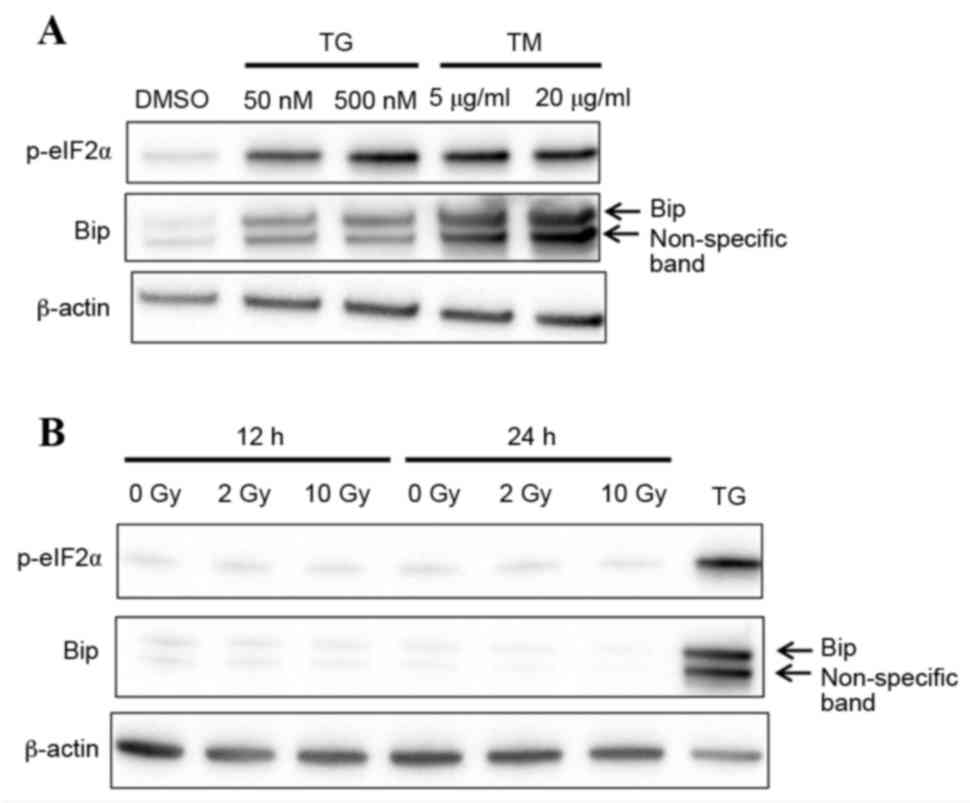
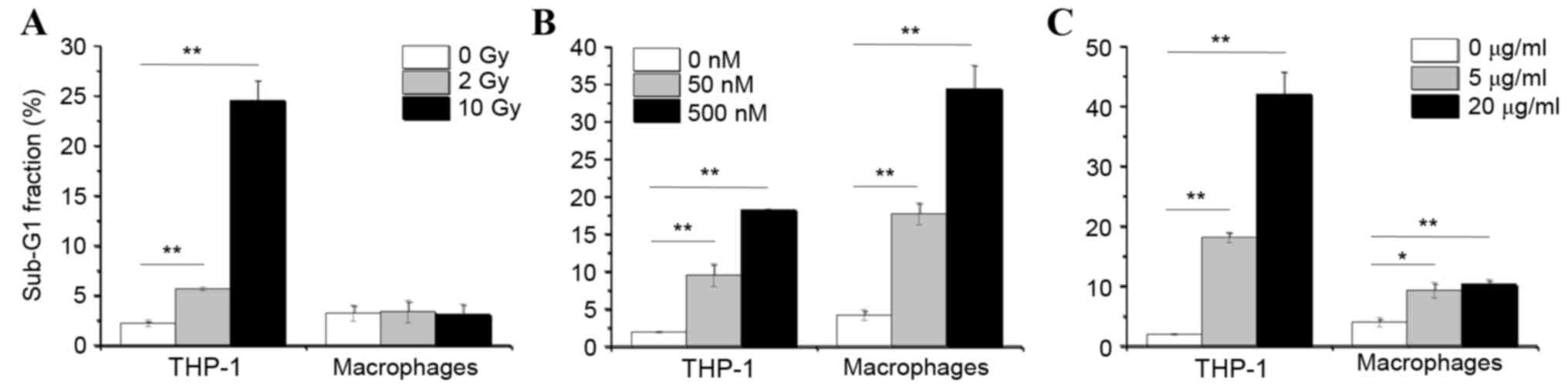
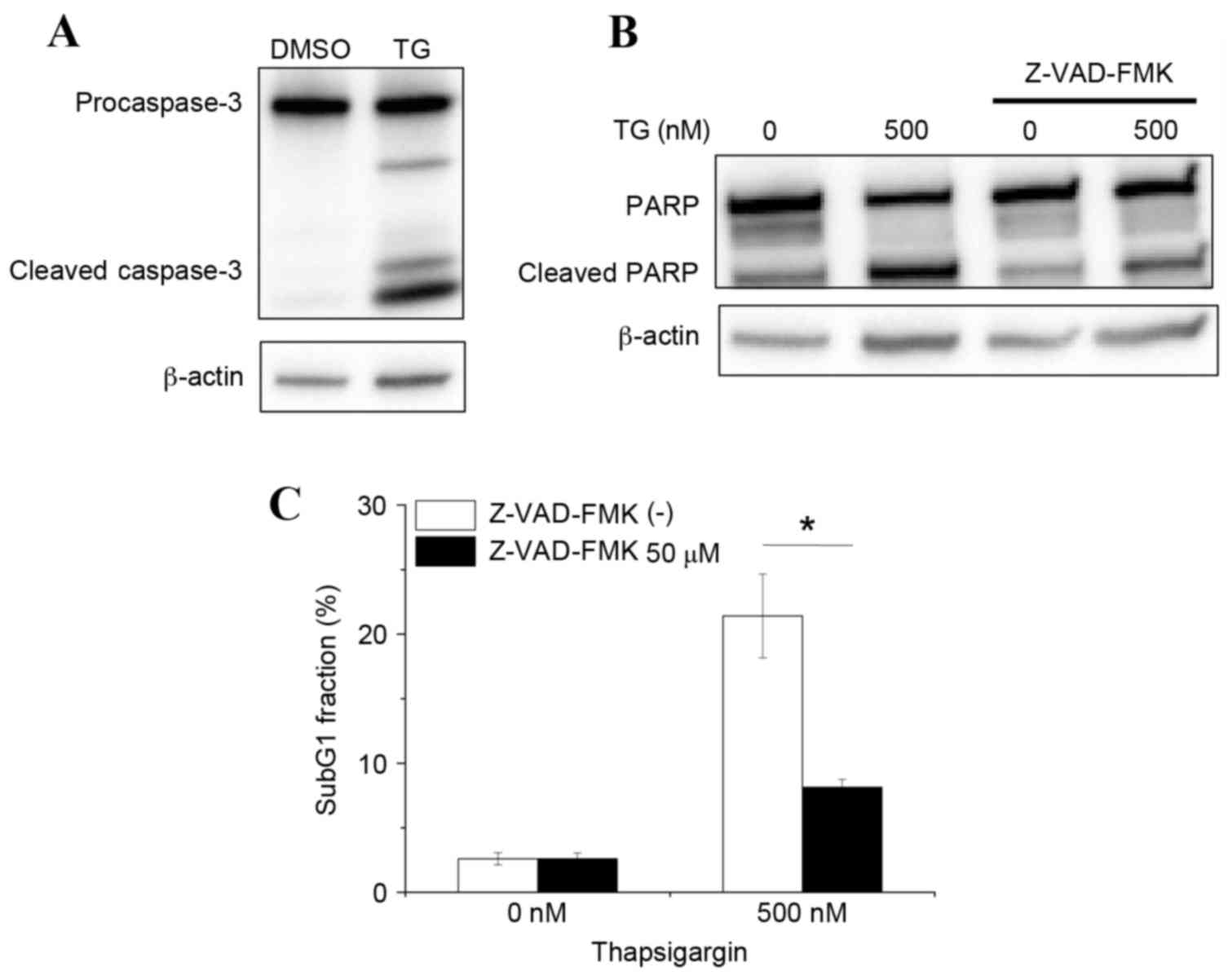
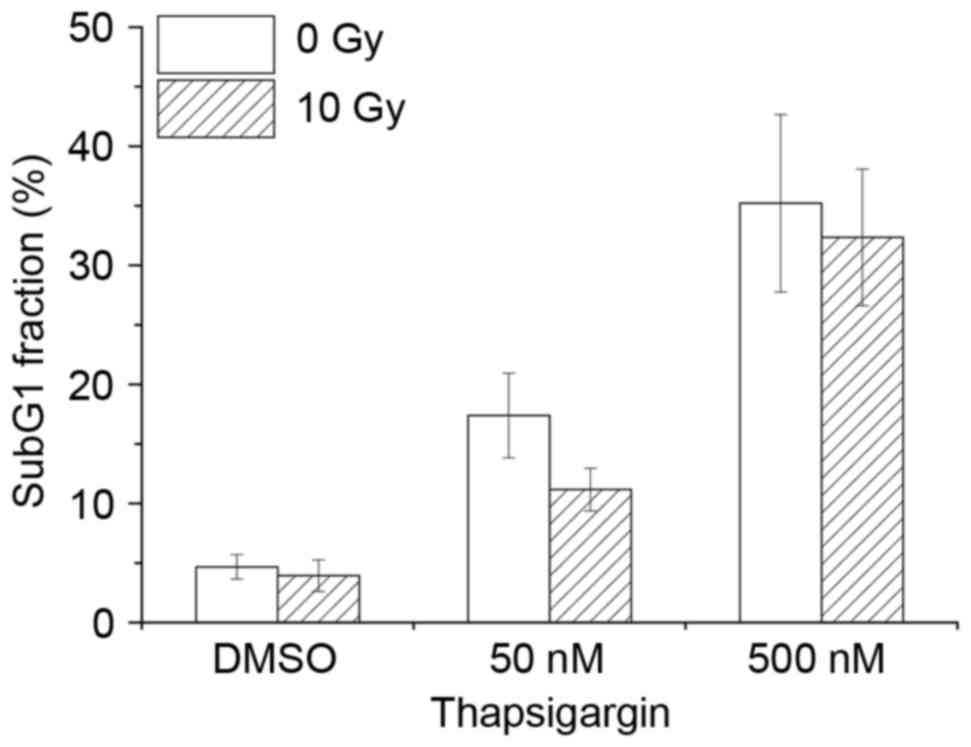
|
1
|
Murray PJ and Wynn TA: Protective and
pathogenic functions of macrophage subsets. Nat Rev Immunol.
11:723–737. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Schultze JL, Schmieder A and Goerdt S:
Macrophage activation in human diseases. Semin Immunol. 27:249–256.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Qian BZ and Pollard JW: Macrophage
diversity enhances tumor progression and metastasis. Cell.
