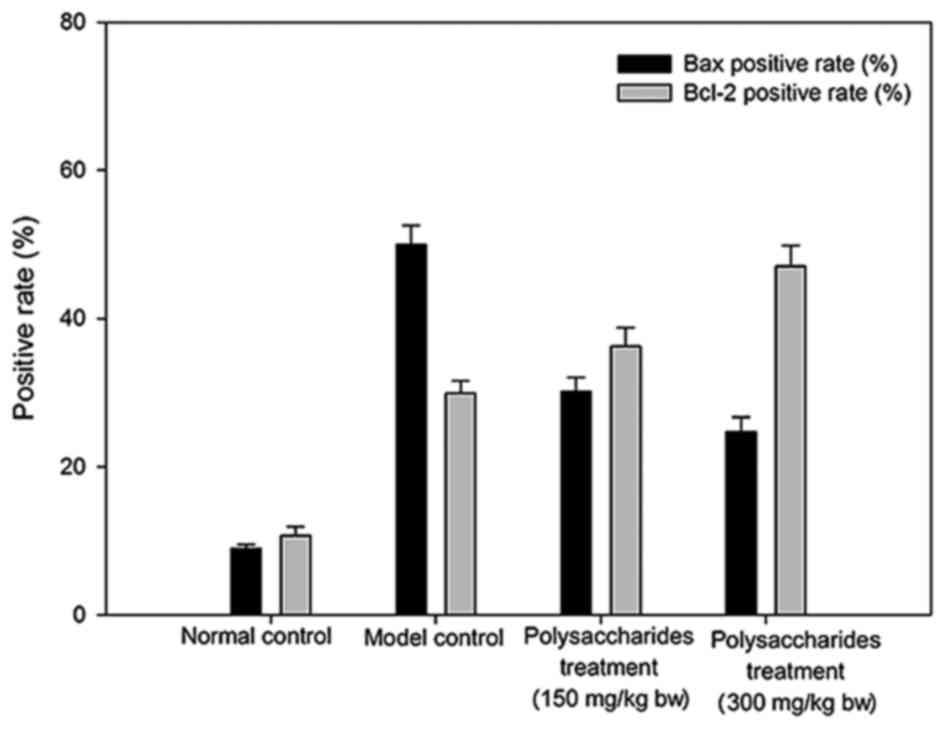
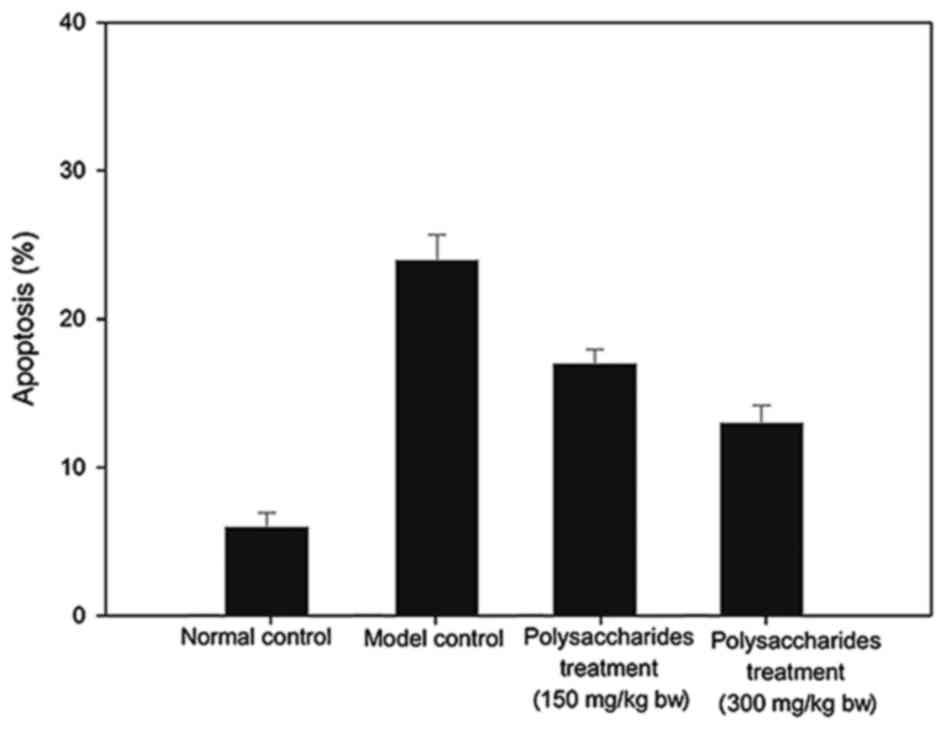
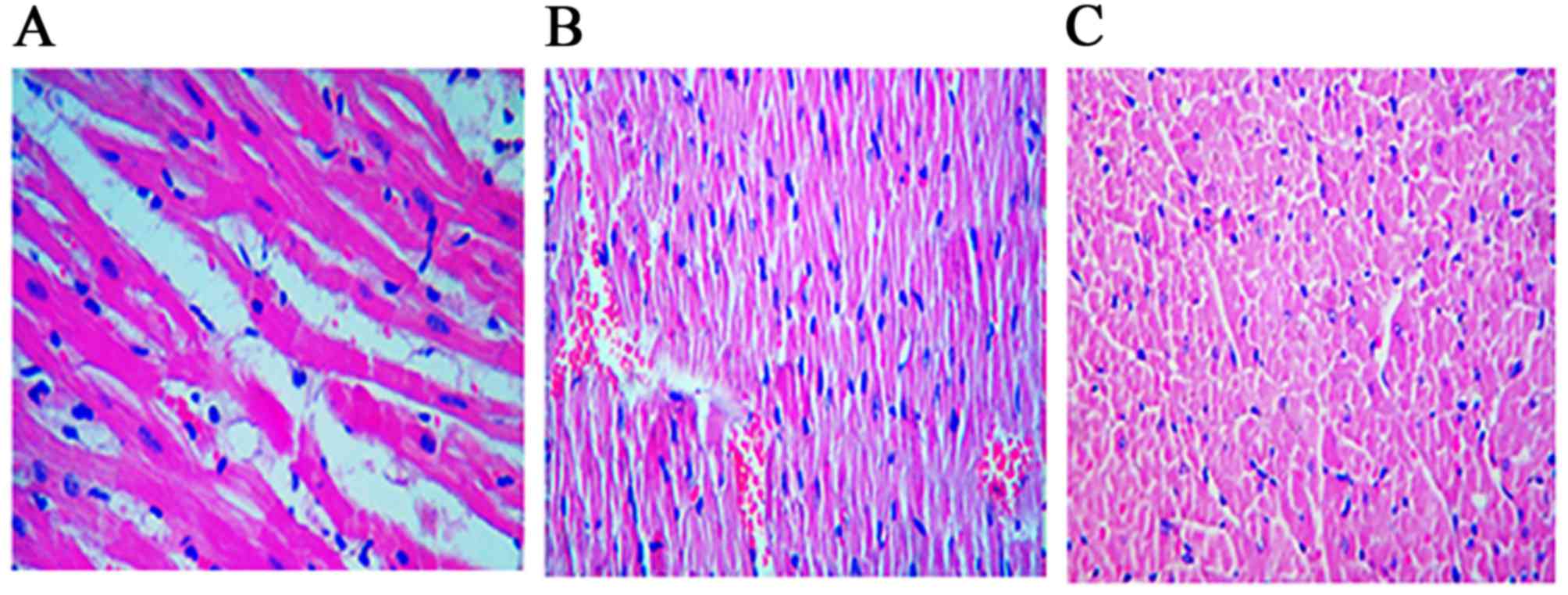
|
1
|
Keeley EC, Boura JA and Grines CL: Primary
angioplasty versus intravenous thrombolytic therapy for acute
myocardial infarction: A quantitative review of 23 randomised
trials. Lancet. 361:13–20. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zweier JL: Measurement of
superoxide-derived free radicals in the reperfused heart. Evidence
for a free radical mechanism of reperfusion injury. J Biol Chem.
263:1353–1357. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mocan A, Vlase L, Vodnar DC, Gheldiu AM,
Oprean R and Crişan G: Antioxidant, antimicrobial effects and
phenolic profile of Lycium barbarum L. Flowers. Molecules.
