Sun Y, Zhou S, Cao J and
Wang F: The preventive effects of heparin-superoxide dismutase on
carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver failure and hepatic
fibrosis in mice. Mol Cell Biochem. 327:219–228. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ljubuncic P, Abu-Salach O and Bomzon A:
Ursodeoxycholic acid and superoxide anion. World J Gastroenterol.
11:4875–4878. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|