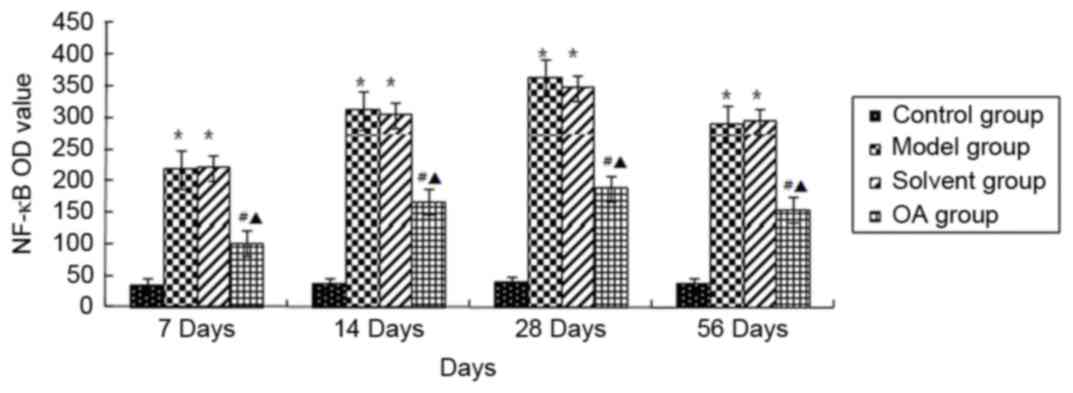
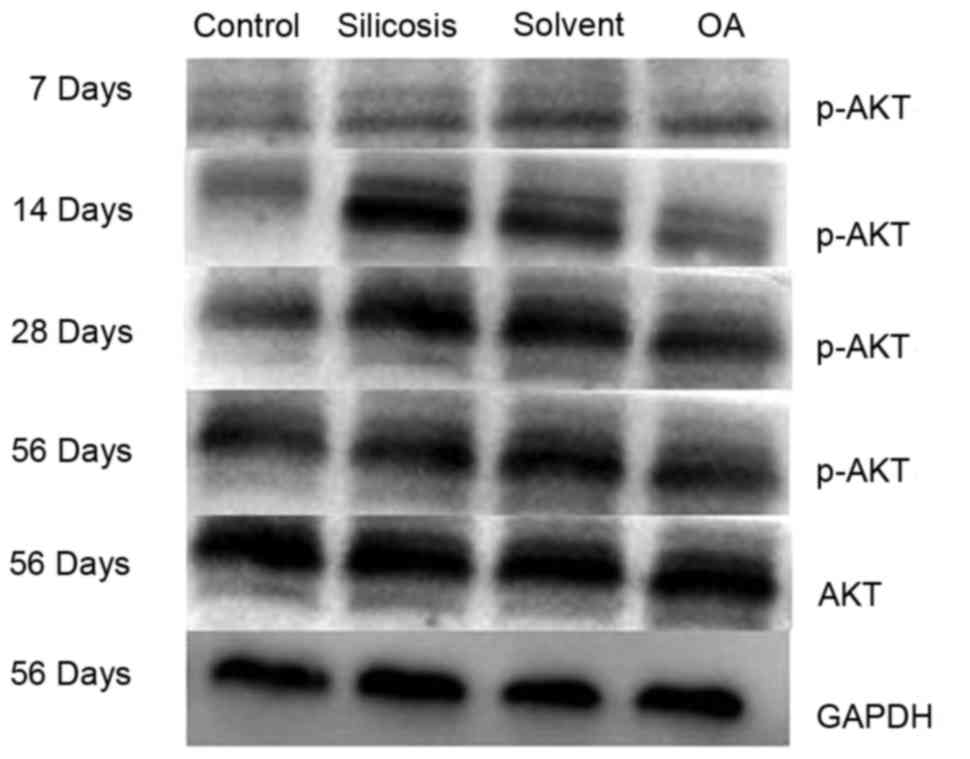
|
1
|
Rimal B, Greenberg AK and Rom WN: Basic
pathogenetic mechanisms in silicosis: Current understanding. Curr
Opin Pulm Med. 11:169–173. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Flynn MR and Susi P: Engineering controls
for selected silica and dust exposures in the construction
industry-a review. Appl Occup Environ Hyg. 18:268–277. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Leung CC, Yu IT and Chen W: Silicosis.
