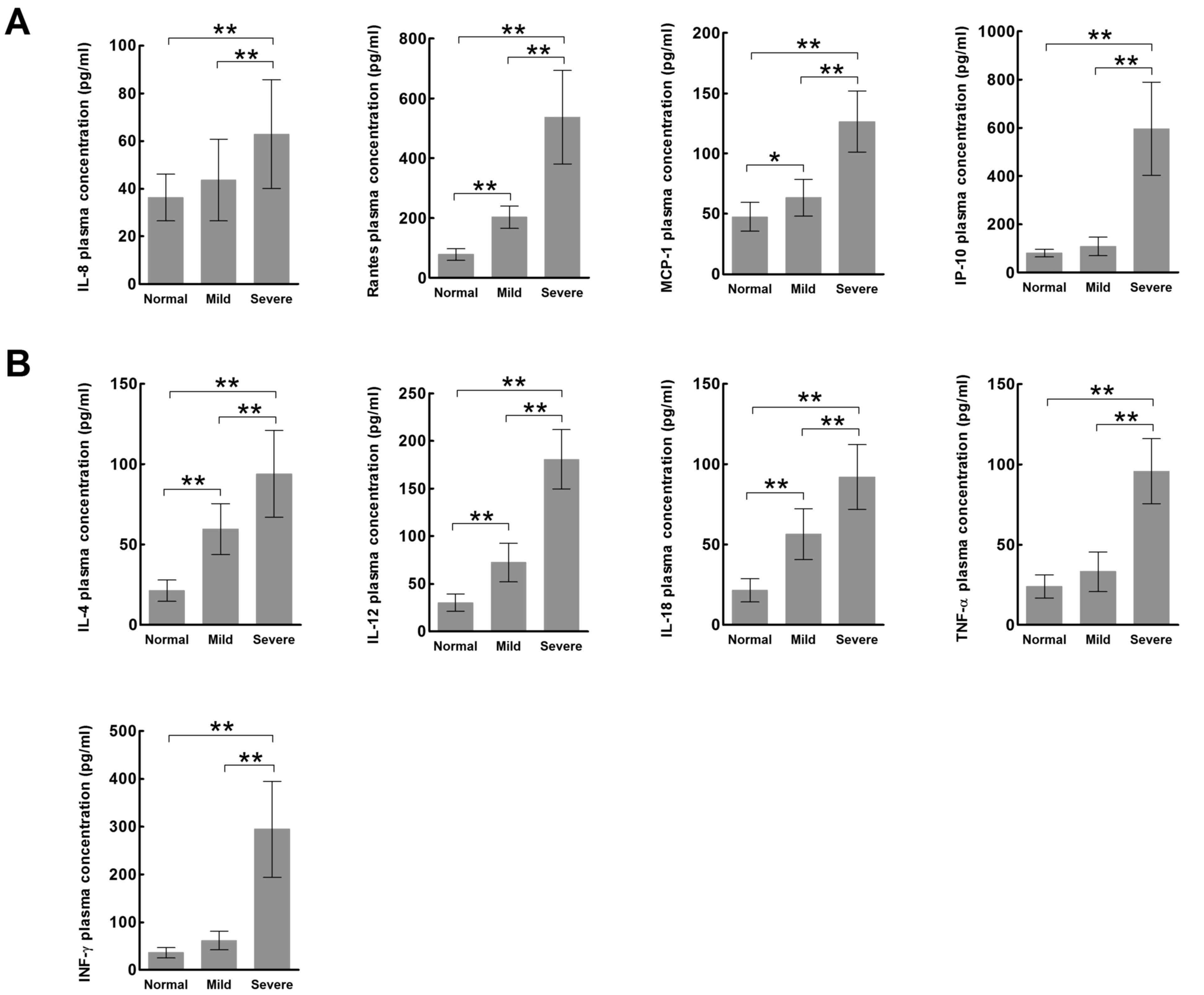
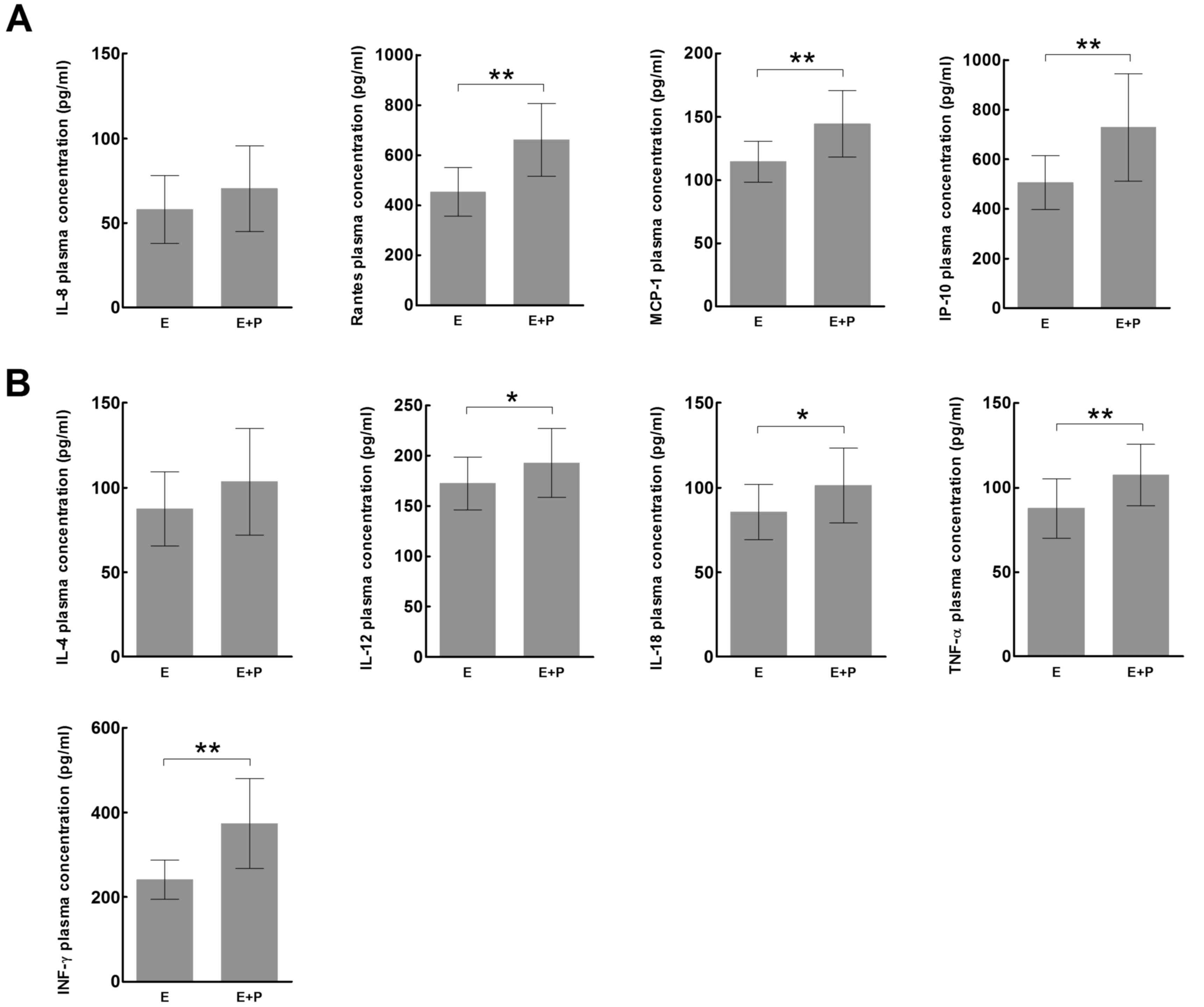
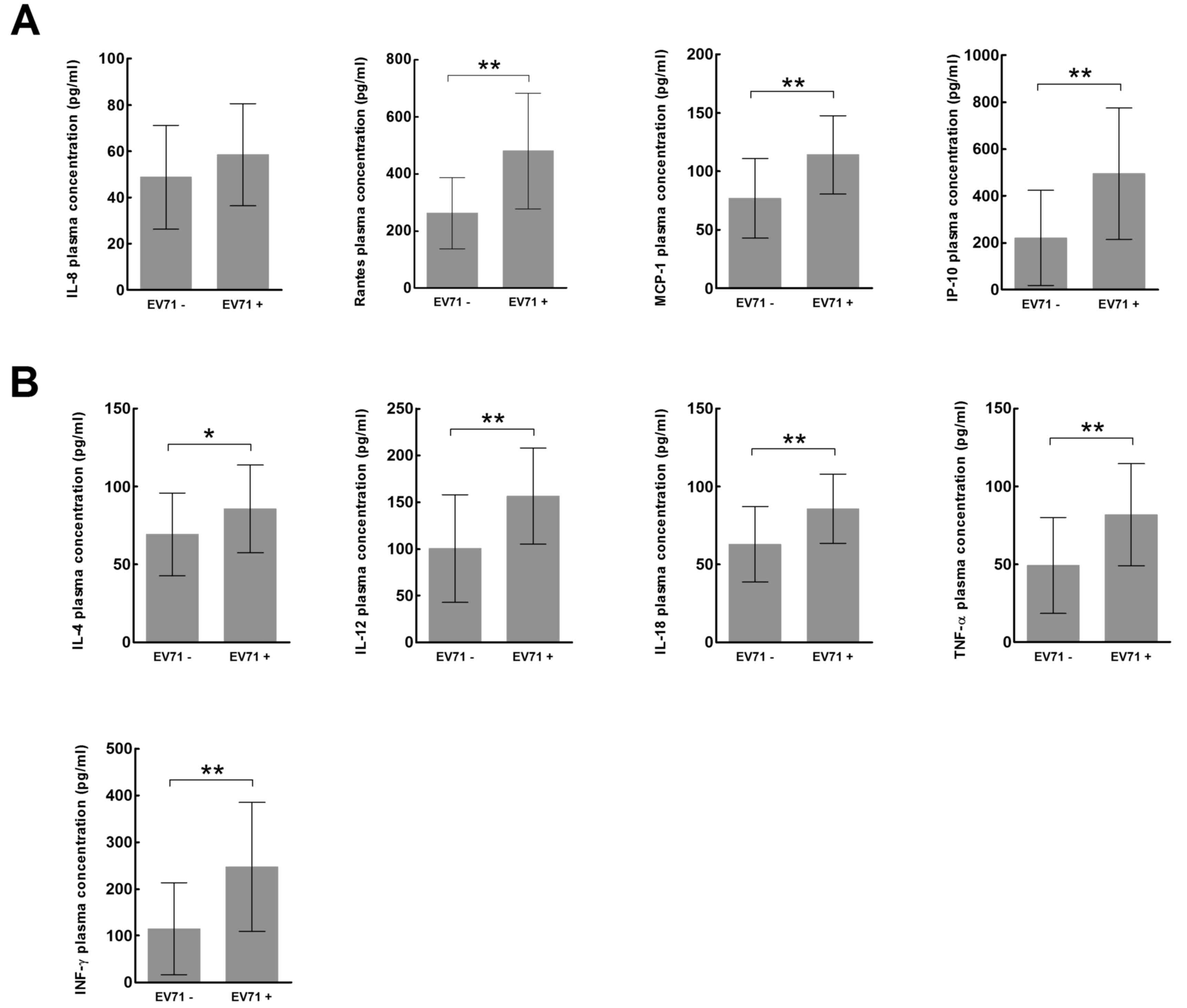
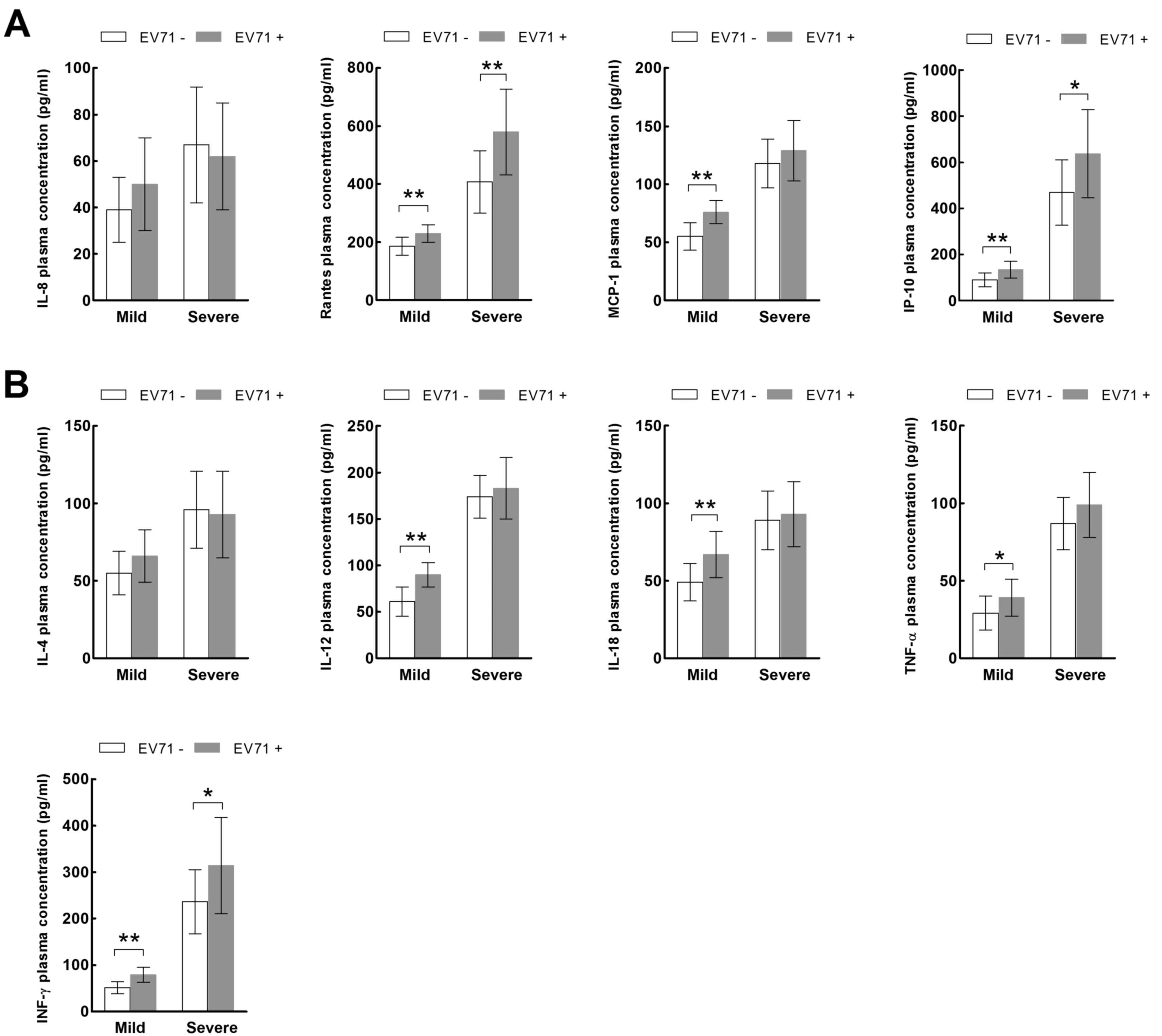
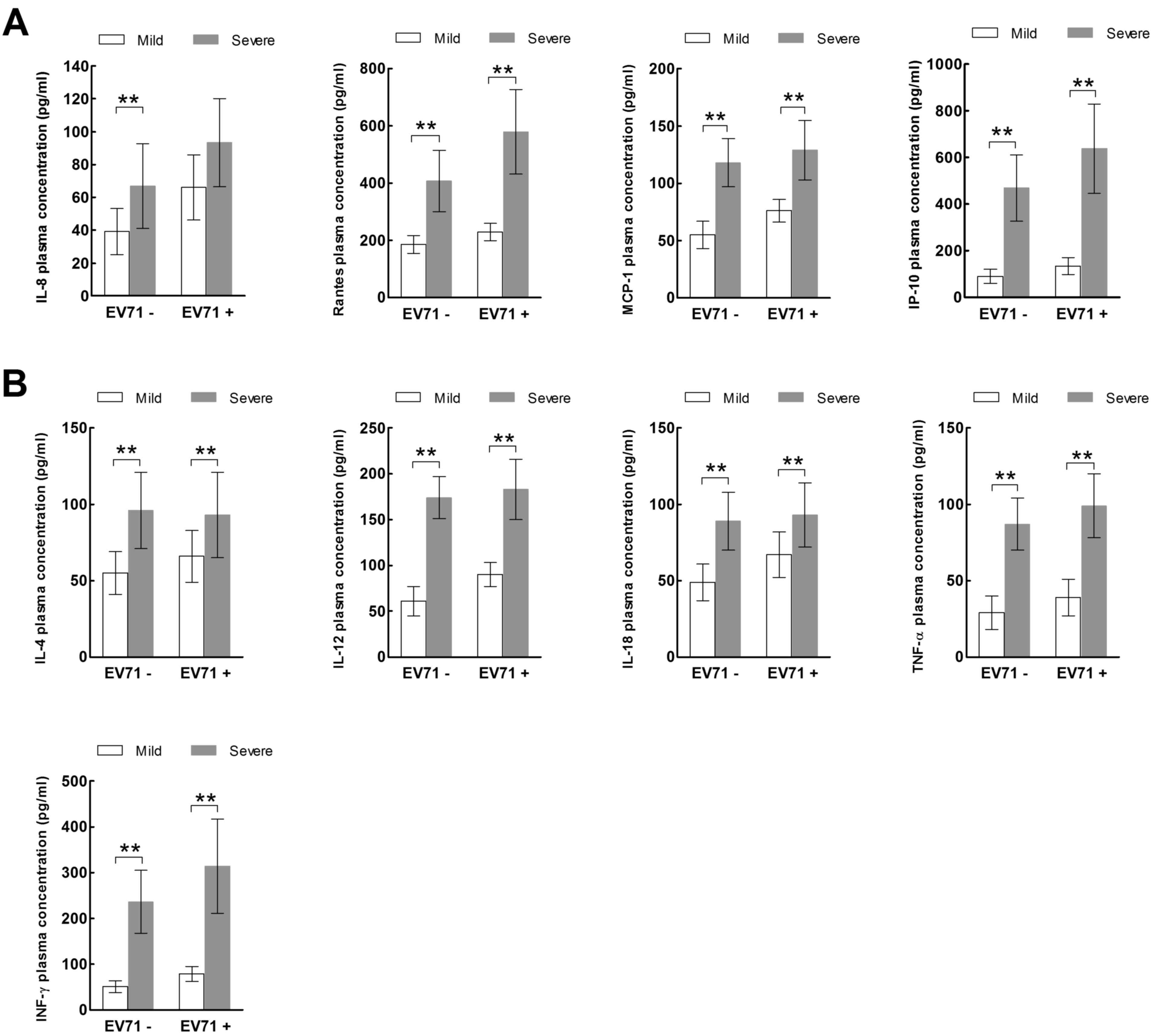
|
1
|
Huang X, Wei H, Wu S, Du Y, Liu L, Su J,
Xu Y, Wang H, Li X, Wang Y, et al: Epidemiological and etiological
characteristics of hand, foot and mouth disease in Henan, China,
2008–2013. Sci Rep. 5:89042015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Solomon T, Lewthwaite P, Perera D, Cardosa
MJ, McMinn P and Ooi MH: Virology, epidemiology, pathogenesis, and
control of enterovirus 71. Lancet Infect Dis. 10:778–790. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li J, Huo X, Dai Y, Yang Z, Lei Y, Jiang
Y, Li G, Zhan J and Zhan F: Evidences for intertypic and intratypic
recombinant events in EV71 of hand, foot and mouth disease during
an epidemic in Hubei Province, China, 2011. Virus Res. 169:195–202.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yang L, Hu J and Zhou Z: Central nervous
system damage associated with hand-foot-mouth disease induced by
enterovirus 71. J Appl Clin Pediatr. 23:1782–1785. 2008.
