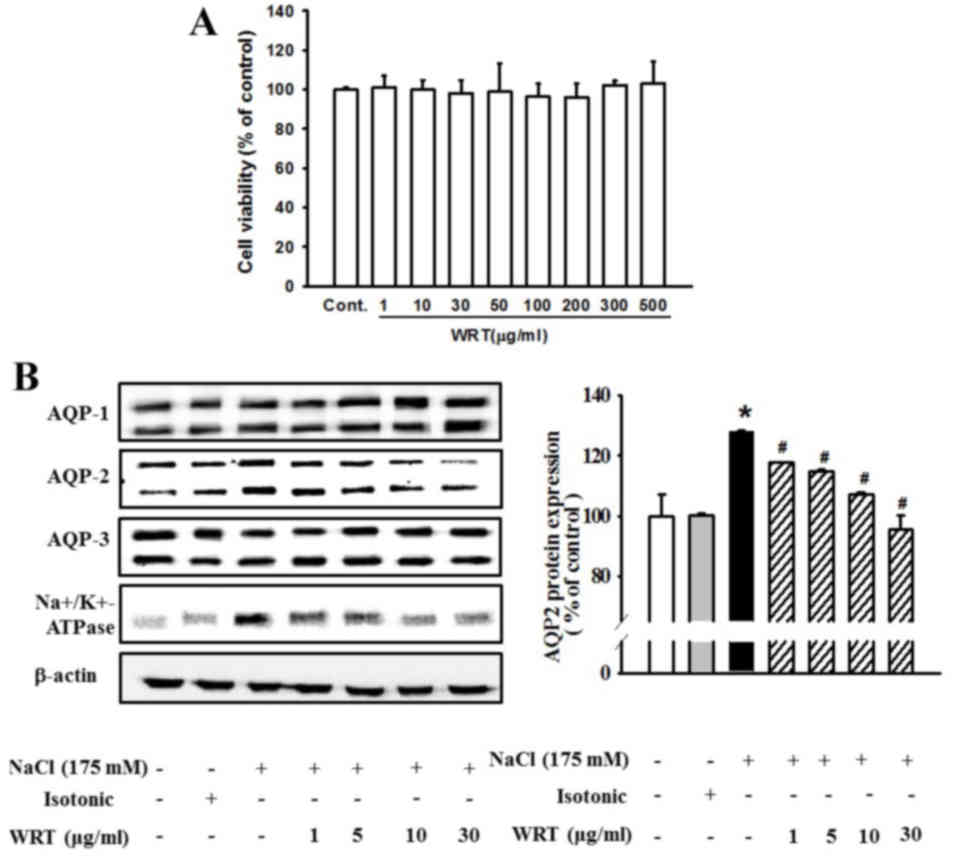
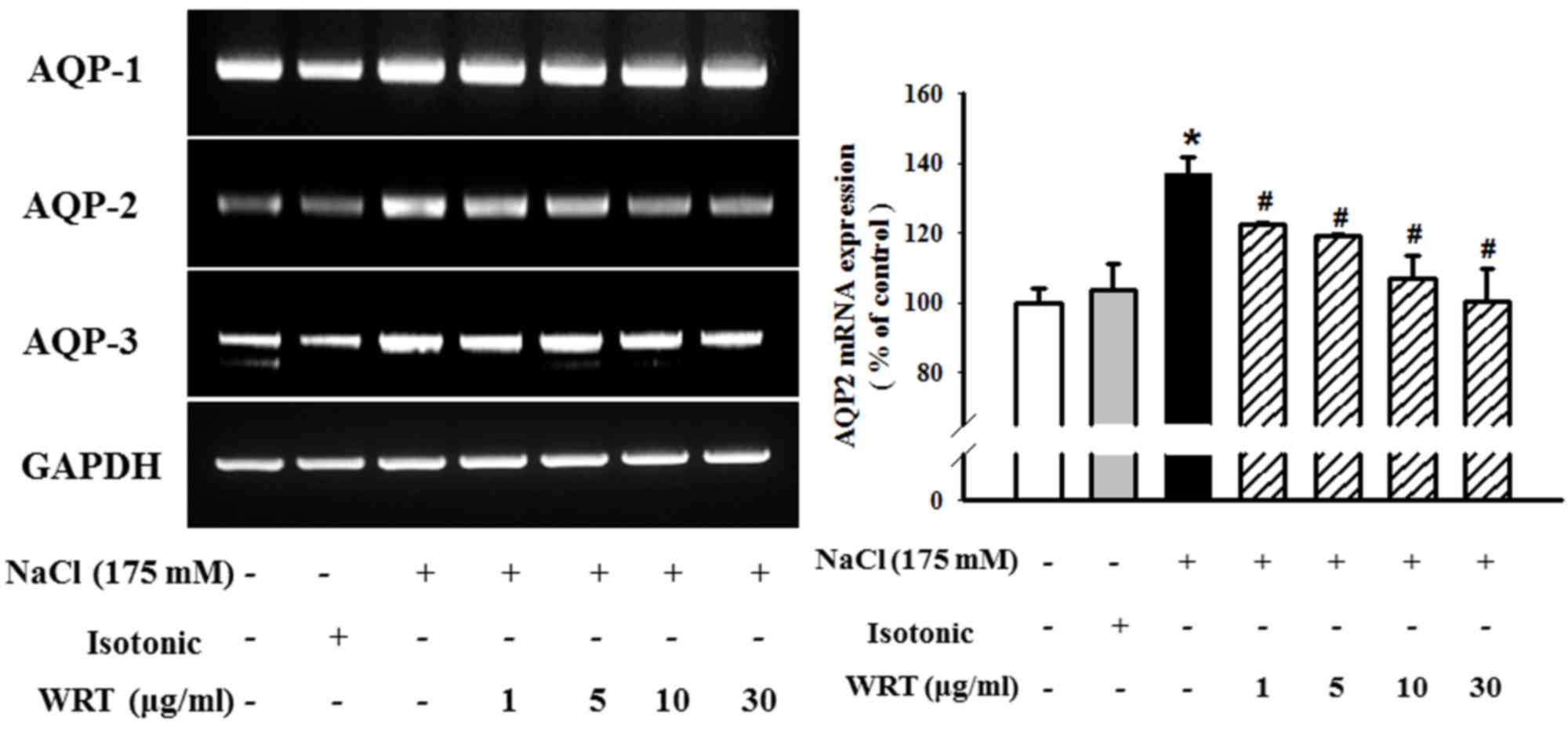
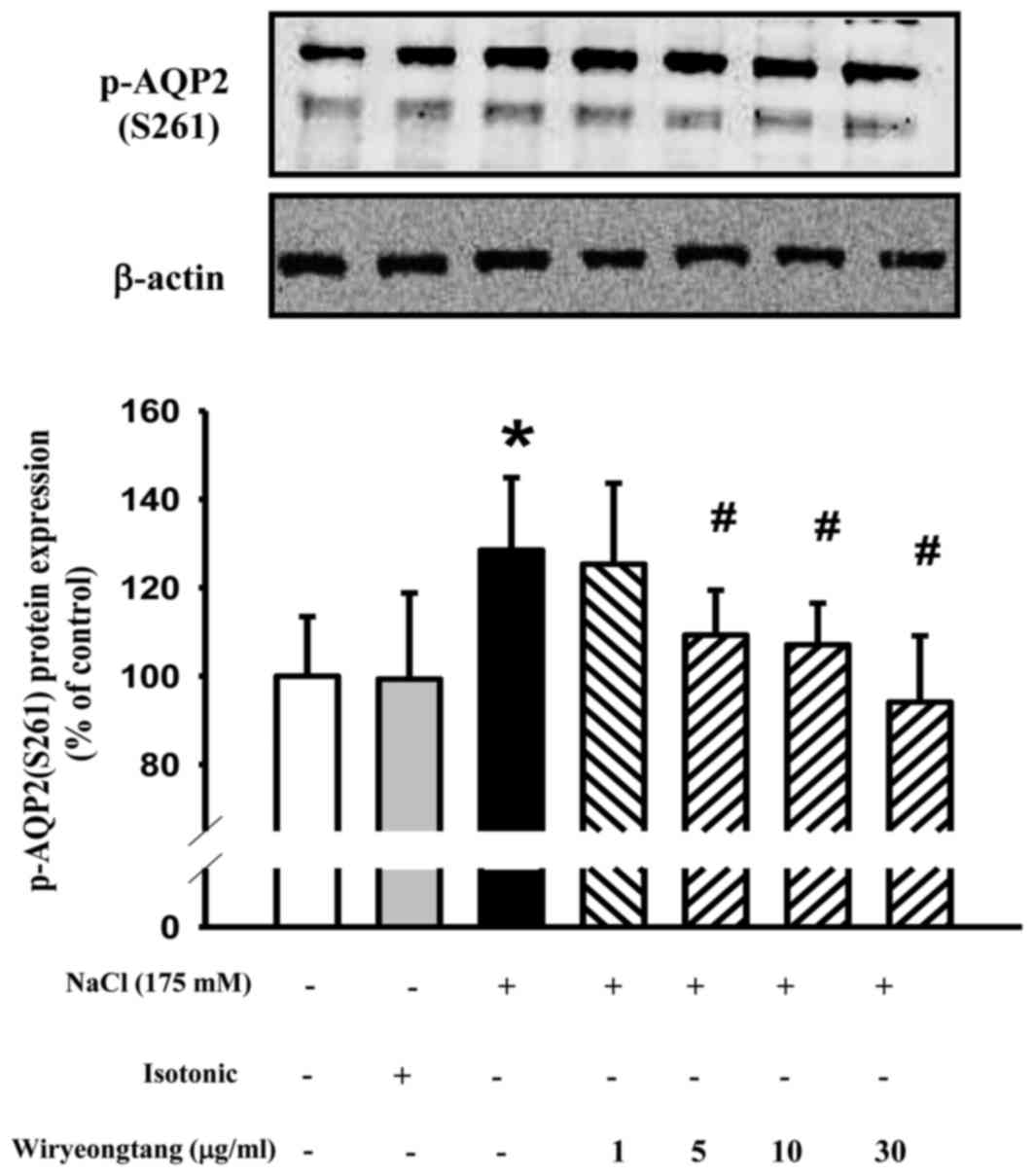
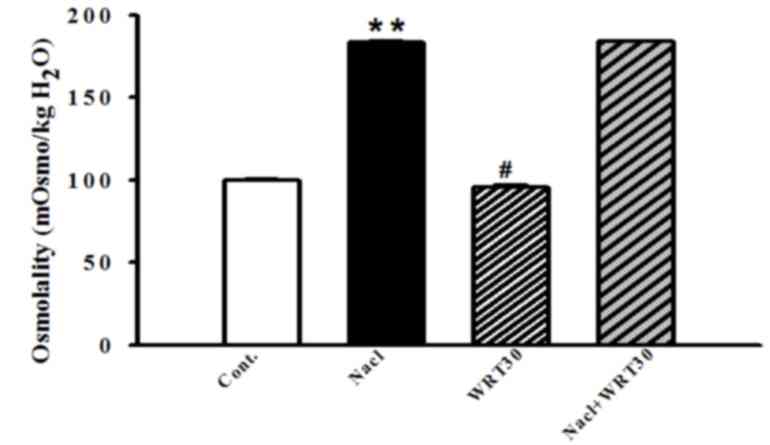
|
1
|
Klussmann E, Maric K and Rosenthal W: The
mechanisms of aquaporin control in the renal collecting duct. Rev
Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 141:33–95. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lee SM, Lee YJ, Yoon JJ, Kang DG and Lee
HS: Effect of Poria cocos on hypertonic stress-induced water
channel expression and apoptosis in renal collecting duct cells. J
Ethnopharmacol. 141:368–376. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Day RE, Kitchen P, Owen DS, Bland C,
Marshall L, Conner AC, Bill RM and Conner MT: Human aquaporins:
Regulators of transcellular water flow. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1840:1492–1506. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nielsen S, Frøkiaer J, Marples D, Kwon TH,
Agre P and Knepper MA: Aquaporins in the kidney: From molecules to
medicine. Physiol Rev. 82:205–244. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Storm R, Klussmann E, Geelhaar A,
Rosenthal W and Maric K: Osmolality and solute composition are
strong regulators of AQP2 expression in renal principal cells. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 284:F189–F198. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hozawa S, Holtzman EJ and Ausiello DA:
cAMP motifs regulating transcription in the aquaporin 2 gene. Am J
Physiol. 270:C1695–C1702. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Umenishi F, Narikiyo T, Vandewalle A and
Schrier RW: cAMP regulates vasopressin-induced AQP2 expression via
protein kinase A-independent pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1758:1100–1105. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hasler U, Jeon US, Kim JA, Mordasini D,
Kwon HM, Féraille E and Martin PY: Tonicity-responsive enhancer
binding protein is an essential regulator of aquaporin-2 expression
in renal collecting duct principal cells. J Am Soc Nephrol.
