|
1
|
Min YG: The pathophysiology, diagnosis and
treatment of allergic rhinitis. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2:65–76. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Meltzer EO, Nathan R, Derebery J, Stang
PE, Campbell UB, Yeh WS, Corrao M and Stanford R: Sleep, quality of
life, and productivity impact of nasal symptoms in the United
States: Findings from the Burden of Rhinitis in America survey.
Allergy Asthma Proc. 30:pp. 244–254. 2009; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Makino Y, Noguchi E, Takahashi N,
Matsumoto Y, Kubo S, Yamada T, Imoto Y, Ito Y, Osawa Y, Shibasaki
M, et al: Apolipoprotein A-IV is a candidate target molecule for
the treatment of seasonal allergic rhinitis. J Allergy Clin
Immunol. 126:1163–1169.e5. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nathan RA: The burden of allergic
rhinitis. Allergy Asthma Proc. 28:pp. 3–9. 2007; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
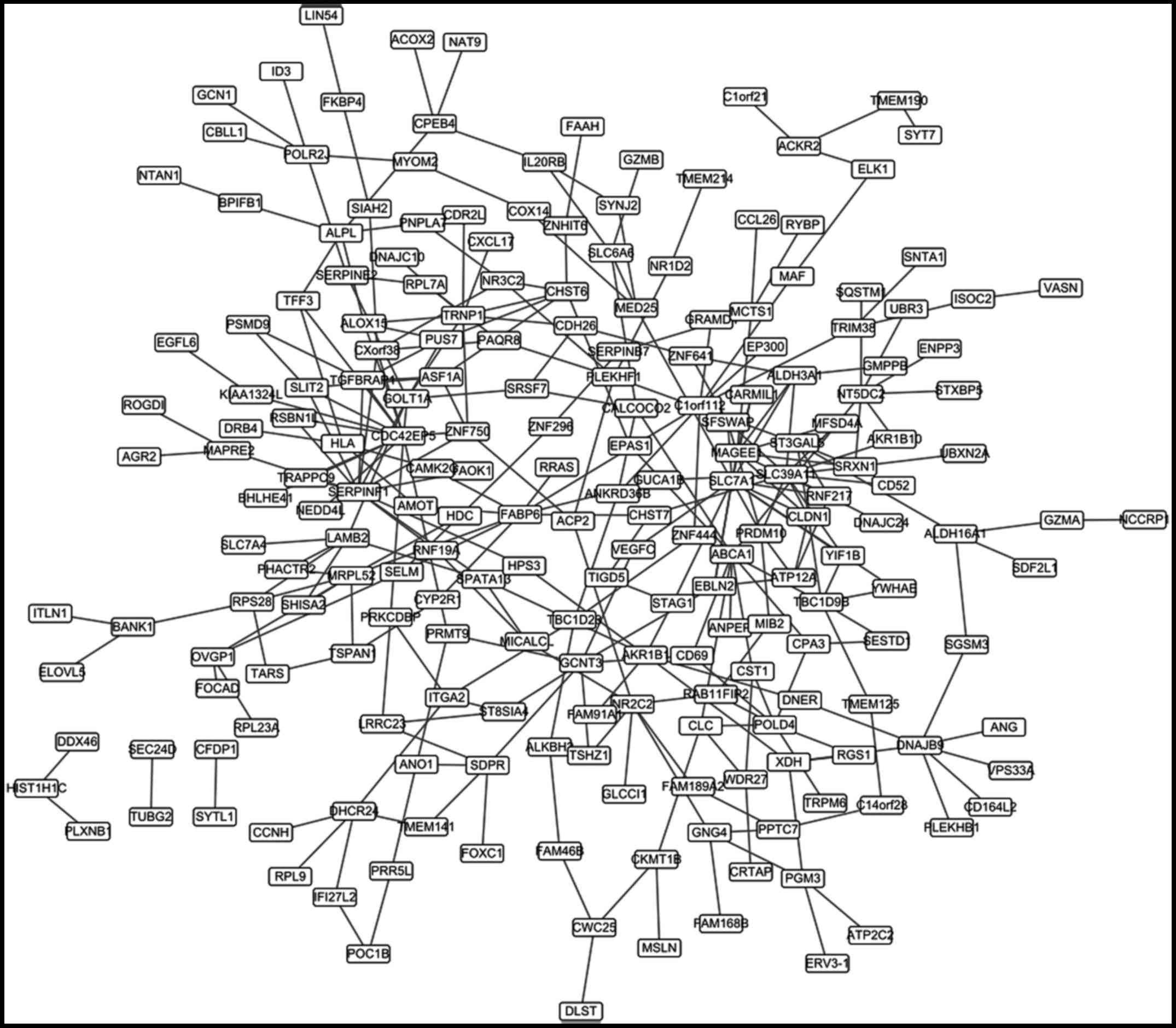
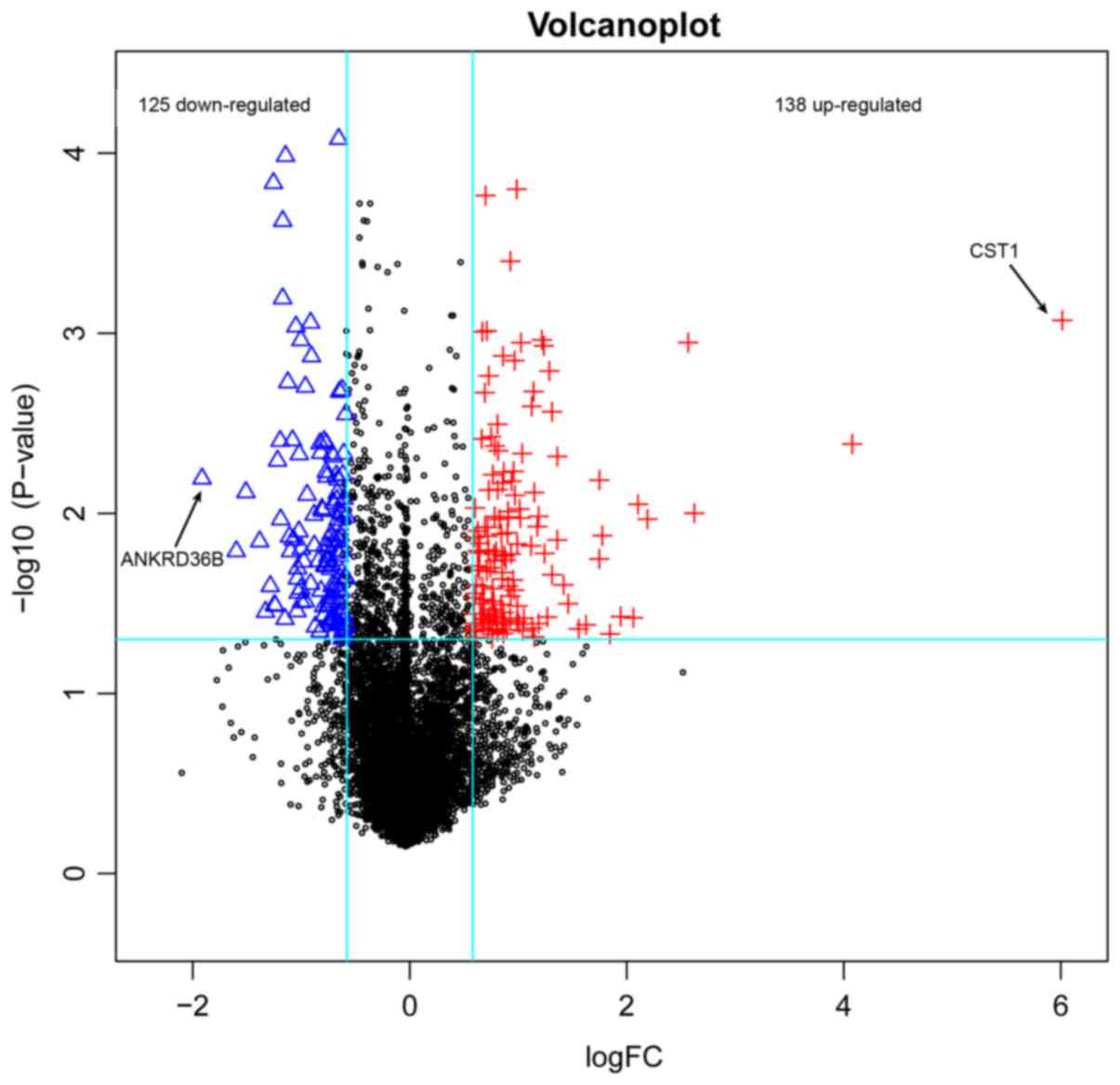
