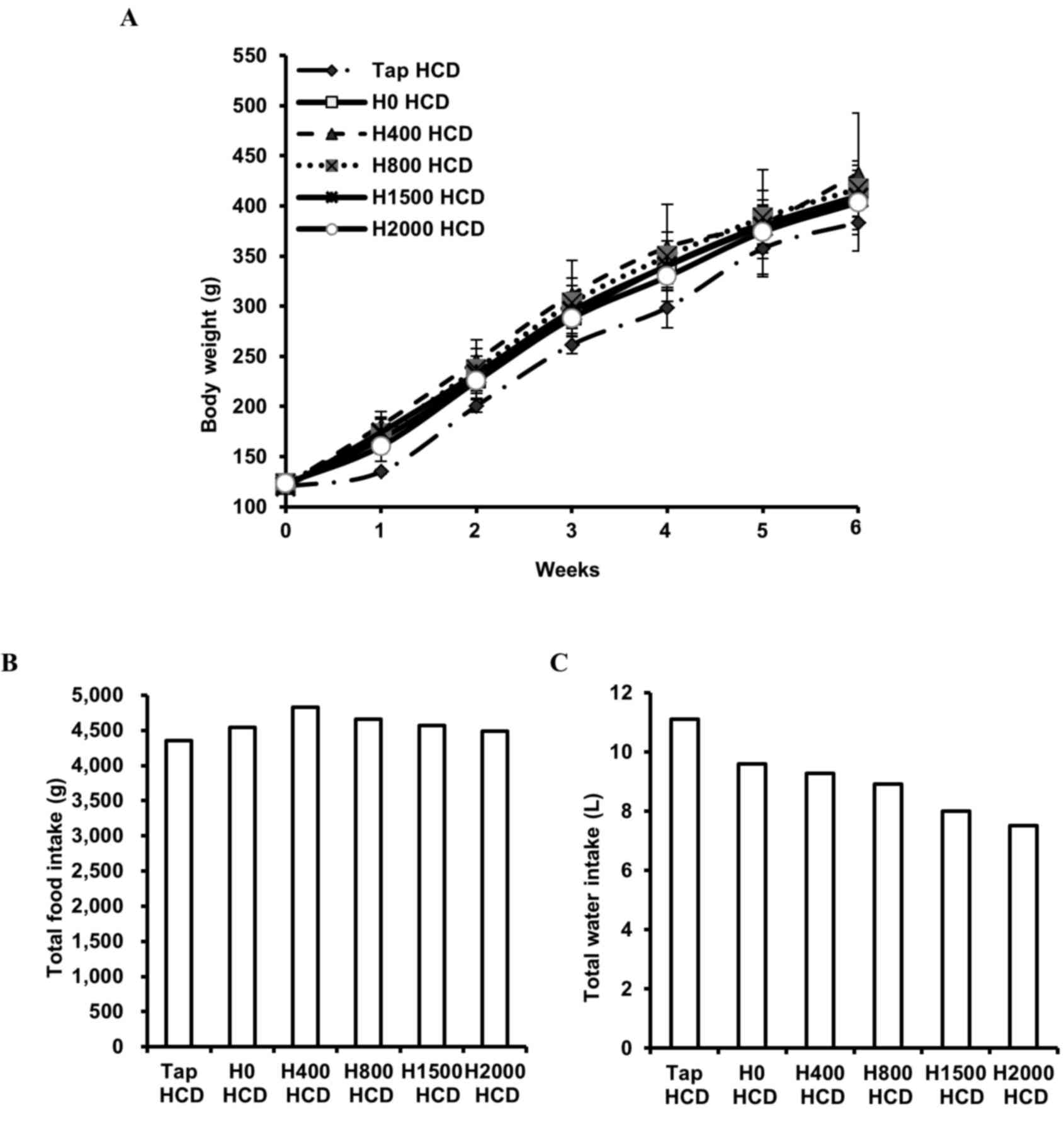
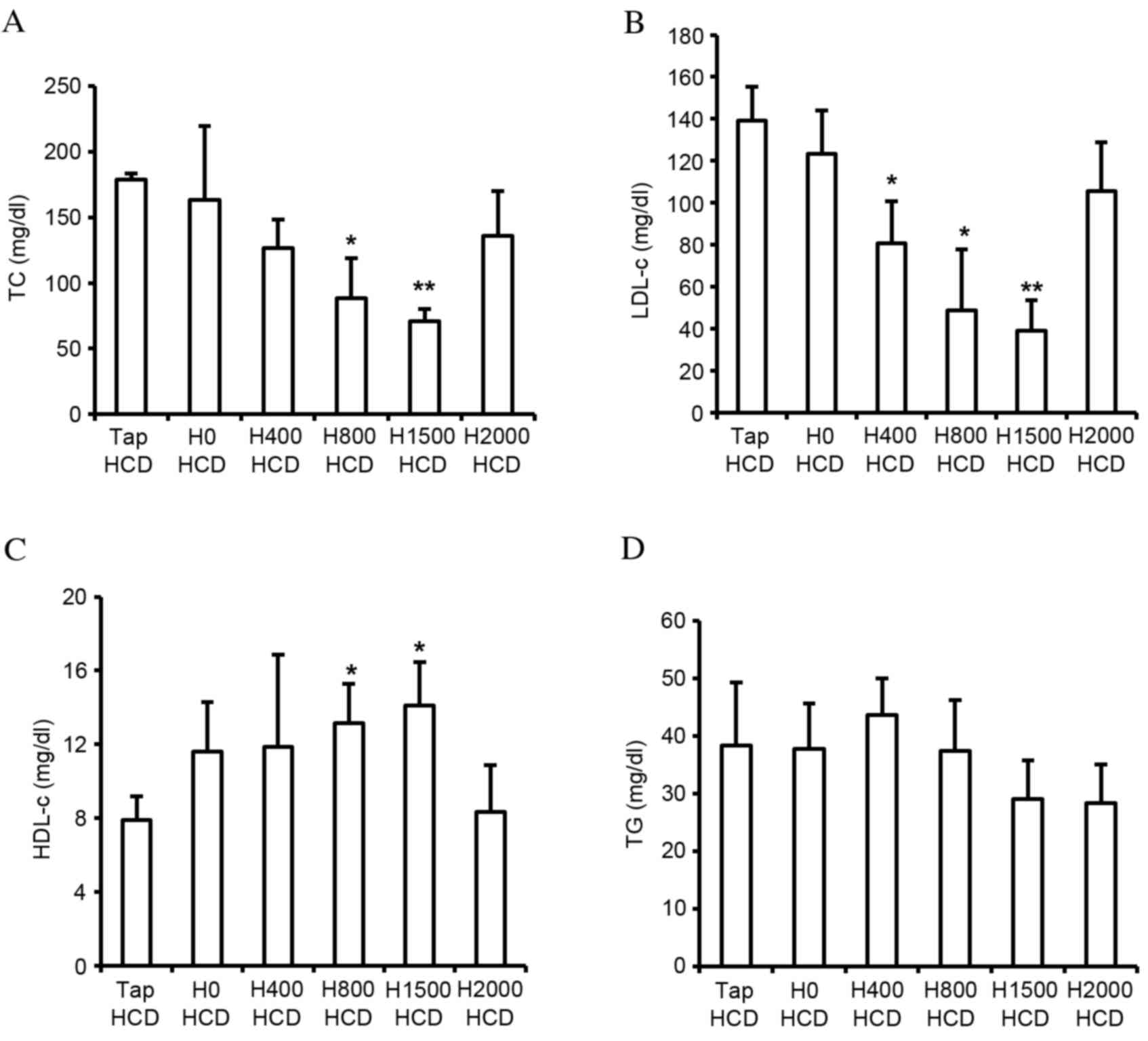
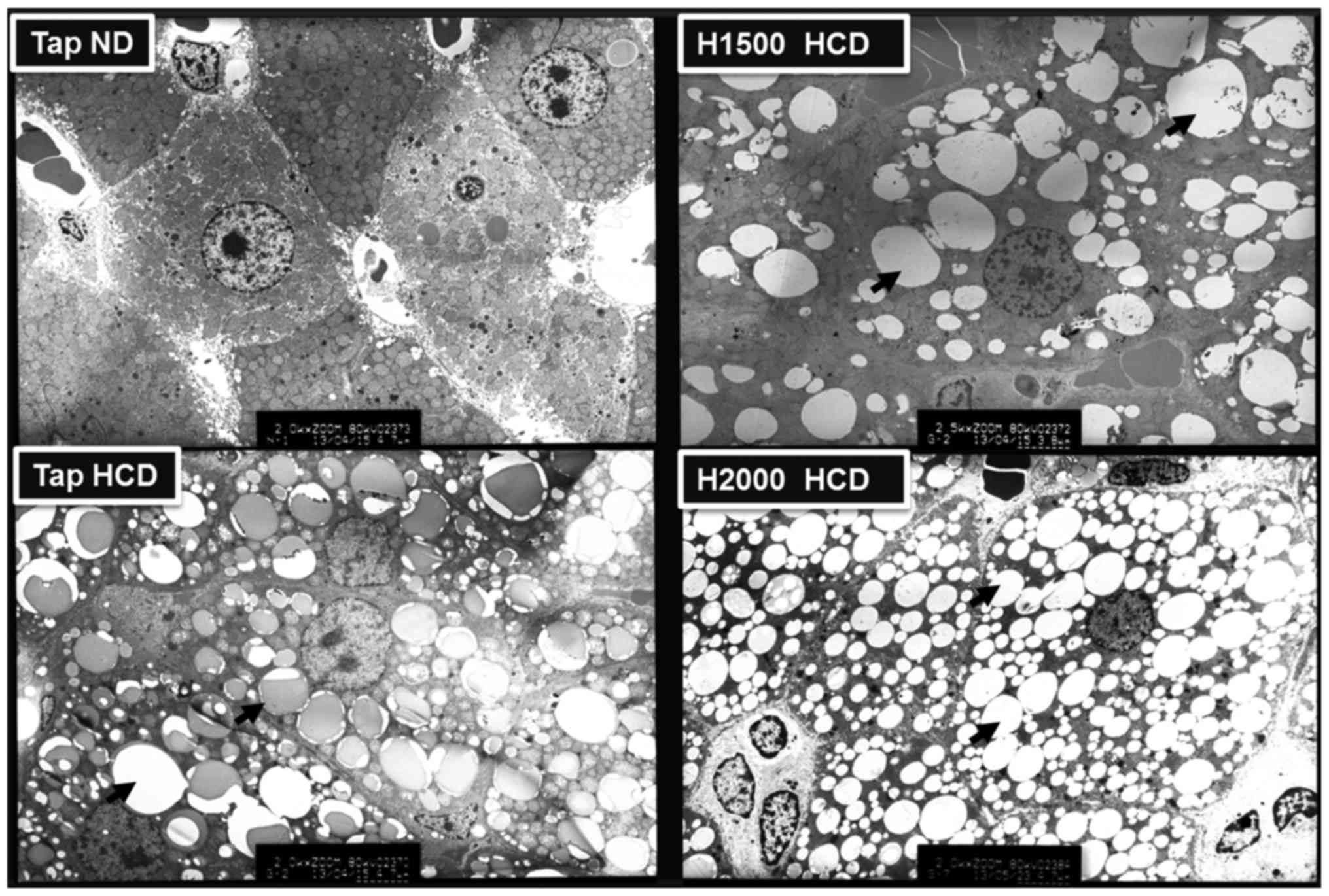
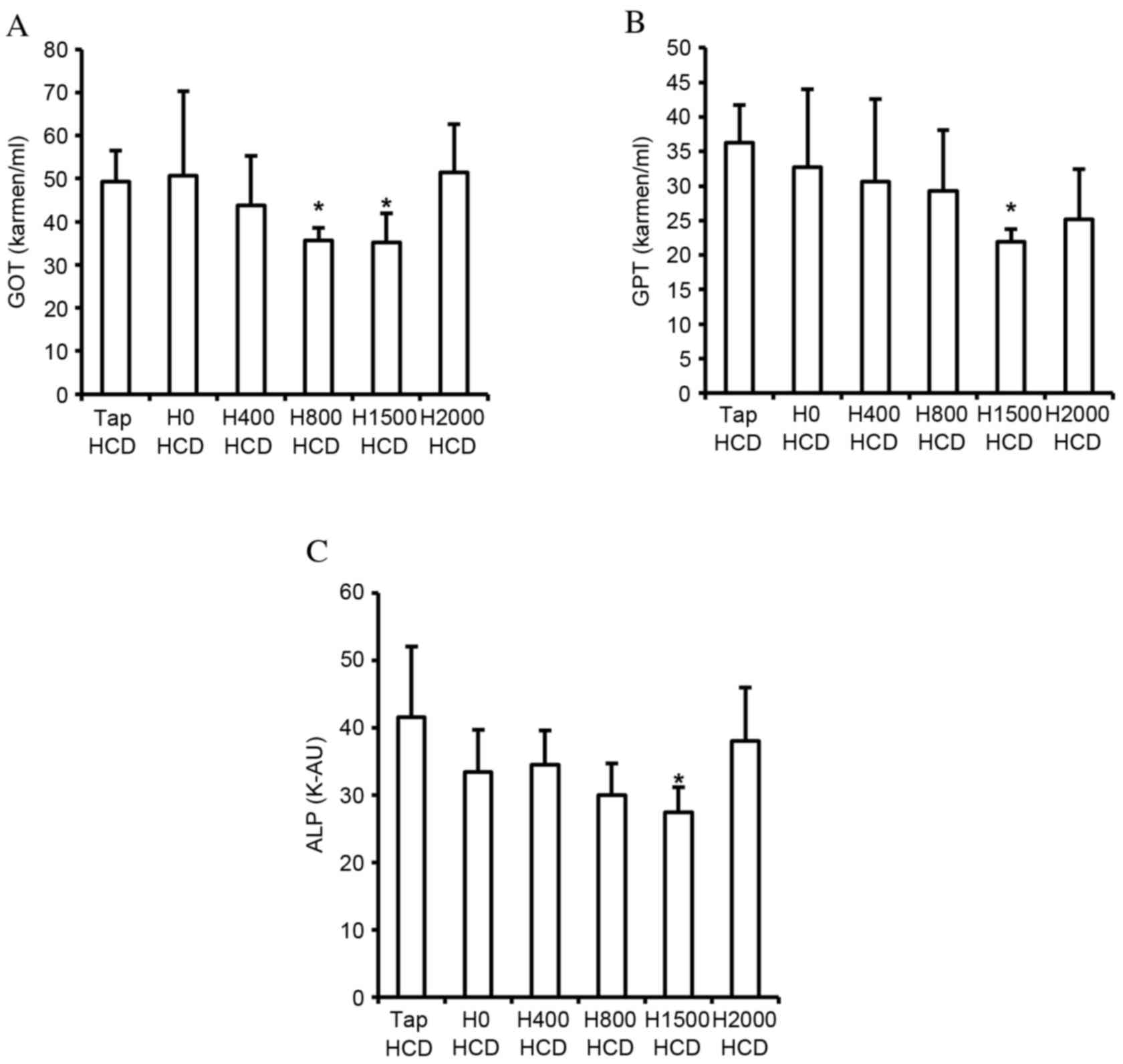
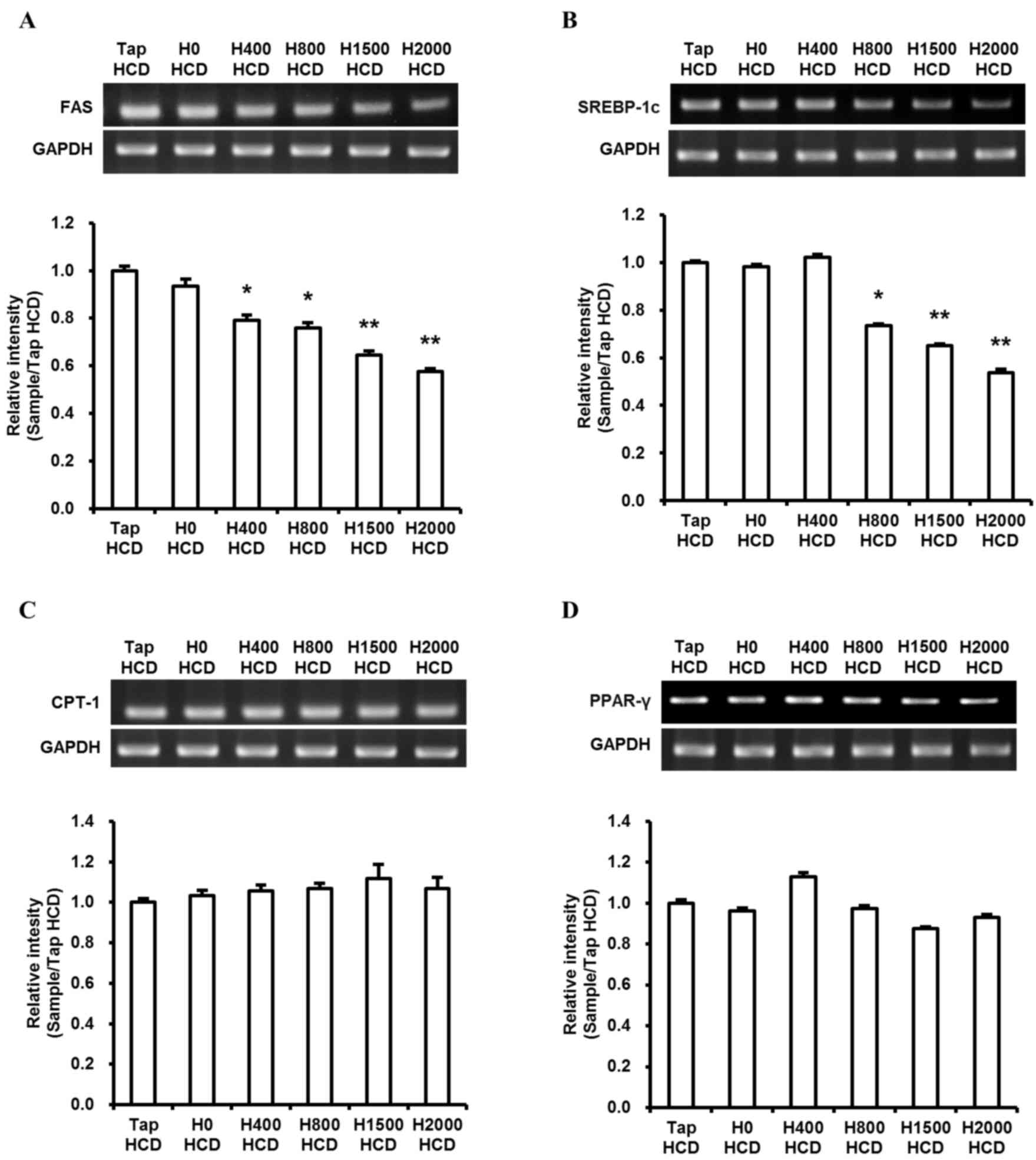
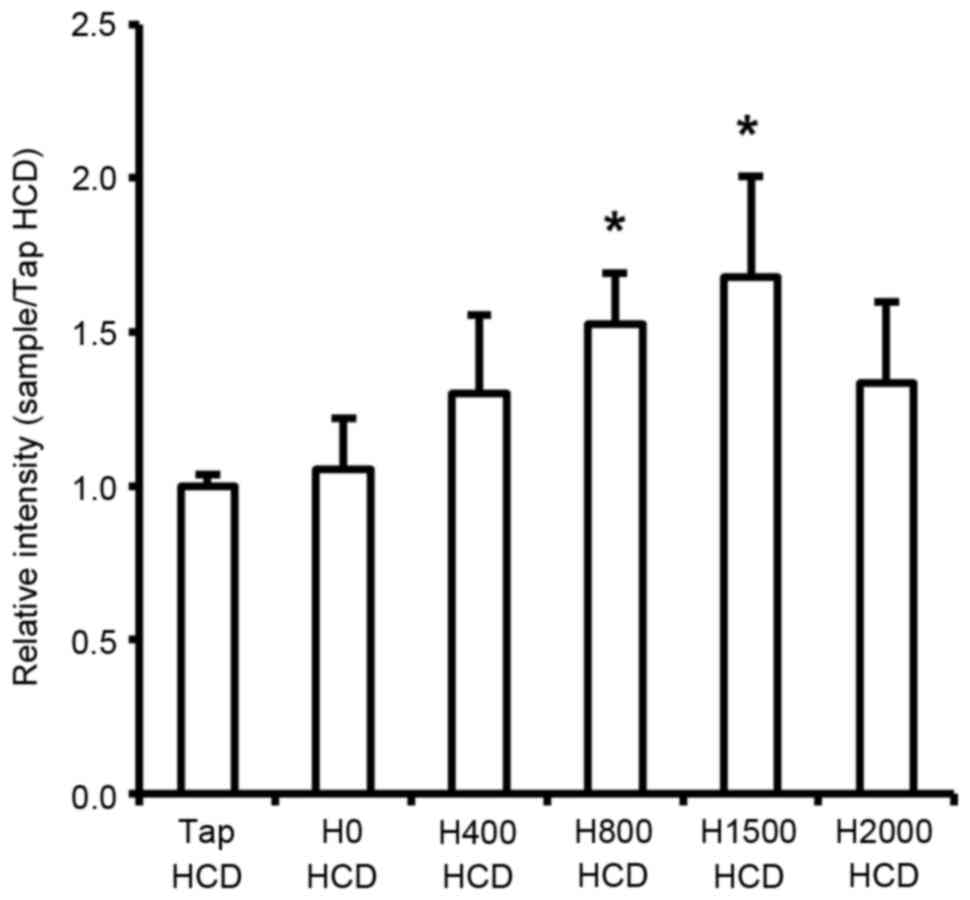
|
1
|
Ma Y, Wang W, Zhang J, Lu Y, Wu W, Yan H
and Wang Y: Hyperlipidemia and atherosclerotic lesion development
in Ldlr-deficient mice on a long-term high-fat diet. PLoS One.
