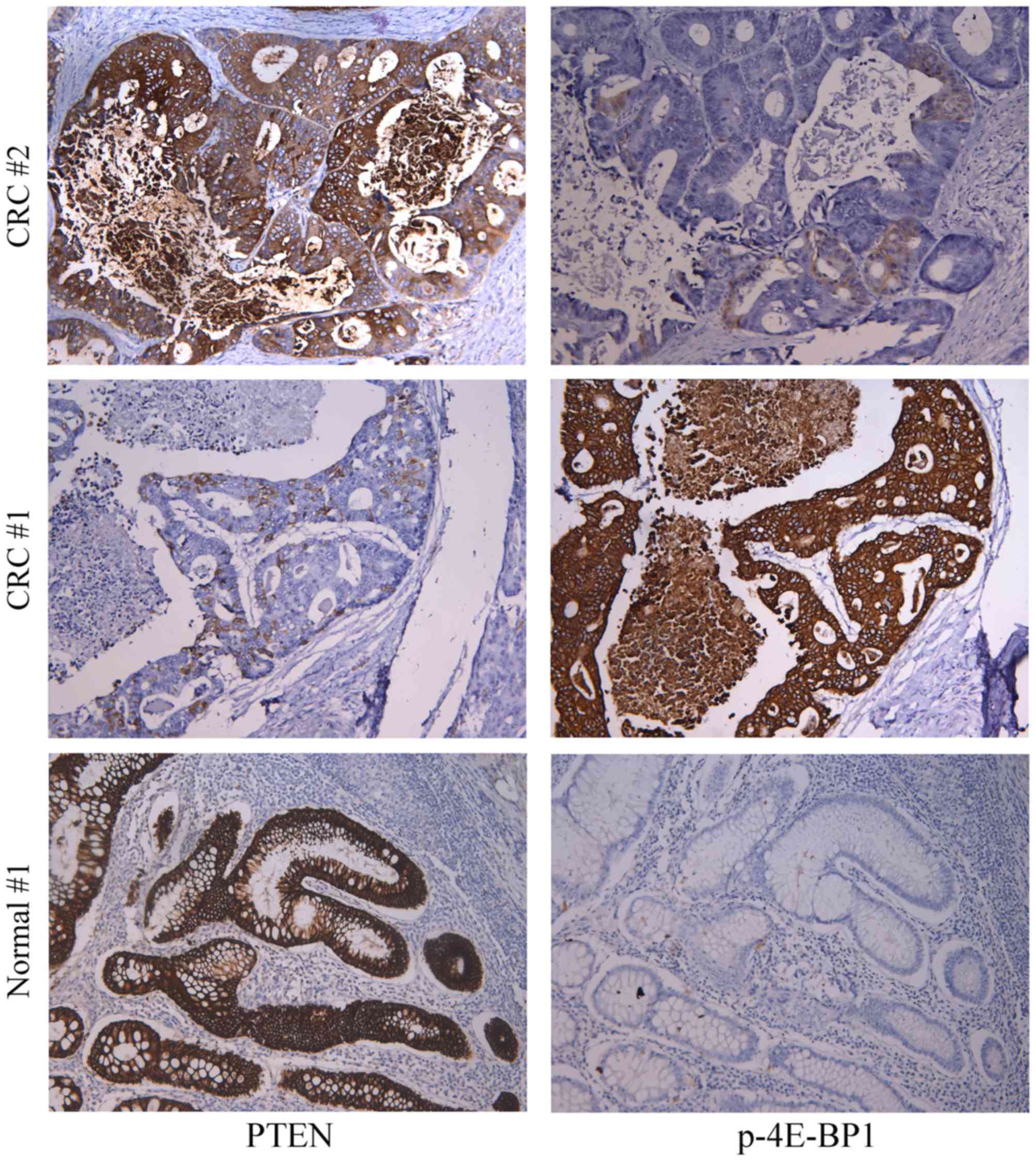
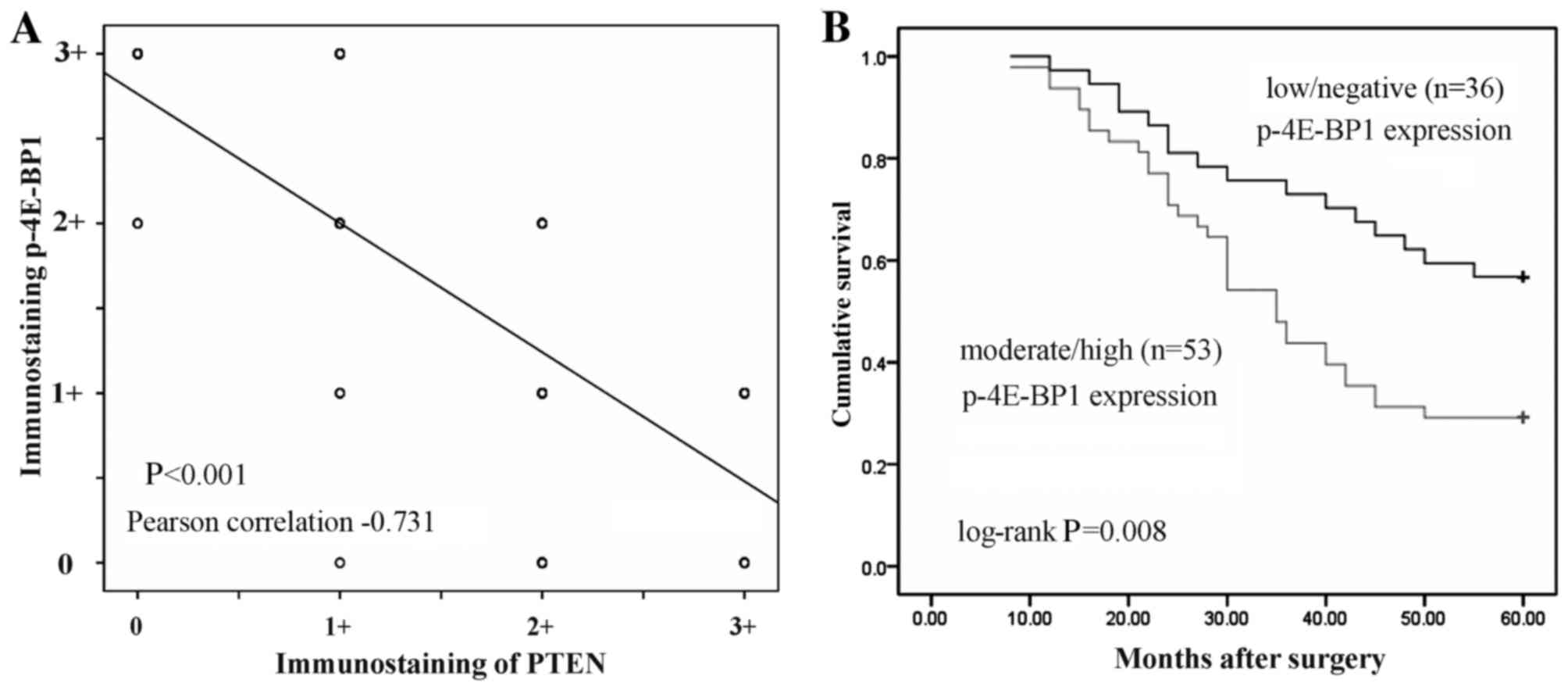
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Saif MW and Chu E: Biology of colorectal
cancer. Cancer J. 16:196–201. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Armengol G, Rojo F, Castellvi J, Iglesias
C, Cuatrecasas M, Pons B, Baselga J and Cajal Ramón y S: 4E-binding
protein 1: A key molecular ‘funnel factor’ in human cancer with
clinical implications. Cancer Res. 67:7551–7555. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Magagnin MG, van den Beucken T, Sergeant
K, Lambin P, Koritzinsky M, Devreese B and Wouters BG: The mTOR
target 4E-BP1 contributes to differential protein expression during
normoxia and hypoxia through changes in mRNA translation
efficiency. Proteomics. 8:1019–1028. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Barnhart BC, Lam JC, Young RM, Houghton
PJ, Keith B and Simon MC: Effects of 4E-BP1 expression on hypoxic
cell cycle inhibition and tumor cell proliferation and survival.