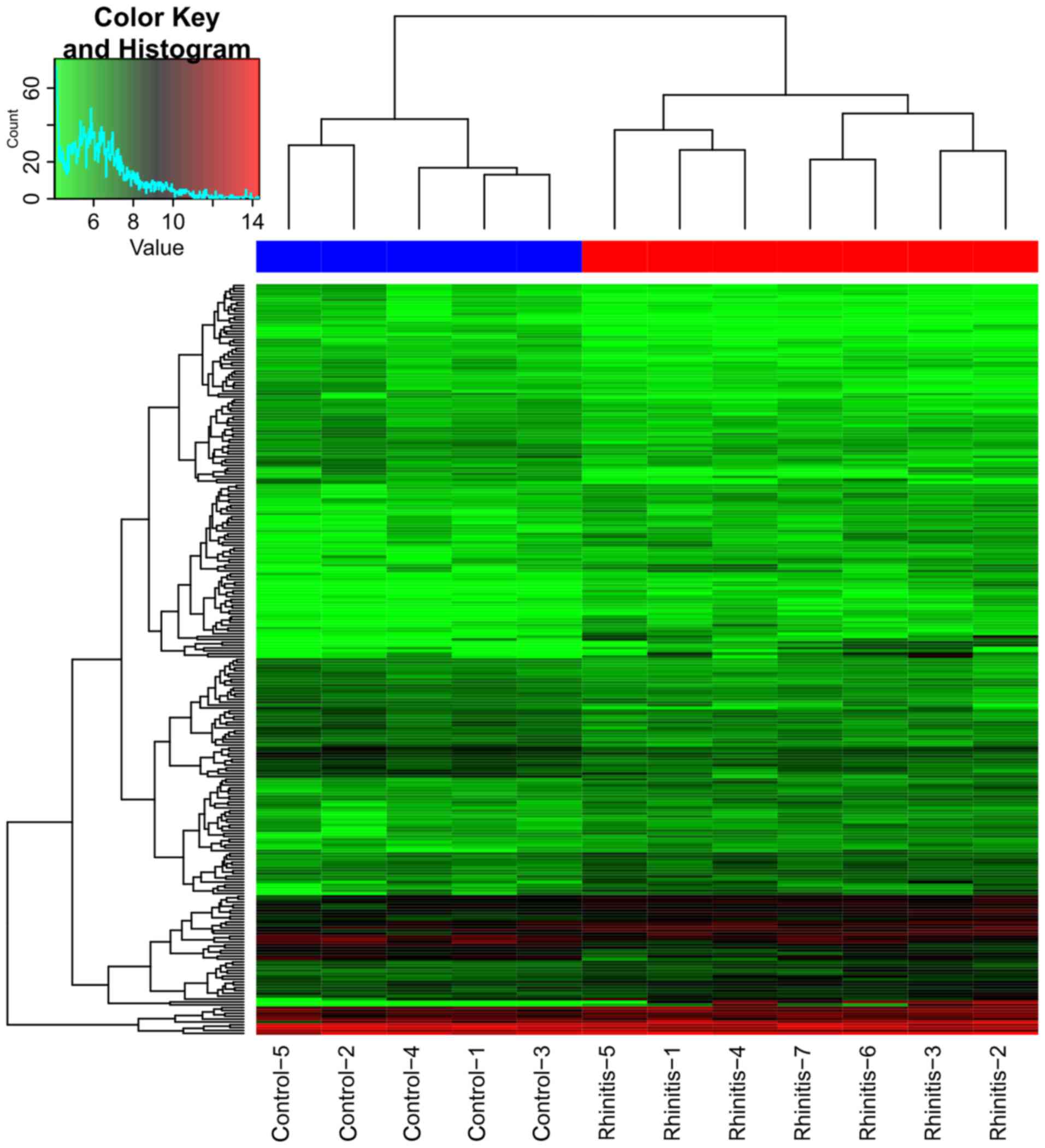
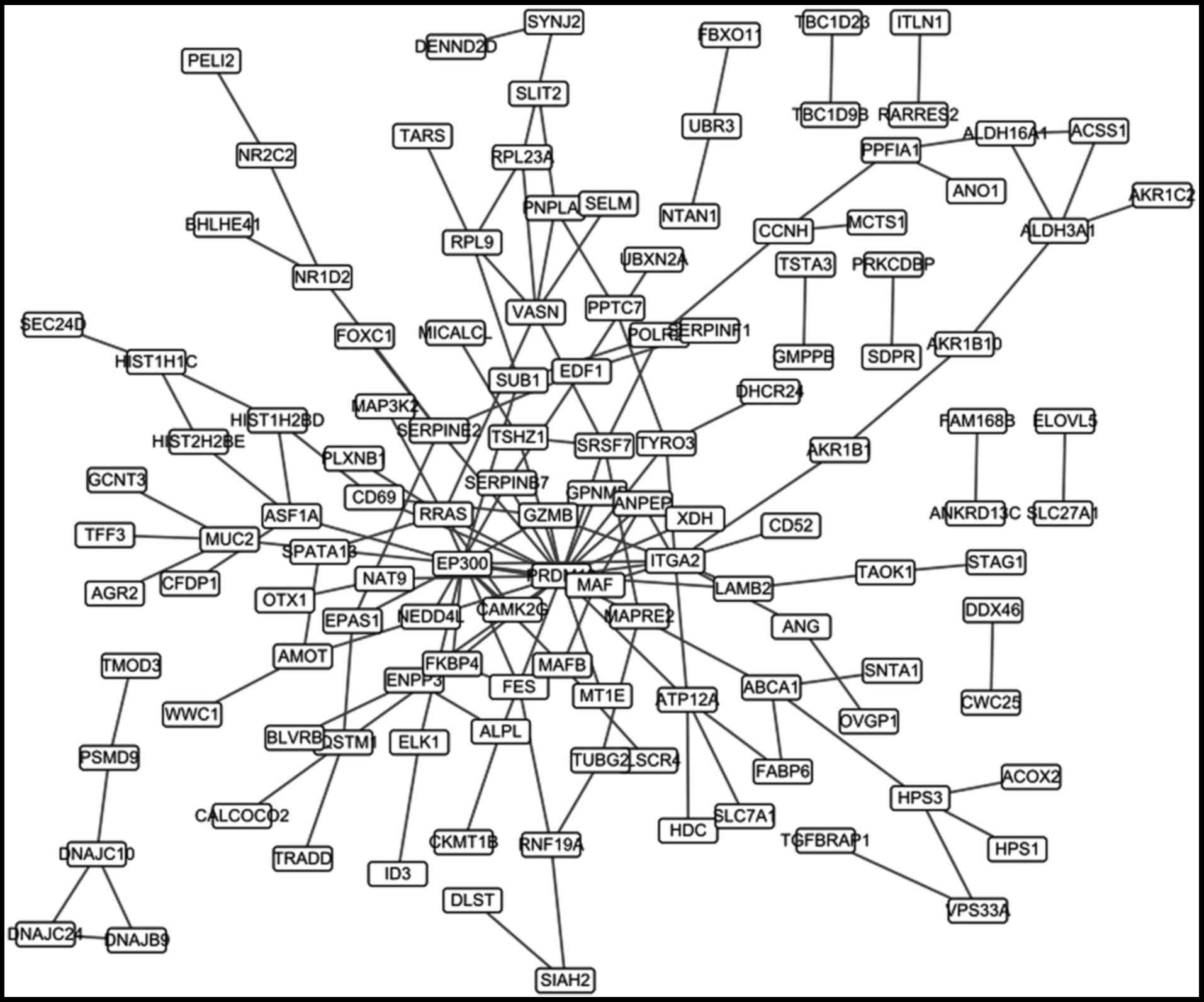
5
|
Passalacqua G and Durham SR; Global
Allergy and Asthma European Network, : Allergic rhinitis and its
impact on asthma update: Allergen immunotherapy. J Allergy Clin
Immunol. 119:881–891. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Calderon MA, Alves B, Jacobson M, Hurwitz
B, Sheikh A and Durham S: Allergen injection immunotherapy for
seasonal allergic rhinitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
24:CD0019362007.
|
|
7
|
Andiappan AK, Wang de Y, Anantharaman R,
Parate PN, Suri BK, Low HQ, Li Y, Zhao W, Castagnoli P, Liu J and
Chew FT: Genome-wide association study for atopy and allergic
rhinitis in a singapore chinese population. PLoS One. 6:e197192011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dávila I, Mullol J, Ferrer M, Bartra J,
del Cuvillo A, Montoro J, Jáuregui I, Sastre J and Valero A:
Genetic aspects of allergic rhinitis. J Investig Allergol Clin
Immunol. 19 Suppl 1:S25–S31. 2009.
