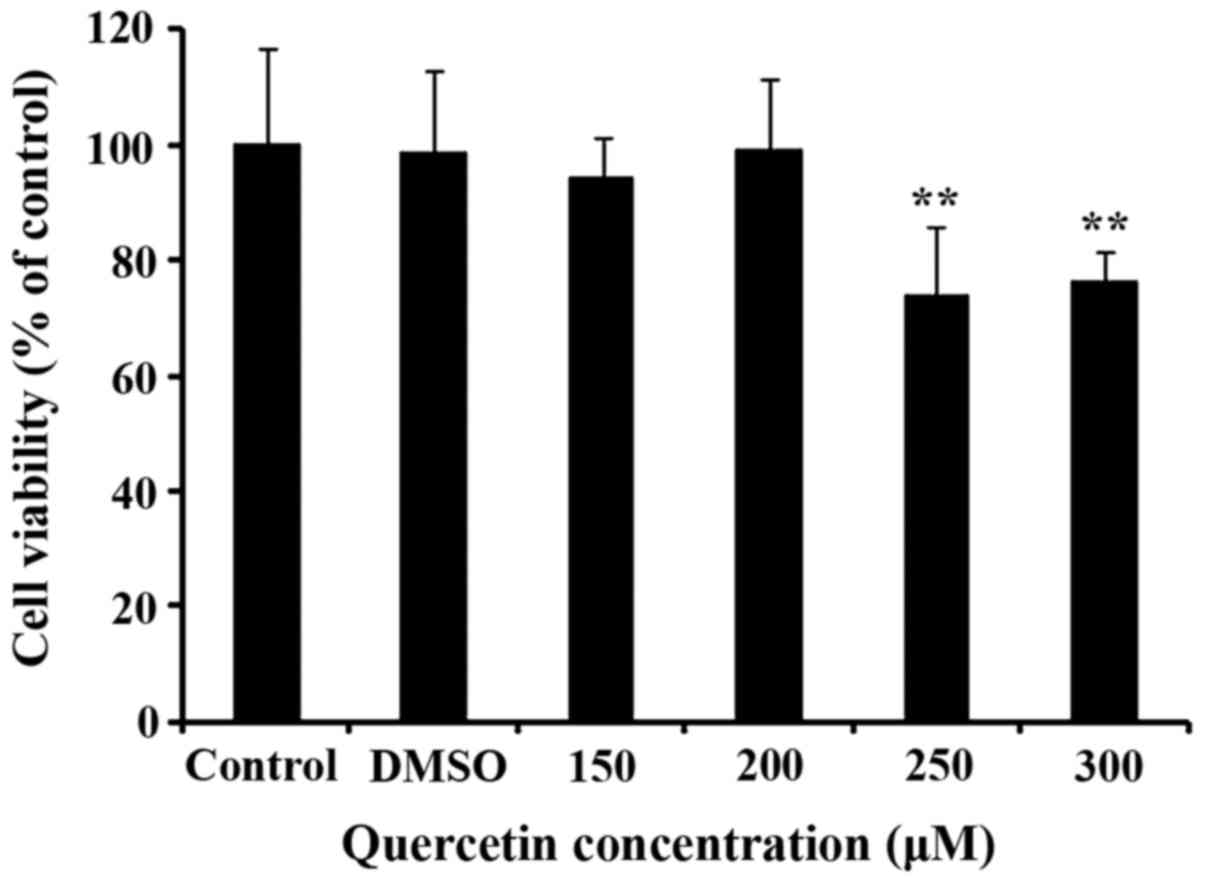
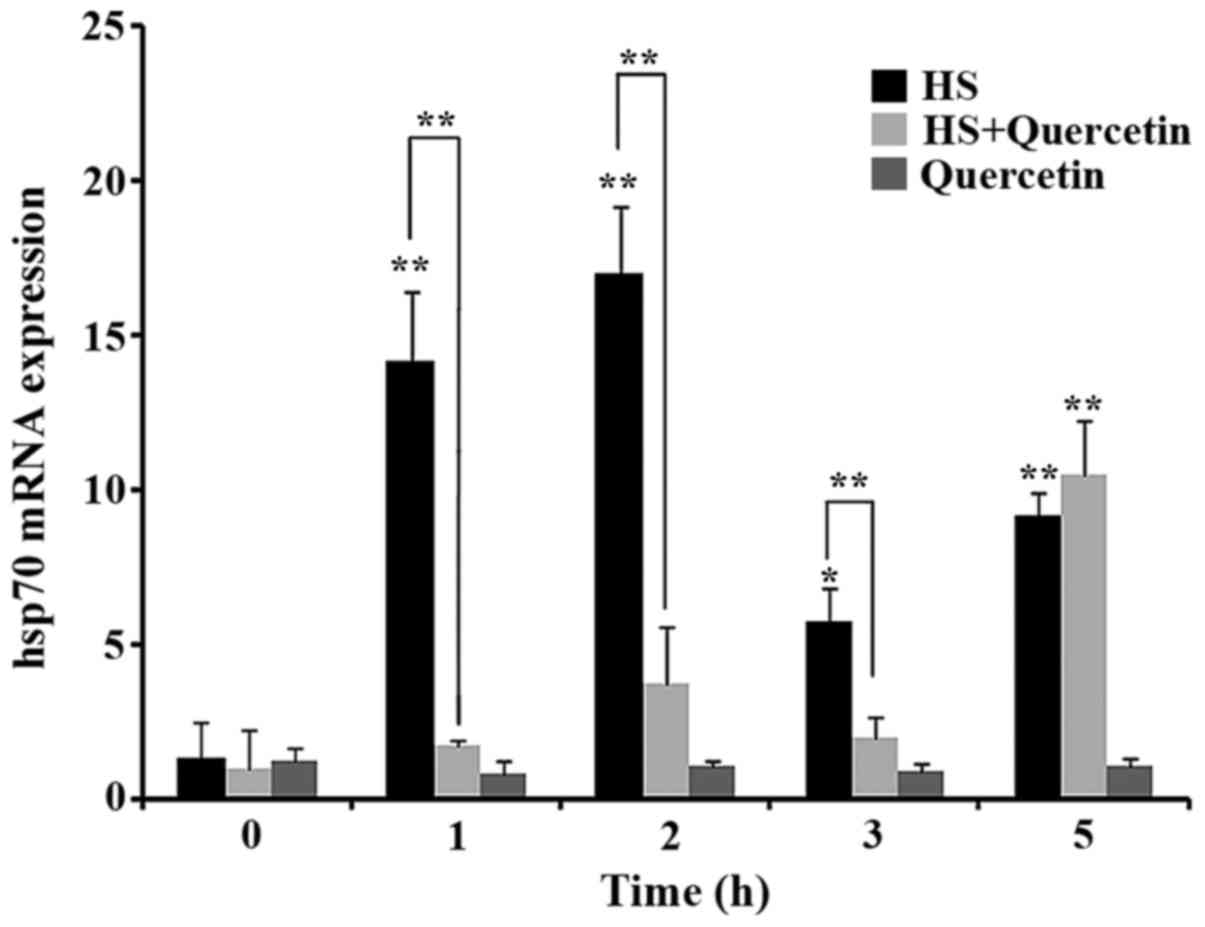
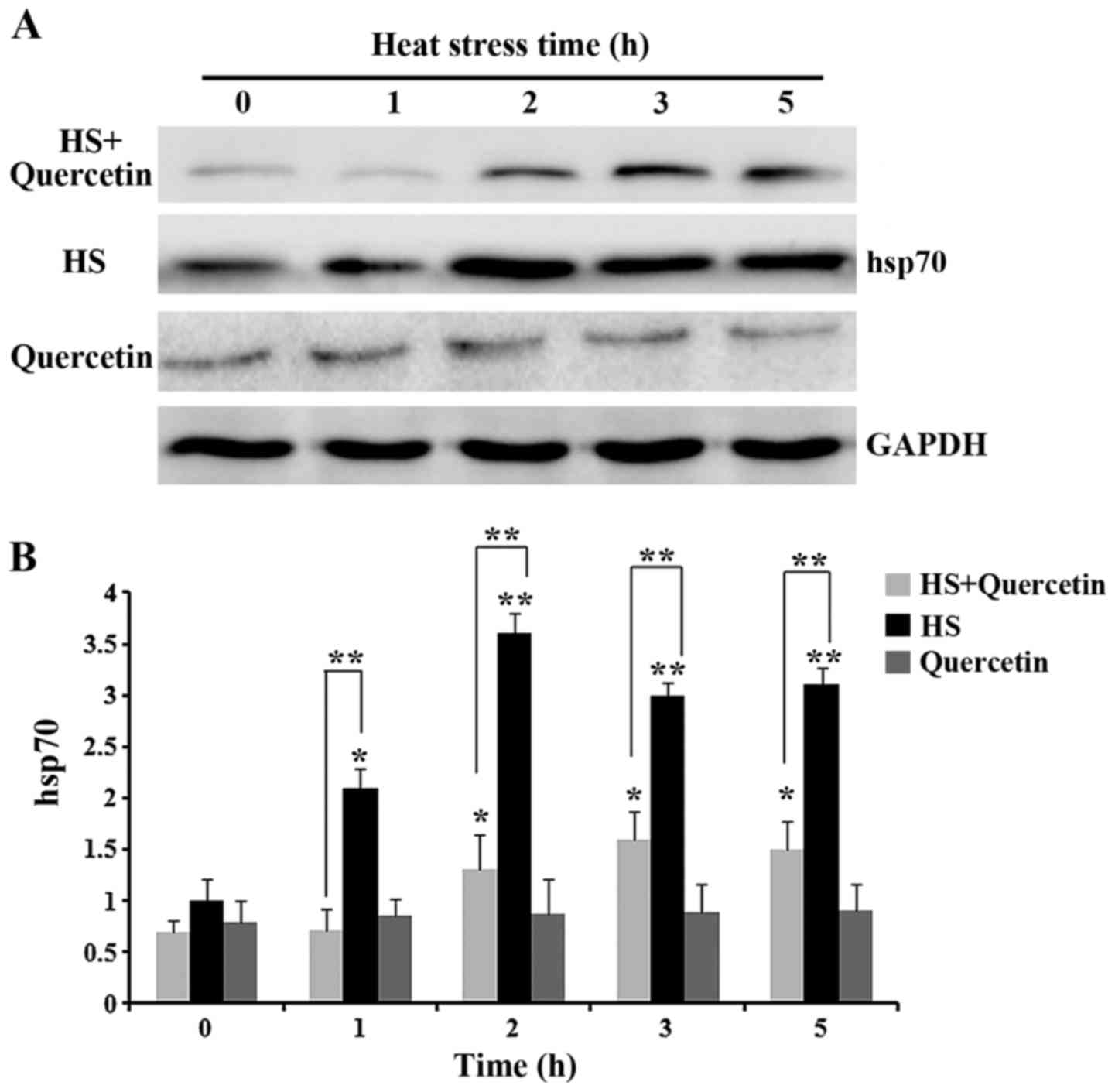
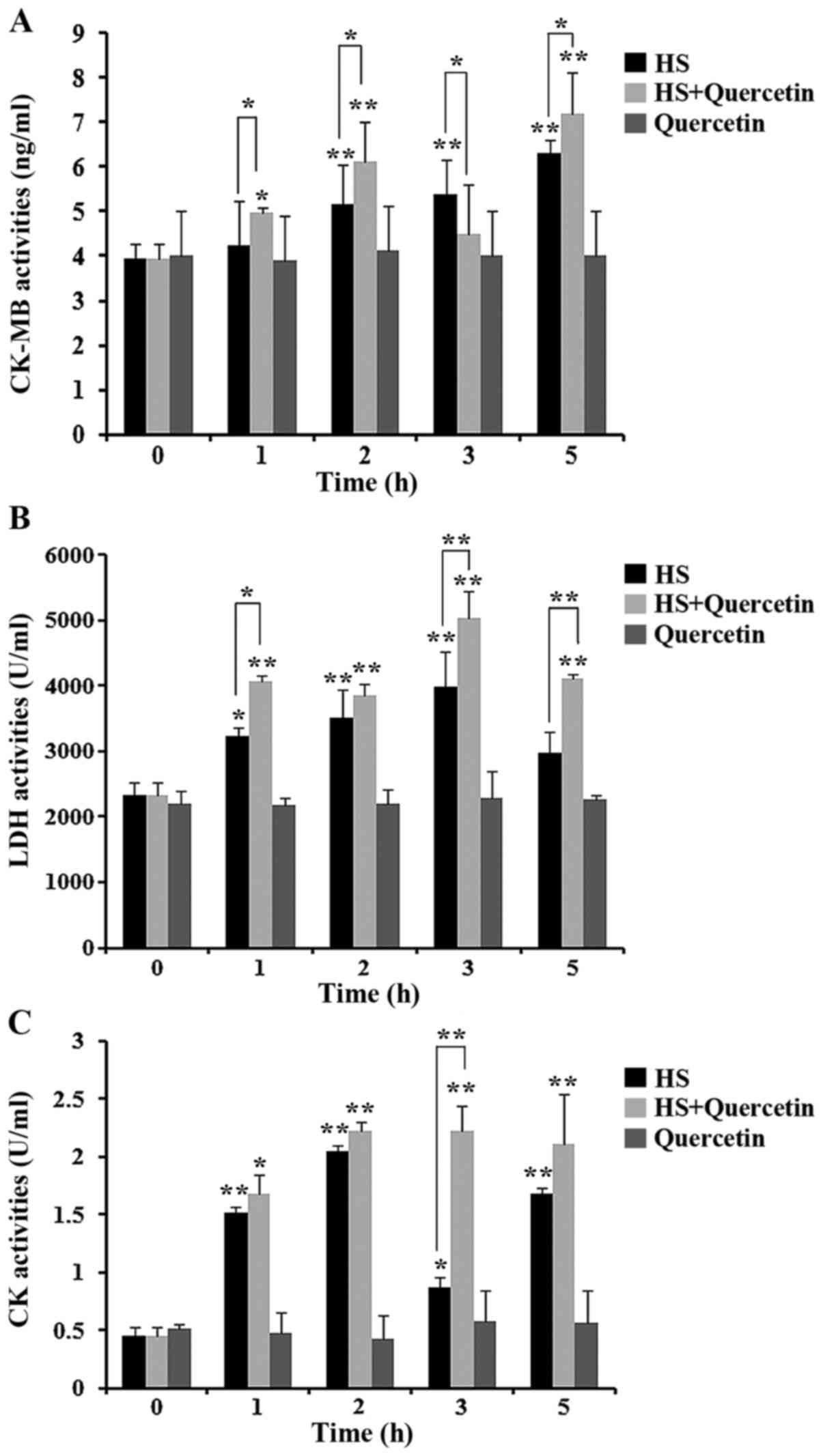
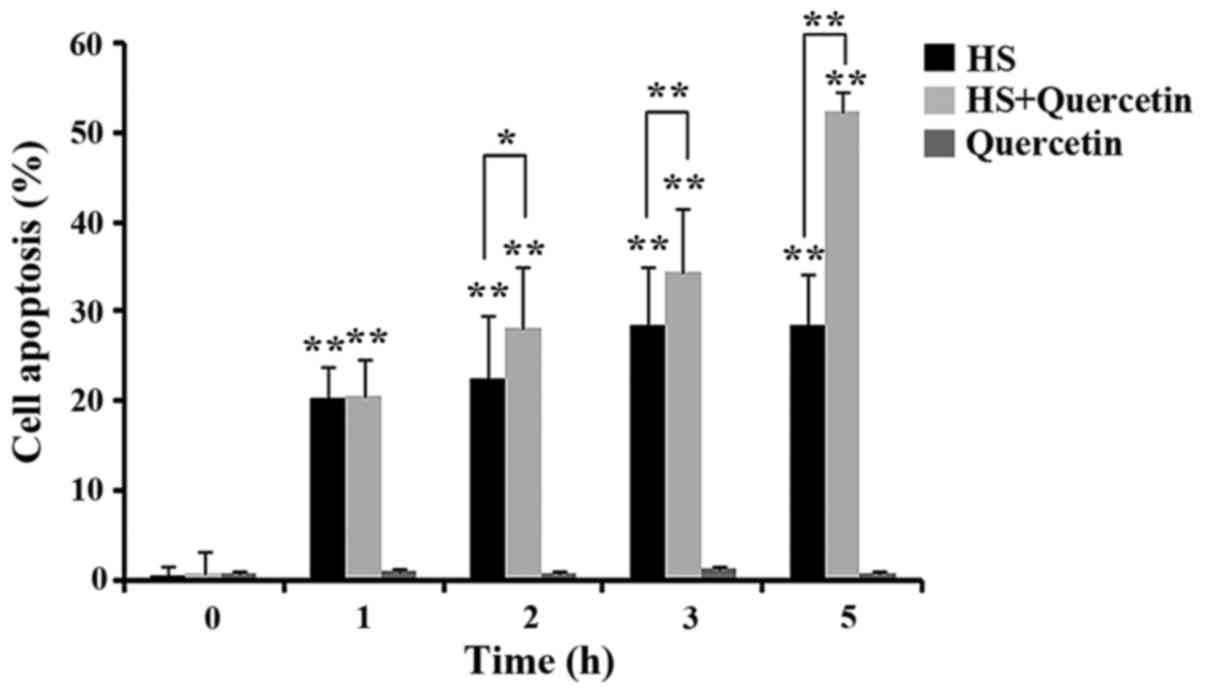
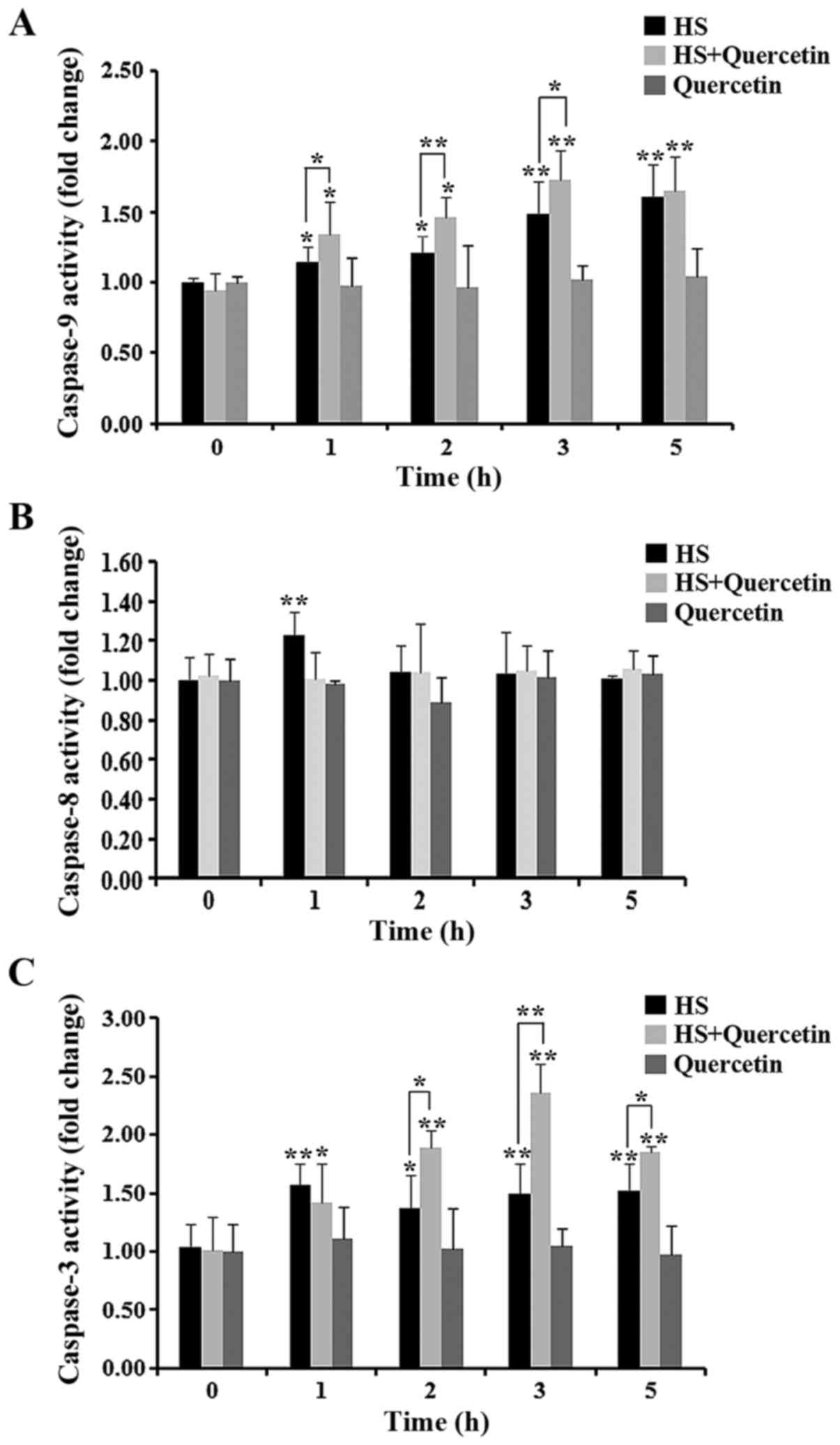
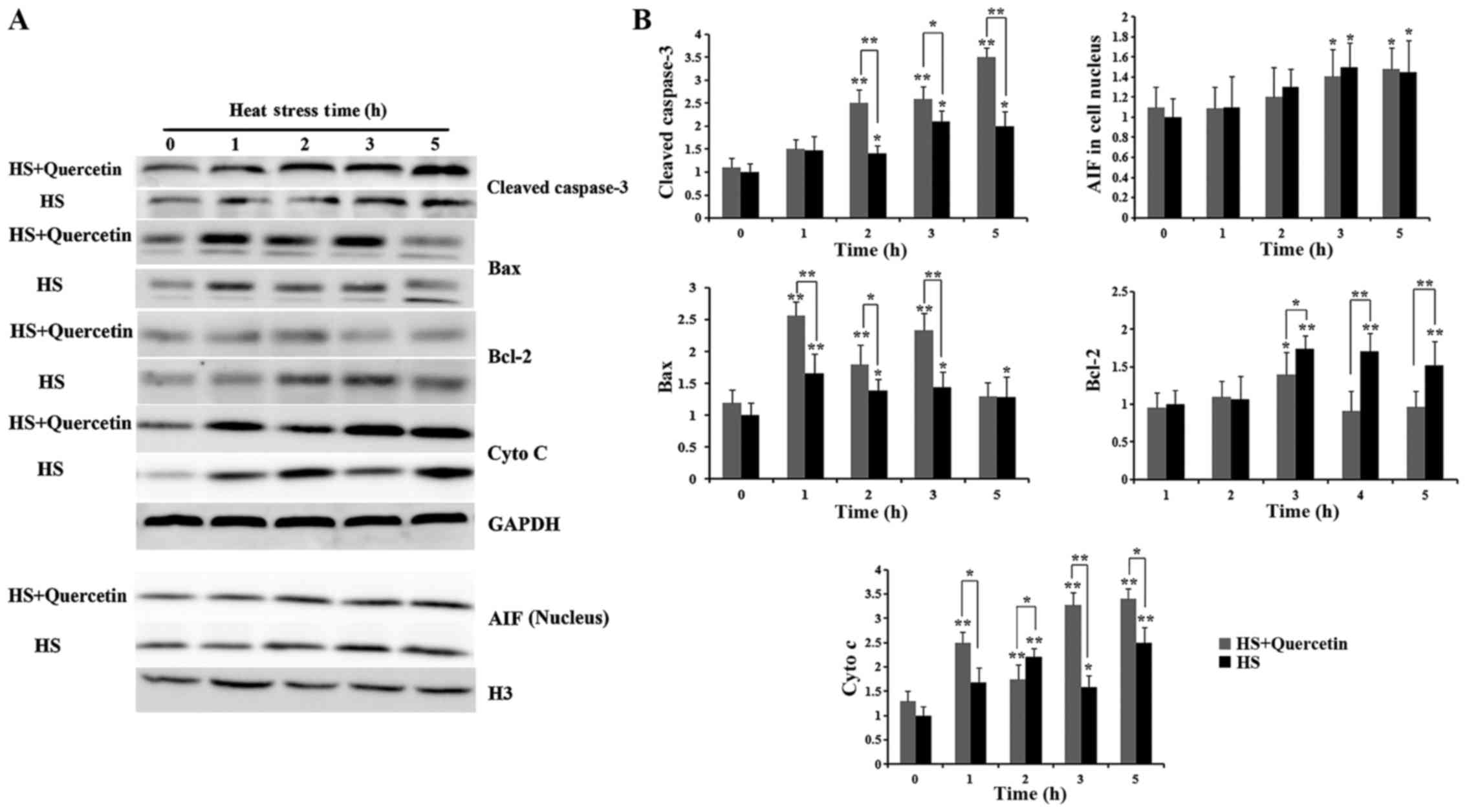
|
1
|
Selye H: A syndrome produced by diverse
nocuous agents. Nature. 138:321936. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Geraert PA, Guillaumin S and Leclercq B:
Are genetically lean broilers more resistant to hot climate? Brit
Poultry Sci. 34:643–653. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