Lancet. 379:2008–2018. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Thomas CR and Kelley TR: A Brief Review of
silicosis in the United states. Environ Health Insights. 4:21–26.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Occupational Health Technical Service
Network: Silicosis. http://www.zybw.com/zybw_list.aspx?c=31&a=60&t=xq&m=502Accessed.
January 5–2014.
|
|
6
|
Hamilton RF Jr, Thakur SA and Holian A:
Silica binding and toxicity in alveolar macrophages. Free Radic
Biol Med. 44:1246–1258. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang L, He YL, Li QZ, Hao XH, Zhang ZF,
Yuan JX, Bai YP, Jin YL, Liu N and Chen G: N-acetylcysteine
alleviated silica-induced lung fibrosis in rats by down-regulation
of ROS and mitochondrial apoptosis signaling. Toxicol Mech Methods.
24:212–219. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Porter DW, Millecchia LL, Willard P,
Robinson VA, Ramsey D, McLaurin J, Khan A, Brumbaugh K, Beighley
CM, Teass A and Castranova V: Nitric oxide and reactive oxygen
species production causes progressive damage in rats after
cessation of silica inhalation. Toxicol Sci. 90:188–197. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu J: Oleanolic acid and ursolic acid:
Research perspectives. J Ethnopharmacol. 100:92–94. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pollier J and Goossens A: Oleanolic acid.
Phytochemistry. 77:10–15. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chung S, Yoon HE, Kim SJ, Kim SJ, Koh ES,
Hong YA, Park CW, Chang YS and Shin SJ: Oleanolic acid attenuates
renal fibrosis in mice with unilateral ureteral obstruction via
facilitating nuclear translocation of Nrf2. Nutr Metab (Lond).
11:22014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kulkarni AA, Thatcher TH, Olsen KC,
Maggirwar SB, Phipps RP and Sime PJ: PPAR-γ Ligands Repress
TGFb-induced myofibroblast differentiation by targeting the
PI3K/Akt pathway: Implications for therapy of fibrosis. PLoS One.
6:e159092011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Thakur SA, Beamer CA, Migliaccio CT and
Holian A: Critical role of MARCO in crystalline silica-induced
pulmonary inflammation. Toxicol Sci. 108:462–471. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lim Y, Kim JH, Kim KA, Chang HS, Park YM,
Ahn BY and Phee YG: Silica-induced apoptosis in vitro and in vivo.
Toxicol Lett. 108:335–339. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sun Y, Yang F, Yan J, Li Q, Wei Z, Feng H,
Wang R, Zhang L and Zhang X: New anti-fibrotic mechanisms of
n-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline in silicon dioxide-induced
silicosis. Life Sci. 87:232–239. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fubini B and Hubbard A: Reactive Oxygen
Species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) generation by
silica in inflammation and fibrosis. Free Radic Biol Med.
34:1507–1516. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Palabiyik SS, Girgin G, Tutkun E, Yilmaz
OH and Baydar T: Immunomodulation and oxidative stress in denim
sandblasting workers: Changes caused by silica exposure. Arh Hig
Rada Toksikol. 64:431–437. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pelclová D, Fenclová Z, Syslová K, Vlčková
S, Lebedová J, Pecha O, Běláček J, Navrátil T, Kuzma M and Kačer P:
Oxidative stress markers in exhaled breath condensate in lung
fibroses are not significantly affected by systemic diseases. Ind
Health. 49:746–754. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang JW, Lv GC, Yao JM and Hong XP:
Assessment of serum antioxidant status in patients with silicosis.
J Int Med Res. 38:884–889. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Scarfì S, Magnone M, Ferraris C, Pozzolini
M, Benvenuto F, Benatti U and Giovine M: Ascorbic acid pre-treated
quartz stimulates TNF-alpha release in RAW264.7 murine macrophages
through ROS production and membrane lipid peroxidation. Respir Res.
