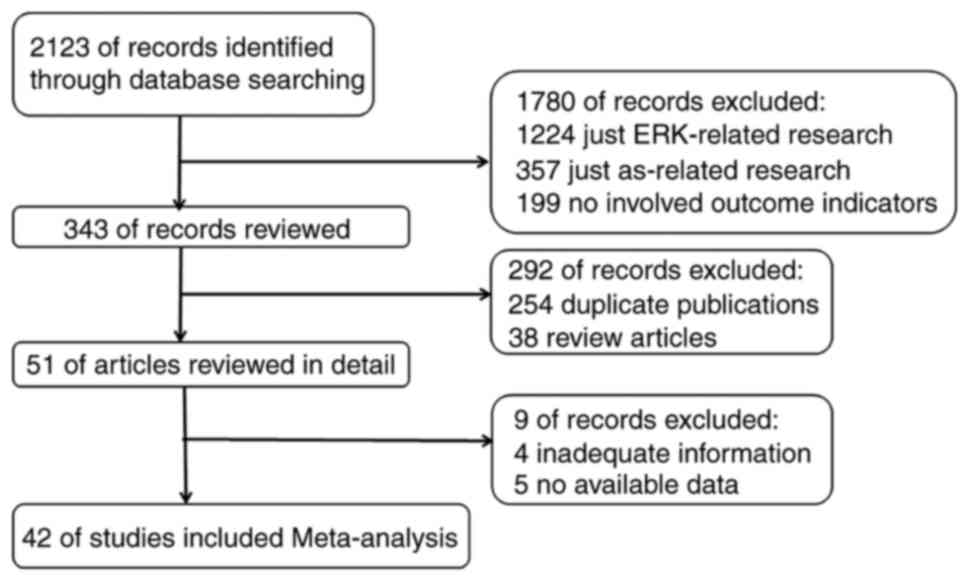
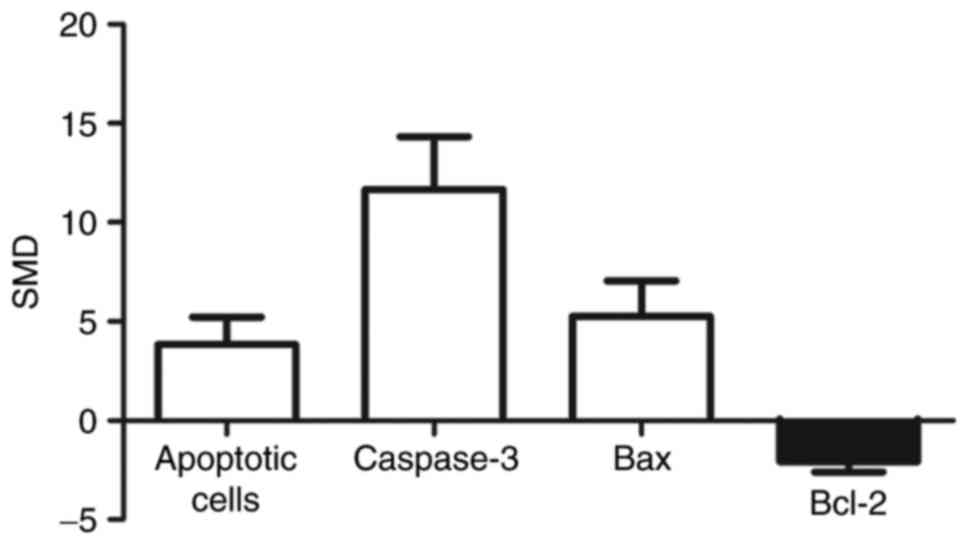
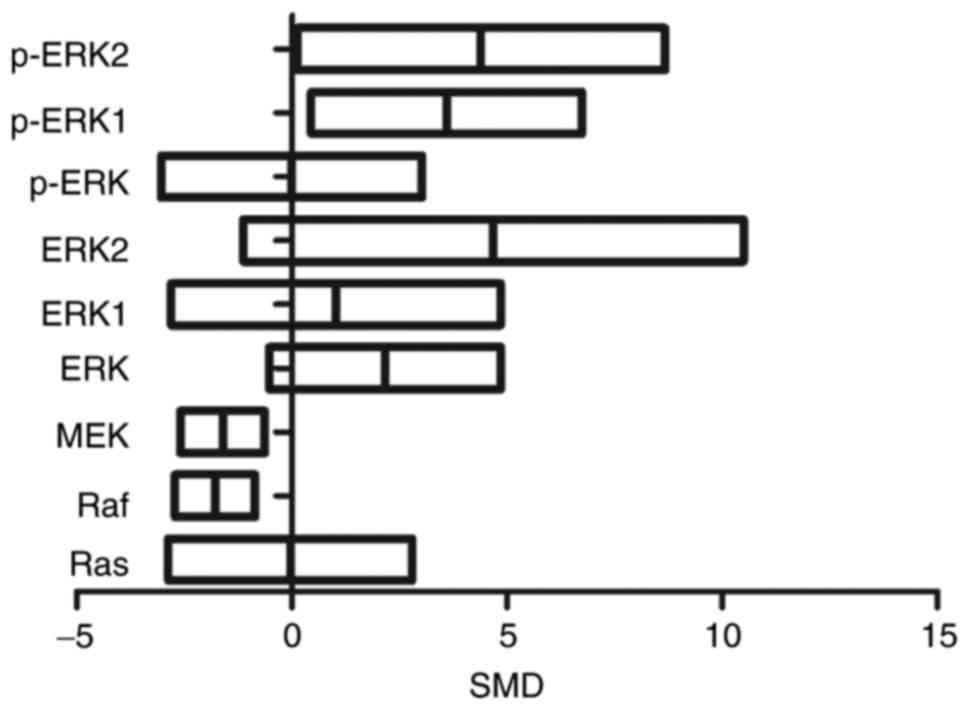
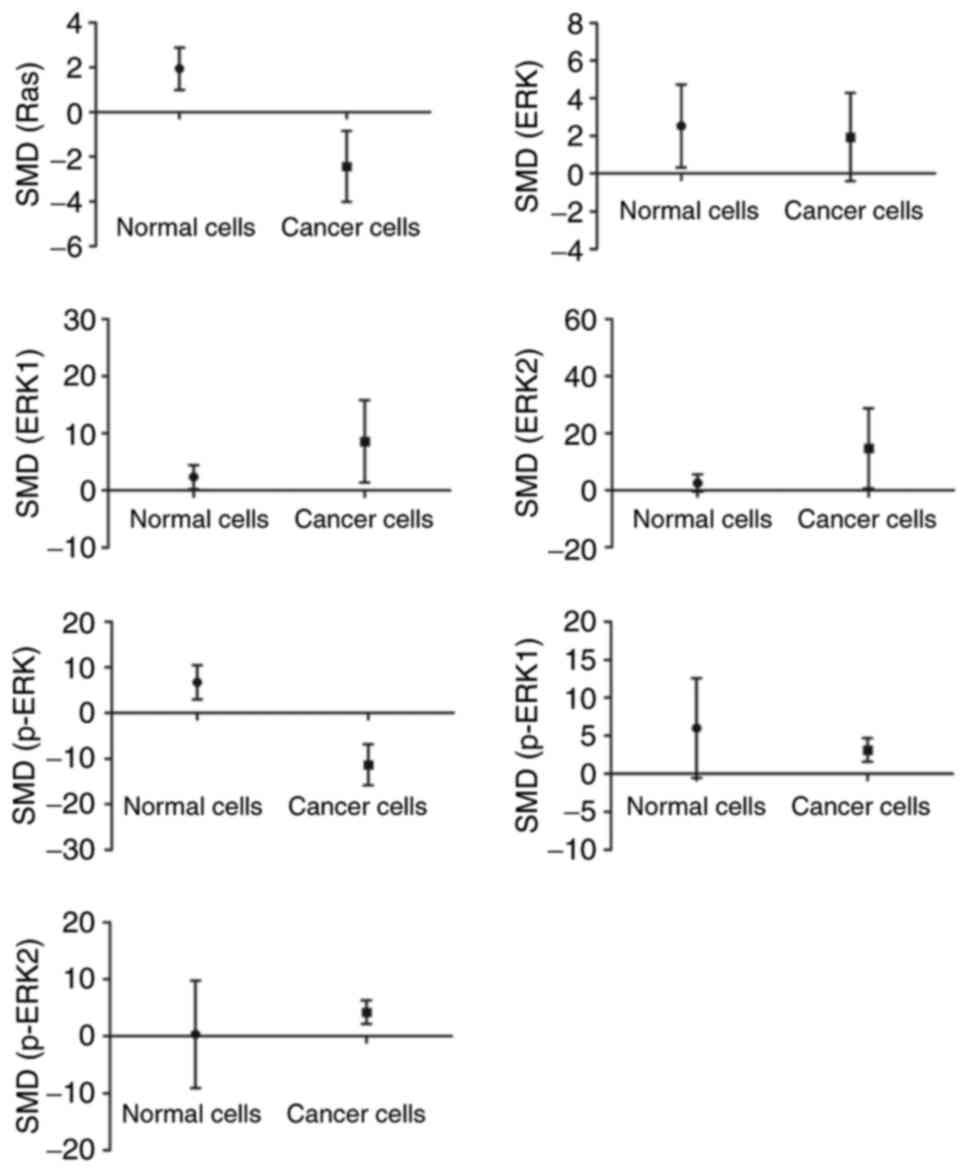
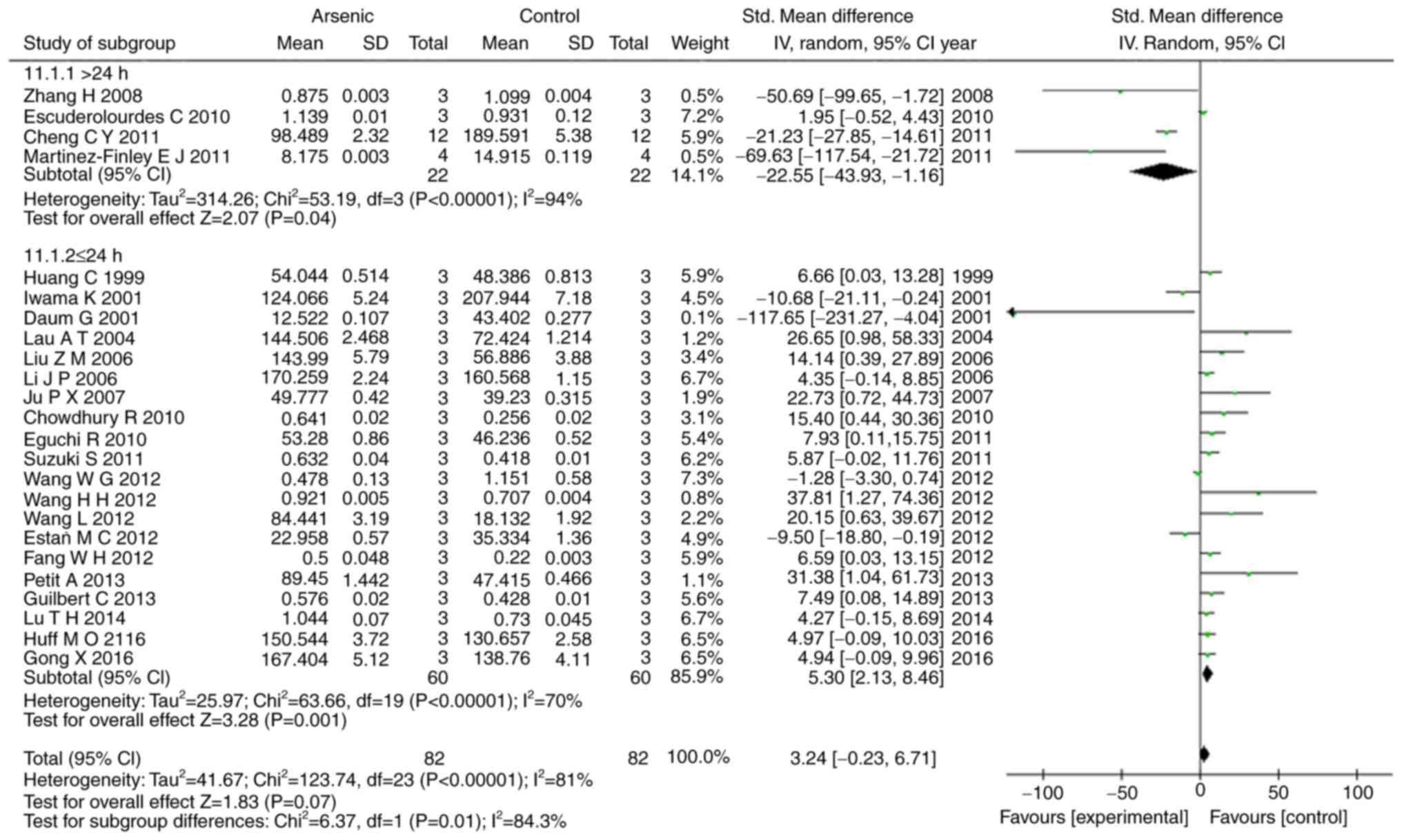