Cancer Biol Ther. 7:1441–1449. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rojo F, Najera L, Lirola J, Jiménez J,
Guzmán M, Sabadell MD, Baselga J and Cajal Ramon y S: 4E-binding
protein 1, a cell signaling hallmark in breast cancer that
correlates with pathologic grade and prognosis. Clin Cancer Res.
13:81–89. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Castellvi J, Garcia A, Rojo F,
Ruiz-Marcellan C, Gil A, Baselga J and Cajal Ramon y S:
Phosphorylated 4E binding protein 1: A hallmark of cell signaling
that correlates with survival in ovarian cancer. Cancer.
107:1801–1811. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Benavente S, Vergés R, Hermosilla E,
Fumanal V, Casanova N, García A, Ramón Y, Cajal S and Giralt J:
Overexpression of phosphorylated 4E-BP1 predicts for tumor
recurrence and reduced survival in cervical carcinoma treated with
postoperative radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
75:1316–1322. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Castellvi J, Garcia A, Ruiz-Marcellan C,
Hernández-Losa J, Peg V, Salcedo M, Gil-Moreno A and Cajal Ramon y
S: Cell signaling in endometrial carcinoma: Phosphorylated
4E-binding protein-1 expression in endometrial cancer correlates
with aggressive tumors and prognosis. Hum Pathol. 40:1418–1426.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yeh CJ, Chuang WY, Chao YK, Liu YH, Chang
YS, Kuo SY, Tseng CK, Chang HK and Hsueh C: High expression of
phosphorylated 4E-binding protein 1 is an adverse prognostic factor
in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Virchows Arch. 458:171–178.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jiao X, Pan J, Qian J, Luo T, Wang Z, Yu G
and Wang J: Overexpression of p-4ebp1 in Chinese gastric cancer
patients and its correlation with prognosis.
Hepatogastroenterology. 60:921–926. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG,
Greene FL and Trotti A: AJCC cancer staging manual. 7th. New York:
Springer; 2010
|
|
13
|
Ueno H, Kajiwara Y, Shimazaki H, Shinto E,
Hashiguchi Y, Nakanishi K, Maekawa K, Katsurada Y, Nakamura T,
Mochizuki H, et al: New criteria for histologic grading of
colorectal cancer. Am J Surg Pathol. 36:193–201. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rousseau B, Chibaudel B, Bachet JB, Larsen
AK, Tournigand C, Louvet C, André T and de Gramont A: GERCOR
(French Oncology Research Group): Stage II and stage III colon
cancer: Treatment advances and future directions. Cancer J.
16:202–209. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
De Sousa E, Melo F, Vermeulen L, Fessler E
and Medema JP: Cancer heterogeneity-a multifaceted view. EMBO Rep.
14:686–695. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Walker AS, Johnson EK, Maykel JA,
Stojadinovic A, Nissan A, Brucher B, Champagne BJ and Steele SR:
Future directions for the early detection of colorectal cancer
recurrence. J Cancer. 5:272–280. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sinicrope FA and Sargent DJ: Molecular
pathways: Microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer:
Prognostic, predictive, and therapeutic implications. Clin Cancer
Res. 18:1506–1512. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Roth AD, Tejpar S, Delorenzi M, Yan P,
Fiocca R, Klingbiel D, Dietrich D, Biesmans B, Bodoky G, Barone C,
et al: Prognostic role of KRAS and BRAF in stage II and III
resected colon cancer: Results of the translational study on the
PETACC-3, EORTC 40993, SAKK 60–00 trial. J Clin Oncol. 28:466–474.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Watanabe T, Kobunai T, Yamamoto Y, Matsuda
K, Ishihara S, Nozawa K, Yamada H, Hayama T, Inoue E, Tamura J, et
al: Chromosomal instability (CIN) phenotype, CIN high or CIN low,
predicts survival for colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol.
