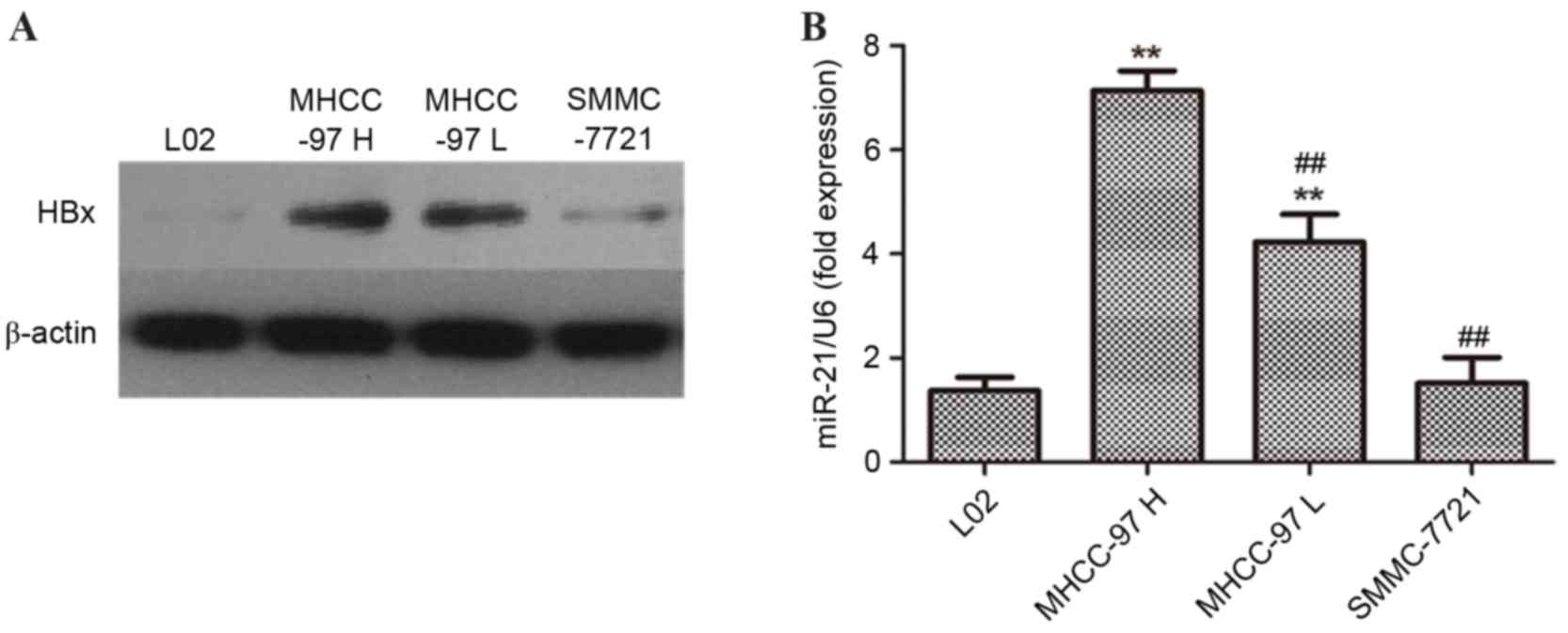
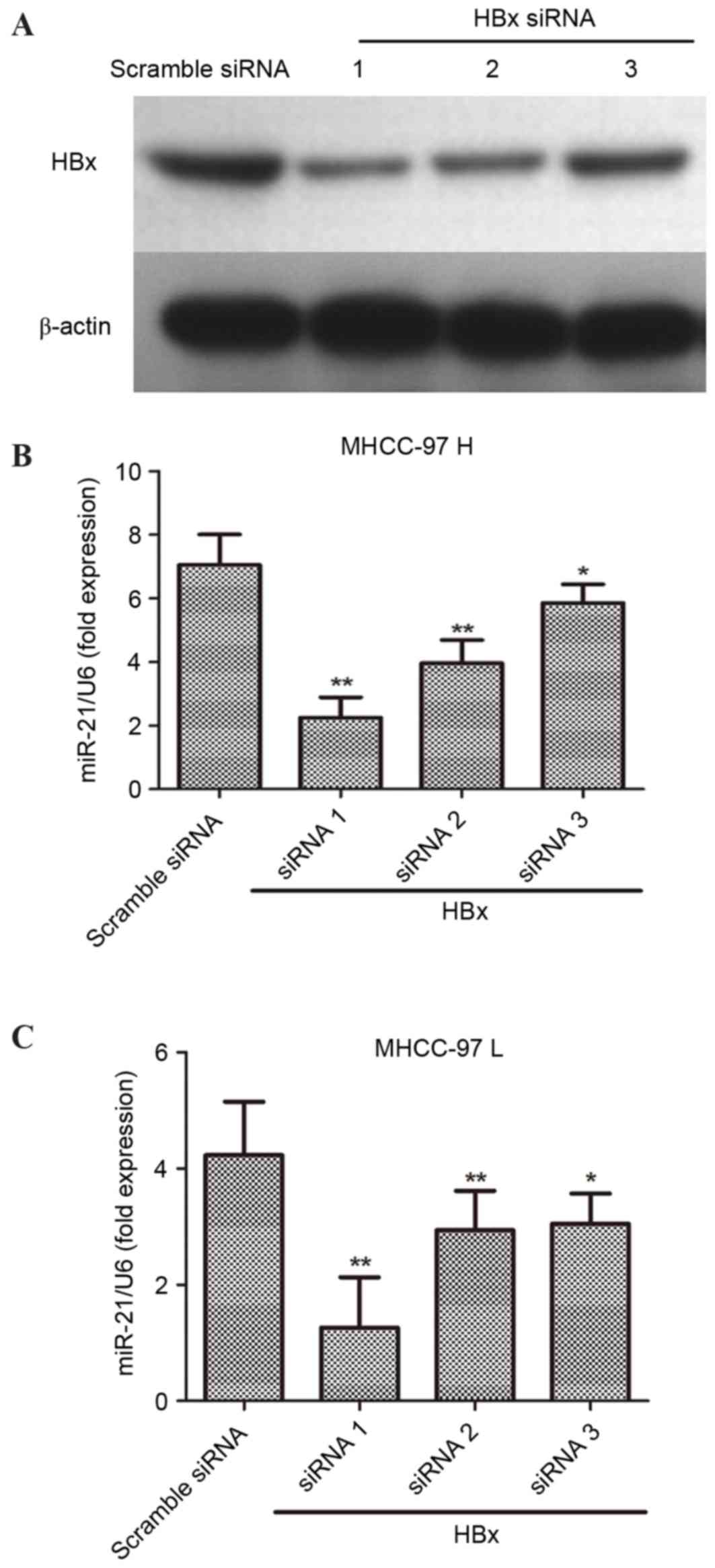
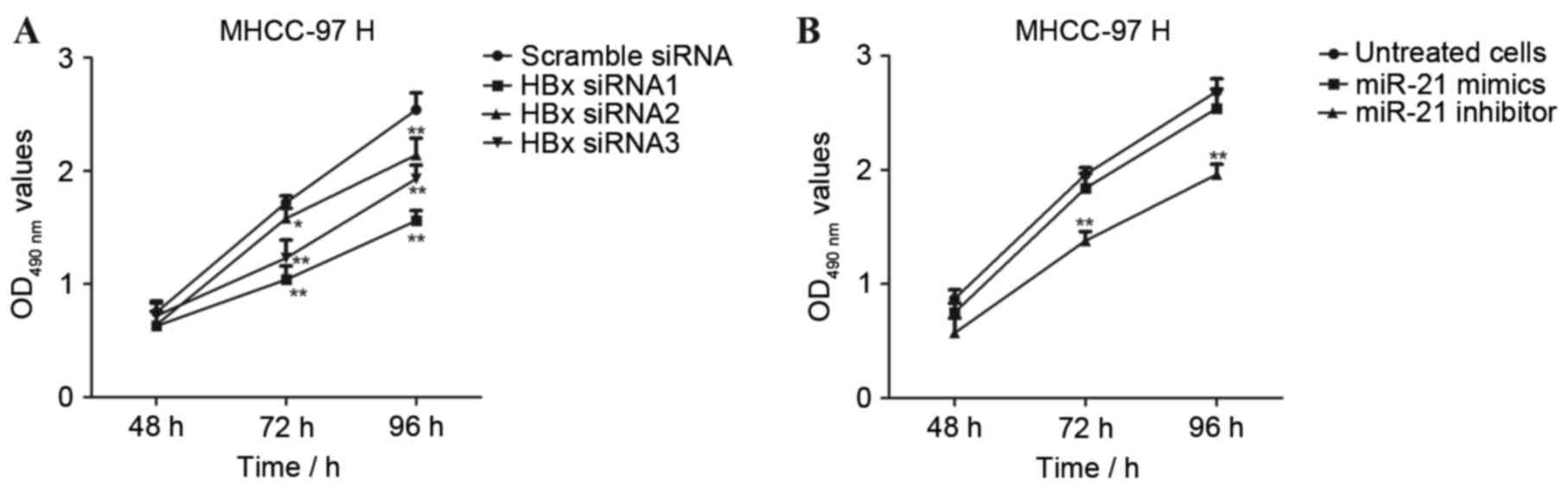
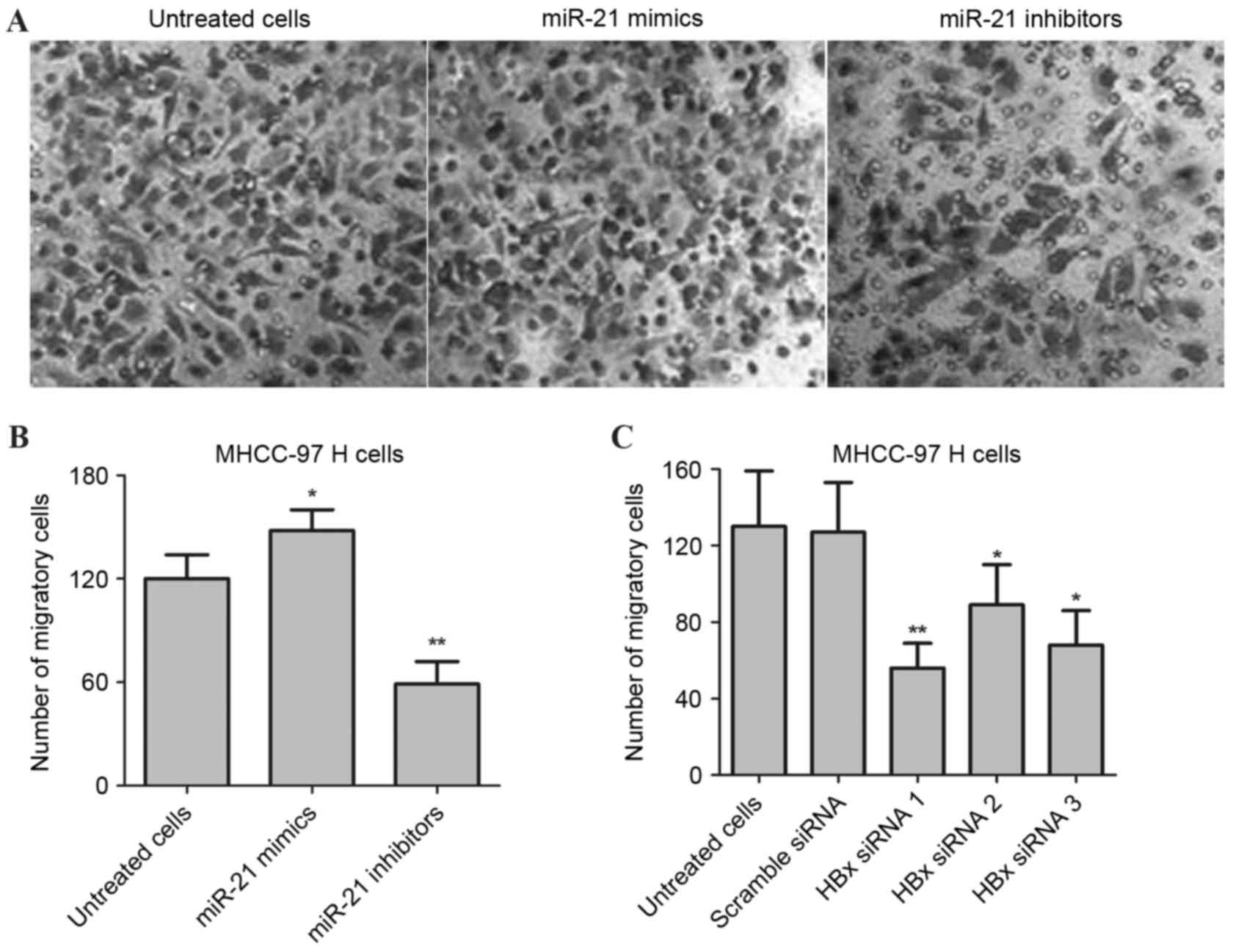
|
1
|
Waller LP, Deshpande V and Pyrsopoulos N:
Hepatocellular carcinoma: A comprehensive review. World J Hepatol.
7:2648–2663. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wogan GN, Kensler TW and Groopman JD:
Present and future directions of translational research on
aflatoxin and hepatocellular carcinoma. A review. Food Addit Contam
Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess. 29:249–257. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lin HJ, Kao ST, Siao YM and Yeh CC: The
Chinese medicine Sini-San inhibits HBx-induced migration and
invasiveness of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. BMC
