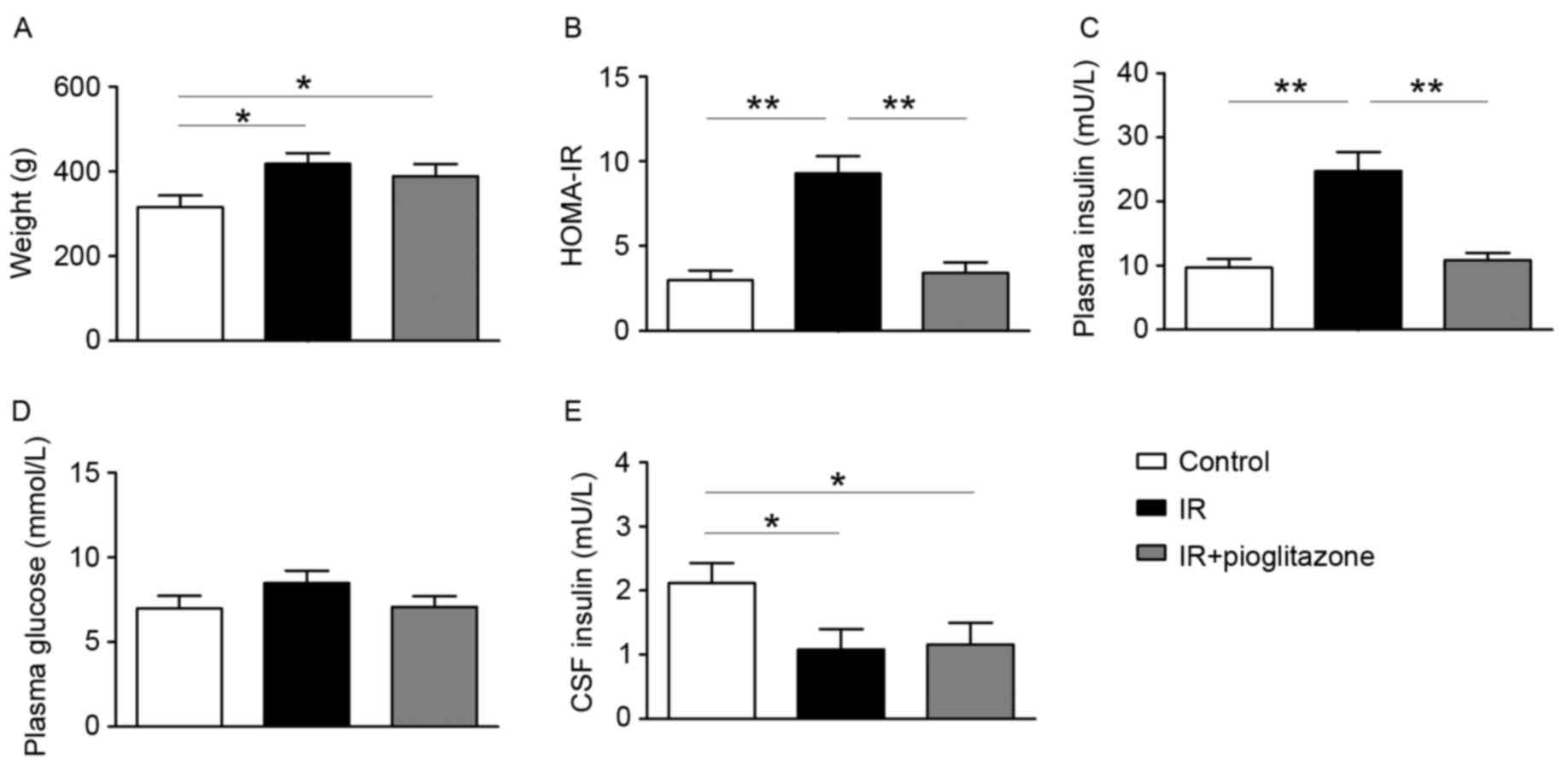
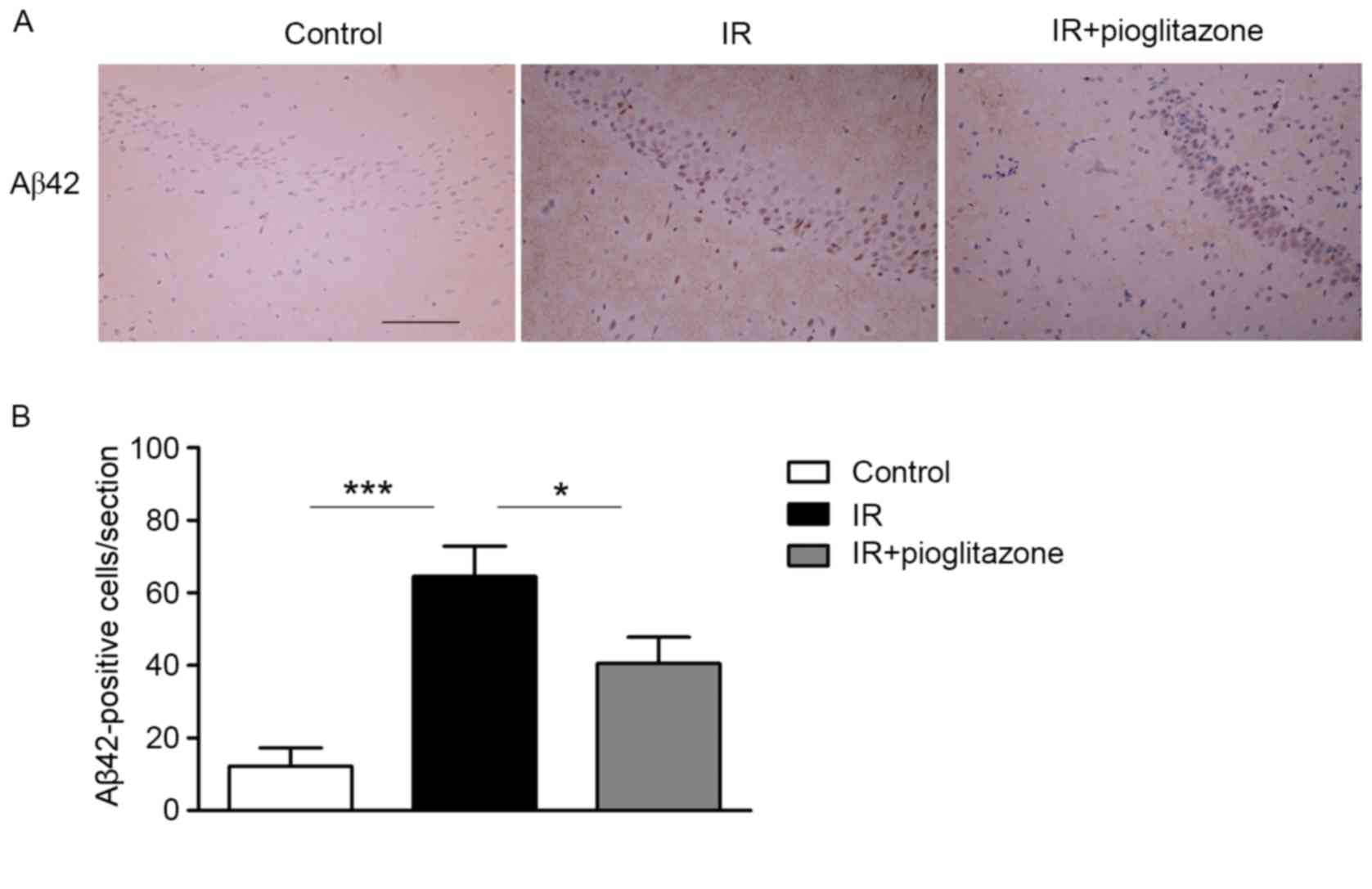
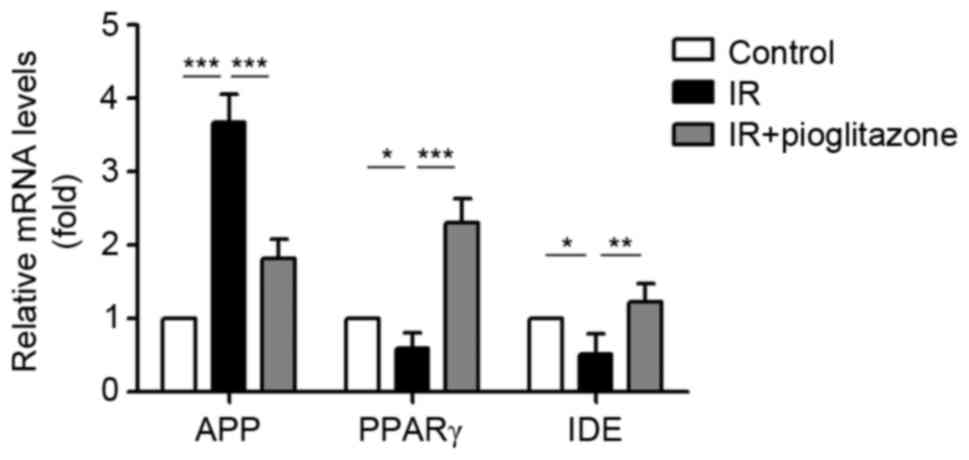
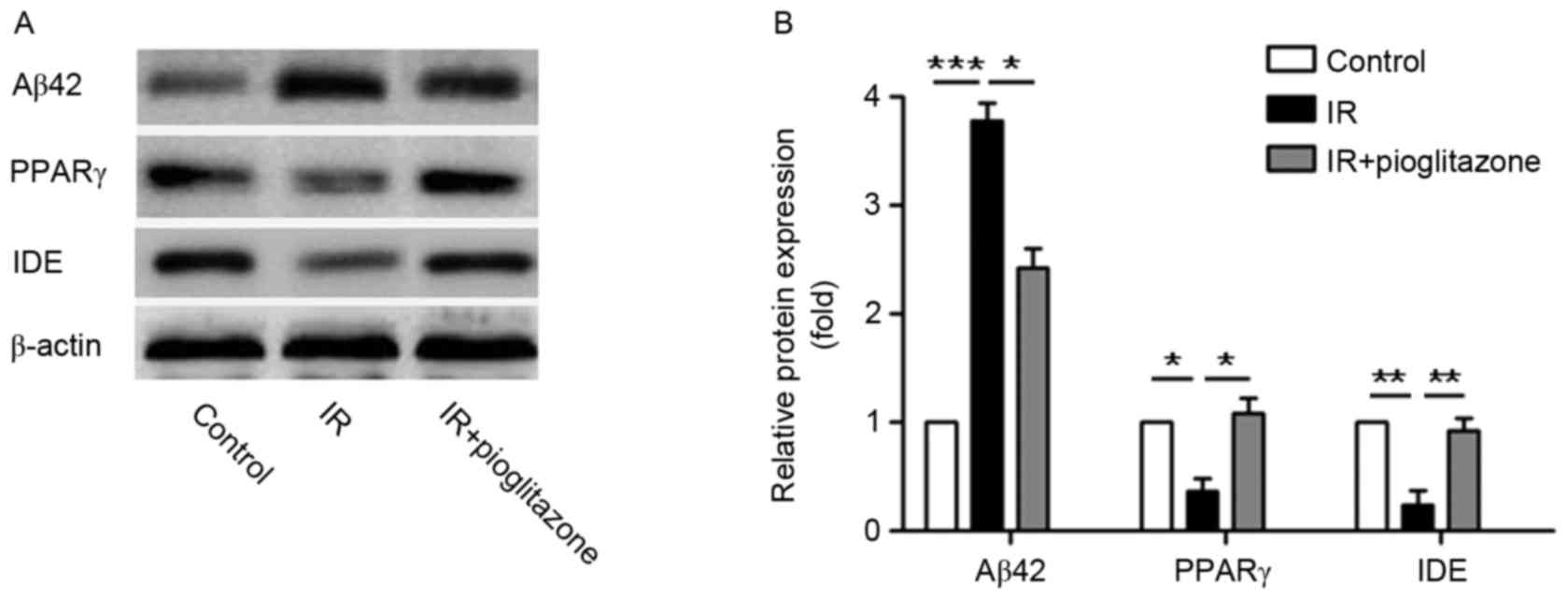
|
1
|
Musiek ES and Holtzman DM: Three
dimensions of the amyloid hypothesis: Time, space and ‘wingmen’.
Nat Neurosci. 18:800–806. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Talbot K and Wang HY: The nature,
significance, and glucagon-like peptide-1 analog treatment of brain
insulin resistance in Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 10:(1
Suppl). S12–S25. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tolppanen AM, Solomon A, Soininen H and
Kivipelto M: Midlife vascular risk factors and Alzheimer's disease:
Evidence from epidemiological studies. J Alzheimers Dis.