|
|
9
|
Hanuskova E and Plevkova J: The role of
histamine H4 receptors as a potential targets in allergic rhinitis
and asthma. Open J Mol Int Physiol. 3:6–14. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Bunyavanich S, Melen E, Wilk JB, Granada
M, Soto-Quiros ME, Avila L, Lasky-Su J, Hunninghake GM, Wickman M,
Pershagen G, et al: Thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) is
associated with allergic rhinitis in children with asthma. Clin Mol
Allergy. 9:12011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Thompson JA, Tan J and Greene CS:
Cross-platform normalization of microarray and RNA-seq data for
machine learning applications. Peerj. 4:e16212016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Diboun I, Wernisch L, Orengo CA and
Koltzenburg M: Microarray analysis after RNA amplification can
detect pronounced differences in gene expression using limma. BMC
Genomics. 7:2522006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhao Z, Guo AY, van den Oord EJ, Aliev F,
Jia P, Edenberg HJ, Riley BP, Dick DM, Bettinger JC, Davies AG, et
al: Multi-species data integration and gene ranking enrich
significant results in an alcoholism genome-wide association study.
BMC Genomics. 13 Suppl 8:S162012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang J, Yu H, Liu BH, Zhao Z, Liu L, Ma
LX, Li YX and Li YY: DCGL v2.0: An R package for unveiling
differential regulation from differential co-expression. PLoS One.
8:e797292013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yu H, Liu BH, Ye ZQ, Li C, Li YX and Li
YY: Link-based quantitative methods to identify differentially
coexpressed genes and gene pairs. BMC Bioinformatics. 12:3152011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Kuhn M,
Simonovic M, Roth A, Minguez P, Doerks T, Stark M, Muller J, Bork
P, et al: The STRING database in 2011: Functional interaction
networks of proteins, globally integrated and scored. Nucleic Acids
Res. 39(Database Issue): D561–568. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Franceschini A, Szklarczyk D, Frankild S,
Kuhn M, Simonovic M, Roth A, Lin J, Minguez P, Bork P, von Mering C
and Jensen LJ: STRING v9.1: Protein-protein interaction networks,
with increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res.
41(Database Issue): D808–D815. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Brehmer D: Endonasal phototherapy with
Rhinolight for the treatment of allergic rhinitis. Expert Rev Med
Devices. 7:21–26. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhu XL, Ai ZH, Wang J, Xu YL and Teng YC:
Weighted gene co-expression network analysis in identification of
endometrial cancer prognosis markers. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
13:4607–4611. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Blood Pressure Lowering Treatment
Trialists' Collaboration, ; Turnbull F, Neal B, Pfeffer M, Kostis
J, Algert C, Woodward M, Chalmers J, Zanchetti A and MacMahon S:
Blood pressure-dependent and independent effects of agents that
inhibit the renin-angiotensin system. J Hypertens. 25:951–958.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bernstein KE, Ong FS, Blackwell WL, Shah
KH, Giani JF, Gonzalez-Villalobos RA, Shen XZ, Fuchs S and Touyz
RM: A modern understanding of the traditional and nontraditional
biological functions of angiotensin-converting enzyme. Pharmacol
Rev. 65:1–46. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Okwan-Duodu D, Datta V, Shen XZ, Goodridge
HS, Bernstein EA, Fuchs S, Liu GY and Bernstein KE:
Angiotensin-converting enzyme overexpression in mouse
myelomonocytic cells augments resistance to Listeria and
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem.
285:39051–39060. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Song GG, Kim JH and Lee YH: Associations
between the insertion/deletion polymorphism of the
angiotensin-converting enzyme and susceptibility to aortic
aneurysms: A meta-analysis. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst.
16:211–218. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lin H, Lin D and Zheng CQ:
Angiotensin-converting enzyme insertion/deletion polymorphism
associated with allergic rhinitis susceptibility: Evidence from
1410 subjects. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 15:593–600.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Evans RM: The steroid and thyroid hormone
receptor superfamily. Science. 240:889–895. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
LaForce C: Use of nasal steroids in
managing allergic rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 103:S388–S394.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mygind N: Topical steroid treatment for
allergic rhinitis and allied conditions. Clin Otolaryngol Allied
Sci. 7:343–352. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Benson M, Strannegård IL, Strannegård O
and Wennergren G: Topical steroid treatment of allergic rhinitis
decreases nasal fluid TH2 cytokines, eosinophils, eosinophil
cationic protein and IgE but has no significant effect on
IFN-gamma, IL-1beta, TNF-alpha, or neutrophils. J Allergy Clin
Immunol. 106:307–312. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Proud D, Baumgarten CR, Naclerio RM and
Ward PE: Kinin metabolism in human nasal secretions during
experimentally induced allergic rhinitis. J Immunol. 138:428–434.