St-Pierre NR, Cobanov B and Schnitkey G:
Economic losses from heat stress by US livestock industries. J
Dairy Sci. 86:E52–E77. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Teeter RG and Belay T: Broiler management
during acute heat stress. Anim Feed Sci Tech. 58:127–142. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
N'dri AL, Mignon-Grasteau S, Sellier N,
Beaumont C and Tixier-Boichard M: Interactions between the naked
neck gene, sex, and fluctuating ambient temperature on heat
tolerance, growth, body composition, meat quality, and sensory
analysis of slow growing meat-type broilers. Livest Sci. 110:33–45.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Gathiram P, Gaffin SL, Brock-Utne JG and
Wells MT: Time course of endotoxemia and cardiovascular changes in
heat-stressed primates. Aviat Space Environ Med. 58:1071–1074.
1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhao W, Wisniewski M, Wang W, Liu J and
Liu Y: Heat-induced oxidative injury contributes to inhibition of
Botrytis cinerea spore germination and growth. World J Microbiol
Biotechnol. 30:951–957. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gathiram P, Wells MT, Raidoo D, Brock-Utne
JG and Gaffin SL: Portal and systemic plasma lipopolysaccharide
concentrations in heat-stressed primates. Circ Shock. 25:223–230.
1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yu JM, Bao ED, Yan JY and Lei L:
Expression and localization of Hsps in the heart and blood vessel
of heat-stressed broilers. Cell Stress Chaperones. 13:327–335.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu D, Xu J, Song EB, Tang S, Zhang XH,
Kemper N, Hartung J and Bao ED: Acetyl salicylic acid protected
against heat stress damage in chicken myocardial cells and may
associate with induced Hsp27 expression. Cell Stress Chaperones.
20:687–696. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gisolfi CV, Matthes RD, Kregel KC and
Oppliger R: Splanchnic sympathetic nerve activity and circulating
catecholamines in the hyperthermic rat. J Appl Physiol (1985).
70:1821–1826. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rai UC and Ambwany P: Cardiovascular
changes during varied thermal stress. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol.
24:119–125. 1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
De Maio A: Heat shock proteins: Facts,
thoughts, and dreams. Shock. 11:1–12. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li Z and Srivastava P: Heat-shock
proteins. Curr Protoc Immunol. 58:1T:A.1T.1–A.1T.6. 2004.
|
|
15
|
Clarke AR: Molecular chaperones in protein
folding and translocation. Curr Opin Struc Biol. 6:43–50. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Young JC: Mechanisms of the Hsp70
chaperone system. Biochem Cell Biol. 88:291–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Préville X, Salvemini F, Giraud S,
Chaufour S, Paul C, Stepien G, Ursini MV and Arrigo AP: Mammalian
small stress proteins protect against oxidative stress through
their ability to increase glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
activity and by maintaining optimal cellular detoxifying machinery.