Complement Altern Med. 15:3482015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tanaka M, Katayama F, Kato H, Tanaka H,
Wang J, Qiao YL and Inoue M: Hepatitis B and C virus infection and
hepatocellular carcinoma in China: A review of epidemiology and
control measures. J Epidemiol. 21:401–416. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xu Y, Li L, Xiang X, Wang H, Cai W, Xie J,
Han Y, Bao S and Xie Q: Three common functional polymorphisms in
microRNA encoding genes in the susceptibility to hepatocellular
carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gene.
527:584–593. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pollicino T and Saitta C: Occult hepatitis
B virus and hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol.
20:5951–5961. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ali A, Abdel-Hafiz H, Suhail M, Al-Mars A,
Zakaria MK, Fatima K, Ahmad S, Azhar E, Chaudhary A and Qadri I:
Hepatitis B virus, HBx mutants and their role in hepatocellular
carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 20:10238–10248. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lin L, Yin X, Hu X, Wang Q and Zheng L:
The impact of hepatitis B virus×protein and microRNAs in
hepatocellular carcinoma: A comprehensive analysis. Tumour Biol.
35:11695–11700. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Motavaf M, Safari S, Jourshari Saffari M
and Alavian SM: Hepatitis B virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma:
The role of the virus×protein. Acta Virol. 57:389–396. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kouwaki T, Okamoto T, Ito A, Sugiyama Y,
Yamashita K, Suzuki T, Kusakabe S, Hirano J, Fukuhara T, Yamashita
A, et al: Hepatocyte factor JMJD5 regulates hepatitis B virus
replication through interaction with HBx. J Virol. 90:3530–3542.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Carmona S, Ely A, Crowther C, Moolla N,
Salazar FH, Marion PL, Ferry N, Weinberg MS and Arbuthnot P:
Effective inhibition of HBV replication in vivo by anti-HBx short
hairpin RNAs. Mol Ther. 13:411–421. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim CM, Koike K, Saito I, Miyamura T and
Jay G: HBx gene of hepatitis B virus induces liver cancer in
transgenic mice. Nature. 351:317–320. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Feng H, Zhang J, Li X and Chen WN:
HBX-mediated migration of HBV-replicating HepG2 cells: Insights on
development of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2009:9302682009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gong J, He XX and Tian A: Emerging role of
microRNA in hepatocellular carcinoma (Review). Oncol Lett.
