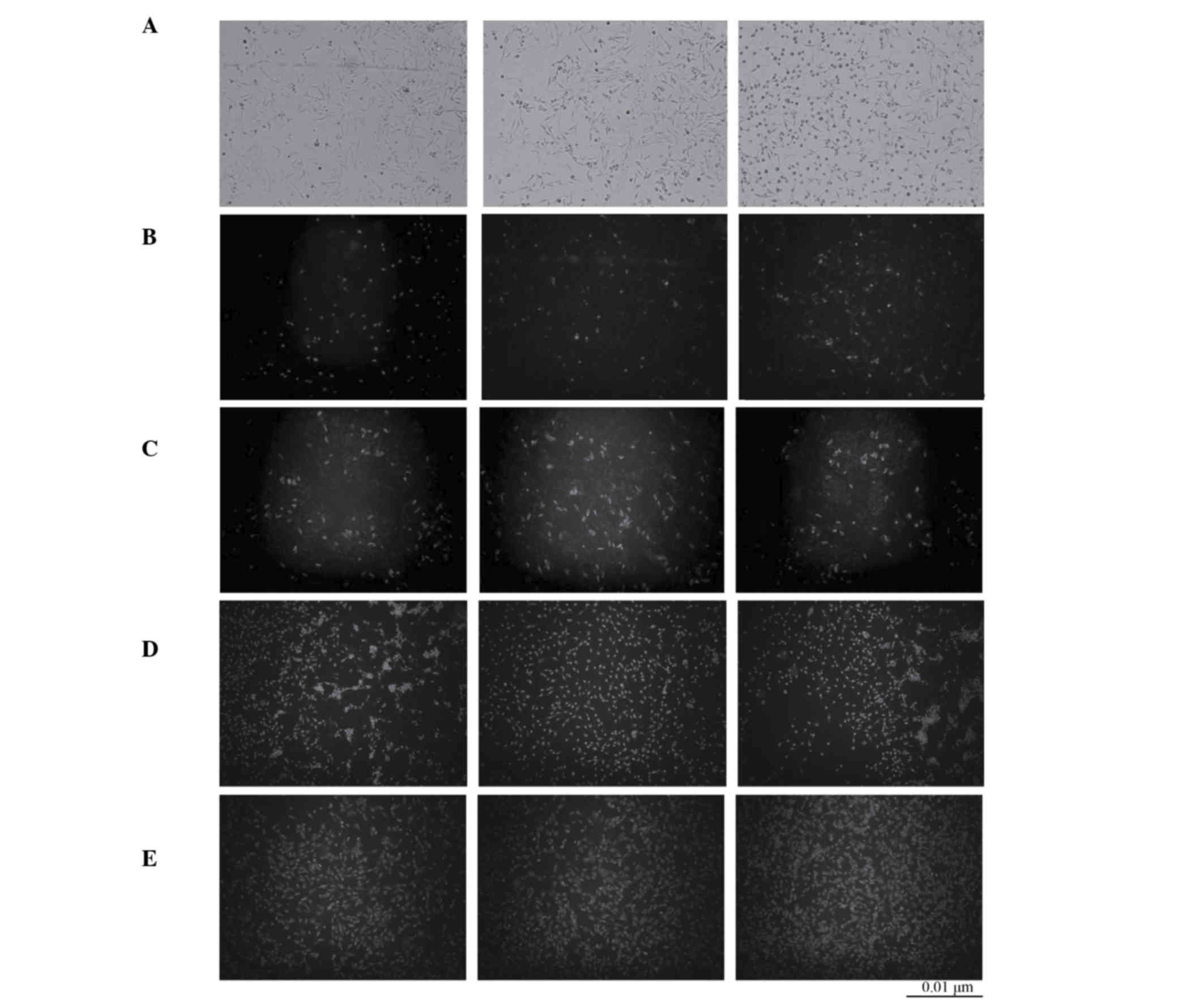
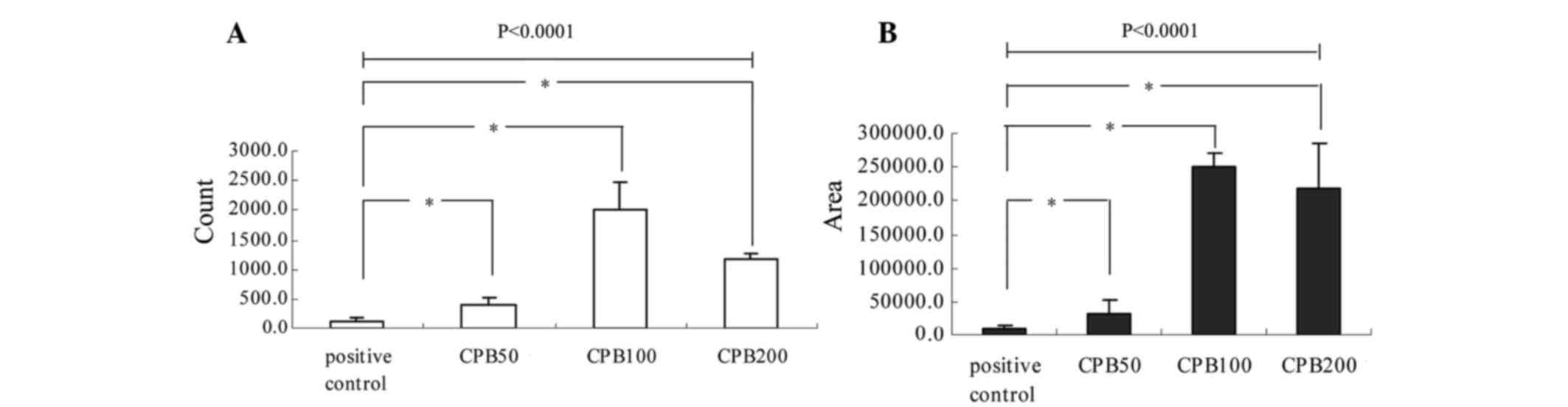
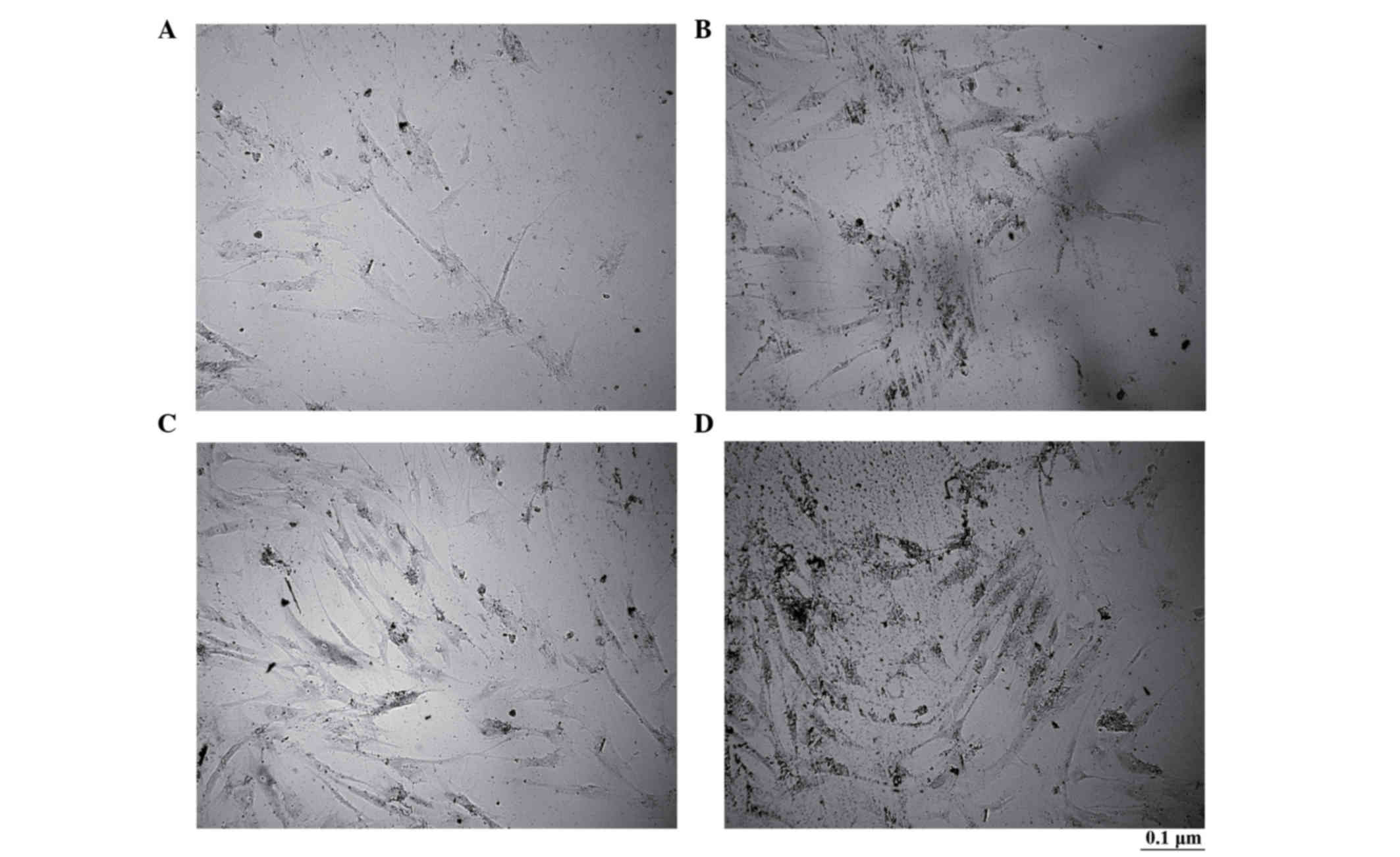
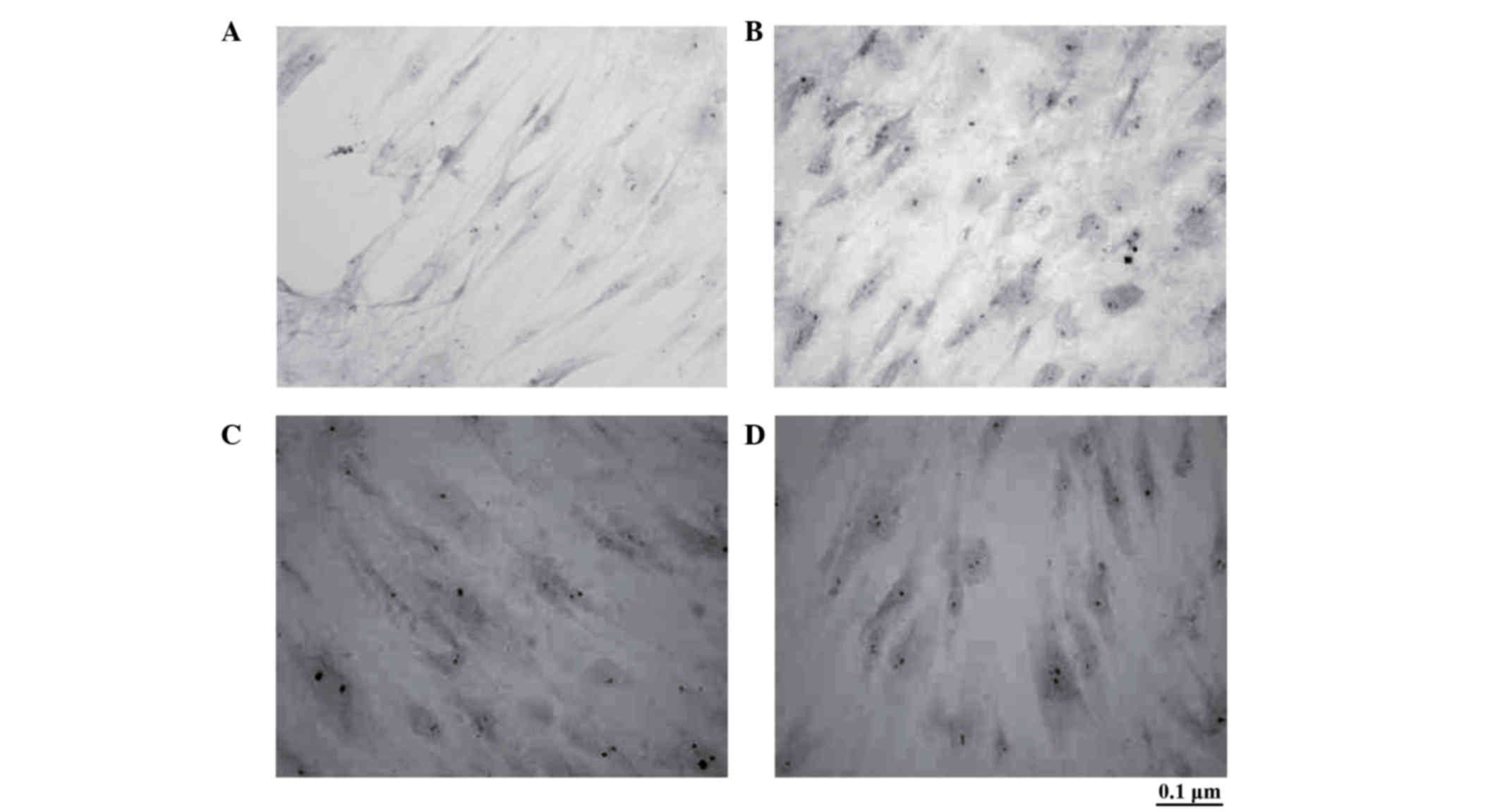
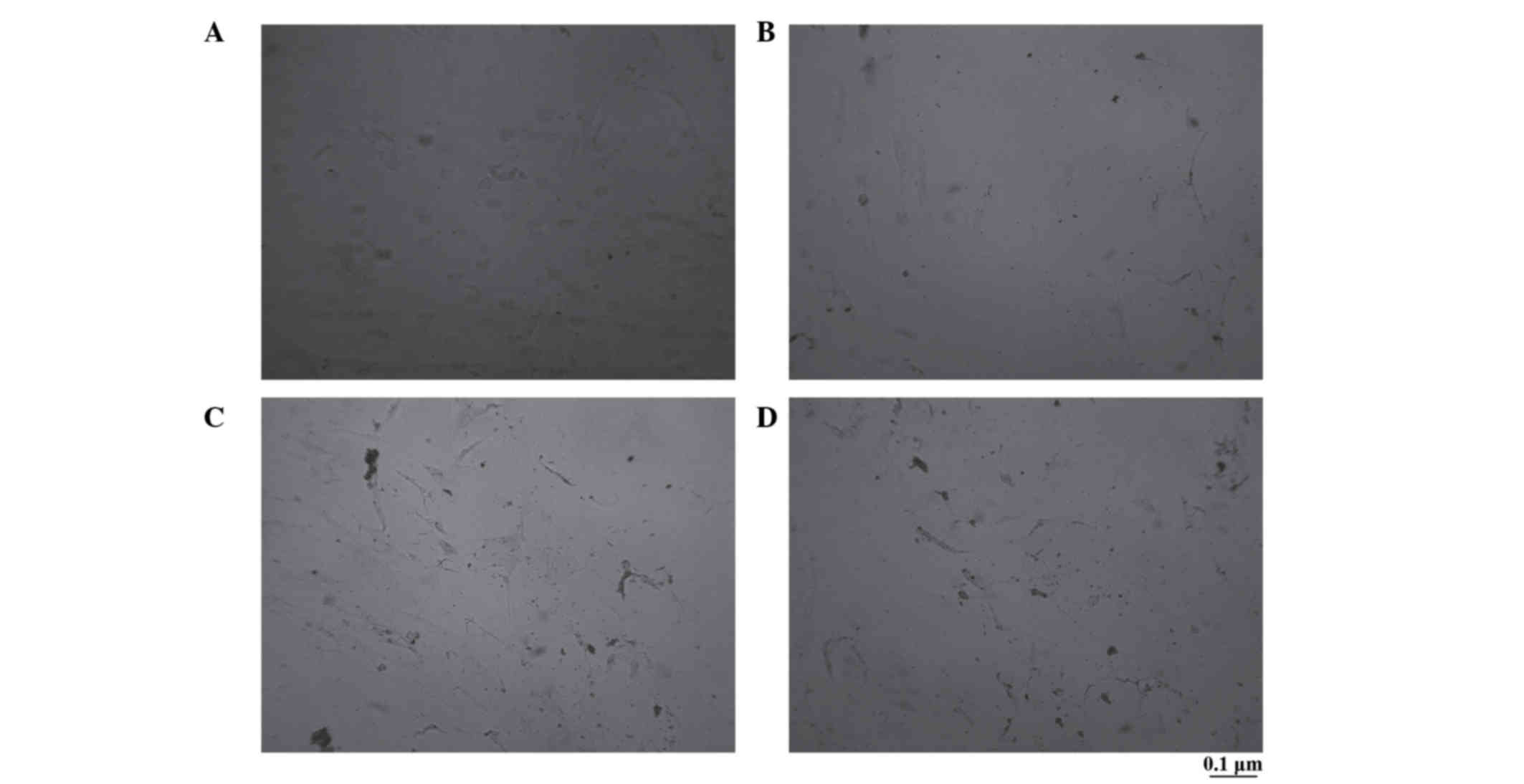
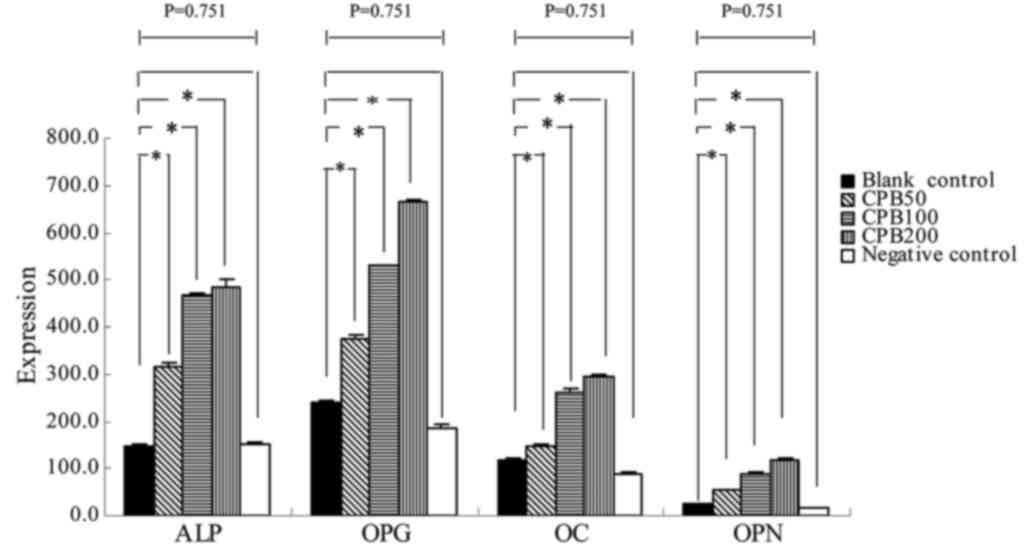
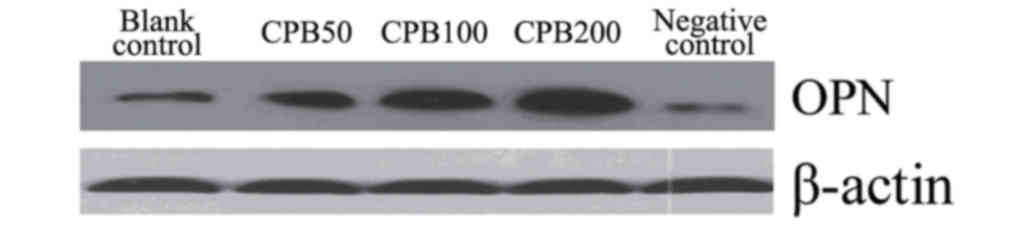
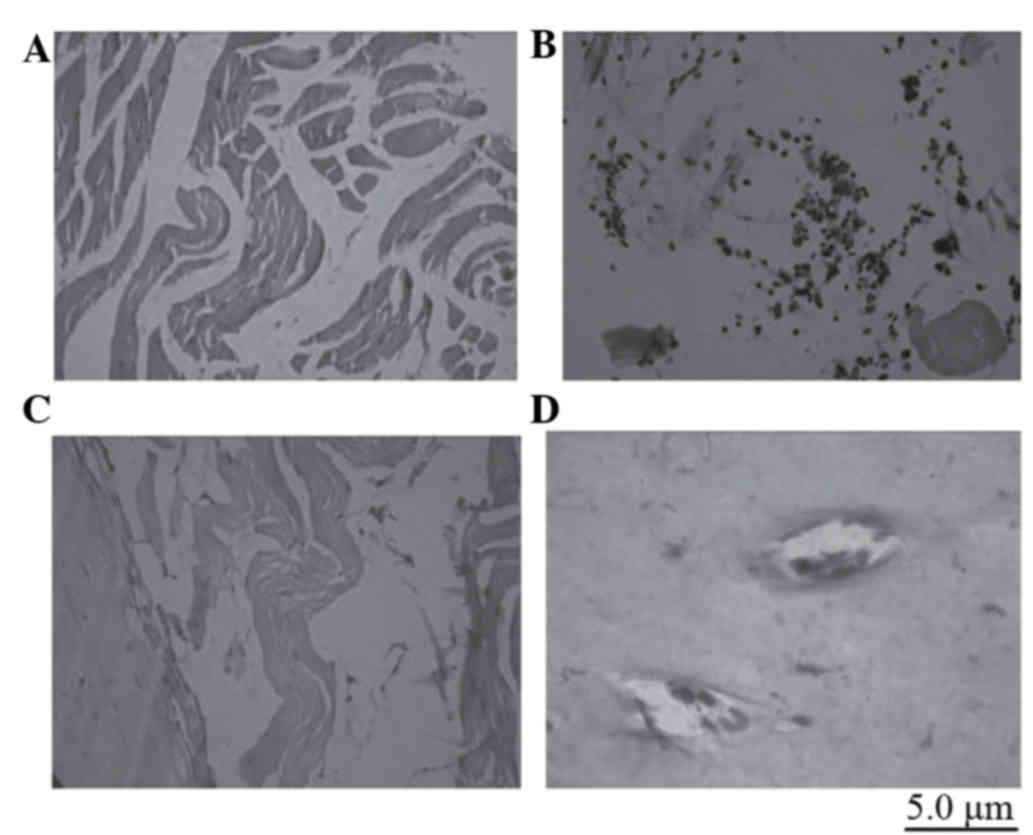