Exp Cell Res. 247:61–78. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ruddock LW and Klappa P: Oxidative stress:
Protein folding with a novel redox switch. Curr Biol. 9:R400–R402.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Song E, Tang S, Xu J, Yin B, Bao E and
Hartung J: Lenti-siRNA Hsp60 promote bax in mitochondria and
induces apoptosis during heat stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
481:125–131. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang X, Qian Z, Zhu H, Tang S, Wu D,
Zhang M, Kemper N, Hartung J and Bao E: HSP90 gene expression
induced by aspirin is associated with damage remission in a chicken
myocardial cell culture exposed to heat stress. Br Poult Sci.
57:462–473. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Duan Y, Huang S, Yang J, Niu P, Gong Z,
Liu X, Xin L, Currie W and Wu T: HspA1A facilitates DNA repair in
human bronchial epithelial cells exposed to Benzo [a] pyrene and
interacts with casein kinase 2. Cell Stress Chaperones. 19:271–279.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Beckmann RP, Mizzen LE and Welch WJ:
Interaction of Hsp 70 with newly synthesized proteins: Implications
for protein folding and assembly. Science. 248:850–854. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li SQ, Wang DM, Shu YJ, Wan XD, Xu ZS and
Li EZ: Proper heat shock pretreatment reduces acute liver injury
induced by carbon tetrachloride and accelerates liver repair in
mice. J Toxicol Pathol. 26:365–373. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Riabowol KT, Mizzen LA and Welch WJ: Heat
shock is lethal to fibroblasts microinjected with antibodies
against hsp70. Science. 242:433–436. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hutter JJ, Mestril R, Tam EK, Sievers RE,
Dillmann WH and Wolfe CL: Overexpression of heat shock protein 72
in transgenic mice decreases infarct size in vivo. Circulation.
94:1408–1411. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang X, Yuan B, Dong W, Yang B, Yang Y,
Lin X and Gong G: Induction of heat-shock protein 70 expression by
geranylgeranylacetone shows cytoprotective effects in
cardiomyocytes of mice under humid heat stress. PLos One.
9:e935362014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mailhos C, Howard MK and Latchman DS: Heat
shock protects neuronal cells from programmed cell death by
apoptosis. Neuroscience. 55:621–627. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yurinskaya MM, Mitkevich VA, Kozin SA,
Evgen'ev MB, Makarov AA and Vinokurov MG: HSP70 protects human
neuroblastoma cells from apoptosis and oxidative stress induced by
amyloid peptide isoAsp7-Aβ (1–42). Cell Death Dis. 6:e19772015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Beere HM, Wolf BB, Cain K, Mosser DD,
Mahboubi A, Kuwana T, Tailor P, Morimoto RI, Cohen GM and Green DR:
Heat-shock protein 70 inhibits apoptosis by preventing recruitment
of procaspase-9 to the Apaf-1 apoptosome. Nat Cell Biol. 2:469–475.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Saleh A, Srinivasula SM, Balkir L, Robbins
PD and Alnemri ES: Negative regulation of the Apaf-1 apoptosome by
Hsp70. Nat Cell Biol. 2:476–483. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ravagnan L, Gurbuxani S, Susin SA, Maisse
C, Daugas E, Zamzami N, Mak T, Jäättelä M, Penninger JF, Garrido C
and Kroemer G: Heat-shock protein 70 antagonizes apoptosis-inducing
factor. Nat Cell Biol. 3:839–843. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen HB, Zhang XC, Cheng YF, Abdelnasir A,
Tang S, Kemper N, Hartung J and Bao ED: Association of heat shock
protein 70 expression with rat myocardial cell damage during heat
stress in vitro and in vivo. Genet Mol Res. 14:1994–2005. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang M, Lv YJ, Yue Z, Islam A, Rehana B,
Bao E and Hartung J: Effects of transportation on expression of
Hsp90, Hsp70, Hsp27 and αB-crystallin in the pig stomach. Vet Rec.
169:3122011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Aghdassi A, Phillips P, Dudeja V,
Dhaulakhandi D, Sharif R, Dawra R, Lerch MM and Saluja A: Heat
shock protein 70 increases tumorigenicity and inhibits apoptosis in
pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 67:616–625. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Larocca LM, Ranelletti FO, Maggiano N,
Rutella S, La Barbera EO, Rumi C, Serra F, Voso MT, Piantelli M,
Teofili L and Leone G: Differential sensitivity of leukemic and
normal hematopoietic progenitors to the killing effect of
hyperthermia and quercetin used in combination: Role of heat-shock
protein-70. Int J Cancer. 73:75–83. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wei YQ, Zhao X, Kariya Y, Fukata H,
Teshigawara K and Uchida A: Induction of apoptosis by quercetin:
Involvement of heat shock protein. Cancer Res. 54:4952–4957.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kalmar B and Greensmith L: Induction of
heat shock proteins for protection against oxidative stress. Adv
Drug Deliver Rev. 61:310–318. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Marber MS, Mestril R, Chi SH, Sayen MR,
Yellon DM and Dillmann WH: Overexpression of the rat inducible
70-kD heat stress protein in a transgenic mouse increases the
resistance of the heart to ischemic injury. J Clin Invest.