20:15060–15071. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gündüz E, Dursun R, Zengin Y, İçer M,
Durgun HM, Kanıcı A, Kaplan İ, Alabalık U, Gürbüz H and Güloğlu C:
Lycium barbarum extract provides effective protection against
paracetamol-induced acute hepatotoxicity in rats. Int J Clin Exp
Med. 8:7898–7905. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tang HL, Chen C, Wang SK and Sun GJ:
Biochemical analysis and hypoglycemic activity of a polysaccharide
isolated from the fruit of Lycium barbarum L. Int J Biol Macromol.
77:235–242. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gao K, Liu M, Cao J, Yao M, Lu Y, Li J,
Zhu X, Yang Z and Wen A: Protective effects of Lycium barbarum
polysaccharide on 6-OHDA-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells through
the ROS-NO pathway. Molecules. 20:293–308. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cheng J, Zhou ZW, Sheng HP, He LJ, Fan XW,
He ZX, Sun T, Zhang X, Zhao RJ, Gu L, et al: An evidence-based
update on the pharmacological activities and possible molecular
targets of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides. Drug Des Devel Ther.
9:33–78. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Huang L, Lin Y, Tian G and Ji G:
Isolation, purification and physico-chemical properties of
immunoactive constituents from the fruit of Lycium barbarum L. Yao
Xue Xue Bao. 33:512–516. 1998.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gan L, Zhang SH, Liu Q and Xu HB: A
polysaccharide-protein complex from Lycium barbarum upregulates
cytokine expression in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells.
Eur J Pharmacol. 471:217–222. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gan L, Hua ZS, Liang YX and Xu Bi H:
Immunomodulation and antitumor activity by a polysaccharide-protein
complex from Lycium barbarum. Int Immunopharmacol. 4:563–569. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Niu AJ, Wu JM, Yu DH and Wang R:
Protective effect of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides on oxidative
damage in skeletal muscle of exhaustive exercise rats. Int J Biol
Macromol. 42:447–449. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu W, Xu J, Zhu R, Zhu Y, Zhao Y, Chen P,
Pan C, Yao W and Gao X: Fingerprinting profile of polysaccharides
from Lycium barbarum using multiplex approaches and chemometrics.
Int J Biol Macromol. 78:230–237. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ha KT, Yoon SJ, Choi DY, Kim DW, Kim JK
and Kim CH: Protective effect of Lycium chinense fruit on carbon
tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity. J Ethnopharmacol. 96:529–535.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Luo Q, Cai Y, Yan J, Sun M and Corke H:
Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effects and antioxidant activity of
fruit extracts from Lycium barbarum. Life Sci. 76:137–149. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gong H, Shen P, Jin L, Xing C and Tang F:
Therapeutic effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide (LBP) on
irradiation or chemotherapy-induced myelosuppressive mice. Cancer
Biother Radiopharm. 20:155–162. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yu X, Xu Z, Mi M, Xu H, Zhu J, Wei N, Chen
K, Zhang Q, Zeng K, Wang J, et al: Dietary taurine supplementation
ameliorates diabetic retinopathy via anti-excitotoxicity of
glutamate in streptozotocin-induced Sprague-Dawley rats. Neurochem
Res. 33:500–507. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Takatani T, Takahashi K, Uozumi Y, Matsuda
T, Ito T, Schaffer SW, Fujio Y and Azuma J: Taurine prevents the
ischemia-induced apoptosis in cultured neonatal rat cardiomyocytes
through Akt/caspase-9 pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
316:484–489. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fu DT and O'Neill RA: Monosaccharide
composition analysis of oligosaccharides and glycoproteins by
high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 227:377–384.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Parikh A and Madamwar D: Partial
characterization of extracellular polysaccharides from
cyanobacteria. Bioresour Technol. 97:1822–1827. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ver A, Csermely P, Bányász T, Kovács T and
Somogyi J: Alterations in the properties and isoform ratios of
brain Na+/K(+)-ATPase in streptozotocin diabetic rats. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1237:143–150. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Grosman N: Similar effects of ether
phospholipids, PAF and lyso-PAF on the Ca(2+)-ATPase activity of
rat brain synaptosomes and leukocyte membranes. Int
Immunopharmacol. 1:1321–1329. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jordan RC, Catzavelos GC, Barrett AW and
Speight PM: Differential expression of bcl-2 and bax in squamous
cell carcinomas of the oral cavity. Eur J Cancer B Oral Oncol.