|
1
|
Amini AR, Laurencin CT and Nukavarapu SP:
Differential analysis of peripheral blood- and bone marrow-derived
endothelial progenitor cells for enhanced vascularization in bone
tissue engineering. J Orthop Res. 30:1507–1515. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Takekawa M, Matsuda M and Ohotubo S:
Effect of irradiation on autogenous bone transplantation in rat
parietal bone. Histol Histopathol. 15:7–19. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Erlwein O and McClure M: Gene delivery the
key to gene therapy: The case for foamy viruses. Ther Deliv.
2:681–684. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Moawad HM and Jain H: Fabrication of
nano-macroporous glass-ceramic bioscaffold with a water soluble
pore former. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 23:307–314. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fazil M, Md S, Haque S, Kumar M, Baboota
S, Sahni JK and Ali J: Development and evaluation of rivastigmine
loaded chitosan nanoparticles for brain targeting. Eur J Pharm Sci.
47:6–15. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yadav A, Lomash V, Samim M and Flora SJ:
Curcumin encapsulated in chitosan nanoparticles: A novel strategy
for the treatment of arsenic toxicity. Chem Biol Interact.
199:49–61. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Al Faqeh H, Nor Hamdan BM, Chen HC,
Aminuddin BS and Ruszymah BH: The potential of intra-articular
injection of chondrogenic-induced bone marrow stem cells to retard
the progression of osteoarthritis in a sheep model. Exp Gerontol.