32:531–540. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Toda N, Ayajiki K and Okamura T:
Obesity-induced cerebral hypoperfusion derived from endothelial
dysfunction: One of the risk factors for Alzheimer's disease. Curr
Alzheimer Res. 11:733–744. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Craft S: Insulin resistance syndrome and
Alzheimer disease: Pathophysiologic mechanisms and therapeutic
implications. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 20:298–301. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang F, Song YF, Yin J, Liu ZH, Mo XD,
Wang DG, Gao LP and Jing YH: Spatial memory impairment is
associated with hippocampal insulin signals in ovariectomized rats.
PLoS One. 9:e1044502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tucsek Z, Toth P, Sosnowska D, Gautam T,
Mitschelen M, Koller A, Szalai G, Sonntag WE, Ungvari Z and Csiszar
A: Obesity in aging exacerbates blood-brain barrier disruption,
neuroinflammation, and oxidative stress in the mouse hippocampus:
Effects on expression of genes involved in beta-amyloid generation
and Alzheimer's disease. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci.
69:1212–1226. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Grasso G, Mielczarek P, Niedziolka M and
Silberring J: Metabolism of cryptic peptides derived from
neuropeptide FF precursors: The involvement of insulin-degrading
enzyme. Int J Mol Sci. 15:16787–16799. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Park SA: A common pathogenic mechanism
linking type-2 diabetes and Alzheimer's disease: Evidence from
animal models. J Clin Neurol. 7:10–18. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Baker LD, Cross DJ, Minoshima S, Belongia
D, Watson GS and Craft S: Insulin resistance and Alzheimer-like
reductions in regional cerebral glucose metabolism for cognitively
normal adults with prediabetes or early type 2 diabetes. Arch
Neurol. 68:51–57. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jolivalt CG, Lee CA, Beiswenger KK, Smith
JL, Orlov M, Torrance MA and Masliah E: Defective insulin signaling
pathway and increased glycogen synthase kinase-3 activity in the
brain of diabetic mice: Parallels with Alzheimer's disease and
correction by insulin. J Neurosci Res. 86:3265–3274. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Schubert M, Gautam D, Surjo D, Ueki K,
Baudler S, Schubert D, Kondo T, Alber J, Galldiks N, Küstermann E,
et al: Role for neuronal insulin resistance in neurodegenerative
diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:3100–3105. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Sato T, Hanyu H, Hirao K, Kanetaka H,
Sakurai H and Iwamoto T: Efficacy of PPAR-γ agonist pioglitazone in
mild Alzheimer disease. Neurobiol Aging. 32:1626–1633. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nicolakakis N, Aboulkassim T, Ongali B,
Lecrux C, Fernandes P, Rosa-Neto P, Tong XK and Hamel E: Complete
rescue of cerebrovascular function in aged Alzheimer's disease
transgenic mice by antioxidants and pioglitazone, a peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor γ agonist. J Neurosci.
28:9287–9996. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Geldmacher DS, Fritsch T, McClendon MJ and
Landreth G: A randomized pilot clinical trial of the safety of
pioglitazone in treatment of patients with Alzheimer's disease.
Arch Neuro. 68:45–50. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wang Z, Yan Z, Zhang B, Rao Z, Zhang Y,
Liu J, Yu L, Zhao Y, Yang B, Wu T and Gao J: Identification of a
5-gene signature for clinical and prognostic prediction in gastric
cancer patients upon microarray data. Med Oncol. 30:6782013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pérez MJ and Quintanilla RA: Therapeutic
actions of the thiazolidinediones in Alzheimer's disease. PPAR Res.
2015:9572482015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Craft S: Insulin resistance syndrome and
Alzheimer's disease: Age- and obesity-related effects on memory,
amyloid, and inflammation. Neurobiol Aging. 26:65–69. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sato N, Takeda S, Uchio-Yamada K, Ueda H,
Fujisawa T, Rakugi H and Morishita R: Role of insulin signaling in
the interaction between Alzheimer disease and diabetes mellitus: A
missing link to therapeutic potential. Curr Aging Sci. 4:118–127.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Najem D, Bamji-Mirza M, Chang N, Liu QY
and Zhang W: Insulin resistance, neuroinflammation, and Alzheimer's
disease. Rev Neurosci. 25:509–525. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mayeux R, Honig LS, Tang MX, Manly J,
Stern Y, Schupf N and Mehta PD: Plasma A[beta]40 and A[beta]42 and
Alzheimer's disease: Relation to age, mortality, and risk.
