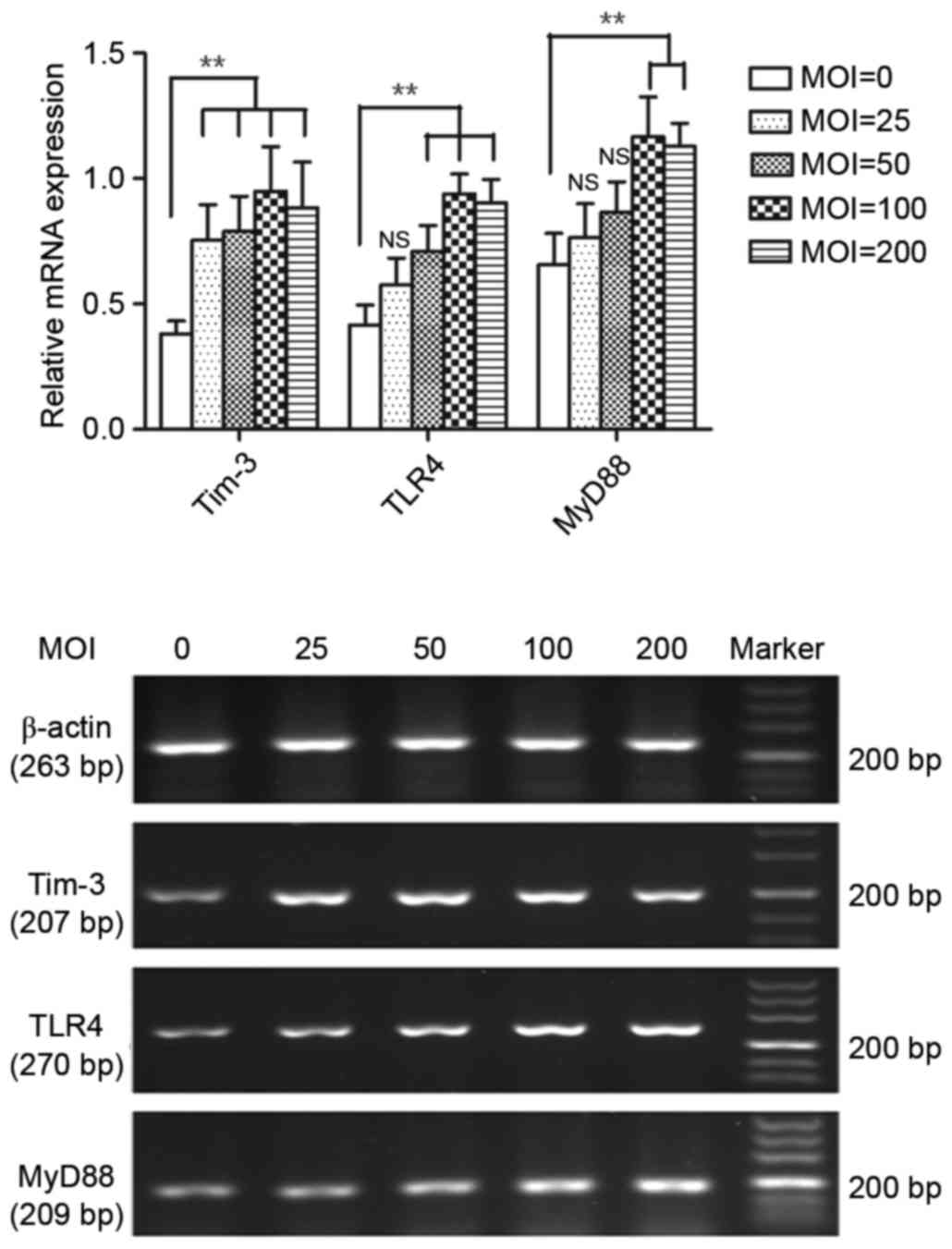
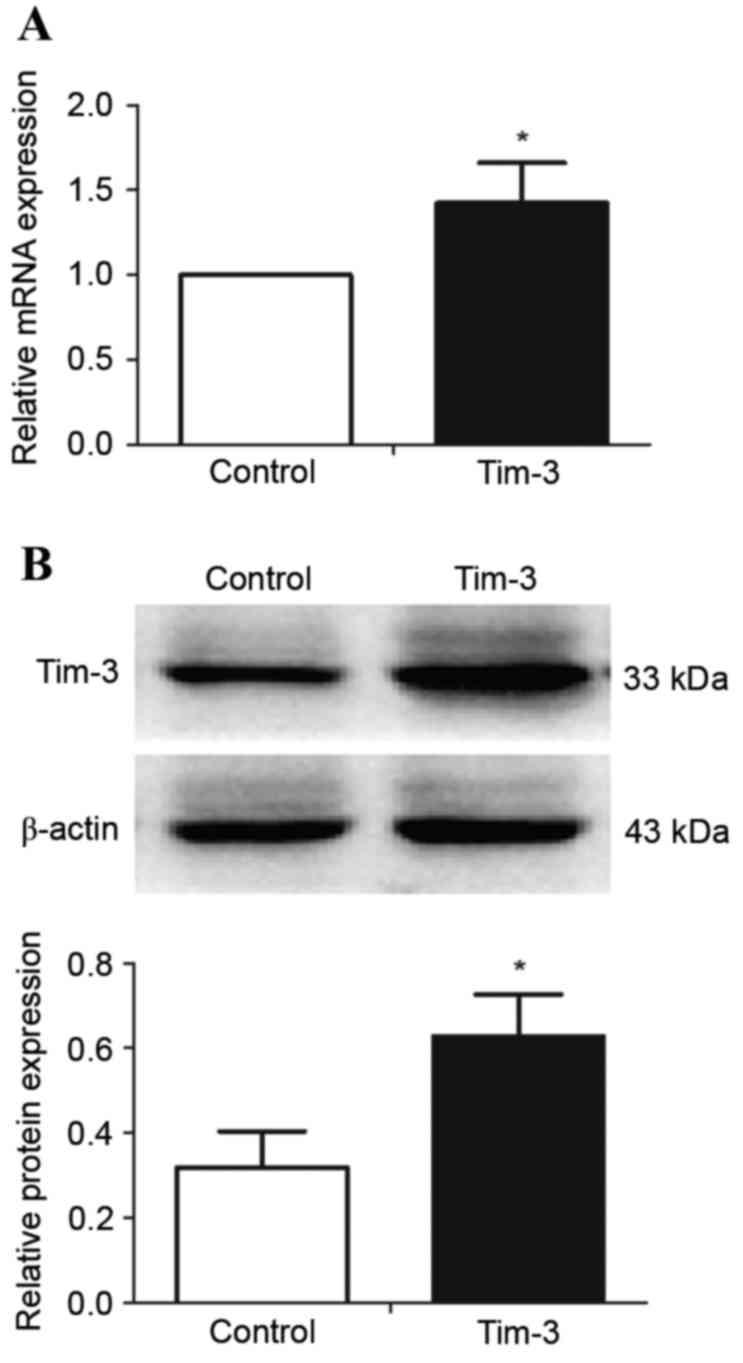
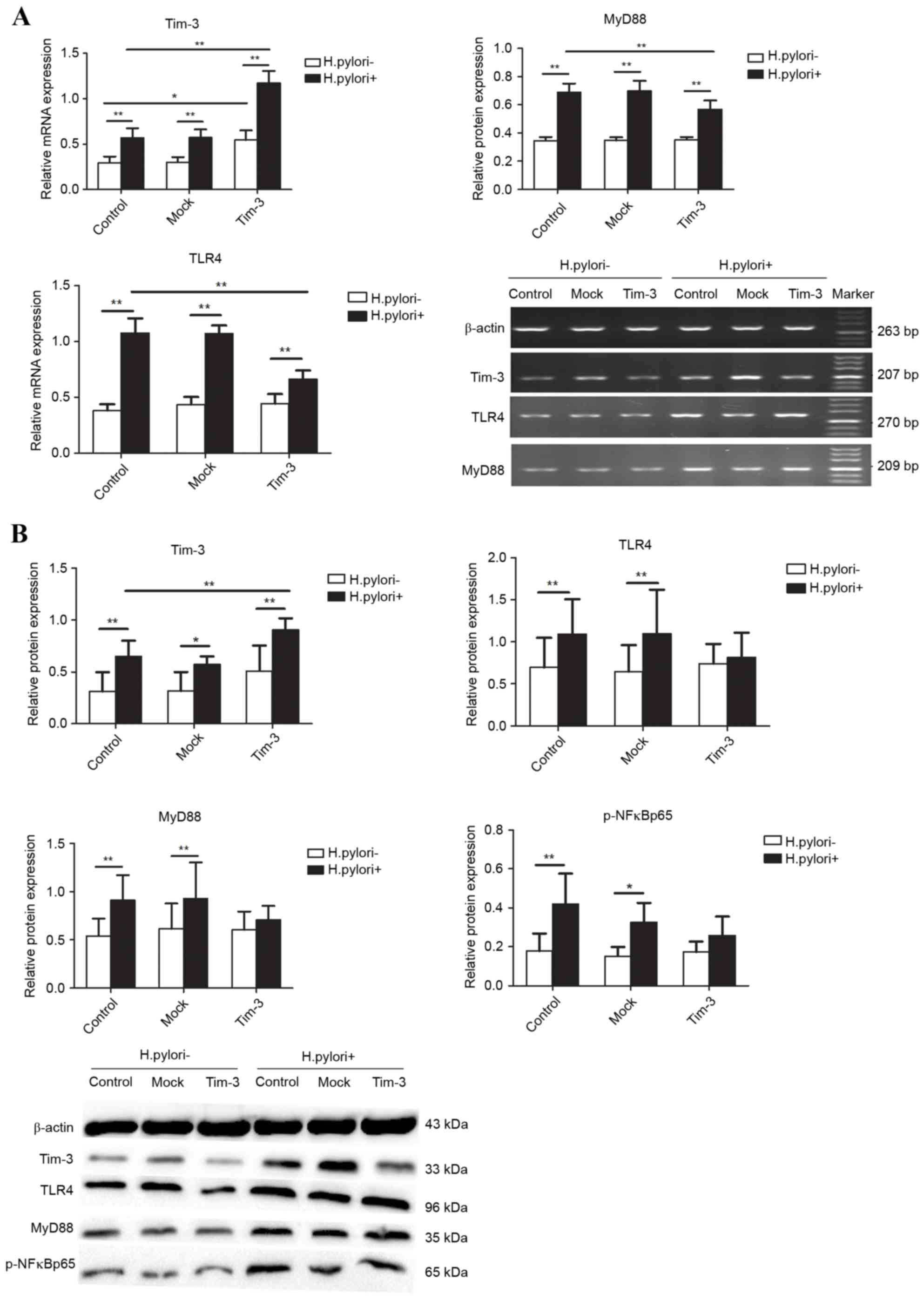
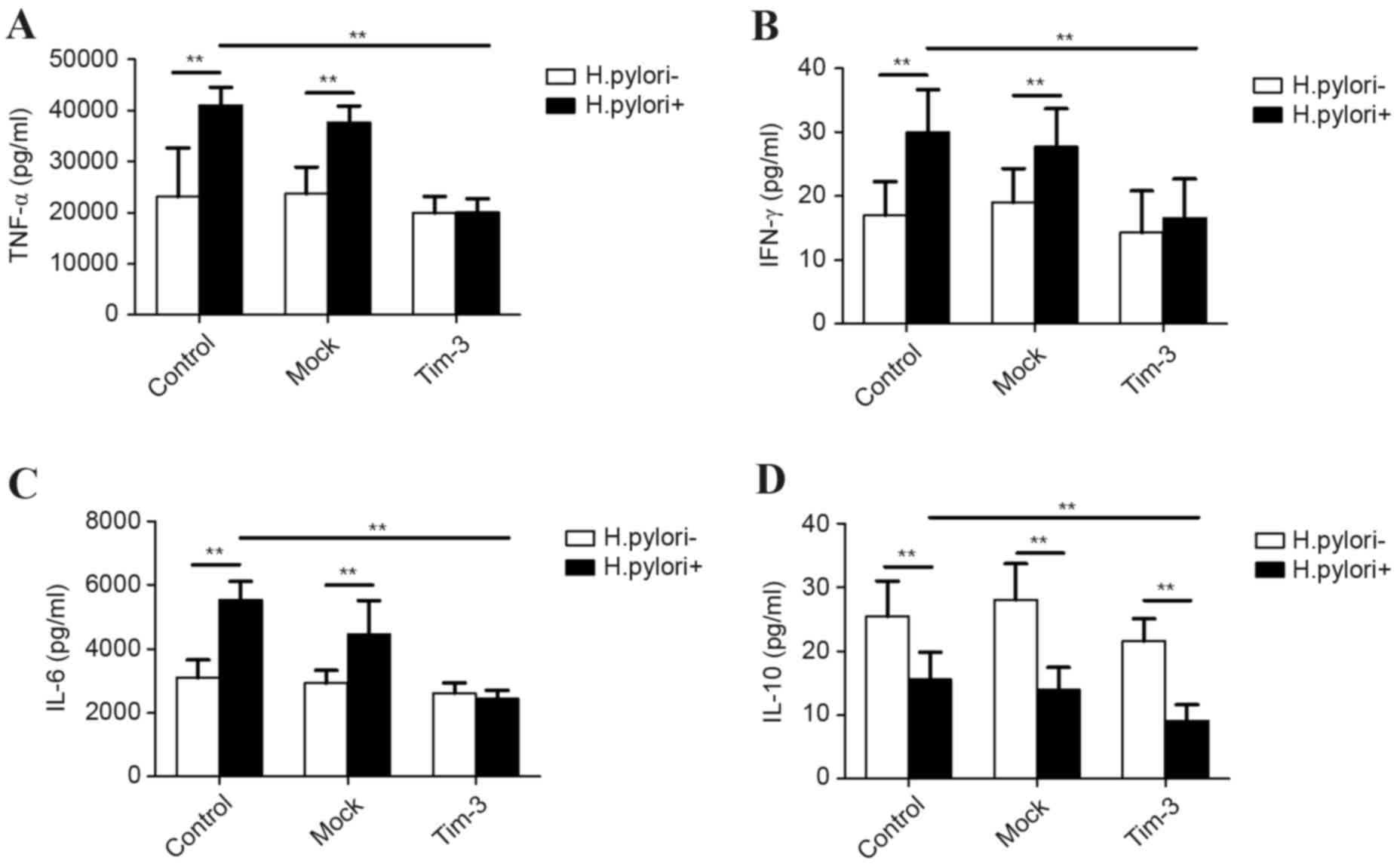
|
1
|
Koch M, Meyer TF and Moss SF:
Inflammation, immunity, vaccines for Helicobacter pylori infection.
Helicobacter. 18:(Suppl 1). S18–S23. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Demiray E and Bekmen N: Helicobacter
pylori infection and phagocytosis. Mikrobiyol Bul. 42:177–184.
2008.(In Turkish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Duque Arango G and Descoteaux A:
Macrophage cytokines: Involvement in immunity and infectious
diseases. Front Immunol. 5:4912014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rad R, Ballhorn W, Voland P, Eisenächer K,
Mages J, Rad L, Ferstl R, Lang R, Wagner H, Schmid RM, et al:
