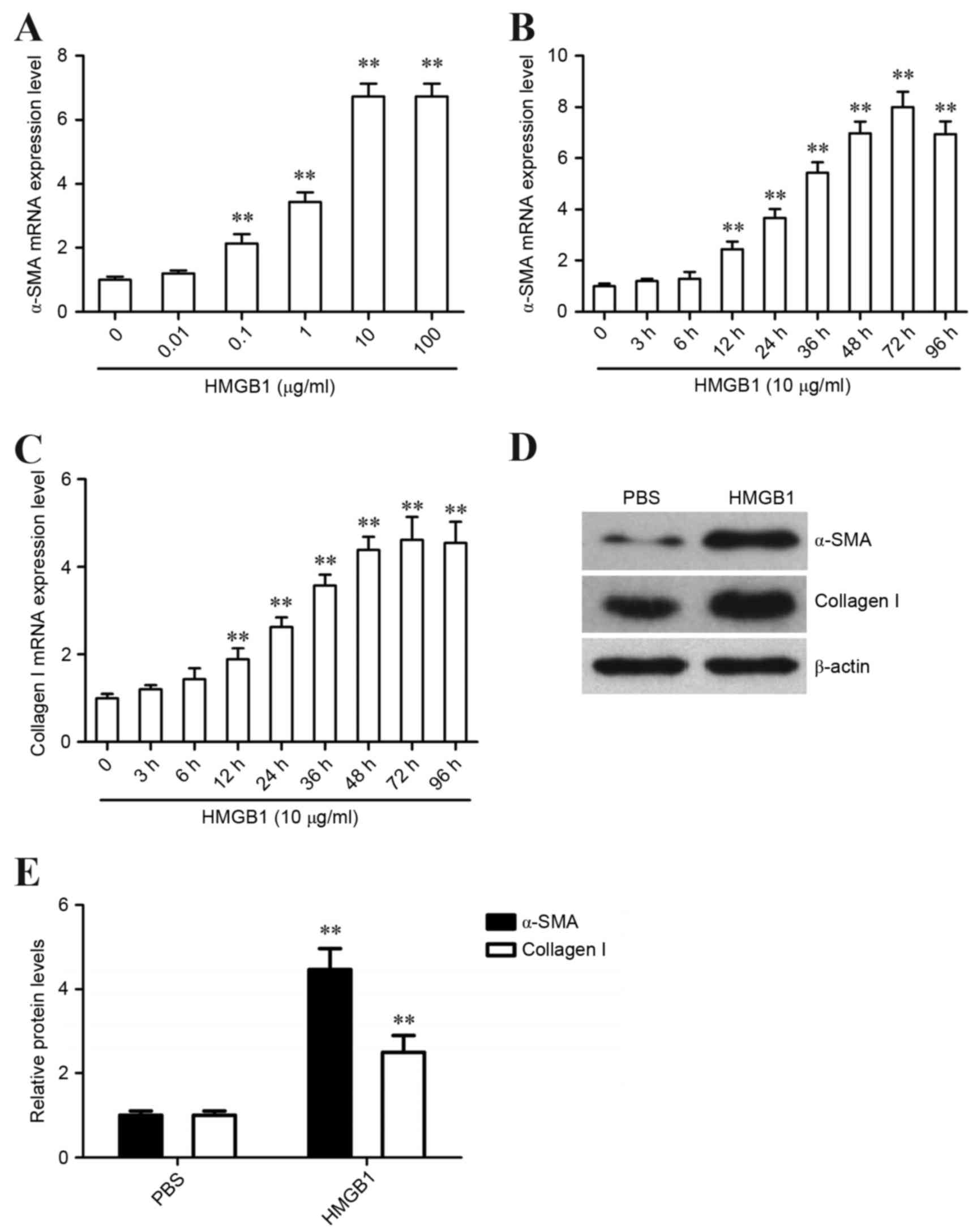
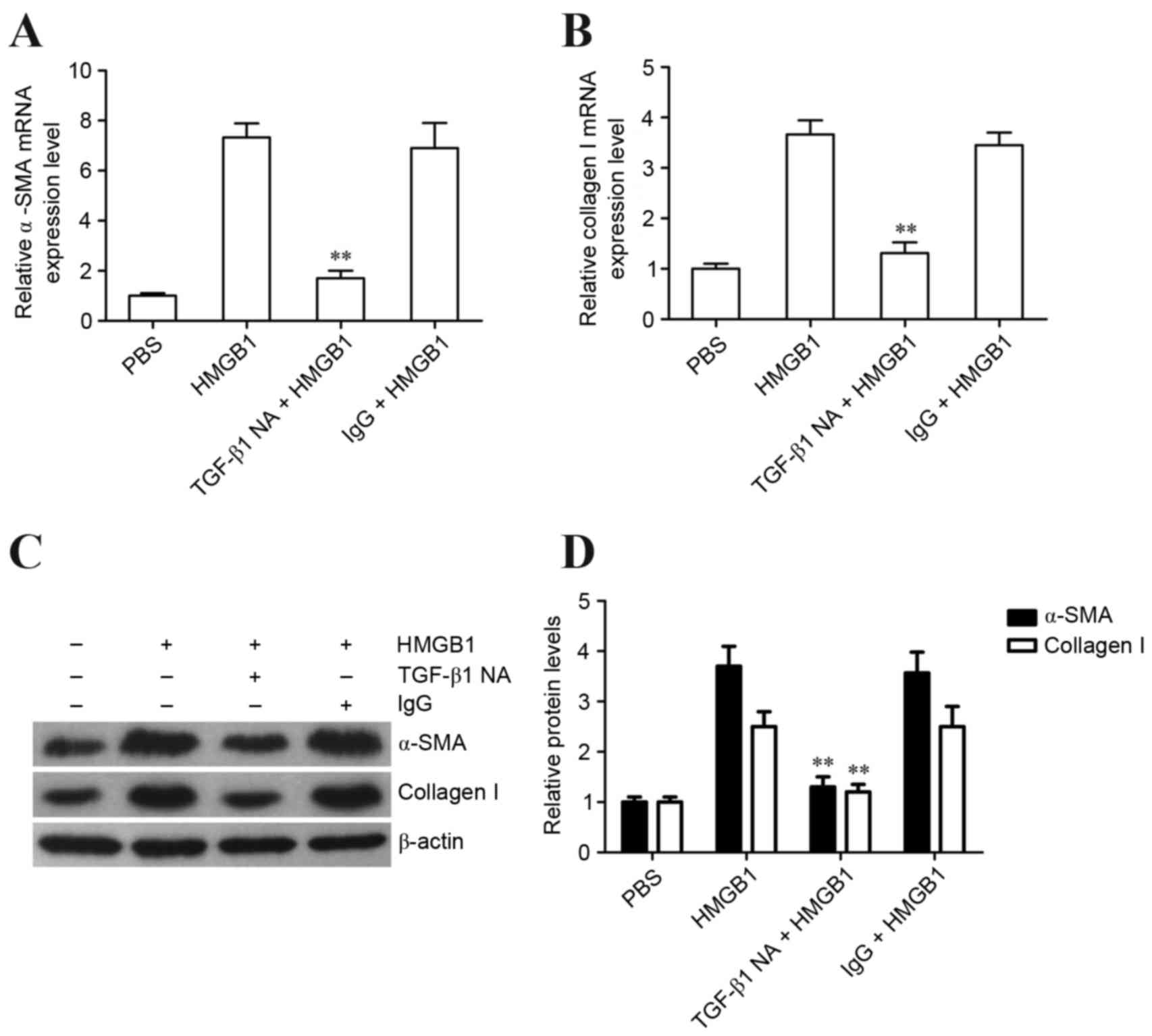
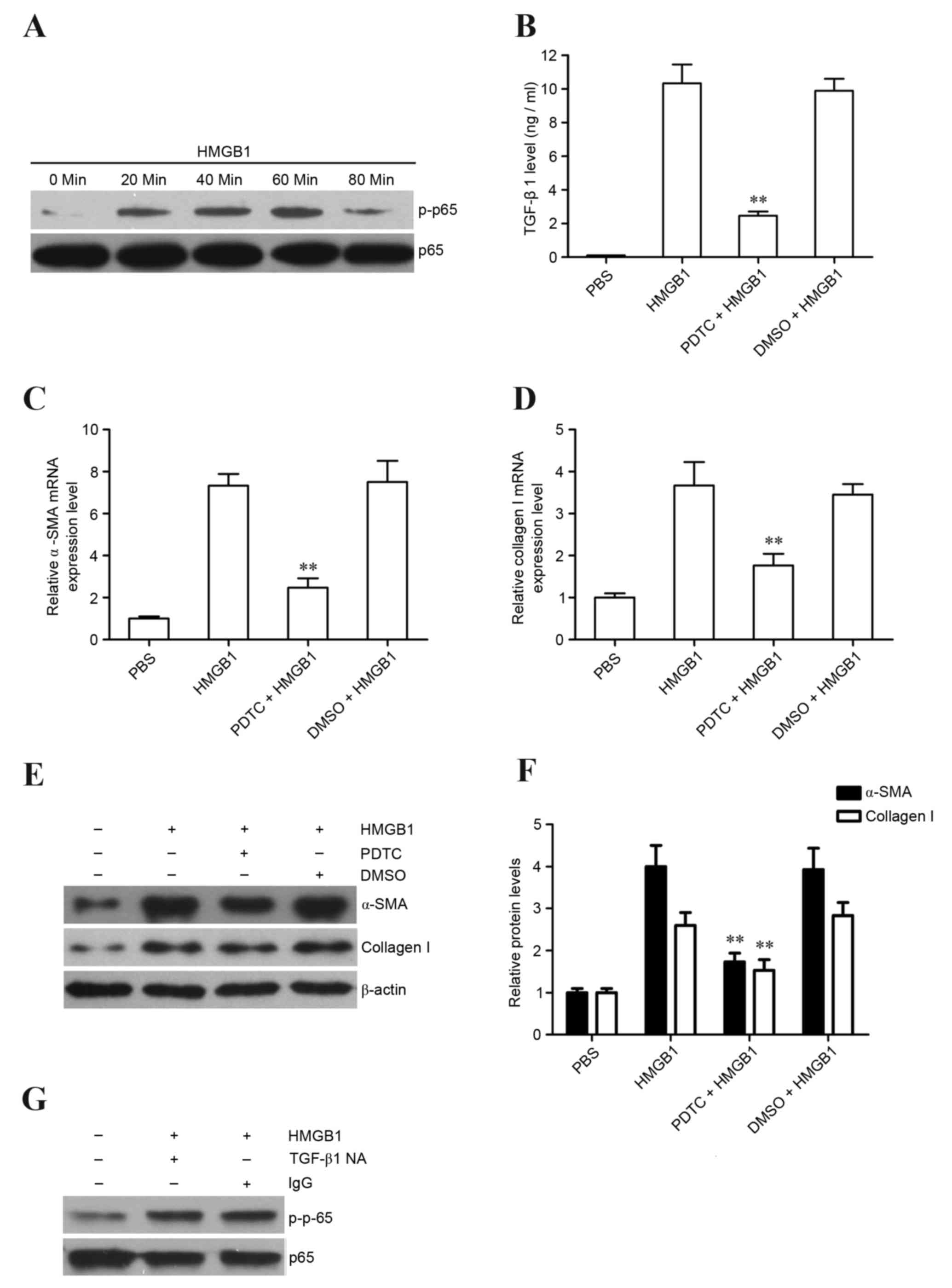
|
1
|
Górka J, Szczeklik W, Włudarczyk A, Łoboda
P, Chmura Ł and Musiał J: Rapidly progressive interstitial lung
fibrosis in a patient with amyopathic dermatomyositis and anti-MDA5
antibodies. Pol Arch Med Wewn. 125:685–686. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
MacKenzie B, Korfei M, Henneke I, Sibinska
Z, Tian X, Hezel S, Dilai S, Wasnick R, Schneider B, Wilhelm J, et
al: Increased FGF1-FGFRc expression in idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis. Respir Res. 16:832015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Curtis JR, Sarsour K, Napalkov P, Costa LA
and Schulman KL: Incidence and complications of interstitial lung
disease in users of tocilizumab, rituximab, abatacept and
anti-tumor necrosis factor α agents, a retrospective cohort study.