95:1446–1456. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Salo DC, Donovan CM and Davies KJ: HSP70
and other possible heat shock or oxidative stress proteins are
induced in skeletal muscle, heart and liver during exercise. Free
Radic Biol Med. 11:239–246. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Skidmore R, Gutierrez JA, Guerriero V Jr
and Kregel KC: HSP70 induction during exercise and heat stress in
rats: Role of internal temperature. Am J Physiol. 268:R92–R97.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Nakanoma T, Ueno M, Iida M, Hirata R and
Deguchi N: Effects of quercetin on the heat-induced cytotoxicity of
prostate cancer cells. Int J Urol. 8:623–630. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Fujita M, Nagai M, Murata M, Kawakami K,
Irino S and Takahara J: Synergistic cytotoxic effect of quercetin
and heat treatment in a lymphoid cell line (OZ) with low HSP70
expression. Leuk Res. 21:139–145. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Haagensen L, Jensen DH and Gesser H:
Dependence of myosin-ATPase on structure bound creatine kinase in
cardiac myfibrils from rainbow trout and freshwater turtle. Comp
Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 150:404–409. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Britton CV, Hernandez A and Roberts R:
Plasma creatine kinase isoenzyme determinations in infants and
children. Characterization in normal patients and after cardiac
catheterization and surgery. Chest. 77:758–760. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhu L, Bao ED, Zhao R and Hartung J:
Expression of heat shock protein 60 in the tissues of transported
piglets. Cell Stress Chaperones. 14:61–69. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ganaie AH, Shanker G, Bumla NA, Ghasura
RS, Mir NA, Wani SA and Dudhatra GB: Biochemical and physiological
changes during thermal stress in bovines. J Vet Sci Technol.
4:10001262013.
|
|
47
|
Nisar NA, Sultana M, Waiz HA, Para PA and
Dar SA: Oxidative stress-threat to animal health and production.
Int J Livest Res. 3:76–83. 2013.
|
|
48
|
Musch MW, Kapil A and Chang EB: Heat shock
protein 72 binds and protects dihydrofolate reductase against
oxidative injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 313:185–192. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zou J, Salminen WF, Roberts SM and Voellmy
R: Correlation between glutathione oxidation and trimerization of
heat shock factor 1, an early step in stress induction of the Hsp
response. Cell Stress Chaperones. 3:130–141. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ashkenazi A and Dixit VM: Death receptors:
Signaling and modulation. Science. 281:1305–1308. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zou H, Li Y, Liu X and Wang X: An APAF-1·
cytochrome c multimeric complex is a functional apoptosome that
activates procaspase-9. J Biol Chem. 274:11549–11556. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I,
Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Alnemri ES and Wang X: Cytochrome c and
dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an
apoptotic protease cascade. Cell. 91:479–489. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Matsumori Y, Northington FJ, Hong SM,
Kayama T, Sheldon RA, Vexler ZS, Ferriero DM, Weinstein PR and Liu
J: Reduction of caspase-8 and-9 cleavage is associated with
increased c-FLIP and increased binding of Apaf-1 and Hsp70 after
neonatal hypoxic/ischemic injury in mice overexpressing Hsp70.
Stroke. 37:507–512. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Gordon SA, Abou-Jaoude W, Hoffman RA,
McCarthy SA, Kim YM, Zhou X, Zhang XR, Simmons RL, Chen Y, Schall L
and Ford HR: Nitric oxide induces murine thymocyte apoptosis by
oxidative injury and a p53-dependent mechanism. J Leukoc Biol.
70:87–95. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Fröhlich M, Jaeger A, Weiss DG and
Kriehuber R: Inhibition of BCL-2 leads to increased apoptosis and
delayed neuronal differentiation in human ReNcell VM cells in
vitro. Int J Dev Neurosci. 48:9–17. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kelly S, Zhang ZJ, Zhao H, Xu L, Giffard
RG, Sapolsky RM, Yenari MA and Steinberq GK: Gene transfer of HSP72
protects cornu ammonis 1 region of the hippocampus neurons from
global ischemia: Influence of Bcl-2. Ann Neurol. 52:160–167. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yenari MA, Liu J, Zheng Z, Vexler ZS, Lee
JE and Giffard RG: Antiapoptotic and anti-inflammatory mechanisms
of heat-shock protein protection. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1053:74–83.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Yin Y, Hawkins KL, Dweolf WC and
Morgentaler A: Heat stress causes testicular germ cell apoptosis in
adult mice. J Androl. 18:159–165. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Isom SC, Prather RS and Rucker EB III:
Heat stress-induced apoptosis in porcine in vitro fertilized and
parthenogenetic preimplantation-stage embryos. Mol Repord Dev.
74:574–581. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|