17:1521–1531. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kwon ED, Jung KY, Edsall LC, Kim HY,
García-Pérez A and Burg MB: Osmotic regulation of synthesis of
glycerol phosphocholine from phosphatidylcholine in MDCK cells. Am
J Physiol. 268:C402–C412. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bell LM, Leong ML, Kim B, Wang E, Park J,
Hemmings BA and Firestone GL: Hyperosmotic stress stimulates
promoter activity and regulates cellular utilization of the serum-
and glucocorticoid-inducible protein kinase (Sgk) by a p38
MAPK-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem. 275:25262–25272. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen S, Grigsby CL, Law CS, Ni X, Nekrep
N, Olsen K, Humphreys MH and Gardner DG: Tonicity-dependent
induction of Sgk1 expression has a potential role in
dehydration-induced natriuresis in rodents. J Clin Inves.
119:1647–1658. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Riedlinger JE, Tan PW and Lu W: Ping wei
san, a Chinese medicine for gastrointestinal disorders. Ann
Pharmacother. 35:228–235. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lin E, Ho L, Lin MS, Huang MH and Chen WC:
Wu-Ling-San formula prophylaxis against recurrent calcium oxalate
nephrolithiasis-a prospective randomized controlled trial. Afr J
Tradit Complement Altern Med. 10:199–209. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yun GY: Oriental Herbal Formula Science.
Publisher myeongbo; Seoul: pp. 198–204. 1985
|
|
15
|
Lee YP, Lee YJ, Lee SM, Yoon JJ, Kim HY,
Kang DG and Lee HS: Effect of atractylodes macrocephala on
hypertonic stress-induced water channel protein expression in renal
collecting duct cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2012:6508092012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Knepper MA, Kwon TH and Nielsen S:
Molecular physiology of water balance. N Engl J Med. 372:1349–1358.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wehner F: Cell volume-regulated cation
channels. Contrib Nephrol. 152:25–53. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jeon US, Kim JA, Sheen MR and Kwon HM: How
tonicity regulates genes: Story of TonEBP transcriptional
activator. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 187:241–247. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nakayama Y, Peng T, Sands JM and Bagnasco
SM: The TonE/TonEBP pathway mediates tonicity-responsive regulation
of UT-A urea transporter expression. J Biol Chem. 275:38275–38280.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Náray-Fejes-Tóth A and Fejes-Tóth G: The
sgk, an aldosterone induced gene in mineralocorticoid target cells,
regulates the epithelial sodium channel. Kidney Int. 57:1290–1294.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Salyer SA, Parks J, Barati MT, Lederer ED,
Clark BJ, Klein JD and Khundmiri SJ: Aldosterone regulates Na(+),
K(+) ATPase activity in human renal proximal tubule cells through
mineralocorticoid receptor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1833:2143–2152.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Baines D: Kinases as targets for ENaC
regulation. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 6:50–64. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Vella J, Zammit C, Di Giovanni G, Muscat R
and Valentino M: The central role of aquaporins in the
pathophysiology of ischemic stroke. Front Cell Neurosci. 9:1082015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tait MJ, Saadoun S, Bell BA and
Papadopoulos MC: Water movements in the brain: Role of aquaporins.
Trends Neurosci. 31:37–43. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhai XY, Fenton RA, Andreasen A, Thomsen
JS and Christensen EI: Aquaporin-1 is not expressed in descending
thin limbs of short-loop nephrons. J Am Soc Nephrol. 18:2937–2944.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
van Balkom BW, van Raak M, Breton S,
Pastor-Soler N, Bouley R, van der Sluijs P, Brown D and Deen PM:
Hypertonicity is involved in redirecting the aquaporin-2 water
channel into the basolateral, instead of the apical, plasma
membrane of renal epithelia cells. J Biol Chem. 278:1101–1107.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Boone M and Deen PM: Physiology and
pathophysiology of the vasopressin-regulated renal water
reabsorption. Pflugers Arch. 456:1005–1024. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gilbert ML, Yang L, Su T and McKnight GS:
Expression of a dominant negative PKA mutation in the kidney
elicits a diabetes insipidus phenotype. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
308:F627–F638. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Breyer JA, Bain RP, Evans JK, Nahman NS
Jr, Lewis EJ, Cooper M, McGill J and Berl T: Predictors of the
progression of renal insufficiency patients with insulin-dependent
diabetes and overt diabetic nephropathy the collaborative study
group. Kidney Int. 50:1651–1658. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hoyer PB, Fitz TA and Niswender GD:
Hormone-independent activation of adenylate cyclase in large
steroidogenic ovine luteal cells does not result in increased
progesterone secretion. Endocrinology. 114:604–608. 1984.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yip KP and Sham JS: Mechanisms of
vasopressin-induced intracellular Ca2+ oscillations in rat inner
medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
300:F540–F548. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|