7:e358352012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang X, Wu C, Wu H, Sheng L, Su Y, Zhang
X, Luan H, Sun G, Sun X, Tian Y, et al: Anti-hyperlipidemic effects
and potential mechanisms of action of the caffeoylquinic acid-rich
Pandanus tectorius fruit extract in hamsters fed a high fat-diet.
PLoS One. 8:e619222013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Daniels SR: Management of hyperlipidemia
in pediatrics. Curr Opin Cardiol. 27:92–97. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cholesterol Treatment Trialists' (CTT)
Collaboration. Baigent C, Blackwell L, Emberson J, Holland LE,
Reith C, Bhala N, Peto R, Barnes EH, Keech A, et al: Efficacy and
safety of more intensive lowering of LDL cholesterol: A
meta-analysis of data from 170,000 participants in 26 randomised
trials. Lancet. 376:1670–1681. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Berry JD, Dyer A, Cai X, Garside DB, Ning
H, Thomas A, Greenland P, Van Horn L, Tracy RP and Lloyd-Jones DM:
Lifetime risks of cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med.
366:321–329. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Harchaoui KE, Visser ME, Kastelein JJ,
Stroes ES and Dallinga-Thie GM: Triglycerides and cardiovascular
risk. Curr Cardiol Rev. 5:216–222. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang ZH, Miyahara H, Takeo J, Hatanaka A
and Katayama M: Pollock oil supplementation modulates
hyperlipidemia and ameliorates hepatic steatosis in mice fed a
high-fat diet. Lipids Health Dis. 10:1892011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yao Z, Liu XC and Gu YE: Schisandra
chinensis Baill, a Chinese medicinal herb, alleviates
high-fat-diet-inducing non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in rats. Afr J
Tradit Complement Altern Med. 11:222–227. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Carrier B, Wen S, Zigouras S, Browne RW,
Li Z, Patel MS, Williamson DL and Rideout TC: Alpha-lipoic acid
reduces LDL-particle number and PCSK9 concentrations in high-fat
fed obese Zucker rats. PLoS One. 9:e908632014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Singh AB, Kan CF, Shende V, Dong B and Liu
J: A novel posttranscriptional mechanism for dietary
cholesterol-mediated suppression of liver LDL receptor expression.