10:252009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jiang ZY, Zou L, Shi SS, Lu YR, Dong J,
Yang CH, Lu YC and Dai GK: Effects of curcumin on TNF-alpha and
TGF-beta1 in serum and lung tissue of SiO2-induced fibrosis in
mice. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 25:399–401. 2009.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li Z, Xue J, Yan S, Chen P and Chen L:
Association between tumor necrosis factor-α 308G/A gene
polymorphism and silicosis susceptibility: A meta-analysis. PLoS
One. 8:e766142013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Miao RM, Zhang XT, Yan YL, He EQ, Guo P,
Zhang YY, Zhao DK, Yang ZG, Chen J, Yao MY, et al: Change of serum
TGF-beta1 and TNF-alpha in silicosis patients. Zhonghua Lao Dong
Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 29:606–607. 2011.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Slavov E, Miteva L, Prakova G, Gidikova P
and Stanilova S: Correlation between TNF-alpha and
IL-12p40-containing cytokines in silicosis. Toxicol Ind Health.
26:479–486. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ortiz LA, Lasky J, Gozal E, Ruiz V,
Lungarella G, Cavarra E, Brody AR, Friedman M, Pardo A and Selman
M: Tumor necrosis factor receptor deficiency alters matrix
metalloproteinase 13/tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1
expression in murine silicosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
163:244–252. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xu H, Yang F, Sun Y, Yuan Y, Cheng H, Wei
Z, Li S, Cheng T, Brann D and Wang R: A New Antifibrotic Target of
Ac-SDKP: Inhibition of Myofibroblast Differentiation in Rat Lung
with Silicosis. PLoS One. 7:e403012012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fan LH, Liu TF, Guo M, Liu ML, Wang ZP and
Si SJ: Effect of schisandrin B on lung mRNA expression of
transforming growth factor-beta1 signal transduction molecule in
rat lungs exposed to silica. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye
Bing Za Zhi. 29:255–259. 2011.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Maron-Gutierrez T, Castiglione RC, Xisto
DG, Oliveira MG, Cruz FF, Peçanha R, Carreira-Junior H, Ornellas
DS, Moraes MO, Takiya CM, et al: Bone marrow-derived mononuclear
cell therapy attenuates silica-induced lung fibrosis. Eur Respir J.
37:1217–1225. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Porter DW, Ye J, Ma J, Barger M, Robinson
VA, Ramsey D, McLaurin J, Khan A, Landsittel D, Teass A and
Castranova V: Time course of pulmonary response of rats to
inhalation of crystalline silica: NF-kappa B activation,
inflammation, cytokine production, and damage. Inhal Toxicol.
14:349–367. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Di Giuseppe M, Gambelli F, Hoyle GW,
Lungarella G, Studer SM, Richards T, Yousem S, McCurry K, Dauber J,
Kaminski N, et al: Systemic Inhibition of NF-kappaB activation
protects from silicosis. PLoS One. 4:e56892009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen F and Shi X: NF-kappaB, a pivotal
transcription factor in silica-induced diseases. Mol Cell Biochem.
234–235:169–176. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Hubbard AK, Timblin CR, Shukla A, Rincón M
and Mossman BT: Activation of NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression
by silica in lungs of luciferase reporter mice. Am J Physiol Lung
Cell Mol Physiol. 282:L968–L975. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Venkatesan B, Valente AJ, Prabhu SD,
Shanmugam P, Delafontaine P and Chandrasekar B: EMMPRIN activates
multiple transcription factors in cardiomyocytes, and induces
interleukin-18 expression via Rac1-dependent PI3K/Akt/IKK/NF-kappaB
andMKK7/JNK/AP-1 signaling. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 49:655–663. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jing Y, Liu LZ, Jiang Y, Zhu Y, Guo NL,
Barnett J, Rojanasakul Y, Agani F and Jiang BH: Cadmium Increases
HIF-1 and VEGF Expression through ROS, ERK, and AKT signaling
pathways and induces malignant transformation of human bronchial
epithelial cells. Toxicol Sci. 125:10–19. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yasuda T: Activation of Akt leading to
NF-κB up-regulation in chondrocytes stimulated with fibronectin
fragment. Biomed Res. 32:209–215. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Takada K, Nakane T, Masuda K and Ishii H:
Ursolic acid and oleanolic acid, members of pentacyclic
triterpenoid acids, suppress TNF-α-induced E-selectin expression by
cultured umbilical vein endothelial cells. Phytomedicine.
17:1114–1119. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|