|
|
5
|
Ooi MH, Wong SC, Lewthwaite P, Cardosa MJ
and Solomon T: Clinical features, diagnosis, and management of
enterovirus 71. Lancet Neurol. 9:1097–1105. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
The Ministry of Health of the People's
Republic of China: Guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of
hand foot and mouth disease, Beijing, China, 2010. Int J Respir.
30:1473–1475. 2010.
|
|
7
|
Clinical Experts Group of the Ministry of
Health for Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease: Experts consensus on
rescue and treatment of severe cases with enterovirus 71 (EV71)
infection. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 49:675–678. 2011.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lin JY and Shih SR: Cell and tissue
tropism of enterovirus 71 and other enteroviruses infections. J
Biomed Sci. 21:182014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chang LY, Hsiung CA, Lu CY, Lin TY, Huang
FY, Lai YH, Chiang YP, Chiang BL, Lee CY and Huang LM: Status of
cellular rather than humoral immunity is correlated with clinical
outcome of enterovirus 71. Pediatric Res. 60:466–471. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Lin TY, Chang LY, Huang YC, Hsu KH, Chiu
CH and Yang KD: Different proinflammatory reactions in fatal and
non-fatal enterovirus 71 infections: Implications for early
recognition and therapy. Acta Paediatr. 91:632–635. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang SM, Lei HY, Yu CK, Wang JR, Su IJ and
Liu CC: Acute chemokine response in the blood and cerebrospinal
fluid of children with enterovirus 71-associated brainstem
encephalitis. J Infect Dis. 198:1002–1006. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang SM, Lei HY, Huang KJ, Wu JM, Wang JR,
Yu CK, Su IJ and Liu CC: Pathogenesis of enterovirus 71 brainstem
encephalitis in pediatric patients: Roles of cytokines and cellular
immune activation in patients with pulmonary edema. J Infect Dis.
188:564–570. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Napolitano LM: Immune stimulation in
sepsis: To be or Not to be? Chest. 127:1882–1885. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
van den Berghe G, Wouters P, Weekers F,
Verwaest C, Bruyninckx F, Schetz M, Vlasselaers D, Ferdinande P,
Lauwers P and Bouillon R: Intensive insulin therapy in the
critically ill patients. N Engl J Med. 345:1359–1367. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lekkou A, Karakantza M, Mouzaki A,
Kalfarentzos F and Gogos CA: Cytokine production and monocyte
HLA-DR expression as predictors of outcome for patients with
community-acquired severe infections. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol.
11:161–167. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wan S, Xia C and Morel L: IL-6 produced by
dendritic cell from lupus-prone mice inhibits CD4+CD25+ T cell
regulatory functions. J Immunol. 178:271–279. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Woods PS, Tazi MF, Chesarino NM, Amer AO
and Davis IC: TGF-β-induced IL-6 prevents development of acute lung
injury in influenza A virus-infected F508del CFTR-heterozygous
mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 308:L1136–L1144. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang SM, Lei HY, Huang MC, Su LY, Lin HC,
Yu CK, Wang JL and Liu CC: Modulation of cytokine production by
intravenous immunoglobnlin in patients with enterovirus
71-associated brainstem encephalitis. J Clin Viral. 37:47–52. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wang SM, Lei HY, Su LY, Wu JM, Yu CK, Wang
JR and Liu CC: Cerebrospinal fluid cytokines in enterovirus 71
brain stem encephalitis and echovirus meningitis infections of
varying severity. Clin Microbiol Infect. 13:677–682. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|