32B:394–400. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Buerke M, Murohara T, Skurk C, Nuss C,
Tomaselli K and Lefer AM: Cardioprotective effect of insulin-like
growth factor I in myocardial ischemia followed by reperfusion.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 92:8031–8035. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Miller S, Schick F, Scheule AM, Vogel U,
Hiller R, Strotmann C, Naegele T, Hahn U and Claussen CD:
Conventional high resolution versus fast T(2)-weighted MR imaging
of the heart: Assessment of reperfusion induced myocardial injury
in an animal model. Magn Reson Imaging. 18:1069–1077. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mocan A, Vlase L, Vodnar DC, Bischin C,
Hanganu D, Gheldiu AM, Oprean R, Silaghi-Dumitrescu R and Crișan G:
Polyphenolic content, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of
Lycium barbarum L. and Lycium chinense Mill. leaves. Molecules.
19:10056–10073. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Potterat O: Goji (Lycium barbarum and L.
chinense): Phytochemistry, pharmacology and safety in the
perspective of traditional uses and recent popularity. Planta Med.
76:7–193. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jin M, Huang Q, Zhao K and Shang P:
Biological activities and potential health benefit effects of
polysaccharides isolated from Lycium barbarum L. Int J Biol
Macromol. 54:16–23. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li XM, Ma YL and Liu XJ: Effect of the
Lycium barbarum polysaccharides on age-related oxidative stress in
aged mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 111:504–511. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhao H, Alexeev A, Chang E, Greenburg G
and Bojanowski K: Lycium barbarum glycoconjugates: Effect on human
skin and cultured dermal fibroblasts. Phytomedicine. 12:131–137.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cheng CY, Chung WY, Szeto YT and Benzie
IF: Fasting plasma zeaxanthin response to Fructus barbarum L.
(wolfberry; Kei Tze) in a food-based human supplementation trial.
Br J Nutr. 93:123–130. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xie H and Zhang S: Determination of
taurine in Lycium barbarum L. by high performance liquid
chromatography with OPA-urea pre-column derivatization. Se Pu.
15:54–56. 1997.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gaull GE: Taurine as a conditionally
essential nutrient in man. J Am Coll Nutr. 5:121–125. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sharikabad MN, Aronsen JM, Haugen E,
Pedersen J, Møller AS, Mørk HK, Aass HC, Sejersted OM, Sjaastad I
and Brørs O: Cardiomyocytes from postinfarction failing rat hearts
have improved ischemia tolerance. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
296:H787–H795. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Takayama E, Guo LL, Digerness SB and Pike
MM: Early reperfusion levels of Na(+) and Ca(2+) are strongly
associated with postischemic functional recovery but are
disassociated from K(ATP) channel-induced cardioprotection. J Mol
Cell Cardiol. 37:483–496. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tani M and Neely JR: Role of intracellular
Na+ in Ca2+ overload and depressed recovery of ventricular function
of reperfused ischemic rat hearts. Possible involvement of H+-Na+
and Na+-Ca2+ exchange. Circ Res. 65:1045–1056. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hasenfuss G and Pieske B: Calcium cycling
in congestive heart failure. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 34:951–969. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sjaastad I, Bentzen JG, Semb SO, Ilebekk A
and Sejersted OM: Reduced calcium tolerance in rat cardiomyocytes
after myocardial infarction. Acta Physiol Scand. 175:261–269. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Pieske B, Kretschmann B, Meyer M,
Holubarsch C, Weirich J, Posival H, Minami K, Just H and Hasenfuss
G: Alterations in intracellular calcium handling associated with
the inverse force-frequency relation in human dilated
cardiomyopathy. Circulation. 92:1169–1178. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Pieske B and Houser SR: [Na+]i handling in
the failing human heart. Cardiovasc Res. 57:874–886. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kawasaki H and Kawashima S: Regulation of
the calpain-calpastatin system by membranes (review). Mol Membr
Biol. 13:217–224. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Van der Vusse GJ, Reneman RS and van
Bilsen M: Accumulation of arachidonic acid in ischemic/reperfused
cardiac tissue: Possible causes and consequences. Prostaglandins
Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 57:85–93. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Miyamae M, Camacho SA, Weiner MW and
Figueredo VM: Attenuation of postischemic reperfusion injury is
related to prevention of [Ca2+]m overload in rat hearts. Am J
Physiol. 271:H2145–H2153. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|