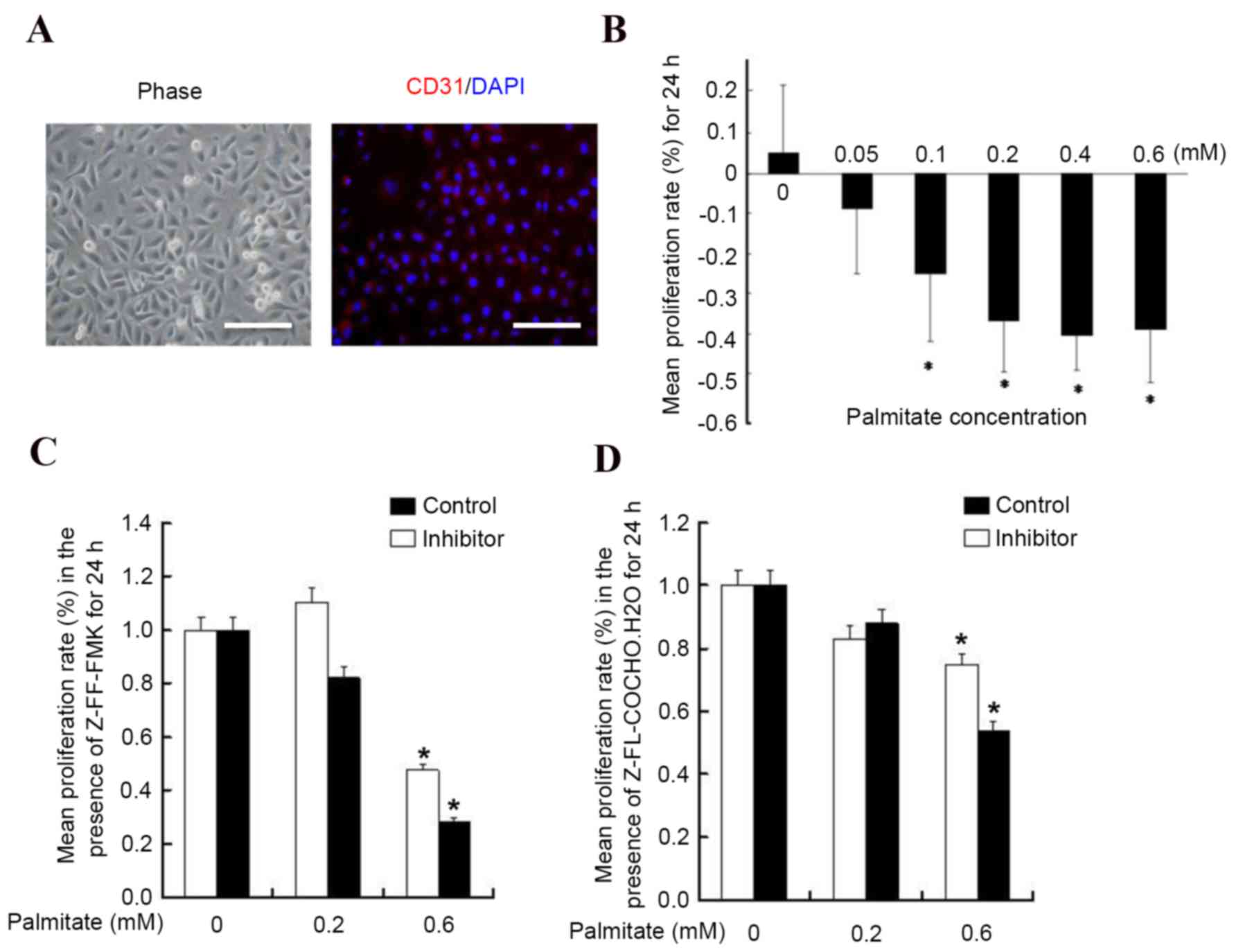
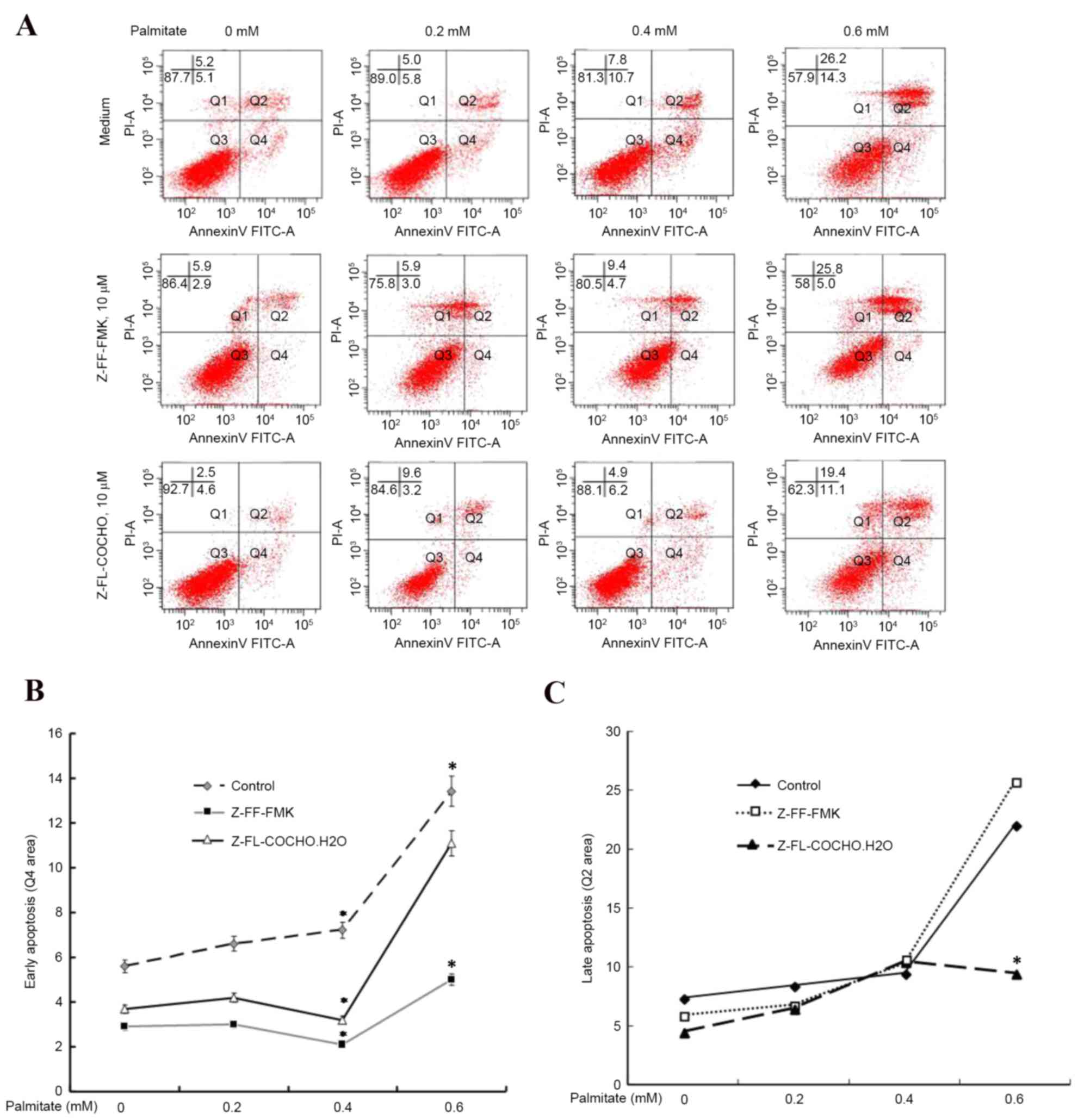
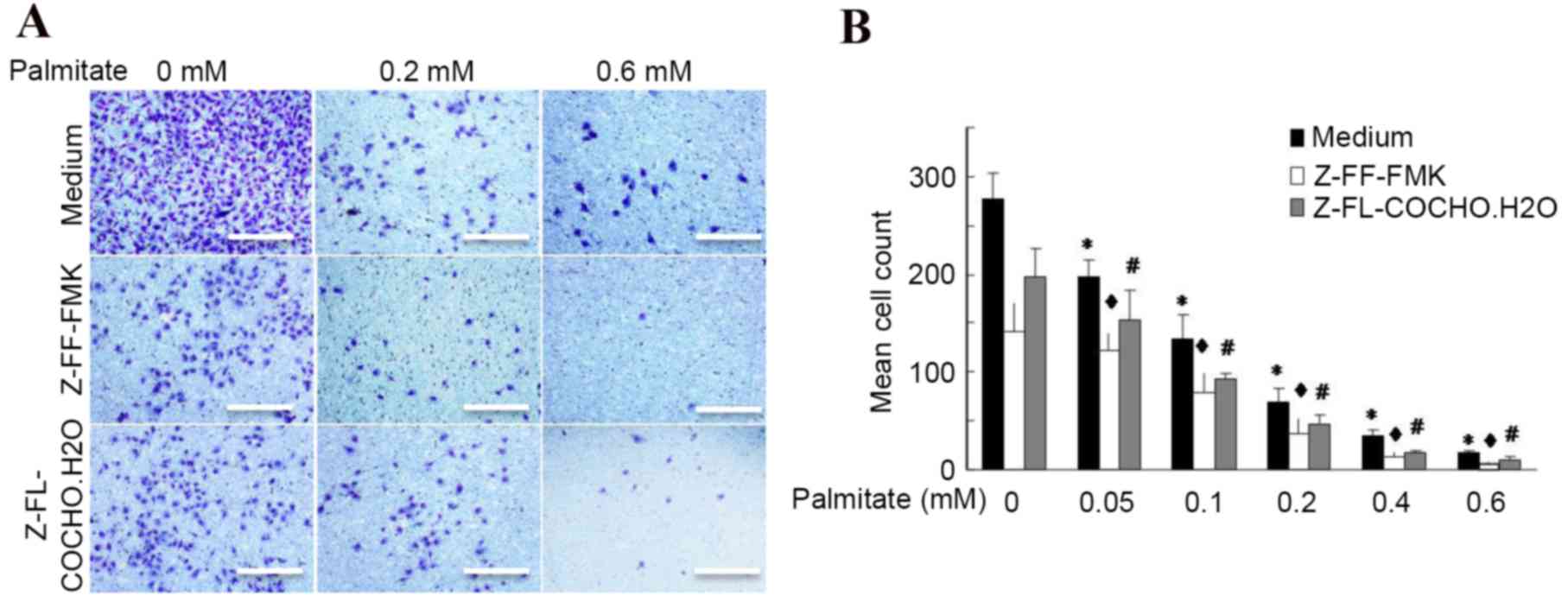
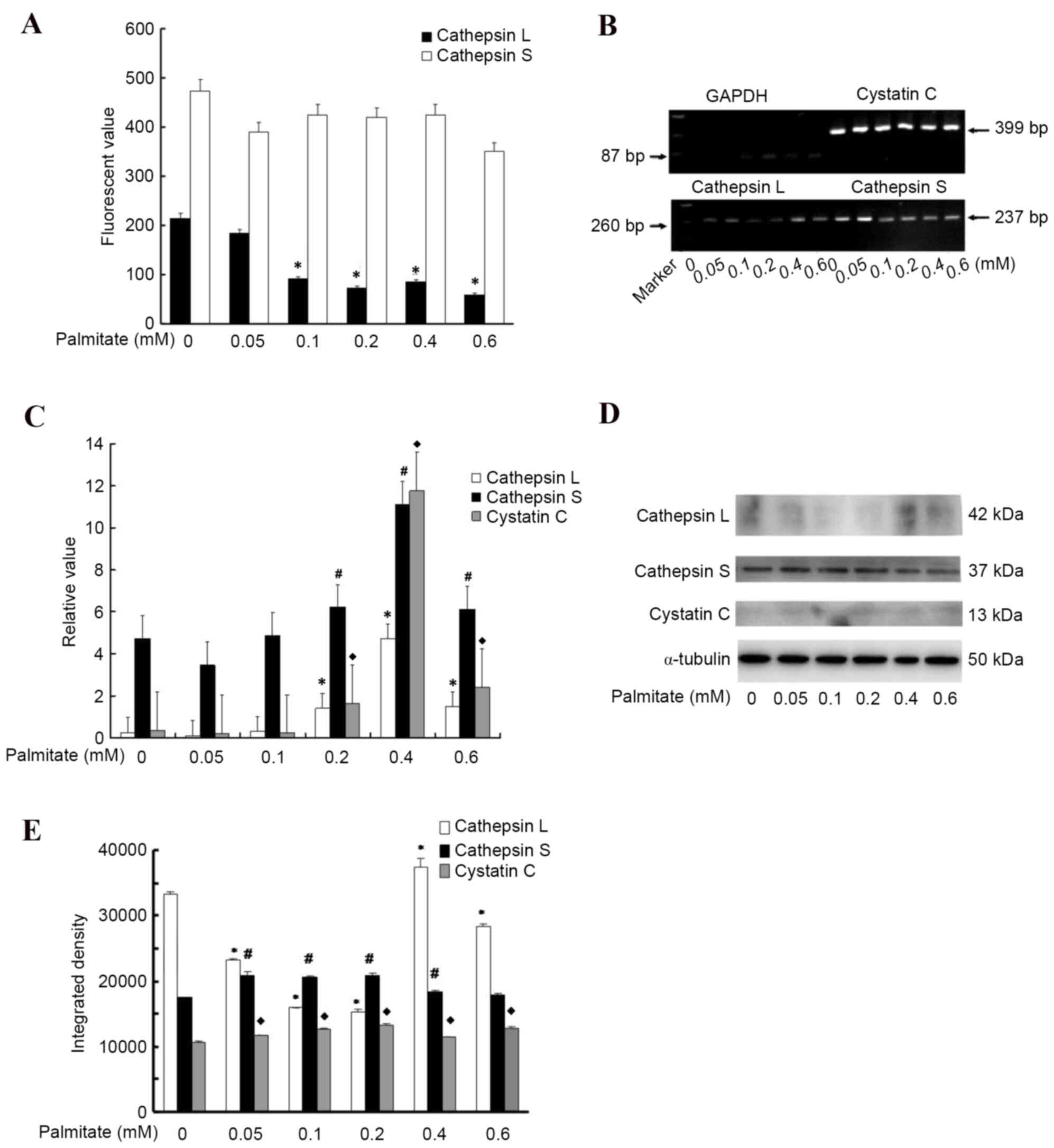
|
1
|
Binet F and Sapieha P: ER stress and
angiogenesis. Cell Metab. 22:560–575. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pourrajab F, Zarch A Vakili,
Hekmatimoghaddam S and Zare-Khormizi MR: MicroRNAs; easy and potent
targets in optimizing therapeutic methods in reparative
angiogenesis. J Cell Mol Med. 19:2702–2714. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Urbich C, Heeschen C, Aicher A, Sasaki K,
Bruhl T, Farhadi MR, Vajkoczy P, Hofmann WK, Peters C, Pennacchio
LA, et al: Cathepsin L is required for endothelial progenitor
cell-induced neovascularization. Nat Med. 11:206–213. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shi GP, Sukhova GK, Kuzuya M, Ye Q, Du J,
Zhang Y, Pan JH, Lu ML, Cheng XW, Iguchi A, et al: Deficiency of
the cysteine protease cathepsin S impairs microvessel growth. Circ
Res. 92:493–500. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Conus S and Simon HU: Cathepsins: Key
modulators of cell death and inflammatory responses. Biochem
Pharmacol. 76:1374–1382. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Droga-Mazovec G, Bojic L, Petelin A,
Ivanova S, Romih R, Repnik U, Salvesen GS, Stoka V, Turk V and Turk
B: Cysteine cathepsins trigger caspase-dependent cell death through
cleavage of bid and antiapoptotic Bcl-2 homologues. J Biol Chem.