Extracellular and intracellular pattern recognition receptors
cooperate in the recognition of Helicobacter pylori.
Gastroenterology. 136:2247–2257. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Freeman GJ, Casasnovas JM, Umetsu DT and
DeKruyff RH: TIM genes: A family of cell surface phosphatidylserine
receptors that regulate innate and adaptive immunity. Immunol Rev.
235:172–189. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mariat C, Sánchez-Fueyo A, Alexopoulos SP,
Kenny J, Strom TB and Zheng XX: Regulation of T cell dependent
immune responses by TIM family members. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B
Biol Sci. 360:1681–1685. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Monney L, Sabatos CA, Gaglia JL, Ryu A,
Waldner H, Chernova T, Manning S, Greenfield EA, Coyle AJ, Sobel
RA, et al: Th1-specific cell surface protein Tim-3 regulates
macrophage activation and severity of an autoimmune disease.
Nature. 415:536–541. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Khademi M, Illés Z, Gielen AW, Marta M,
Takazawa N, Baecher-Allan C, Brundin L, Hannerz J, Martin C, Harris
RA, et al: T Cell Ig- and mucin-domain-containing molecule-3
(TIM-3) and TIM-1 molecules are differentially expressed on human
Th1 and Th2 cells and in cerebrospinal fluid-derived mononuclear
cells in multiple sclerosis. J Immunol. 172:7169–7176. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yang X, Jiang X, Chen G, Xiao Y, Geng S,
Kang C, Zhou T, Li Y, Guo X, Xiao H, et al: T cell Ig mucin-3
promotes homeostasis of sepsis by negatively regulating the TLR
response. J Immunol. 190:2068–2079. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Uchida Y, Ke B, Freitas MC, Yagita H,
Akiba H, Busuttil RW, Najafian N and Kupiec-Weglinski JW: T-cell
immunoglobulin mucin-3 determines severity of liver
ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice in a TLR4-dependent manner.
Gastroenterology. 139:2195–2206. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Frisancho-Kiss S, Davis SE, Nyland JF,
Frisancho JA, Cihakova D, Barrett MA, Rose NR and Fairweather D:
Cutting edge: Cross-regulation by TLR4 and T cell Ig mucin-3
determines sex differences in inflammatory heart disease. J
Immunol. 178:6710–6714. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Schumacher MA, Donnelly JM, Engevik AC,
Xiao C, Yang L, Kenny S, Varro A, Hollande F, Samuelson LC and
Zavros Y: Gastric sonic hedgehog acts as a macrophage
chemoattractant during the immune response to Helicobacter pylori.