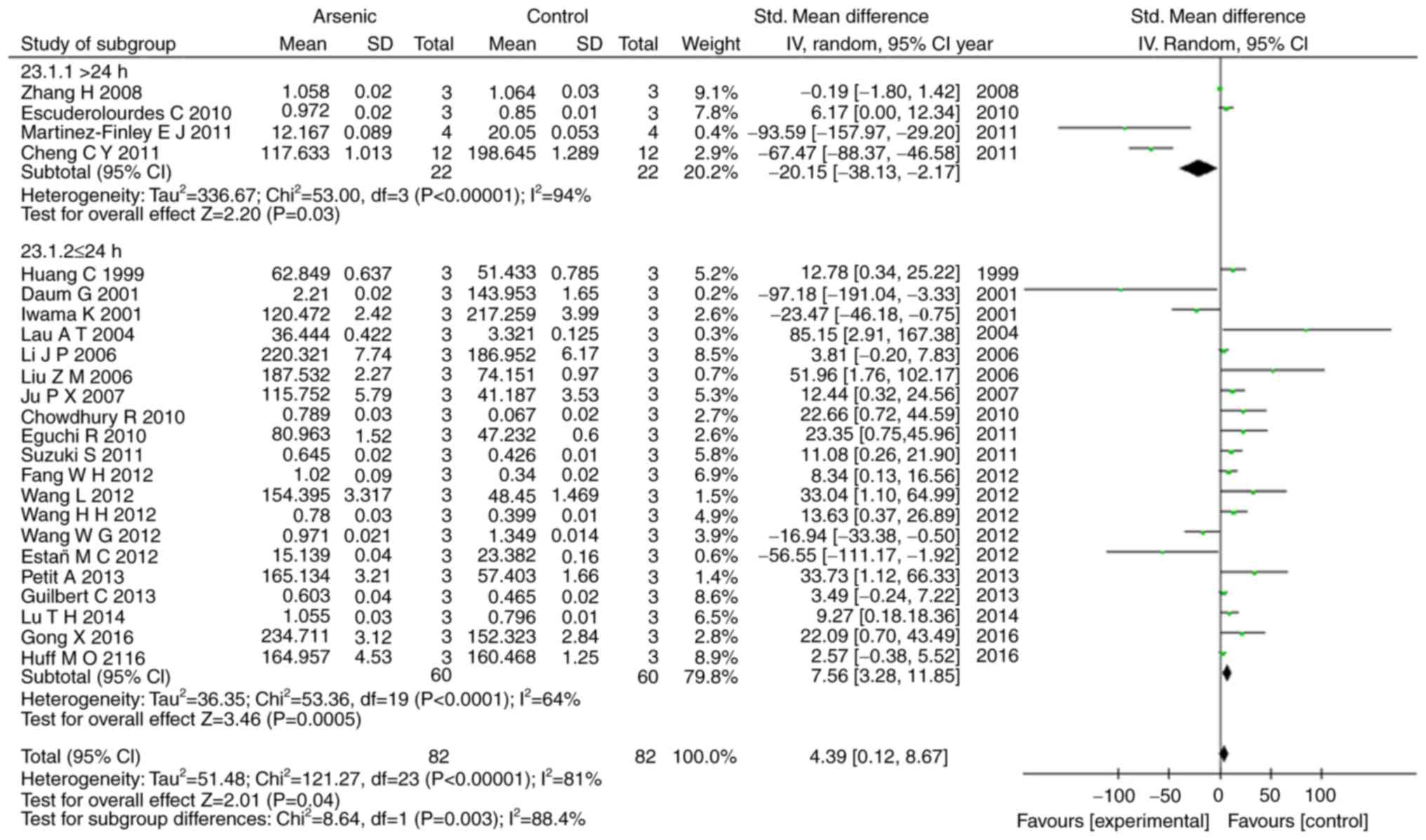
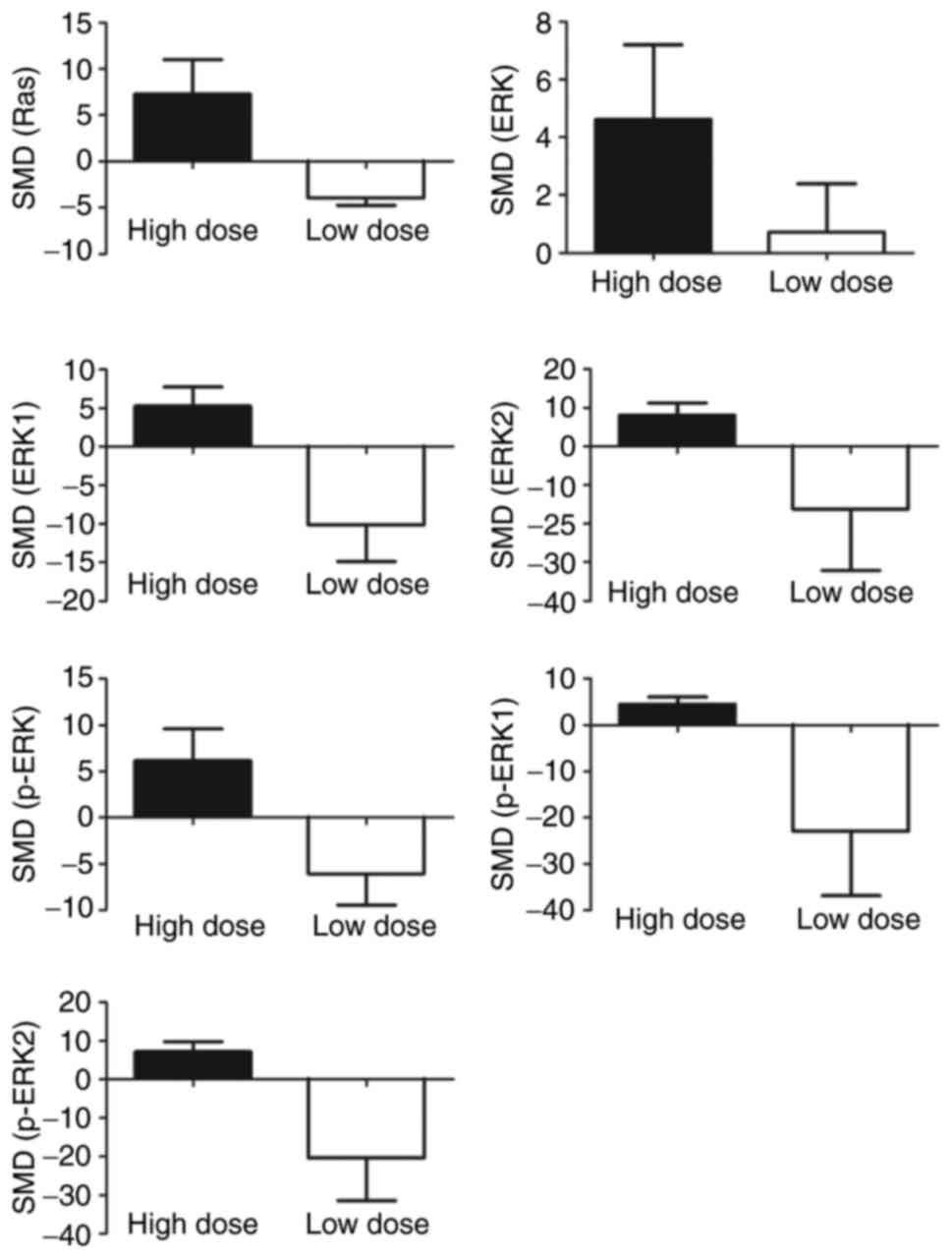
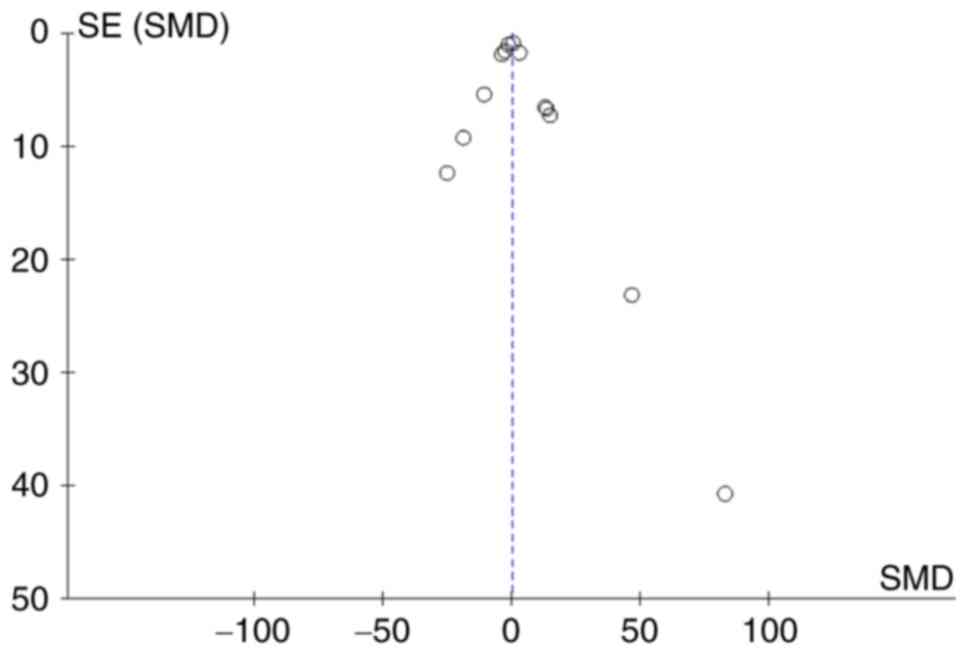
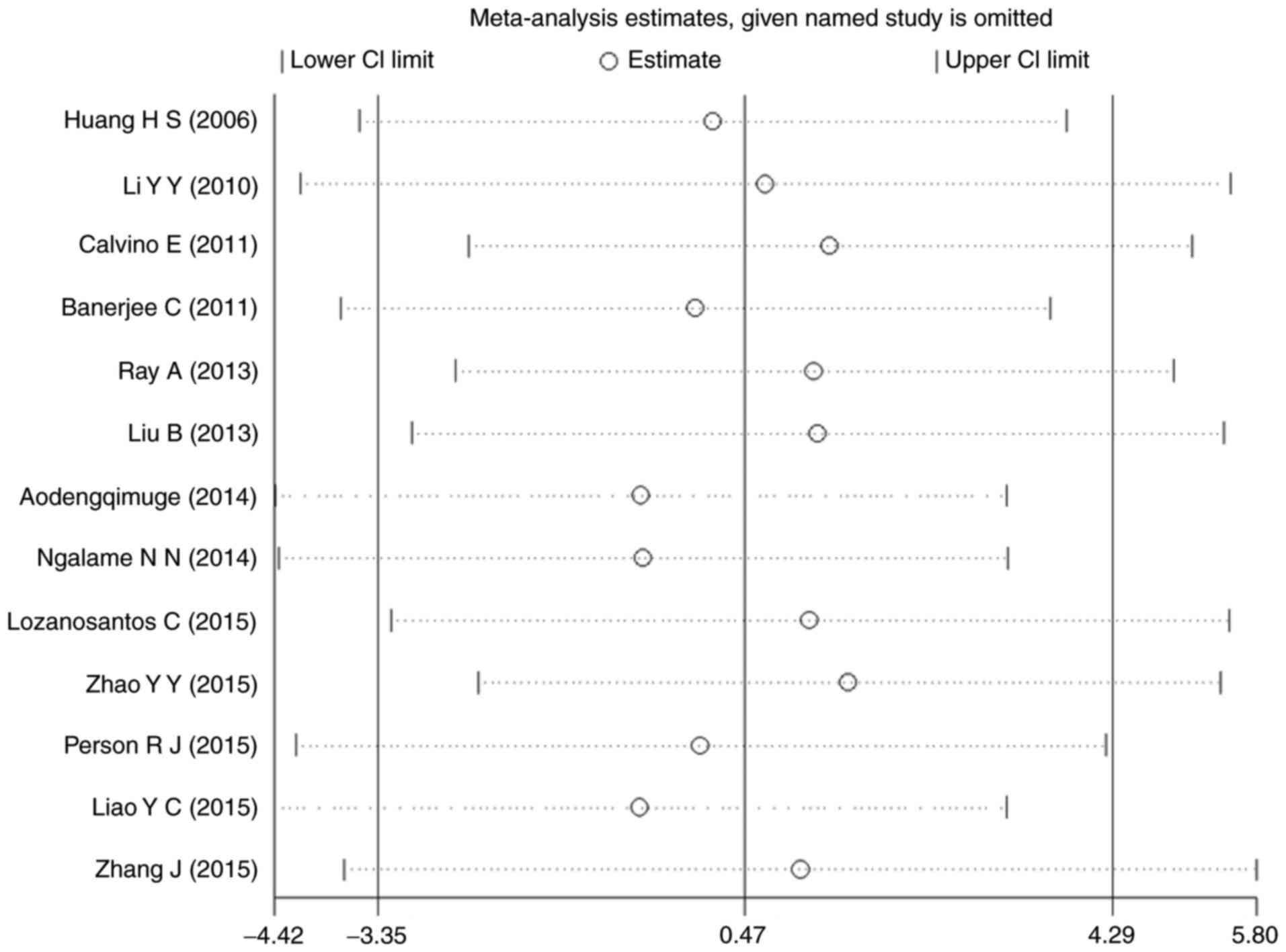