Neurology. 61:1185–1190. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Qiu WQ and Folstein MF: Insulin,
insulin-degrading enzyme and amyloid-beta peptide in Alzheimer's
disease: Review and hypothesis. Neurobiol Aging. 27:190–198. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Neumann KF, Rojo L, Navarrete LP, Farías
G, Reyes P and Maccioni RB: Insulin resistance and Alzheimer's
disease: Molecular links & clinical implications. Curr
Alzheimer Res. 5:438–447. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhao WQ, De Felice FG, Fernandez S, Chen
H, Lambert MP, Quon MJ, Krafft GA and Klein WL: Amyloid beta
oligomers induce impairment of neuronal insulin receprors. Faseb J.
22:246–260. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ho L, Qin W, Pompl PN, Xiang Z, Wang J,
Zhao Z, Peng Y, Cambareri G, Rocher A, Mobbs CV, et al:
Diet-induced insulin resistance promotes amyloidosis in a
transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. FASEB J. 18:902–904.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fernández-Gamba A, Leal MC, Morelli L and
Castaño EM: Insulin-degrading enzyme structure-function
relationship and its possible roles in health and disease. Curr
Pharm Des. 15:3644–3655. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Farris W, Mansourian S, Chang Y, Lindsley
L, Eckman EA, Frosch MP, Eckman CB, Tanzi RE, Selkoe DJ and
Guenette S: Insulin-degrading enzyme regulates the levels of
insulin, amyloid beta-protein, and the beta-amyloid precursor
protein intracellular domain in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:4162–4167. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bertram L, Blacker D, Mullin K, Keeney D,
Jones J, Basu S, Yhu S, McInnis MG, Go RC, Vekrellis K, et al:
Evidence for genetic linkage of Alzheimer's disease to chromosome
10q. Science. 290:2302–2303. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zahniser NR, Goens MB, Hanaway PJ and
Vinych JV: Characterization and regulation of insulin receptors in
rat brain. J Neurochem. 42:1354–1362. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cook DG, Leverenz JB, McMillan PJ, Kulstad
JJ, Ericksen S, Roth RA, Schellenberg GD, Jin LW, Kovacina KS and
Craft S: Reduced hippocampal insulin-degrading enzyme in late-onset
Alzheimer's disease is associated with the apolipoprotein E-epsilon
4 allele. Am J Pathol. 162:313–319. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen J, Li S, Sun W and Li J:
Anti-diabetes drug pioglitazone ameliorates synaptic defects in AD
transgenic mice by inhibiting cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activity.
PLoS One. 10:e01238642015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yin QQ, Pei JJ, Xu S, Luo DZ, Dong SQ, Sun
MH, You L, Sun ZJ and Liu XP: Pioglitazone improves cognitive
function via increasing insulin sensitivity and strengthening
antioxidant defense system in fructose-drinking insulin resistance
rats. PLoS One. 8:e593132013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Searcy JL, Phelps JT, Pancani T, Kadish I,
Popovic J, Anderson KL, Beckett TL, Murphy MP, Chen KC, Blalock EM,
et al: Long-term pioglitazone treatment improves learning and
attenuates pathological markers in a mouse model of Alzheimer's
disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 30:943–961. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lee HK, Kumar P, Fu Q, Rosen KM and
Querfurth HW: The insulin/Akt signaling pathway is targeted by
intracellular beta-amyloid. Mol Biol Cell. 20:1533–1544. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhu X, Wang S, Yu L, Yang H, Tan R, Yin K,
Jin J, Zhao H, Guan D and Xu Y: TL-2 attenuates β-amyloid induced
neuronal apoptosis through the AKT/GSK-3β/β-catenin pathway. Int J
Neuropsychopharmacol. 17:1511–1519. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kwon KJ, Kim HJ, Shin CY and Han SH:
Melatonin potentiates the neuroprotective properties of resveratrol
against beta-amyloid-induced neurodegeneration by modulating
AMP-activated protein kinase pathways. J Clin Neurol. 6:127–137.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|