1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ciprandi G, De Amici M, Tosca M and Fuchs
D: Tryptophan metabolism in allergic rhinitis: The effect of pollen
allergen exposure. Hum Immunol. 71:911–915. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wjst M and Hyppönen E: Vitamin D serum
levels and allergic rhinitis. Allergy. 62:1085–1086. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shi J, Zhang Y, Qi S, Liu G, Dong X, Huang
N, Li W, Chen H and Zhu B: Identification of potential crucial gene
network related to seasonal allergic rhinitis using microarray
data. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 274:231–237. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hauswald B and Yarin YM: Acupuncture in
allergic rhinitis: A mini-review. Allergo J Int. 23:115–119. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yu Y, Wu A, Zhang Z, Yan G, Zhang F, Zhang
L, Shen X, Hu R, Zhang Y, Zhang K and Wang F: Characterization of
the GufA subfamily member SLC39A11/Zip11 as a zinc transporter. J
Nutr Biochem. 24:1697–1708. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bao S and Knoell DL: Zinc modulates airway
epithelium susceptibility to death receptor-mediated apoptosis. Am
J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 290:L433–L441. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Besecker B, Bao S, Bohacova B, Papp A,
Sadee W and Knoell DL: The human zinc transporter SLC39A8 (Zip8) is
critical in zinc-mediated cytoprotection in lung epithelia. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 294:L1127–L1136. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Prasad AS: Clinical, immunological,
anti-inflammatory and antioxidant roles of zinc. Exp Gerontol.
43:370–377. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
AlKhyat THAT, Alturaihy SH and Ali ZA: The
relationship between tumour necrosis factor -alpha and zinc/copper
ratio in iraqi patients with allergic rhinitis. Glob J Sci Front
Res. 13:2013.
|
|
39
|
Hirsch DS, Pirone DM and Burbelo PD: A new
family of Cdc42 effector proteins, CEPs, function in fibroblast and
epithelial cell shape changes. J Biol Chem. 276:875–883. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hall A: Rho GTPases and the actin
cytoskeleton. Science. 279:509–514. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wesselborg S, Bauer MK, Vogt M, Schmitz ML
and Schulze-Osthoff K: Activation of transcription factor NF-kappaB
and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase is mediated by distinct
and separate stress effector pathways. J Biol Chem.
272:12422–12429. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Puls A, Eliopoulos AG, Nobes CD, Bridges
T, Young LS and Hall A: Activation of the small GTPase Cdc42 by the
inflammatory cytokines TNF(alpha) and IL-1, and by the Epstein-Barr
virus transforming protein LMP1. J Cell Sci. 112:2983–2992.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ito TK, Yokoyama M, Yoshida Y, Nojima A,
Kassai H, Oishi K, Okada S, Kinoshita D, Kobayashi Y, Fruttiger M,
et al: A crucial role for CDC42 in senescence-associated
inflammation and atherosclerosis. PLoS One. 9:e1021862014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kim KC and Huang S: Histone
methyltransferases in tumor suppression. Cancer Biol Ther.
2:491–499. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Huang S: Histone methyltransferases, diet
nutrients and tumour suppressors. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:469–476. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Park JA, Kim TH, Lee B, Kwon E and Kim KC:
Expression of PRDM10 in arthritic synovial derived tissues. Genes
Genomics. 35:685–691. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Center CM: Methods of using prdm1 genetic
variants to prognose, diagnose and treat inflammatory bowel
disease. 2011.
|
|
48
|
Horsch M, Aguilar-Pimentel JA, Bönisch C,
Côme C, Kolster-Fog C, Jensen KT, Lund AH, Lee I, Grossman LI,
Sinkler C, et al: Cox4i2, Ifit2, and Prdm11 Mutant Mice: Effective
selection of genes predisposing to an altered airway inflammatory
response from a large compendium of mutant mouse lines. PLoS One.
10:e01345032015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|