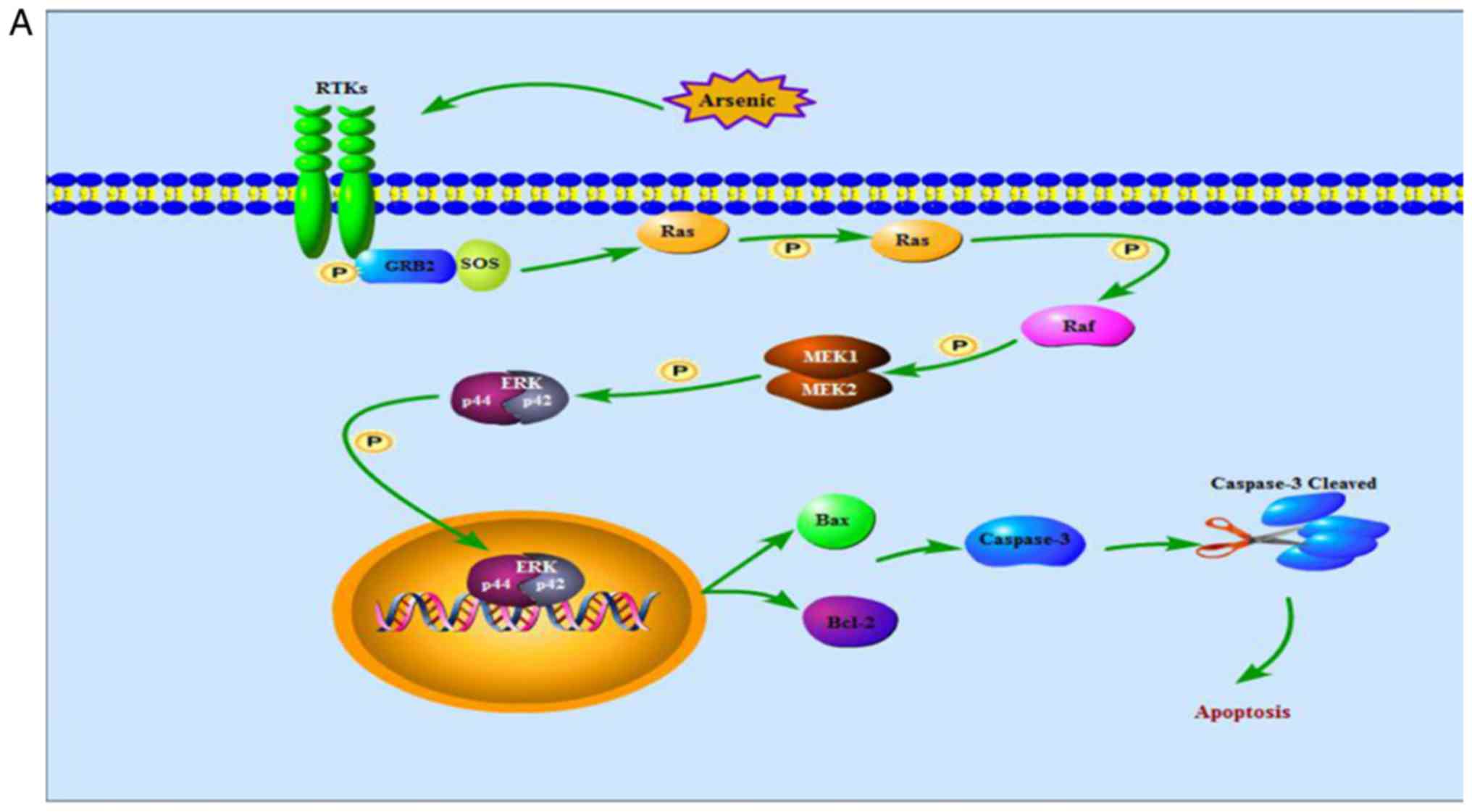
|
1
|
Singh N, Kumar D, Lal K, Raisuddin S and
Sahu AP: Adverse health effects due to arsenic exposure:
Modification by dietary supplementation of jaggery in mice. Toxicol
Appl Pharmacol. 242:247–255. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yen CC, Ho TJ, Wu CC, Chang CF, Su CC,
Chen YW, Jinn TR, Lu TH, Cheng PW, Su YC and Liu SH: Inorganic
arsenic causes cell apoptosis in mouse cerebrum through an
oxidative stress-regulated signaling pathway. Arch Toxicol.
85:565–575. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Eguchi R, Fujimori Y, Takeda H, Tabata C,
Ohta T, Kuribayashi K, Fukuoka K and Nakano T: Arsenic trioxide
induces apoptosis through JNK and ERK in human mesothelioma cells.
