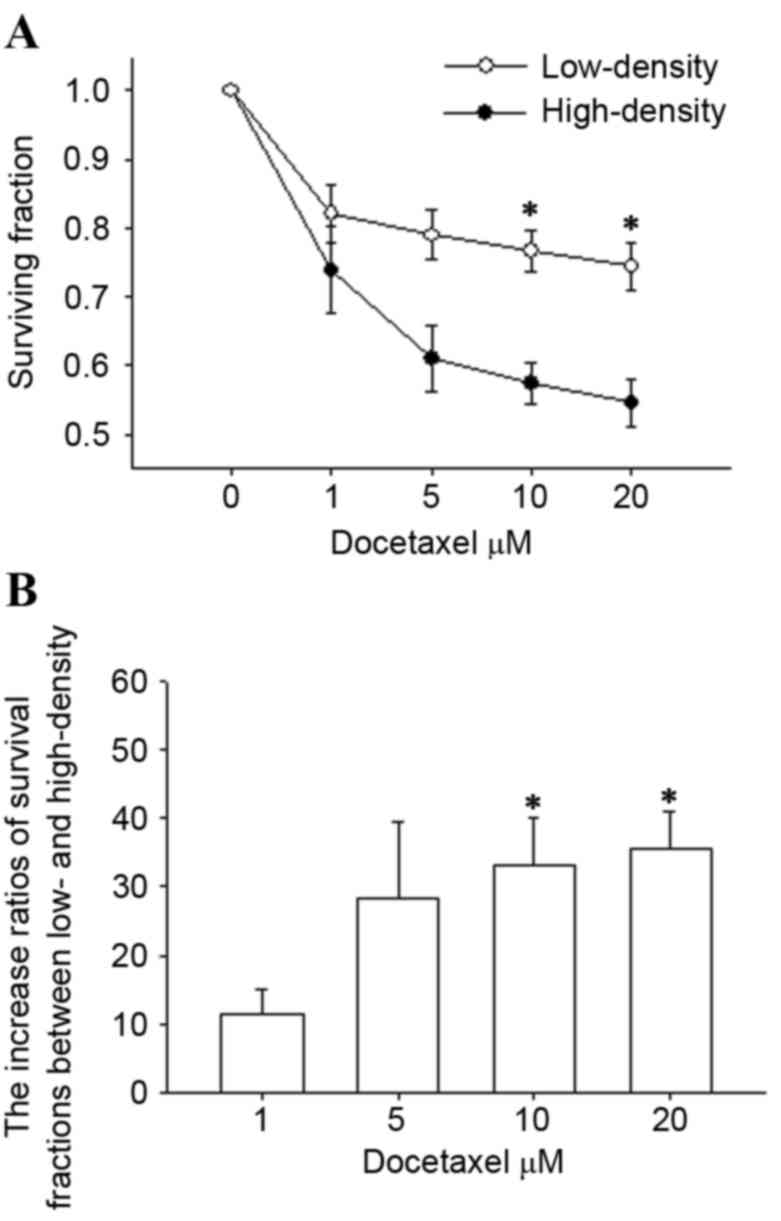
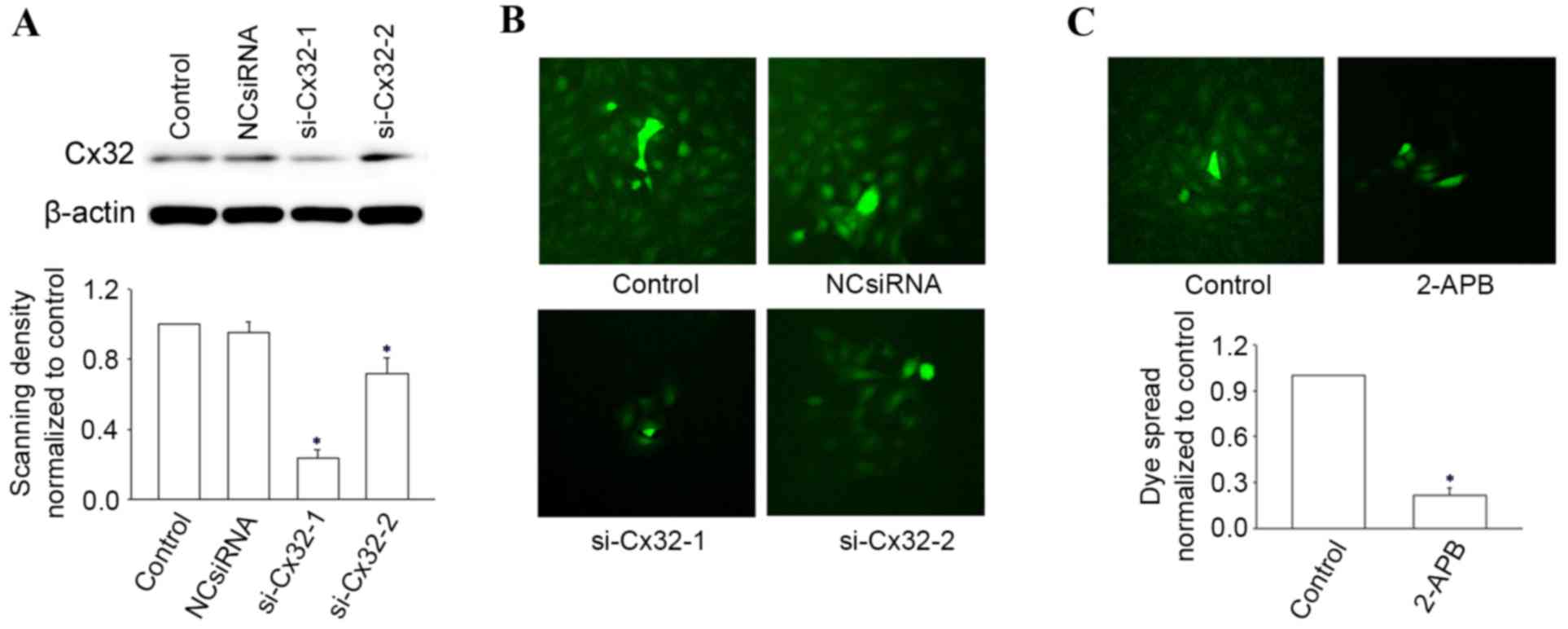
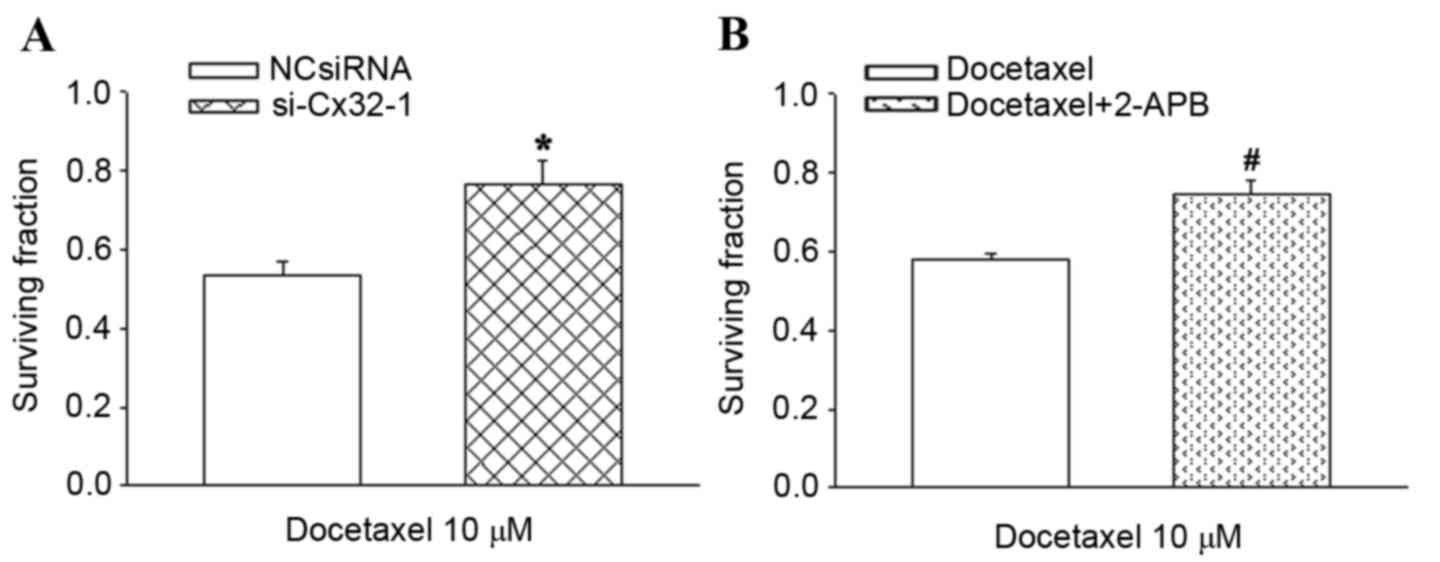
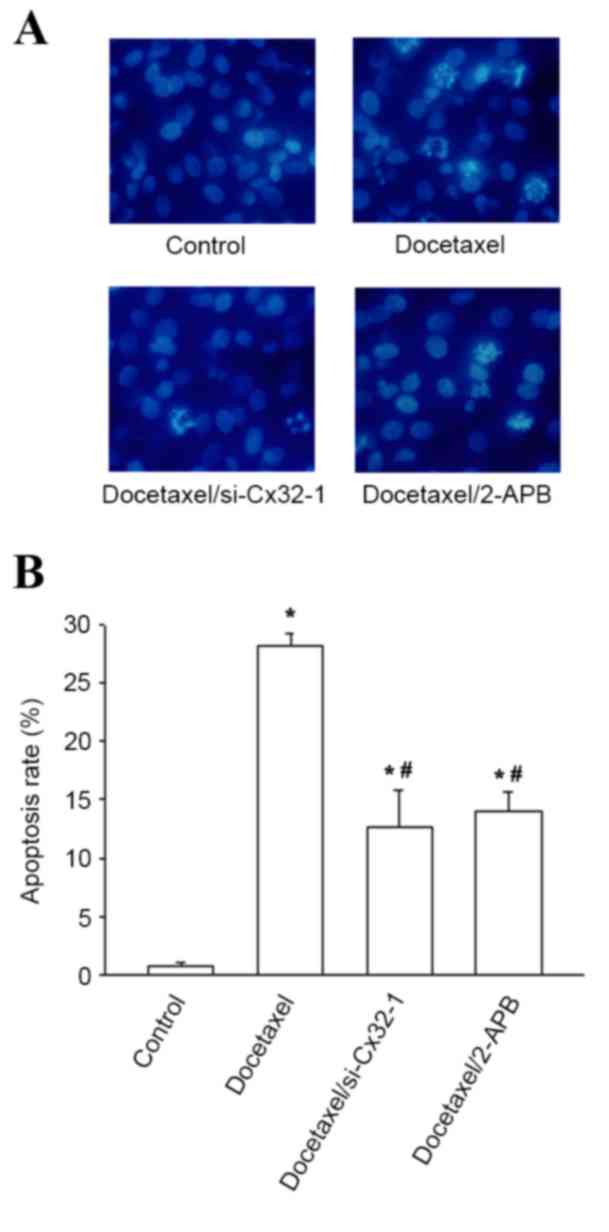
|
1
|
Corsini A and Bortolini M: Drug-induced
liver injury: The role of drug metabolism and transport. J Clin
Pharmacol. 53:463–474. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Amacher DE: The primary role of hepatic
metabolism in idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury. Expert Opin
Drug Metab Toxicol. 8:335–347. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Claesson A and Spjuth O: On mechanisms of
reactive metabolite formation from drugs. Mini Rev Med Chem.
13:720–729. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Daly AK: Drug-induced liver injury: Past,
present and future. Pharmacogenomics. 11:607–611. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hussaini SH and Farrington EA:
Idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury: An overview. Expert Opin
Drug Saf. 6:673–684. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kaplowitz N: Idiosyncratic drug
hepatotoxicity. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 4:489–499. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Senior JR: Evolution of the food and drug
administration approach to liver safety assessment for new drugs:
Current status and challenges. Drug Saf. 37:(Suppl 1). S9–S17.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Regev A: Drug-induced liver injury and
drug development: Industry perspective. Semin Liver Dis.
34:227–239. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Meier Y, Cavallaro M, Roos M, Pauli-Magnus
C, Folkers G, Meier PJ and Fattinger K: Incidence of drug-induced
liver injury in medical inpatients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol.