283:19140–19150. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zheng X, Chu F, Mirkin BL, Sudha T, Mousa
SA and Rebbaa A: Role of the proteolytic hierarchy between
cathepsin Lcathepsin D and caspase-3 in regulation of cellular
susceptibility to apoptosis and autophagy. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1783:2294–2300. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shulman GI: Cellular mechanisms of insulin
resistance. J Clin Invest. 106:171–176. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Boden G and Shulman GI: Free fatty acids
in obesity and type 2 diabetes: Defining their role in the
development of insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction. Eur J
Clin Invest. 32 Suppl 3:S14–S23. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Listenberger LL, Ory DS and Schaffer JE:
Palmitate-induced apoptosis can occur through a
ceramide-independent pathway. J Biol Chem. 276:14890–14895. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Listenberger LL, Han X, Lewis SE, Cases S,
RV Jr, Ory DS Farese and Schaffer JE: Triglyceride accumulation
protects against fatty acid-induced lipotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 100:pp. 3077–3082. 2003; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Paumen MB, Ishida Y, Muramatsu M, Yamamoto
M and Honjo T: Inhibition of carnitine palmitoyltransferase I
augments sphingolipid synthesis and palmitate-induced apoptosis. J
Biol Chem. 272:3324–3329. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cnop M, Hannaert JC, Hoorens A, Eizirik DL
and Pipeleers DG: Inverse relationship between cytotoxicity of free
fatty acids in pancreatic islet cells and cellular triglyceride
accumulation. Diabetes. 50:1771–1777. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ostrander DB, Sparagna GC, Amoscato AA,
McMillin JB and Dowhan W: Decreased cardiolipin synthesis
corresponds with cytochrome c release in palmitate-induced
cardiomyocyte apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 276:38061–38067.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pinter E, Mahooti S, Wang Y, Imhof BA and
Madri JA: Hyperglycemia-induced vasculopathy in the murine
vitelline vasculature: Correlation with PECAM-1/CD31 tyrosine
phosphorylation state. Am J Pathol. 154:1367–1379. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ciapaite J, Van Bezu J, Van Eikenhorst G,
Bakker SJ, Teerlink T, Diamant M, Heine RJ, Krab K, Westerhoff HV
and Schalkwijk CG: Palmitate and oleate have distinct effects on
the inflammatory phenotype of human endothelial cells. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1771:147–154. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Urbich C, Dernbach E, Rössig L, Zeiher AM
and Dimmeler S: High glucose reduces cathepsin L activity and
impairs invasion of circulating progenitor cells. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 45:429–436. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shimabukuro M, Zhou YT, Levi M and Unger
RH: Fatty acid-induced beta cell apoptosis: A link between obesity
and diabetes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:pp. 2498–2502. 1998;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chiu HC, Kovacs A, Ford DA, Hsu FF, Garcia
R, Herrero P, Saffitz JE and Schaffer JE: A novel mouse model of
lipotoxic cardiomyopathy. J Clin Invest. 107:813–822. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gudz TI, Tserng KY and Hoppel CL: Direct
inhibition of mitochondrial respiratory chain complex III by
cell-permeable ceramide. J Biol Chem. 272:24154–24158. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Vafeiadou K, Weech M, Sharma V, Yaqoob P,
Todd S, Williams CM, Jackson KG and Lovegrove JA: A review of the
evidence for the effects of total dietary fat, saturated,
monounsaturated and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids on vascular
function, endothelial progenitor cells and microparticles. Br J
Nutr. 107:303–324. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang CL, Lyngmo V and Nordøy A: The
effects of saturated fatty acids on endothelial cells. Thromb Res.
65:65–75. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Artwohl M, Roden M, Waldhäusl W,
Freudenthaler A and Baumgartner-Parzer SM: Free fatty acids trigger
apoptosis and inhibit cell cycle progression in human vascular
endothelial cells. FASEB J. 18:146–148. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yu H, Yang Z, Ding X, Wang Y and Han Y:
Correlation between the different chain lengths of free fatty acid
oxidation and ability of trophoblastic invasion. Chin Med J (Engl).
127:3378–3382. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dimmeler S, Haendeler J, Galle J and
Zeiher AM: Oxidized low-density lipoprotein induces apoptosis of
human endothelial cells by activation of CPP32-like proteases. A
mechanistic clue to the ‘response to injury’ hypothesis.
Circulation. 95:1760–1763. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sata M and Walsh K: Oxidized LDL activates
fas-mediated endothelial cell apoptosis. J Clin Invest.
