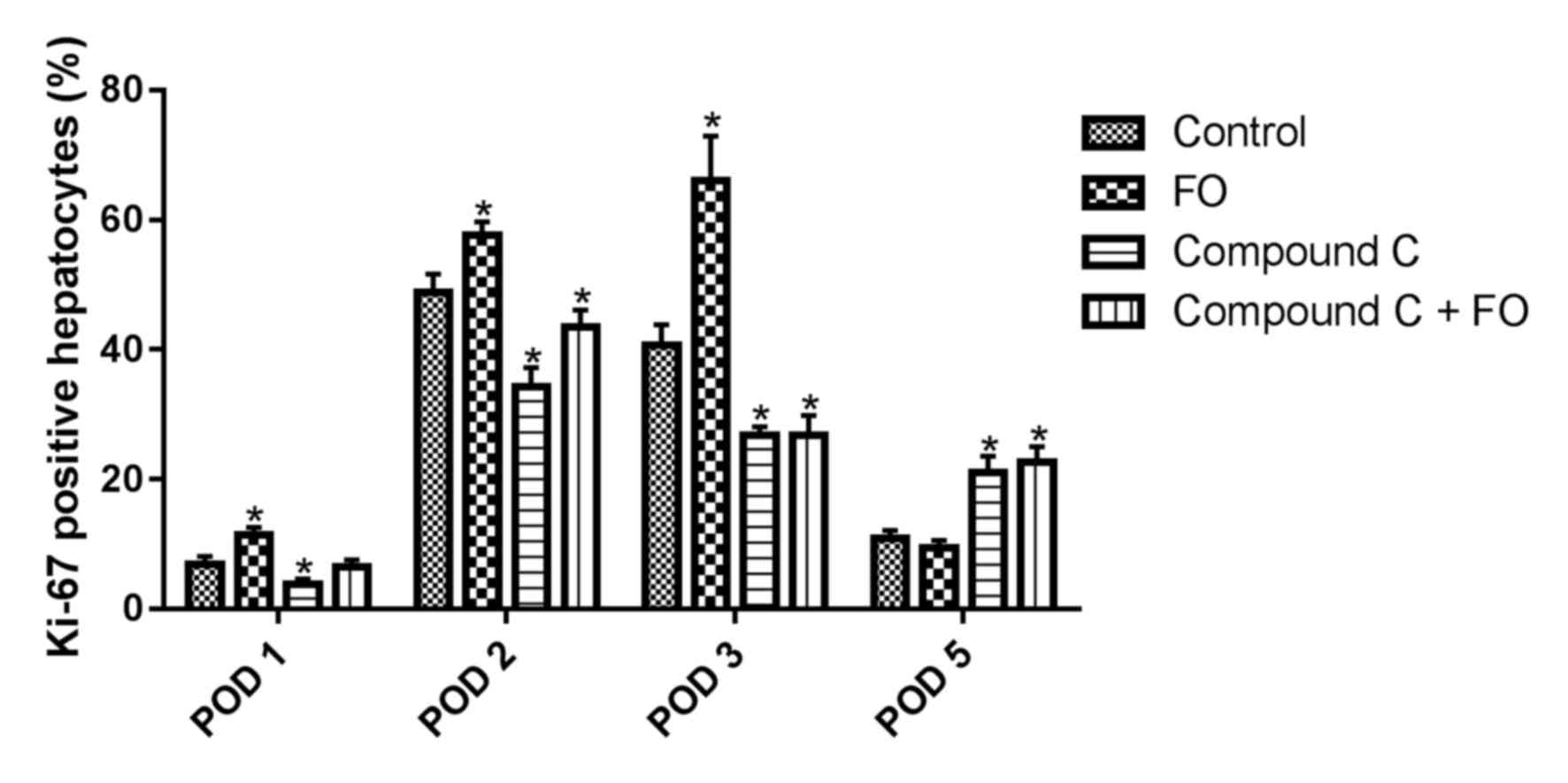
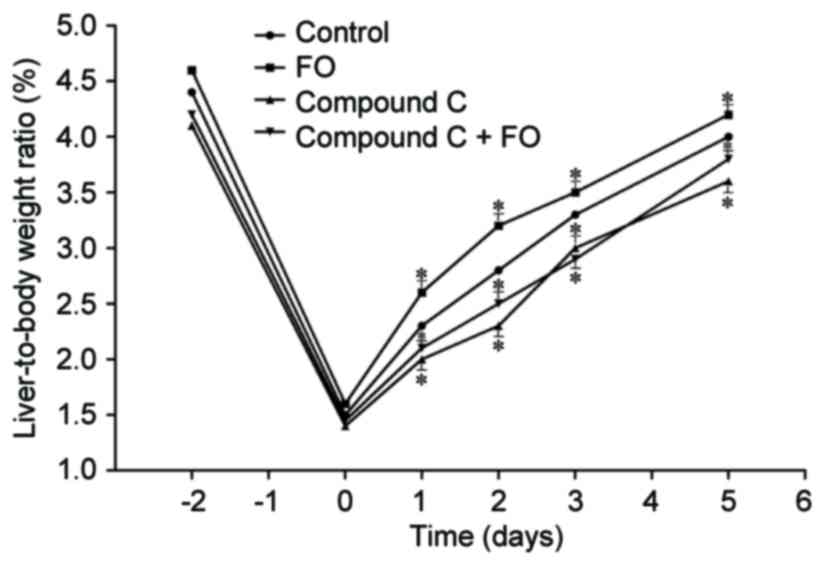
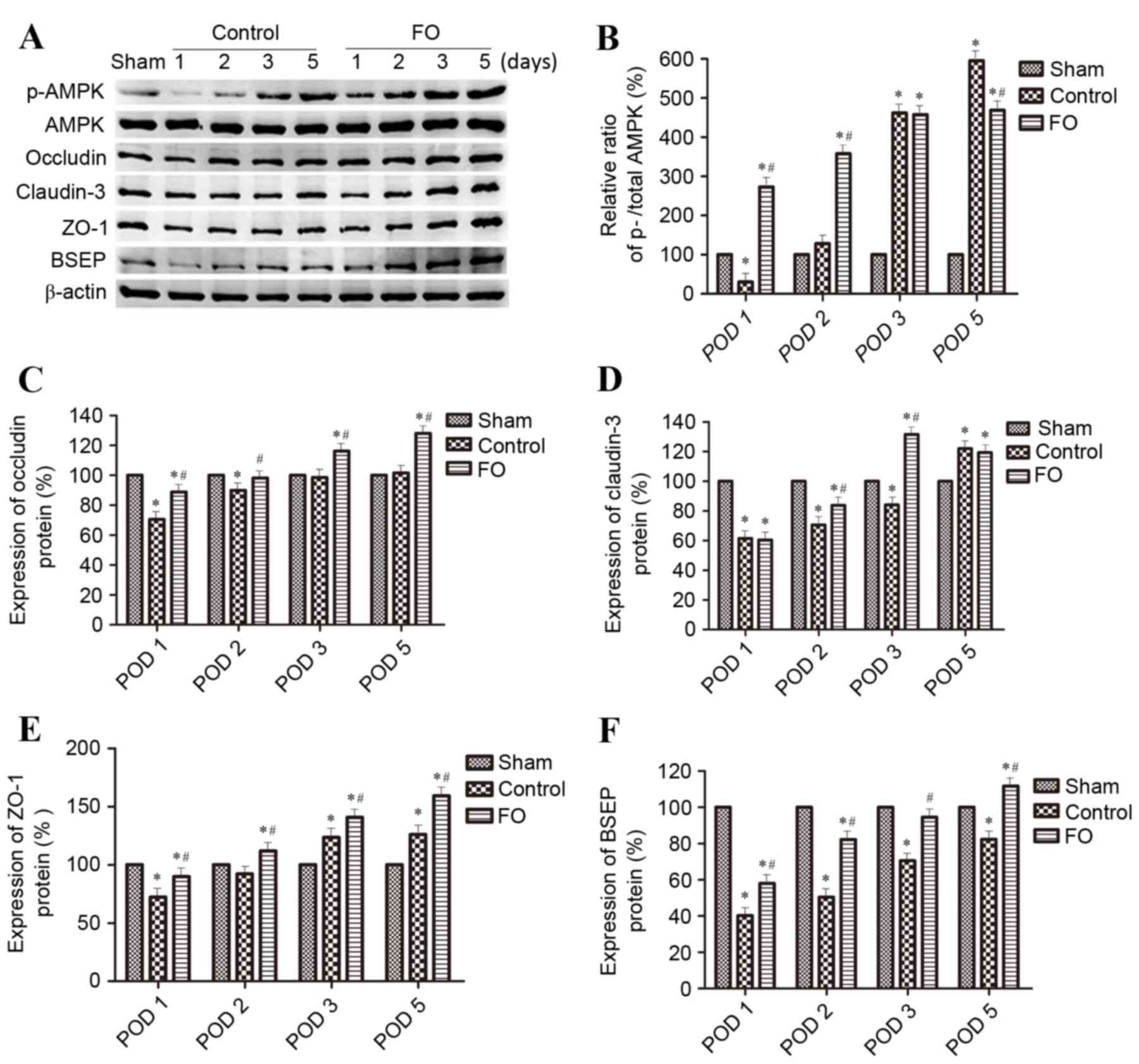
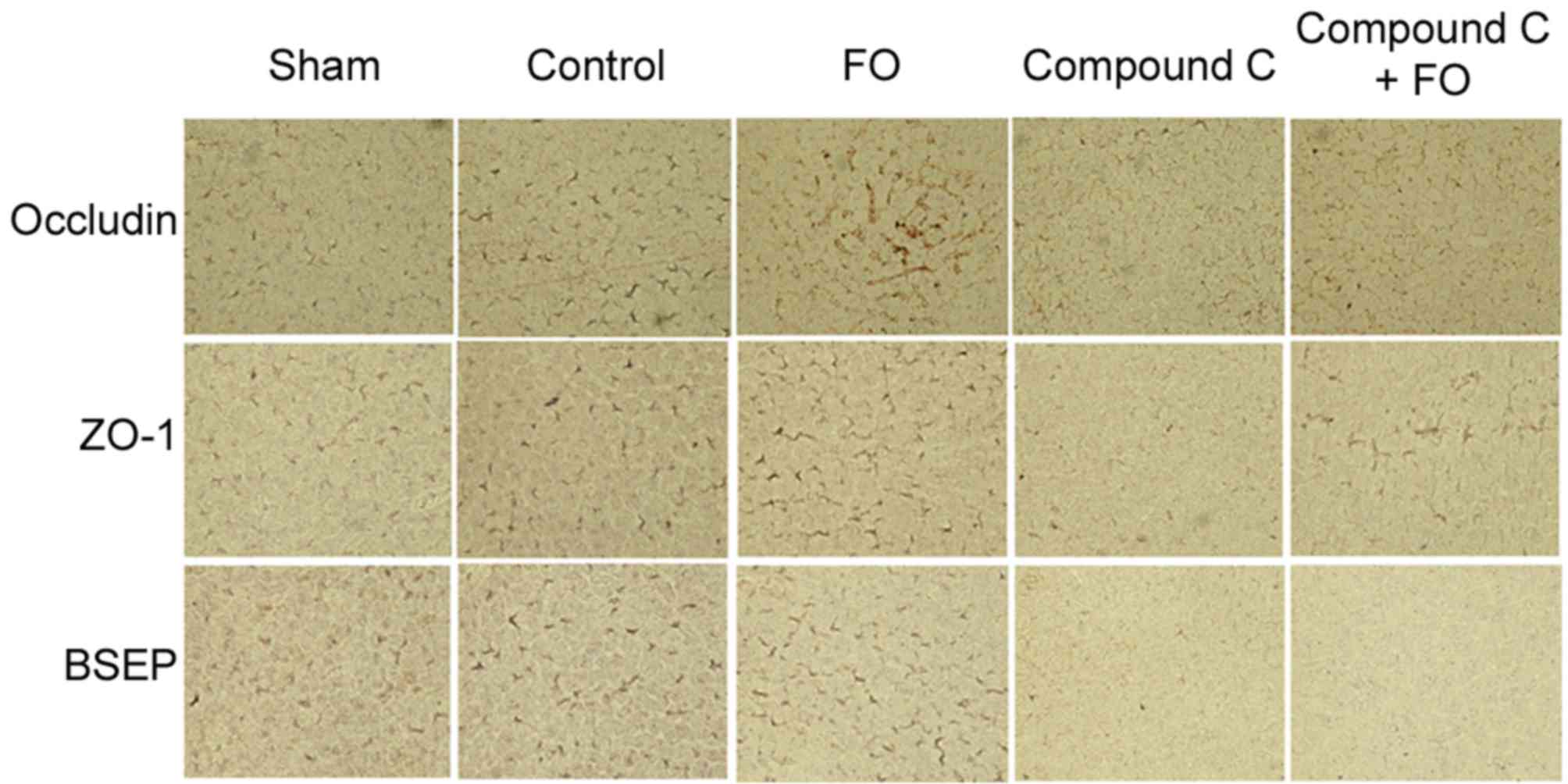
|
1
|
Ding BS, Cao Z, Lis R, Nolan DJ, Guo P,
Simons M, Penfold ME, Shido K, Rabbany SY and Rafii S: Divergent
angiocrine signals from vascular niche balance liver regeneration
and fibrosis. Nature. 505:97–102. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Willenbring H and Grompe M: A therapy for
liver failure found in the JNK yard. Cell. 153:283–284. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fausto N, Campbell JS and Riehle KJ: Liver