141:39–51. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jinushi M, Chiba S, Yoshiyama H, Masutomi
K, Kinoshita I, Dosaka-Akita H, Yagita H, Takaoka A and Tahara H:
Tumor-associated macrophages regulate tumorigenicity and anticancer
drug responses of cancer stem/initiating cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 108:12425–12430. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ostuni R, Kratochvill F, Murray PJ and
Natoli G: Macrophages and cancer: From mechanisms to therapeutic
implications. Trends Immunol. 36:229–239. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bauer M, Goldstein M, Christmann M, Becker
H, Heylmann D and Kaina B: Human monocytes are severely impaired in
base and DNA double-strand break repair that renders them
vulnerable to oxidative stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:21105–21110. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Norbury CJ and Zhivotovsky B: DNA
damage-induced apoptosis. Oncogene. 23:2797–2808. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wu J and Kaufman RJ: From acute ER stress
to physiological roles of the unfolded protein response. Cell Death
Differ. 13:374–384. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Naidoo N: Cellular stress/the unfolded
protein response: Relevance to sleep and sleep disorders. Sleep Med
Rev. 13:195–204. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li J, Lee B and Lee AS: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress-induced apoptosis: Multiple pathways and
activation of p53-up-regulated modulator of apoptosis (PUMA) and
NOXA by p53. J Biol Chem. 281:7260–7270. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Contessa JN, Bhojani MS, Freeze HH,
Rehemtulla A and Lawrence TS: Inhibition of N-linked glycosylation
disrupts receptor tyrosine kinase signaling in tumor cells. Cancer
Res. 68:3803–3809. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yamamori T, Meike S, Nagane M, Yasui H and
Inanami O: ER stress suppresses DNA double-strand break repair and
sensitizes tumor cells to ionizing radiation by stimulating
proteasomal degradation of Rad51. FEBS Lett. 587:3348–3353. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sugimoto K, Toyoshima H, Sakai R, Miyagawa
K, Hagiwara K, Ishikawa F, Takaku F, Yazaki Y and Hirai H: Frequent
mutations in the p53 gene in human myeloid leukemia cell lines.
Blood. 79:2378–2383. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yoshino H, Saitoh T, Kozakai M and
Kashiwakura I: Effects of ionizing radiation on retinoic
acid-inducible gene-I-like receptors. Biomed Rep. 3:59–62.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nagelkerke A, Bussink J, van der Kogel AJ,
Sweep FC and Span PN: The PERK/ATF4/LAMP3-arm of the unfolded
protein response affects radioresistance by interfering with the
DNA damage response. Radiother Oncol. 108:415–421. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee ES, Lee HJ, Lee YJ, Jeong JH, Kang S
and Lim YB: Chemical chaperones reduce ionizing radiation-induced
endoplasmic reticulum stress and cell death in IEC-6 cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 450:1005–1009. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gotoh T, Oyadomari S, Mori K and Mori M:
Nitric oxide-induced apoptosis in RAW 264.7 macrophages is mediated
by endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway involving ATF6 and CHOP. J
Biol Chem. 277:12343–12350. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Devries-Seimon T, Li Y, Yao PM, Stone E,
Wang Y, Davis RJ, Flavell R and Tabas I: Cholesterol-induced
macrophage apoptosis requires ER stress pathways and engagement of
the type A scavenger receptor. J Cell Biol. 171:61–73. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sagara Y and Inesi G: Inhibition of the
sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ transport ATPase by thapsigargin at
subnanomolar concentrations. J Biol Chem. 266:13503–13506.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lytton J, Westlin M and Hanley MR:
Thapsigargin inhibits the sarcoplasmic or endoplasmic reticulum
Ca-ATPase family of calcium pumps. J Biol Chem. 266:17067–17071.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Duksin D and Mahoney WC: Relationship of
the structure and biological activity of the natural homologues of
tunicamycin. J Biol Chem. 257:3105–3109. 1982.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dubois C, Prevarskaya N and Vanden Abeele
F: The calcium-signaling toolkit: Updates needed. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1863:1337–1343. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Buckley BJ and Whorton AR: Tunicamycin
increases intracellular calcium levels in bovine aortic endothelial
cells. Am J Physiol. 273:C1298–C1305. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Suzuki K, Gerelchuluun A, Hong Z, Sun L,
Zenkoh J, Moritake T and Tsuboi K: Celecoxib enhances
radiosensitivity of hypoxic glioblastoma cells through endoplasmic
reticulum stress. Neuro Oncol. 15:1186–1199. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yasui H, Takeuchi R, Nagane M, Meike S,
Nakamura Y, Yamamori T, Ikenaka Y, Kon Y, Murotani H, Oishi M, et
al: Radiosensitization of tumor cells through endoplasmic reticulum
stress induced by PEGylated nanogel containing gold nanoparticles.
Cancer Lett. 347:151–158. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|