47:458–464. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zou D, Han W, You S, Ye D, Wang L, Wang S,
Zhao J, Zhang W, Jiang X, Zhang X and Huang Y: In vitro
study of enhanced osteogenesis induced by HIF-1α-transduced bone
marrow stem cells. Cell Prolif. 44:234–243. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bhakta G, Rai B, Lim ZX, Hui JH, Stein GS,
van Wijnen AJ, Nurcombe V, Prestwich GD and Cool SM: Hyaluronic
acid-based hydrogels functionalized with heparin that support
controlled release of bioactive BMP-2. Biomaterials. 33:6113–6122.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hunziker EB, Enggist L, Küffer A, Buser D
and Liu Y: Osseointegration: The slow delivery of BMP-2 enhances
osteoinductivity. Bone. 51:98–106. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Santos JL, Pandita D, Rodrigues J, Pêgo
AP, Granja PL and Tomás H: Non-viral gene delivery to mesenchymal
stem cells: Methods, strategies and application in bone tissue
engineering and regeneration. Curr Gene Ther. 11:46–57. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fernández MS, Arias JI, Martínez MJ, Saenz
L, Neira-Carrillo A, Yazdani-Pedram M and Arias JL: Evaluation of a
multilayered chitosan-hydroxy-apatite porous composite enriched
with fibronectin or an in vitro-generated bone-like extracellular
matrix on proliferation and diferentiation of osteoblasts. J Tissue
Eng Regen Med. 6:497–504. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Peschel D, Zhang K, Fischer S and Groth T:
Modulation of osteogenic activity of BMP-2 by cellulose and
chitosan derivatives. Acta Biomater. 8:183–193. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee D and Mohapatra SS: Chitosan
nanoparticle-mediated gene transfer. Methods Mol Biol. 433:127–140.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu MT, Zhang QH, Zhai JJ and Liang X:
Construction and analysis of one kind of chitosan-coated BMP-2
nanoparticles as genetic carrier. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue
Ban. 42:485–489. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hou J, Wang J, Cao L, Qian X, Xing W, Lu J
and Liu C: Segmental bone regeneration using rhBMP-2-loaded
collagen/chitosan microspheres composite scaffold in a rabbit
model. Biomed Mater. 7:0350022012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Canter HI, Vargel I, Korkusuz P, Oner F,
Gungorduk DB, Cil B, Karabulut E, Sargon MF and Erk Y: Effect of
use of slow release of bone morphogenetic protein-2 and
transforming growth factor-Beta-2 in a chitosan gel matrix on
cranial bone graft survival in experimental cranial critical size
defect model. Ann Plast Surg. 64:342–350. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yilgor P, Tuzlakoglu K, Reis RL, Hasirci N
and Hasirci V: Incorporation of a sequential BMP-2/BMP-7 delivery
system into chitosan-based scaffolds for bone tissue engineering.
Biomaterials. 30:3551–3559. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kim S, Tsao H, Kang Y, Young DA, Sen M,
Wenke JC and Yang Y: In vitro evaluation of an injectable
chitosan gel for sustained local delivery of BMP-2 for osteoblastic
differentiation. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 99:380–390.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhao L, Tang M, Weir MD, Detamore MS and
Xu HH: Osteogenic media and rhBMP-2-induced differentiation of
umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells encapsulated in alginate
microbeads and integrated in an injectable calcium
phosphate-chitosan fibrous scaffold. Tissue Eng Part A. 17:969–979.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shi Z, Neoh KG, Kang ET, Poh CK and Wang
W: Surface functionalization of titanium with carboxymethyl
chitosan and immobilized bone morphogenetic protein-2 for enhanced
osseointegration. Biomacromolecules. 10:1603–1611. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Luca L, Rougemont AL, Walpoth BH, Gurny R
and Jordan O: The effects of carrier nature and pH on
rhBMP-2-induced ectopic bone formation. J Control Release.
147:38–44. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mishra S, Rajyalakshmi A and
Balasubramanian K: Compositional dependence of hematopoietic stem
cells expansion on bioceramic composite scaffolds for bone tissue
engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 100:2483–2491. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Do TN, Lee WH, Loo CY, Zavgorodniy AV and
Rohanizadeh R: Hydroxyapatite nanoparticles as vectors for gene
delivery. Ther Deliv. 3:623–632. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee GS, Park JH, Shin US and Kim HW:
Direct deposited porous scaffolds of calcium phosphate cement with
alginate for drug delivery and bone tissue engineering. Acta
Biomater. 7:3178–3186. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen J, Chen H, Li P, Diao H, Zhu S, Dong
L, Wang R, Guo T, Zhao J and Zhang J: Simultaneous regeneration of
articular cartilage and subchondral bone in vivo using MSCs induced
by a spatially controlled gene delivery system in bilayered
integrated scaffolds. Biomaterials. 32:4793–4805. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Park DJ, Choi BH, Zhu SJ, Huh JY, Kim BY
and Lee SH: Injectable bone using chitosan-alginate gel/mesenchymal
stem cells/BMP-2 composites. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 33:50–54.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|