J Lipid Res. 55:1397–1407. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kim H, Bartley GE, Arvik T, Lipson R, Nah
SY, Seo K and Yokoyama W: Dietary supplementation of chardonnay
grape seed flour reduces plasma cholesterol concentration, hepatic
steatosis, and abdominal fat content in high-fat diet-induced obese
hamsters. J Agric Food Chem. 62:1919–1925. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim S, Chun SY, Lee DH, Lee KS and Nam KS:
Mineral-enriched deep-sea water inhibits the metastatic potential
of human breast cancer cell lines. Int J Oncol. 43:1691–1700.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Katsuda S, Yasukawa T, Nakagawa K, Miyake
M, Yamasaki M, Katahira K, Mohri M, Shimizu T and Hazama A:
Deep-sea water improves cardiovascular hemodynamics in Kurosawa and
Kusanagi-Hypercholesterolemic (KHC) rabbits. Biol Pharm Bull.
31:38–44. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee KS, Shin JS, Kwon YS, Moon DS and Nam
KS: Suppression of cancer progression and metastasis in HT-29 human
colorectal adenocarcinomas by deep sea water. Biotechnol Bioproc
Eng. 18:194–200. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Fu ZY, Yang FL, Hsu HW and Lu YF: Drinking
deep seawater decreases serum total and low-density
lipoprotein-cholesterol in hypercholesterolemic subjects. J Med
Food. 15:535–541. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ha BG, Shin EJ, Park JE and Shon YH:
Anti-diabetic effect of balanced deep-sea water and its mode of
action in high-fat diet induced diabetic mice. Mar Drugs.
11:4193–4212. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hataguchi Y, Tai H, Nakajima H and Kimata
H: Drinking deep-sea water restores mineral imbalance in atopic
eczema/dermatitis syndrome. Eur J Clin Nutr. 59:1093–1096. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hsu CL, Chang YY, Chiu CH, Yang KT, Wang
Y, Fu SG and Chen YC: Cardiovascular protection of deep-seawater
drinking water in high-fat/cholesterol fed hamsters. Food Chem.
127:1146–1152. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hwang HS, Kim HA, Lee SH and Yun JW:
Anti-obesity and antidiabetic effects of deep sea water on ob/ob
mice. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 11:531–539. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hwang HS, Kim SH, Yoo YG, Chu YS, Shon YH,
Nam KS and Yun JW: Inhibitory effect of deep-sea water on
differentiation of 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mar Biotechnol (NY).
11:161–168. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li PC, Pan CH, Sheu MJ, Wu CC, Ma WF and
Wu CH: Deep sea water prevents balloon angioplasty-induced
hyperplasia through MMP-2: An in vitro and in vivo study. PLoS One.
9:e969272014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Miyamura M, Yoshioka S, Hamada A, Takuma
D, Yokota J, Kusunose M, Kyotani S, Kawakita H, Odani K, Tsutsui Y
and Nishioka Y: Difference between deep seawater and surface
seawater in the preventive effect of atherosclerosis. Biol Pharm
Bull. 27:1784–1787. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sheu MJ, Chou PY, Lin WH, Pan CH, Chien
YC, Chung YL, Liu FC and Wu CH: Deep sea water modulates blood
pressure and exhibits hypolipidemic effects via the AMPK-ACC
pathway: An in vivo study. Mar Drugs. 11:2183–2202. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yoshioka S, Hamada A, Cui T, Yokota J,
Yamamoto S, Kusunose M, Miyamura M, Kyotani S, Kaneda R, Tsutsui Y,
et al: Pharmacological activity of deep-sea water: Examination of
hyperlipemia prevention and medical treatment effect. Biol Pharm
Bull. 26:1552–1559. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Reitman S and Frankel S: A colorimetric
method for the determination of serum glutamic oxalacetic and
glutamic pyruvic transaminases. Am J Clin Pathol. 28:56–63. 1957.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Vuppalanchi R and Chalasani N:
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis:
Selected practical issues in their evaluation and management.