J Cell Physiol. 226:762–768. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ray A, Chatterjee S, Mukherjee S and
Bhattacharya S: Interplay of loss of ERK dependence and
amplification of apoptotic signals in arsenic treated rat
hepatocytes. Natl Acad Sci Lett. 36:599–602. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lau AT, Li M, Xie R, He QY and Chiu JF:
Opposed arsenite-induced signaling pathways promote cell
proliferation or apoptosis in cultured lung cells. Carcinogenesis.
25:21–28. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li JP, Lin JC and Yang JL: ERK activation
in arsenite-treated G1-enriched CL3 cells contributes to survival,
DNA repair inhibition, and micronucleus formation. Toxicol Sci.
89:164–172. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lozano-Santos C, Amigo-Jiménez I,
Nova-Gurumeta S, Pérez-Sanz N, García-Pardo A and García-Marco JA:
Arsenic trioxide synergistically potentiates the cytotoxic effect
of fludarabine in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells by further
inactivating the AKT and ERK signaling pathways. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 461:243–248. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ge Y, Xu G and Zhang C: The effects of
arsenious acid on the apoptosis and the expression of ERK-1 protein
of human hepatocarcinoma cells. J Anhui Med Univ. 40:412–414.
2005.
|
|
9
|
Escudero-Lourdes C, Medeiros MK,
Cárdenas-González MC, Wnek SM and Gandolfi JA: Low level exposure
to monomethyl arsenous acid-induced the over-production of
inflammation-related cytokines and the activation of cell signals
associated with tumor progression in a urothelial cell model.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 244:162–173. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang WG, Ma LL and Sun BL: Arsenic
trioxide induces apoptosis and inhibit activity of ERK in HL-60
cells. J Mod Oncol. 20:39–42. 2012.
|
|
11
|
Daum G, Pham J and D eou J: Arsenite
inhibits Ras-dependent activation of ERK but activates ERK in the
presence of oncogenic Ras in baboon vascular smooth muscle cells.
Mol Cell Biochem. 217:131–136. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Benbrahim-Tallaa L, Waterland RA, Styblo
M, Achanzar WE, Webber MM and Waalkes MP: Molecular events
associated with arsenic-induced malignant transformation of human
prostatic epithelial cells: Aberrant genomic DNA methylation and
K-ras oncogene activation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 206:288–298.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chowdhury R, Chatterjee R, Giri AK, Mandal
C and Chaudhuri K: Arsenic-induced cell proliferation is associated
with enhanced ROS generation, ERK signaling and CyclinA expression.
Toxicol Lett. 198:263–271. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li YY, Jiang YF, Yang YY, Wang R, Zhang
BY, Li L and Mu XL: Effects of JNK ERK signaling pathway in
proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induced by
NaAsO2. Prog Mod Biomed. 8:1464–1466. 2010.
|
|
15
|
Suzuki S, Inaba H, Satoh T, Okazaki T and
Takahashi S: Activation of ERK and p38 by the addition of arsenic
trioxide in Flt3-ITD cells. Open J Blood Dis. 1:9–11. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Guilbert C, Annis MG, Dong Z, Siegel PM,
Miller WH Jr and Mann KK: Arsenic trioxide overcomes
rapamycin-induced feedback activation of AKT and ERK signaling to
enhance the anti-tumor effects in breast cancer. PLoS One.
8:e859952013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huff MO, Todd SL, Smith AL, Elpers JT,
Smith AP, Murphy RD, Bleser-Shartzer AS, Hoerter JE, Radde BN and
Klinge CM: Arsenite and cadmium activate MAPK/ERK via membrane
estrogen receptors and G-protein coupled estrogen receptor
signaling in human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Toxicol Sci.
152:62–71. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang L, Kou MC, Weng CY, Hu LW, Wang YJ
and Wu MJ: Arsenic modulates heme oxygenase-1, interleukin-6, and
vascular endothelial growth factor expression in endothelial cells:
Roles of ROS, NF-κB, and MAPK pathways. Arch Toxicol. 86:879–896.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Aodengqimuge, Liu S, Mai S, Li X, Li Y, Hu
M, Yuan S and Song L: AP-1 activation attenuates the
arsenite-induced apoptotic response in human bronchial epithelial
cells by up-regulating HO-1 expression. Biotechnol Lett.
36:1927–1936. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gong X, Ivanov VN and Hei TK:
2,3,5,6-Tetramethylpyrazine (TMP) down-regulated arsenic-induced
heme oxygenase-1 and ARS2 expression by inhibiting Nrf2, NF-κB,
AP-1 and MAPK pathways in human proximal tubular cells. Arch
Toxicol. 90:2187–2200. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Person RJ, Ngalame NN, Makia NL, Bell MW,
Waalkes MP and Tokar EJ: Chronic inorganic arsenic exposure in
vitro induces a cancer cell phenotype in human peripheral lung
epithelial cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 286:36–43. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huang C, Ma WY, Li J, Goranson A and Dong
Z: Requirement of ERK, but not JNK, for arsenite-induced cell
transformation. J Biol Chem. 274:14595–14601. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Martinez-Finley EJ, Goggin SL, Labrecque
MT and Allan AM: Reduced expression of MAPK/ERK genes in perinatal
arsenic-exposed offspring induced by glucocorticoid receptor
deficits. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 33:530–537. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Estañ MC, Calviño E, de Blas E,
Boyano-Adánez Mdel C, Mena ML, Gómez-Gómez M, Rial E and Aller P:
2-Deoxy-D-glucose cooperates with arsenic trioxide to induce
apoptosis in leukemia cells: Involvement of IGF-1R-regulated
Akt/mTOR, MEK/ERK and LKB-1/AMPK signaling pathways. Biochem
Pharmacol. 84:1604–1616. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zheng TH, Guo QJ, Wang FM and Liu XH:
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) participates in
the glioma apoptosis induced by As2O3. J Mod Oncol. 14:1341–1344.