30:2256–2264. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
O'Connell MJ, Lavery I, Yothers G, Paik S,
Clark-Langone KM, Lopatin M, Watson D, Baehner FL, Shak S, Baker J,
et al: Relationship between tumor gene expression and recurrence in
four independent studies of patients with stage II/III colon cancer
treated with surgery alone or surgery plus adjuvant fluorouracil
plus leucovorin. J Clin Oncol. 28:3937–3944. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Heesom KJ, Gampel A, Mellor H and Denton
RM: Cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation of the translational
repressor eIF-4E binding protein-1 (4E-BP1). Curr Biol.
11:1374–1379. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Topisirovic I, Ruiz-Gutierrez M and Borden
KL: Phosphorylation of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor
eIF4E contributes to its transformation and mRNA transport
activities. Cancer Res. 64:8639–8642. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Halilovic E, She QB, Ye Q, Pagliarini R,
Sellers WR, Solit DB and Rosen N: PIK3CA mutation uncouples tumor
growth and cyclin D1 regulation from MEK/ERK and mutant KRAS
signaling. Cancer Res. 70:6804–6814. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Averous J and Proud CG: When translation
meets transforma-tion: The mTOR story. Oncogene. 25:6423–6435.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Petricoin EF III, Espina V, Araujo RP,
Midura B, Yeung C, Wan X, Eichler GS, Johann DJ Jr, Qualman S,
Tsokos M, et al: Phosphoprotein pathway mapping: Akt/mammalian
target of rapamycin activation is negatively associated with
childhood rhabdomyosarcoma survival. Cancer Res. 67:3431–3440.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
O'Reilly KE, Warycha M, Davies MA, Rodrik
V, Zhou XK, Yee H, Polsky D, Pavlick AC, Rosen N, Bhardwaj N, et
al: Phosphorylated 4E-BP1 is associated with poor survival in
melanoma. Clin Cancer Res. 15:2872–2878. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Avdulov S, Li S, Michalek V, Burrichter D,
Peterson M, Perlman DM, Manivel JC, Sonenberg N, Yee D, Bitterman
PB and Polunovsky VA: Activation of translation complex eIF4F is
essential for the genesis and maintenance of the malignant
phenotype in human mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Cell.
5:553–563. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Diab-Assaf M, Abou-Khouzam R,
Saadallah-Zeidan N, Habib K, Bitar N, Karam W, Liagre B, Harakeh S
and Azar R: Expression of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E and 4E
binding protein 1 in colorectal carcinogenesis. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:404–413. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Simi L, Pratesi N, Vignoli M, Sestini R,
Cianchi F, Valanzano R, Nobili S, Mini E, Pazzagli M and Orlando C:
High-resolution melting analysis for rapid detection of KRAS, BRAF,
and PIK3CA gene mutations in colorectal cancer. Am J Clin Pathol.
130:247–253. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
She QB, Halilovic E, Ye Q, Zhen W,
Shirasawa S, Sasazuki T, Solit DB and Rosen N: 4E-BP1 is a key
effector of the oncogenic activation of the AKT and ERK signaling
pathways that integrates their function in tumors. Cancer Cell.
18:39–51. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hsieh AC, Costa M, Zollo O, Davis C,
Feldman ME, Testa JR, Meyuhas O, Shokat KM and Ruggero D: Genetic
dissection of the oncogenic mTOR pathway reveals druggable
addiction to translational control via 4EBP-eIF4E. Cancer Cell.
17:249–261. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Weng LP, Smith WM, Brown JL and Eng C:
PTEN inhibits insulin-stimulated MEK/MAPK activation and cell
growth by blocking IRS-1 phosphorylation and IRS-1/Grb-2/Sos
complex formation in a breast cancer model. Hum Mol Genet.
10:605–616. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|