Gastroenterology. 142:1150–1159.e6. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Deen NS, Gong L, Naderer T, Devenish RJ
and Kwok T: Analysis of the relative contribution of phagocytosis,
LC3-associated phagocytosis, and canonical autophagy during
helicobacter pylori infection of macrophages. Helicobacter.
20:449–459. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang Y, Lu Y, Ma L, Cao X, Xiao J, Chen
J, Jiao S, Gao Y, Liu C, Duan Z, et al: Activation of vascular
endothelial growth factor receptor-3 in macrophages restrains
TLR4-NF-κB signaling and protects against endotoxin shock.
Immunity. 40:501–514. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Byun EB, Sung NY, Byun EH, Song DS, Kim
JK, Park JH, Song BS, Park SH, Lee JW, Byun MW and Kim JH: The
procyanidin trimer C1 inhibits LPS-induced MAPK and NF-κB signaling
through TLR4 in macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol. 15:450–456. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Käbisch R, Mejias-Luque R, Gerhard M and
Prinz C: Involvement of toll-like receptors on Helicobacter
pylori-induced immunity. PLoS One. 9:e1048042014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Su YL, Yang JC, Lee H, Sheu F, Hsu CH, Lin
SL and Chow LP: The C-terminal disulfide bonds of Helicobacter
pylori GroES are critical for IL-8 secretion via the TLR4-dependent
pathway in gastric epithelial cells. J Immunol. 194:3997–4007.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fujihara M, Muroi M, Tanamoto K, Suzuki T,
Azuma H and Ikeda H: Molecular mechanisms of macrophage activation
and deactivation by lipopolysaccharide: Roles of the receptor
complex. Pharmacol Ther. 100:171–194. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pathak SK, Basu S, Bhattacharyya A, Pathak
S, Banerjee A, Basu J and Kundu M: TLR4-dependent NF-kappaB
activation and mitogen- and stress-activated protein kinase
1-triggered phosphorylation events are central to Helicobacter
pylori peptidyl prolyl cis-, trans-isomerase (HP0175)-mediated
induction of IL-6 release from macrophages. J Immunol.
177:7950–7958. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Maeda S, Akanuma M, Mitsuno Y, Hirata Y,
Ogura K, Yoshida H, Shiratori Y and Omata M: Distinct mechanism of
Helicobacter pylori-mediated NF-kappa B activation between gastric
cancer cells and monocytic cells. J Biol Chem. 276:44856–44864.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mandell L, Moran AP, Cocchiarella A,
Houghton J, Taylor N, Fox JG, Wang TC and Kurt-Jones EA: Intact
gram-negative Helicobacter pylori, Helicobacter felis, and
Helicobacter hepaticus bacteria activate innate immunity via
toll-like receptor 2 but not toll-like receptor 4. Infect Immun.
72:6446–6454. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Anderson DE: TIM-3 as a therapeutic target
in human inflammatory diseases. Expert Opin Ther Targets.
11:1005–1009. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang Y, Ma CJ, Wang JM, Ji XJ, Wu XY,
Moorman JP and Yao ZQ: Tim-3 regulates pro- and anti-inflammatory
cytokine expression in human CD14+ monocytes. J Leukoc Biol.
91:189–196. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hu S, Xie Y, Zhou N, Jin L, Tan Y, Liu D,
Gong Y, Liu L, Liu J, Liu W, et al: Expression of T-cell
immunoglobulin- and mucin-domain-containing molecules-1 and −3
(Tim-1 and Tim-3) in Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter.
16:373–381. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gong Y, Tao L, Wang F, Liu W, Jing L, Liu
D, Hu S, Xie Y and Zhou N: Chitosan as an adjuvant for a
Helicobacter pylori therapeutic vaccine. Mol Med Rep. 12:4123–4132.
2015.v. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li SP, Chen XJ, Sun AH, Zhao JF and Yan J:
CagA(+) H. pylori induces Akt1 phosphorylation and inhibits
transcription of p21(WAF1/CIP1) and p27(KIP1) via PI3K/Akt1
pathway. Biomed Environ Sci. 23:273–278. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Anderson AC, Anderson DE, Bregoli L,
Hastings WD, Kassam N, Lei C, Chandwaskar R, Karman J, Su EW,
Hirashima M, et al: Promotion of tissue inflammation by the immune
receptor Tim-3 expressed on innate immune cells. Science.
318:1141–1143. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|