9:1027–1033. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yin J, Bai Z, Song J, Yang Y, Wang J, Han
W, Zhang J, Meng H, Ma X, Yang Y, et al: Differential expression of
serum miR-126, miR-141 and miR-21 as novel biomarkers for early
detection of liver metastasis in colorectal cancer. Chin J Cancer
Res. 26:95–103. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu Z, Wang J, Guo C and Fan X:
MicroRNA-21 mediates epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human
hepatocytes via PTEN/Akt pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 69:24–28.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang J, Xiao Z, Lai D, Sun J, He C, Chu
Z, Ye H, Chen S and Wang J: MiR-21, miR-17 and miR-19a induced by
phosphatase of regenerating liver-3 promote the proliferation and
metastasis of colon cancer. Br J Cancer. 107:352–359. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang CH, Yue J, Pfeffer SR, Handorf CR and
Pfeffer LM: MicroRNA miR-21 regulates the metastatic behavior of
B16 melanoma cells. J Biol Chem. 286:39172–39178. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang X, Wang X, Shen H, Deng R and Xue K:
Combination of miR-21 with circulating tumor cells markers improve
diagnostic specificity of metastatic breast cancer. Cell Biochem
Biophys. 73:87–91. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Soria-Valles C, Gutiérrez-Fernández A,
Guiu M, Mari B, Fueyo A, Gomis RR and López-Otín C: The
anti-metastatic activity of collagenase-2 in breast cancer cells is
mediated by a signaling pathway involving decorin and miR-21.
Oncogene. 33:3054–3063. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lu X, Luo F, Liu Y, Zhang A, Li J, Wang B,
Xu W, Shi L, Liu X, Lu L and Liu Q: The IL-6/STAT3 pathway via
miR-21 is involved in the neoplastic and metastatic properties of
arsenite-transformed human keratinocytes. Toxicol Lett.
237:191–199. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ferraro A, Kontos CK, Boni T, Bantounas I,
Siakouli D, Kosmidou V, Vlassi M, Spyridakis Y, Tsipras I, Zografos
G and Pintzas A: Epigenetic regulation of miR-21 in colorectal
cancer: ITGB4 as a novel miR-21 target and a three-gene network
(miR-21-ITGBeta4-PDCD4) as predictor of metastatic tumor potential.
Epigenetics. 9:129–141. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Connolly EC, Van Doorslaer K, Rogler LE
and Rogler CE: Overexpression of miR-21 promotes an in vitro
metastatic phenotype by targeting the tumor suppressor RHOB. Mol
Cancer Res. 8:691–700. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Spinner DM: MTT growth assays in ovarian
cancer. Methods Mol Med. 39:175–177. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sargent J, Elgie A, Taylor CG, Wilson J,
Alton P and Hill JG: The identification of drug resistance in
ovarian cancer and breast cancer: Application of the MTT assay.
Contrib Gynecol Obstet. 19:64–75. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu H, Huang X, Liu X, Xiao S, Zhang Y,
Xiang T, Shen X, Wang G and Sheng B: MiR-21 promotes human nucleus
pulposus cell proliferation through PTEN/AKT signaling. Int J Mol
Sci. 15:4007–4018. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Koike K, Moriya K, Iino S, Yotsuyanagi H,
Endo Y, Miyamura T and Kurokawa K: High-level expression of
hepatitis B virus HBx gene and hepatocarcinogenesis in transgenic
mice. Hepatology. 19:810–819. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Benhenda S, Cougot D, Neuveut C and
Buendia MA: Liver cell transformation in chronic HBV infection.
Viruses. 1:630–646. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Blumberg BS: Primary and secondary
prevention of liver cancer caused by HBV. Front Biosci (Schol Ed).
2:756–763. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xiong B, Cheng Y, Ma L and Zhang C: MiR-21
regulates biological behavior through the PTEN/PI-3K/Akt signaling
pathway in human colorectal cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 42:219–228.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xu J, Zhang W, Lv Q and Zhu D:
Overexpression of miR-21 promotes the proliferation and migration
of cervical cancer cells via the inhibition of PTEN. Oncol Rep.
33:3108–3116. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|