Arthritis Res Ther. 17:3192015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yamamoto Y, Okamoto I, Otsubo K, Iwama E,
Hamada N, Harada T, Takayama K and Nakanishi Y: Severe acute
interstitial lung disease in a patient with anaplastic lymphoma
kinase rearrangement-positive non-small cell lung cancer treated
with alectinib. Invest New Drugs. 33:1148–1150. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Guo Y, Zhang X, Qin M and Wang X: Changes
in peripheral CD19(+)Foxp3(+) andCD19(+)TGFβ(+) regulatory B cell
populations in rheumatoid arthritis patients with interstitial lung
disease. J Thorac Dis. 7:471–477. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kawai T, Watanabe N, Yokoyama M, Nakazawa
Y, Goto F, Uchiyama T, Higuchi M, Maekawa T, Tamura E, Nagasaka S,
et al: Interstitial lung disease with multiple microgranulomas in
chronic granulomatous disease. J Clin Immunol. 34:933–940. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Glasser SW, Senft AP, Maxfield MD,
Ruetschilling TL, Baatz JE, Page K and Korfhagen TR: Genetic
replacement of surfactant protein-C reduces respiratory syncytial
virus induced lung injury. Respir Res. 14:192013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lin L, Wang Y, Liu W and Huang Y: BAMBI
inhibits skin fibrosis in keloid through suppressing TGF-β1-induced
hypernomic fibroblast cell proliferation and excessive accumulation
of collagen I. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:13227–13234. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tsukui T, Ueha S, Shichino S, Inagaki Y
and Matsushima K: Intratracheal cell transfer demonstrates the
profibrotic potential of resident fibroblasts in pulmonary
fibrosis. Am J Pathol. 185:2939–2948. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Geng J, Huang X, Li Y, Xu X, Li S, Jiang
D, Liang J, Jiang D, Wang C and Dai H: Down-regulation of USP13
mediates phenotype transformation of fibroblasts in idiopathic
pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Res. 16:1242015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ma X, Yang F, Yang S, Rasul A, Li T, Liu
L, Kong M, Guo D and Ma T: Number and distribution of
myofibroblasts and α-smooth muscle actin expression levels in fetal
membranes with and without gestational complications. Mol Med Rep.
12:2784–2792. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jung YS, Liu XW, Chirco R, Warner RB,
Fridman R and Kim HR: TIMP-1 induces an EMT-like phenotypic
conversion in MDCK cells independent of its MMP-inhibitory domain.
PLoS One. 7:e387732012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Watson M, Stott K, Fischl H, Cato L and
Thomas JO: Characterization of the interaction between HMGB1 and
H3-a possible means of positioning HMGB1 in chromatin. Nucleic
Acids Res. 42:848–859. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Little AJ, Corbett E, Ortega F and Schatz
DG: Cooperative recruitment of HMGB1 during V (D)J recombination
through interactions with RAG1 and DNA. Nucleic Acids Res.
41:3289–3301. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhao T, Ren H, Wang X, Liu P, Yan F, Jiang
W, Li Y, Li J, Gribben JG, Jia L and Hao J: Rituximab-induced HMGB1
release is associated with inhibition of STAT3 activity in human
diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Oncotarget. 6:27816–27831. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jiang G, Wang Y, Yun J, Hajrasouliha AR,
Zhao Y, Sun D, Kaplan HJ and Shao H: HMGB1 release triggered by the
interaction of live retinal cells and uveitogenic T cells is
Fas/FasL activation-dependent. J Neuroinflammation. 12:1792015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tabata C, Kanemura S, Tabata R, Masachika
E, Shibata E, Otsuki T, Nishizaki T and Nakano T: Serum HMGB1 as a
diagnostic marker for malignant peritoneal mesothelioma. J Clin
Gastroenterol. 47:684–688. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Laws TR, Clark GC and D'Elia RV: Immune
profiling of the progression of a BALB/c mouse aerosol infection by
Burkholderia pseudomallei and the therapeutic implications of
targeting HMGB1. Int J Infect Dis. 40:1–8. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Qi L, Sun X, Li FE, Zhu BS, Braun FK, Liu
ZQ, Tang JL, Wu C, Xu F, Wang HH, et al: HMGB1 promotes
mitochondrial dysfunction-triggered striatal neurodegeneration via
autophagy and apoptosis activation. PLoS One. 10:e01429012015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Parodi M, Pedrazzi M, Cantoni C, Averna M,
Patrone M, Cavaletto M, Spertino S, Pende D, Balsamo M, Pietra G,
et al: Natural killer (NK)/melanoma cell interaction induces
NK-mediated release of chemotactic high mobility group box-1
(HMGB1) capable of amplifying NK cell recruitment. Oncoimmunology.
4:e10523532015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang FP, Li L, Li J, Wang JY, Wang LY and
Jiang W: High mobility group box-1 promotes the proliferation and
migration of hepatic stellate cells via TLR4-dependent signal
pathways of PI3K/Akt and JNK. PLoS One. 8:e643732013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang W, Lavine KJ, Epelman S, Evans SA,
Weinheimer CJ, Barger PM and Mann DL: Necrotic myocardial cells
release damage-associated molecular patterns that provoke
fibroblast activation in vitro and trigger myocardial inflammation
and fibrosis in vivo. J Am Heart Assoc. 4:e0019932015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang M, Guo Y, Fu H, Hu S, Pan J, Wang Y,
Cheng J, Song J, Yu Q, Zhang S, et al: Chop deficiency prevents
UUO-induced renal fibrosis by attenuating fibrotic signals
originated from Hmgb1/TLR4/NFκB/IL-1β signaling. Cell Death Dis.