regeneration. Hepatology. 43 2 Suppl 1:S45–S53. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wuestefeld T, Pesic M, Rudalska R, Dauch
D, Longerich T, Kang TW, Yevsa T, Heinzmann F, Hoenicke L, Hohmeyer
A, et al: A direct in vivo RNAi screen identifies MKK4 as a key
regulator of liver regeneration. Cell. 153:389–401. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Taub R: Liver regeneration: From myth to
mechanism. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 5:836–847. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Michalopoulos GK: Principles of liver
regeneration and growth homeostasis. Compr Physiol. 3:485–513.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
He VJ: Professor Norbert Hüser: The
function of immune cells for liver regeneration after partial
hepatectomy. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 3:52–54. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Svegliati-Baroni G, Candelaresi C,
Saccomanno S, Ferretti G, Bachetti T, Marzioni M, De Minicis S,
Nobili L, Salzano R, Omenetti A, et al: A model of insulin
resistance and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in rats: Role of
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha and n-3
polyunsaturated fatty acid treatment on liver injury. Am J Pathol.
169:846–860. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pradelli L, Mayer K, Muscaritoli M and
Heller AR: n-3 fatty acid-enriched parenteral nutrition regimens in
elective surgical and ICU patients: A meta-analysis. Crit Care.
16:R1842012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fu D, Wakabayashi Y, Lippincott-Schwartz J
and Arias IM: Bile acid stimulates hepatocyte polarization through
a cAMP-Epac-MEK-LKB1-AMPK pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:pp.