61:135–143. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Thatishetty AV, Agresti N and O'Brien CB:
Chemotherapy-induced hepatotoxicity. Clin Liver Dis. 17:671–686,
ix-x. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bahirwani R and Reddy KR: Drug-induced
liver injury due to cancer chemotherapeutic agents. Semin Liver
Dis. 34:162–171. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim HS, Ryu MH, Zang DY, Ryoo BY, Yang DH,
Cho JW, Lim MS, Kim MJ, Han B, Choi DR, et al: Phase II study of
docetaxel, oxaliplatin, and S-1 therapy in patients with metastatic
gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 19:579–585. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gelmon K: The taxoids: Paclitaxel and
docetaxel. Lancet. 344:1267–1272. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pazdur R, Kudelka AP, Kavanagh JJ, Cohen
PR and Raber MN: The taxoids: Paclitaxel (Taxol) and docetaxel
(Taxotere). Cancer Treat Rev. 19:351–386. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dancey J, Shepherd FA, Gralla RJ and Kim
YS: Quality of life assessment of second-line docetaxel versus best
supportive care in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer
previously treated with platinum-based chemotherapy: Results of a
prospective, randomized phase III trial. Lung Cancer. 43:183–194.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang Z, Liang X, Yu J, Zheng X, Zhu Y, Yan
Y, Dong N, Di L, Song G, Zhou X, et al: Non-genetic risk factors
and predicting efficacy for docetaxel-drug-induced liver injury
among metastatic breast cancer patients. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
27:1348–1352. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liang X, Zhang J, Zhu Y, Lu Y, Zhou X,
Wang Z, Yu J, Yan Y, Di L, Che L, et al: Specific genetic
polymorphisms of IL10-592 AA and IL10-819 TT genotypes lead to the
key role for inducing docetaxel-induced liver injury in breast
cancer patients. Clin Transl Oncol. 15:331–334. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Maeda S and Tsukihara T: Structure of the
gap junction channel and its implications for its biological
functions. Cell Mol Life Sci. 68:1115–1129. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Harris AL: Connexin channel permeability
to cytoplasmic molecules. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 94:120–143. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Patel SJ, Milwid JM, King KR, Bohr S,
Iracheta-Vellve A, Li M, Vitalo A, Parekkadan B, Jindal R and
Yarmush ML: Gap junction inhibition prevents drug-induced liver
toxicity and fulminant hepatic failure. Nat Biotechnol. 30:179–183.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Naiki-Ito A, Asamoto M, Naiki T, Ogawa K,
Takahashi S, Sato S and Shirai T: Gap junction dysfunction reduces
acetaminophen hepatotoxicity with impact on apoptotic signaling and
connexin 43 protein induction in rat. Toxicol Pathol. 38:280–286.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Asamoto M, Hokaiwado N, Murasaki T and
Shirai T: Connexin 32 dominant-negative mutant transgenic rats are
resistant to hepatic damage by chemicals. Hepatology. 40:205–210.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tang N, Wang Q, Wu D, Zhang S, Zhang Y and
Tao L: Differential effects of paclitaxel and docetaxel on gap
junctions affects their cytotoxicities in transfected HeLa cells.
Mol Med Rep. 8:638–644. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Goldberg GS, Bechberger JF and Naus CC: A
pre-loading method of evaluating gap junctional communication by
fluorescent dye transfer. Biotechniques. 18:490–497.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hong X, Wang Q, Yang Y, Zheng S, Tong X,
Zhang S, Tao L and Harris AL: Gap junctions propagate opposite
effects in normal and tumor testicular cells in response to
cisplatin. Cancer Lett. 317:165–171. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tao L and Harris AL: 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl
borate directly inhibits channels composed of connexin26 and/or
connexin32. Mol Pharmacol. 71:570–579. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Todd RC and Lippard SJ: Inhibition of
transcription by platinum antitumor compounds. Metallomics.
1:280–291. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bhalla KN: Microtubule-targeted anticancer
agents and apoptosis. Oncogene. 22:9075–9086. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fulda S: Modulation of apoptosis by
natural products for cancer therapy. Planta Med. 76:1075–1079.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Park HH, Lo YC, Lin SC, Wang L, Yang JK
and Wu H: The death domain superfamily in intracellular signaling
of apoptosis and inflammation. Annu Rev Immunol. 25:561–586. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tong X, Dong S, Yu M, Wang Q and Tao L:
Role of heteromeric gap junctions in the cytotoxicity of cisplatin.
Toxicology. 310:53–60. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Niessen H, Harz H, Bedner P, Krämer K and
Willecke K: Selective permeability of different connexin channels
to the second messenger inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. J Cell Sci.
113:1365–1372. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Circu ML and Aw TY: Glutathione and
apoptosis. Free Radic Res. 42:689–706. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Friesen C, Kiess Y and Debatin KM: A
critical role of glutathione in determining apoptosis sensitivity
and resistance in leukemia cells. Cell Death Differ. 11:(Suppl 1).
S73–S85. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mesnil M, Crespin S, Avanzo JL and
Zaidan-Dagli ML: Defective gap junctional intercellular
communication in the carcinogenic process. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1719:125–145. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Loewenstein WR and Kanno Y: Intercellular
communication and the control of tissue growth: Lack of
communication between cancer cells. Nature. 209:1248–1249. 1966.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hanna EA, Umhauer S, Roshong SL, Piechocki
MP, Fernstrom MJ, Fanning JD and Ruch RJ: Gap junctional
intercellular communication and connexin43 expression in human
ovarian surface epithelial cells and ovarian carcinomas in vivo and
in vitro. Carcinogenesis. 20:1369–1373. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang W, DeMattia JA, Song H and Couldwell
WT: Communication between malignant glioma cells and vascular
endothelial cells through gap junctions. J Neurosurg. 98:846–853.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|