Hepatology. 49:306–317. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Inoue M, Ohtake T, Motomura W, Takahashi
N, Hosoki Y, Miyoshi S, Suzuki Y, Saito H, Kohgo Y and Okumura T:
Increased expression of PPARgamma in high fat diet-induced liver
steatosis in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 336:215–222. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen IS, Chang YY, Hsu CL, Lin HW, Chang
MH, Chen JW, Chen SS and Chen YC: Alleviative effects of
deep-seawater drinking water on hepatic lipid accumulation and
oxidation induced by a high-fat diet. J Chin Med Assoc. 76:95–101.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ma PT, Gil G, Südhof TC, Bilheimer DW,
Goldstein JL and Brown MS: Mevinolin, an inhibitor of cholesterol
synthesis, induces mRNA for low density lipoprotein receptor in
livers of hamsters and rabbits. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
83:8370–8374. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yasunobu Y, Hayashi K, Shingu T, Nomura K,
Ohkura Y, Tanaka K, Kuga Y, Nomura S, Ohtani H, Nishimura T, et al:
Reduction of plasma cholesterol levels and induction of hepatic LDL
receptor by cerivastatin sodium (CAS 143201-11-0, BAY w 6228), a
new inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase,
in dogs. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 11:567–574. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Abad C, Vargas FR, Zoltan T, Proverbio T,
Piñero S, Proverbio F and Marín R: Magnesium sulfate affords
protection against oxidative damage during severe preeclampsia.
Placenta. 36:179–185. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Olatunji LA and Soladoye AO: Increased
magnesium intake prevents hyperlipidemia and insulin resistance and
reduces lipid peroxidation in fructose-fed rats. Pathophysiology.
14:11–15. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gupta M, Solanki MH, Chatterjee PK, Xue X,
Roman A, Desai N, Rochelson B and Metz CN: Maternal magnesium
deficiency in mice leads to maternal metabolic dysfunction and
altered lipid metabolism with fetal growth restriction. Mol Med.
20:332–340. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Niranjan G, Anitha D, Srinivasan AR, Velu
VK, Venkatesh C, Babu MS, Ramesh R and Saha S: Association of
inflammatory sialoproteins, lipid peroxides and serum magnesium
levels with cardiometabolic risk factors in obese children of South
Indian population. Int J Biomed Sci. 10:118–123. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jacqmain M, Doucet E, Després JP, Bouchard
C and Tremblay A: Calcium intake, body composition, and
lipoprotein-lipid concentrations in adults. Am J Clin Nutr.
77:1448–1452. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Miyake S: The mechanism of release of
hepatic enzymes in various liver diseases. II. Altered activity
ratios of GOT to GPT in serum and liver of patients with liver
diseases. Acta Med Okayama. 33:343–358. 1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cremers J, Drent M, Driessen A, Nieman F,
Wijnen P, Baughman R and Koek G: Liver-test abnormalities in
sarcoidosis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 24:17–24. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Morán-Salvador E, López-Parra M,
García-Alonso V, Titos E, Martínez-Clemente M, González-Périz A,
López-Vicario C, Barak Y, Arroyo V and Clària J: Role for PPARγ in
obesity-induced hepatic steatosis as determined by hepatocyte- and
macrophage-specific conditional knockouts. FASEB J. 25:2538–2550.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Deng Q, Li X, Fu S, Yin L, Zhang Y, Wang
T, Wang J, Liu L, Yuan X, Sun G, et al: SREBP-1c gene silencing can
decrease lipid deposits in bovine hepatocytes cultured in vitro.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 33:1568–1578. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chang XX, Yan HM, Xu Q, Xia MF, Bian H,
Zhu TF and Gao X: The effects of berberine on hyperhomocysteinemia
and hyperlipidemia in rats fed with a long-term high-fat diet.
Lipids Health Dis. 11:862012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Benn T, Kim B, Park YK, Yang Y, Pham TX,
Ku CS, Farruggia C, Harness E, Smyth JA and Lee JY: Polyphenol-rich
blackcurrant extract exerts hypocholesterolaemic and hypoglycaemic
effects in mice fed a diet containing high fat and cholesterol. Br
J Nutr. 113:1697–1703. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhao Y, Peng L, Yang LC, Xu XD, Li WJ, Luo
XM and Jin X: Wedelolactone regulates lipid metabolism and improves
hepatic steatosis partly by AMPK Activation and Up-regulation of
expression of PPARα/LPL and LDLR. PLoS One. 10:e01327202015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|