102:1682–1689. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Raymond MA, Désormeaux A, Laplante P,
Vigneault N, Filep JG, Landry K, Pshezhetsky AV and Hébert MJ:
Apoptosis of endothelial cells triggers a caspase-dependent
anti-apoptotic paracrine loop active on VSMC. FASEB J. 18:705–707.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Laplante P, Raymond MA, Gagnon G,
Vigneault N, Sasseville AM, Langelier Y, Bernard M, Raymond Y and
Hébert MJ: Novel fibrogenic pathways are activated in response to
endothelial apoptosis: Implications in the pathophysiology of
systemic sclerosis. J Immunol. 174:5740–5749. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li D, Yang B and Mehta JL: Ox-LDL induces
apoptosis in human coronary artery endothelial cells: Role of PKC,
PTK, bcl-2, and Fas. Am J Physiol. 275:H568–H576. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Choy JC, Granville DJ, Hunt DW and McManus
BM: Endothelial cell apoptosis: Biochemical characteristics and
potential implications for atherosclerosis. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
33:1673–1690. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cirman T, Oresić K, Mazovec GD, Turk V,
Reed JC, Myers RM, Salvesen GS and Turk B: Selective disruption of
lysosomes in HeLa cells triggers apoptosis mediated by cleavage of
Bid by multiple papain-like lysosomal cathepsins. J Biol Chem.
279:3578–3587. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Heinrich M, Neumeyer J, Jakob M, Hallas C,
Tchikov V, Winoto-Morbach S, Wickel M, Schneider-Brachert W,
Trauzold A, Hethke A and Schütze S: Cathepsin D links TNF-induced
acid sphingomyelinase to Bid-mediated caspase-9 and −3 activation.
Cell Death Differ. 11:550–563. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Stoka V, Turk B, Schendel SL, Kim TH,
Cirman T, Snipas SJ, Ellerby LM, Bredesen D, Freeze H, Abrahamson
M, et al: Lysosomal protease pathways to apoptosis. Cleavage of
bid, not pro-caspases, is the most likely route. J Biol Chem.
276:3149–3157. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Guicciardi ME, Leist M and Gores GJ:
Lysosomes in cell death. Oncogene. 23:2881–2890. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Schotte P, Van Criekinge W, Van de Craen
M, Van Loo G, Desmedt M, Grooten J, Cornelissen M, De Ridder L,
Vandekerckhove J, Fiers W, et al: Cathepsin B-mediated activation
of the proinflammatory caspase-11. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
251:379–387. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Vancompernolle K, Van Herreweghe F,
Pynaert G, Van de Craen M, De Vos K, Totty N, Sterling A, Fiers W,
Vandenabeele P and Grooten J: Atractyloside-induced release of
cathepsin B, a protease with caspase-processing activity. FEBS
Lett. 438:150–158. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ishisaka R, Utsumi T, Kanno T, Arita K,
Katunuma N, Akiyama J and Utsumi K: Participation of a cathepsin
L-type protease in the activation of caspase-3. Cell Struct Funct.
24:465–470. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ishisaka R, Kanno T, Akiyama J, Yoshioka
T, Utsumi K and Utsumi T: Activation of caspase-3 by lysosomal
cysteine proteases and its role in
2,2′-azobis-(2-amidinopropane)dihydrochloride (AAPH)-induced
apoptosis in HL-60 cells. J Biochem. 129:35–41. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tsai JY, Lee MJ, Dah-Tsyr Chang M and
Huang H: The effect of catalase on migration and invasion of lung
cancer cells by regulating the activities of cathepsin S, L, and K.
Exp Cell Res. 323:28–40. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhang Q, Han M, Wang W, Song Y, Chen G,
Wang Z and Liang Z: Downregulation of cathepsin L suppresses cancer
invasion and migration by inhibiting transforming growth
factor-β-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncol Rep.
33:1851–1859. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Burden RE, Gormley JA, Jaquin TJ, Small
DM, Quinn DJ, Hegarty SM, Ward C, Walker B, Johnston JA, Olwill SA
and Scott CJ: Antibody-mediated inhibition of cathepsin S blocks
colorectal tumor invasion and angiogenesis. Clin Cancer Res.
15:6042–6051. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Li X, Cheng XW, Hu L, Wu H, Guo-Ping, Hao
CN, Jiang H, Zhu E, Huang Z, Inoue A, et al: Cathepsin S activity
controls ischemia-induced neovascularization in mice. Int J
Cardiol. 183:198–208. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|