6:e18472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ebina M, Taniguchi H, Miyasho T, Yamada S,
Shibata N, Ohta H, Hisata S, Ohkouchi S, Tamada T, Nishimura H, et
al: Gradual increase of high mobility group protein b1 in the lungs
after the onset of acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis. Pulm Med. 2011:9164862011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hamada N, Maeyama T, Kawaguchi T, Yoshimi
M, Fukumoto J, Yamada M, Yamada S, Kuwano K and Nakanishi Y: The
role of high mobility group box 1 in pulmonary fibrosis. Am J
Respir Cell Mol Biol. 39:440–447. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tiringer K, Treis A, Kanolzer S, Witt C,
Ghanim B, Gruber S, Schmidthaler K, Renner S, Dehlink E, Nachbaur
E, et al: Differential expression of IL-33 and HMGB1 in the lungs
of stable cystic fibrosis patients. Eur Respir J. 44:802–805. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Entezari M, Weiss DJ, Sitapara R,
Whittaker L, Wargo MJ, Li J, Wang H, Yang H, Sharma L, Phan BD, et
al: Inhibition of high-mobility group box 1 protein (HMGB1)
enhances bacterial clearance and protects against Pseudomonas
aeruginosa pneumonia in cystic fibrosis. Mol Med. 18:477–485.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li LC, Li DL, Xu L, Mo XT, Cui WH, Zhao P,
Zhou WC, Gao J and Li J: High-mobility group box 1 mediates
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in pulmonary fibrosis
involving transforming growth factor-β1/Smad2/3 signaling. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 354:302–309. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang Z, Sun Z, Liu H, Ren Y, Shao D, Zhang
W, Lin J, Wolfram J, Wang F and Nie S: Connective tissue growth
factor stimulates the proliferation, migration and differentiation
of lung fibroblasts during paraquat-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Mol
Med Rep. 12:1091–1097. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hou F, Wang L, Wang H, Gu J, Li M, Zhang
J, Ling X, Gao X and Luo C: Elevated gene expression of S100A12 is
correlated with the predominant clinical inflammatory factors in
patients with bacterial pneumonia. Mol Med Rep. 11:4345–4352.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Di JM, Pang J, Pu XY, Zhang Y, Liu XP,
Fang YQ, Ruan XX and Gao X: Toll-like receptor 9 agonists promote
IL-8 and TGF-beta1 production via activation of nuclear factor
kappaB in PC-3 cells. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 192:60–67. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Petrosyan F, Culver DA and Reddy AJ: Role
of bronchoalveolar lavage in the diagnosis of acute exacerbations
of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A retrospective study. BMC Pulm
Med. 15:702015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ji H, Tang H, Lin H, Mao J, Gao L, Liu J
and Wu T: Rho/Rock cross-talks with transforming growth
factor-β/Smad pathway participates in lung fibroblast-myofibroblast
differentiation. Biomed Rep. 2:787–792. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sassoli C, Chellini F, Pini A, Tani A,
Nistri S, Nosi D, Zecchi-Orlandini S, Bani D and Formigli L:
Relaxin prevents cardiac fibroblast-myofibroblast transition via
notch-1-mediated inhibition of TGF-β/Smad3 signaling. PLoS One.
8:e638962013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Song J, Zhu Y, Li J, Liu J, Gao Y, Ha T,
Que L, Liu L, Zhu G, Chen Q, et al: Pellino1-mediated TGF-β1
synthesis contributes to mechanical stress induced cardiac
fibroblast activation. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 79:145–156. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bizzarro V, Fontanella B, Carratù A,
Belvedere R, Marfella R, Parente L and Petrella A: Annexin A1
N-terminal derived peptide Ac2-26 stimulates fibroblast migration
in high glucose conditions. PLoS One. 7:e456392012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li W, Xu Q, Deng Y, Yang Z, Xing S, Zhao
X, Zhu P, Wang X, He Z and Gao Y: High-mobility group box 1
accelerates lipopolysaccharide-induced lung fibroblast
proliferation in vitro: involvement of the NF-κB signaling pathway.
Lab Invest. 95:635–647. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Pedroza M, Le TT, Lewis K,
Karmouty-Quintana H, To S, George AT, Blackburn MR, Tweardy DJ and
Agarwal SK: STAT-3 contributes to pulmonary fibrosis through
epithelial injury and fibroblast-myofibroblast differentiation.
FASEB J. 30:129–140. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|