1403–1408. 2011; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
International Transporter Consortium, ;
Giacomini KM, Huang SM, Tweedie DJ, Benet LZ, Brouwer KL, Chu X,
Dahlin A, Evers R, Fischer V, et al: Membrane transporters in drug
development. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 9:215–236. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Woods A, Heslegrave AJ, Muckett PJ, Levene
AP, Clements M, Mobberley M, Ryder TA, Abu-Hayyeh S, Williamson C,
Goldin RD, et al: LKB1 is required for hepatic bile acid transport
and canalicular membrane integrity in mice. Biochem J. 434:49–60.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fu D, Wakabayashi Y, Ido Y,
Lippincott-Schwartz J and Arias IM: Regulation of bile canalicular
network formation and maintenance by AMP-activated protein kinase
and LKB1. J Cell Sci. 123:3294–3302. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Merlen G, Gentric G, Celton-Morizur S,
Foretz M, Guidotti JE, Fauveau V, Leclerc J, Viollet B and
Desdouets C: AMPKα1 controls hepatocyte proliferation independently
of energy balance by regulating Cyclin A2 expression. J Hepatol.
60:152–159. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Homolya L, Fu D, Sengupta P, Jarnik M,
Gillet JP, Vitale-Cross L, Gutkind JS, Lippincott-Schwartz J and
Arias IM: LKB1/AMPK and PKA control ABCB11 trafficking and
polarization in hepatocytes. PLoS One. 9:e919212014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Stehr SN and Heller AR: Omega-3 fatty acid
effects on biochemical indices following cancer surgery. Clin Chim
Acta. 373:1–8. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhu XH, Wu YF, Qiu YD, Jiang CP and Ding
YT: Liver-protecting effects of omega-3 fish oil lipid emulsion in
liver transplantation. World J Gastroenterol. 18:6141–6147. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yan XP, Wang S, Yang Y and Qiu YD: Effects
of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on rat livers after partial
hepatectomy via LKB1-AMPK signaling pathway. Transplant Proc.
43:pp. 3604–3612. 2011; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Qiu YD, Wang S, Yang Y and Yan XP: Omega-3
polyunsaturated fatty acids promote liver regeneration after 90%
hepatectomy in rats. World J Gastroenterol. 18:3288–3295.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Grosse B, Degrouard J, Jaillard D and
Cassio D: Build them up and break them down: Tight junctions of
cell lines expressing typical hepatocyte polarity with a varied
repertoire of claudins. Tissue Barriers. 1:e252102013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Son S, Kojima T, Decaens C, Yamaguchi H,
Ito T, Imamura M, Murata M, Tanaka S, Chiba H, Hirate K and Sawada
N: Knockdown of tight junction protein claudin-2 prevents bile
canalicular formation in WIF-B9 cells. Histochem Cell Biol.
131:411–424. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kojima T, Yamamoto T, Murata M, Chiba H,
Kokai Y and Sawada N: Regulation of the blood-biliary barrier:
Interaction between gap and tight junctions in hepatocytes. Med
Electron Microsc. 36:157–164. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee JH, Koh H, Kim M, Kim Y, Lee SY,
Karess RE, Lee SH, Shong M, Kim JM, Kim J and Chung J:
Energy-dependent regulation of cell structure by AMP-activated
protein kinase. Nature. 447:1017–1020. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Baas AF, Kuipers J, van der Wel NN, Batlle
E, Koerten HK, Peters PJ and Clevers HC: Complete polarization of
single intestinal epithelial cells upon activation of LKB1 by
STRAD. Cell. 116:457–466. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang L, Li J, Young LH and Caplan MJ:
AMP-activated protein kinase regulates the assembly of epithelial
tight junctions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:pp. 17272–17277. 2006;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang YL, Guo H, Zhang CS, Lin SY, Yin Z,
Peng Y, Luo H, Shi Y, Lian G, Zhang C, et al: AMP as a low-energy
charge signal autonomously initiates assembly of AXIN-AMPK-LKB1
complex for AMPK activation. Cell Metab. 18:546–555. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gowans GJ, Hawley SA, Ross FA and Hardie
DG: AMP is a true physiological regulator of AMP-activated protein
kinase by both allosteric activation and enhancing net
phosphorylation. Cell Metab. 18:556–566. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|