2006.
|
|
26
|
Zhang J: Effects of Fluoride, Arsenic and
co-exposure on learning and memory and Ras/ERK pathway in rats
(dissertation). Med Univ Xinjiang. 2015.
|
|
27
|
Luo P, Zhang AH, Zhang KJ, Zeng XP, Fang
WH, Ye JF, Xiao JY, Zhang Y and Wu XY: The change of ERKs
expression in L-02 cell damage process cause by NaAsO2. Chin Soc
Toxicol. 27:387–388. 2013.(In Chinese).
|
|
28
|
Banerjee C, Goswami R, Datta S, Rajagopal
R and Mazumder S: Arsenic-induced alteration in intracellular
calcium homeostasis induces head kidney macrophage apoptosis
involving the activation of calpain-2 and ERK in Clarias batrachus.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 256:44–51. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wu J, Luo RC, Zhang H and Cui YZ:
Inhibitory effect of sorafenib combined with arsenic trioxide on
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao.
28:639–641. 2008.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li P, Gong XJ and Cao W: Effect of ERK
activation and As2O3 in the apoptosis of anaplastic thyroid cancer
cell line FRO. Oncol Prog. 14:879–881. 2016.
|
|
31
|
Ye J: Involvement of JWA and MAPK in
apoptosis induced by Arsenic trioxide in MCF-7 and Hela cells and
cell differentiation induced by TPA in MCF-7 cells (unpublished PhD
thesis). Med Univ Nanjing. 2006.
|
|
32
|
Iwama K, Nakajo S, Aiuchi T and Nakaya K:
Apoptosis induced by arsenic trioxide in leukemia U937 cells is
dependent on activation of p38, inactivation of ERK and the
Ca2+-dependent production of superoxide. Int J Cancer. 92:518–526.
2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Calviño E, Estañ MC, Simón GP, Sancho P,
Boyano-Adánez Mdel C, de Blas E, Bréard J and Aller P: Increased
apoptotic efficacy of lonidamine plus arsenic trioxide combination
in human leukemia cells. Reactive oxygen species generation and
defensive protein kinase (MEK/ERK, Akt/mTOR) modulation. Biochem
Pharmacol. 82:1619–1629. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu ZM and Huang HS: As2O3-induced
c-Src/EGFR/ERK signaling is via Sp1 binding sites to stimulate
p21WAF1/CIP1 expression in human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells.
Cell Signal. 18:244–255. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Huang HS, Liu ZM, Ding L, Chang WC, Hsu
PY, Wang SH, Chi CC and Chuang CH: Opposite effect of ERK1/2 and
JNK on p53-independent p21WAF1/CIP1 activation involved in the
arsenic trioxide-induced human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cellular
cytotoxicity. J Biomed Sci. 13:113–125. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liao YC, Chen YF and Lee TC: Increased
susceptibility of H-Ras(G12V)-transformed human urothelial cells to
the genotoxic effects of sodium arsenite. Arch Toxicol.
89:1971–1979. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang HH: The effect and mechanism study of
sodium arsenic induces cyclooxygenase-2 expression in Human
urothelial cells. unpublished PhD thesisMed Univ China 2012
|
|
38
|
Ngalame NN, Tokar EJ, Person RJ, Xu Y and
Waalkes MP: Aberrant microRNA expression likely controls RAS
oncogene activation during malignant transformation of human
prostate epithelial and stem cells by arsenic. Toxicol Sci.
138:268–277. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ju PX: Signal transduction mechanism for
As2O3-induced non-small cell lung cancer cell apoptosis.
unpublished PhD thesisMed Univ China 2007
|
|
40
|
Petit A, Delaune A, Falluel-Morel A,
Goullé JP, Vannier JP, Dubus I and Vasse M: Importance of ERK
activation in As2O3-induced differentiation and promyelocytic
leukemia nuclear bodies formation in neuroblastoma cells. Pharmacol
Res. 77:11–21. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lu TH, Tseng TJ, Su CC, Tang FC, Yen CC,
Liu YY, Yang CY, Wu CC, Chen KL, Hung DZ and Chen YW: Arsenic
induces reactive oxygen species-caused neuronal cell apoptosis
through JNK/ERK-mediated mitochondria-dependent and GRP
78/CHOP-regulated pathways. Toxicol Lett. 224:130–140. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liu B, Zhao Y, Yu L, He X and Zhang B:
Study on the role of Ras/p-ERK signaling pathway in the reversing
effect of As2O3 on multi-drug-resistance. Chin J Clin Oncol.
40:505–512. 2013.
|
|
43
|
Zhao YY, Yu L, Liu BL, He XJ and Zhang BY:
Downregulation of P-gp, Ras and p-ERK1/2 contributes to the arsenic
trioxide-induced reduction in drug resistance towards doxorubicin
in gastric cancer cell lines. Mol Med Rep. 12:7335–7343. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|