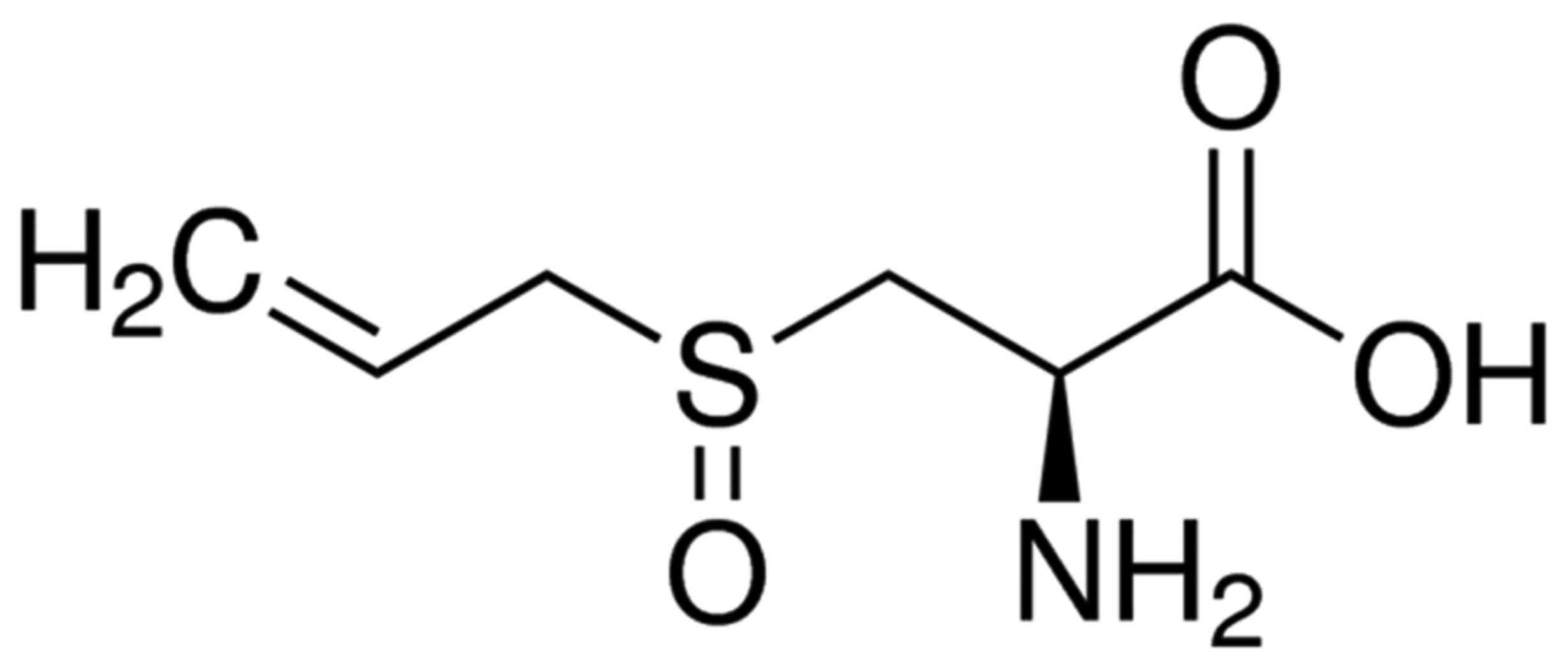
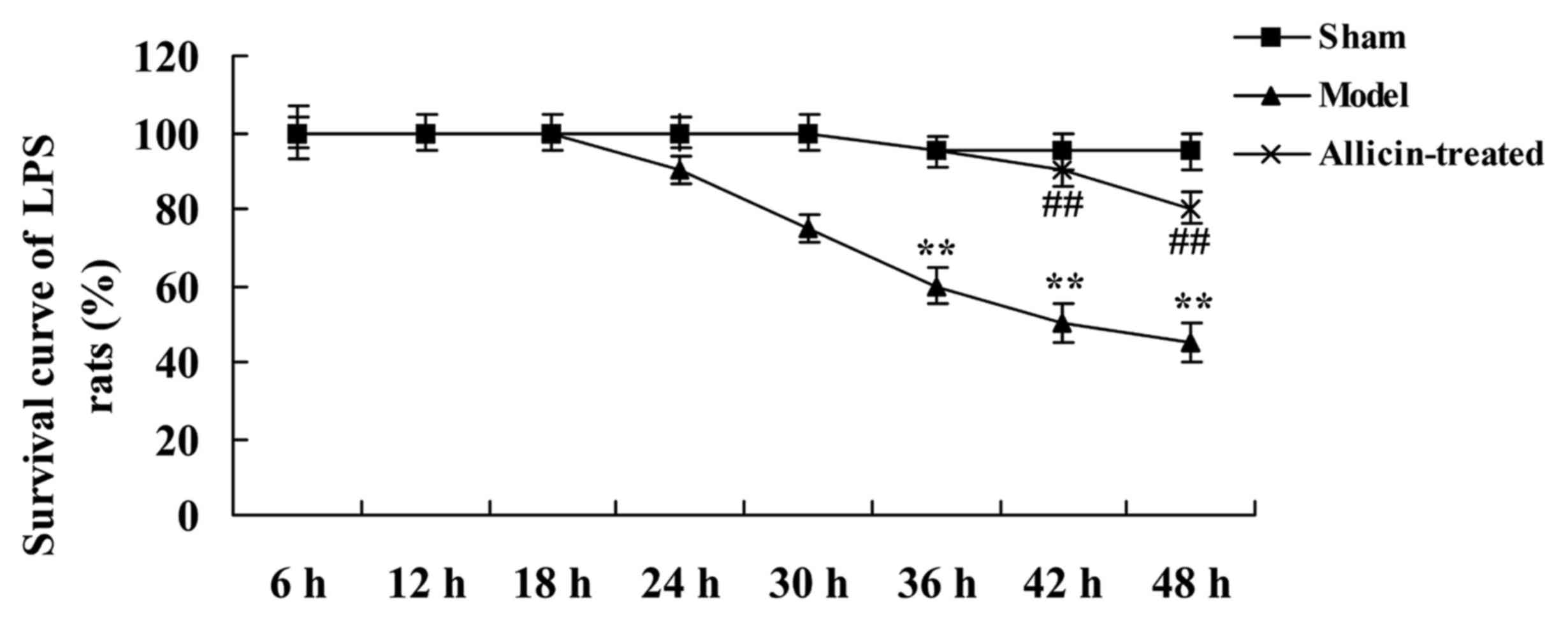
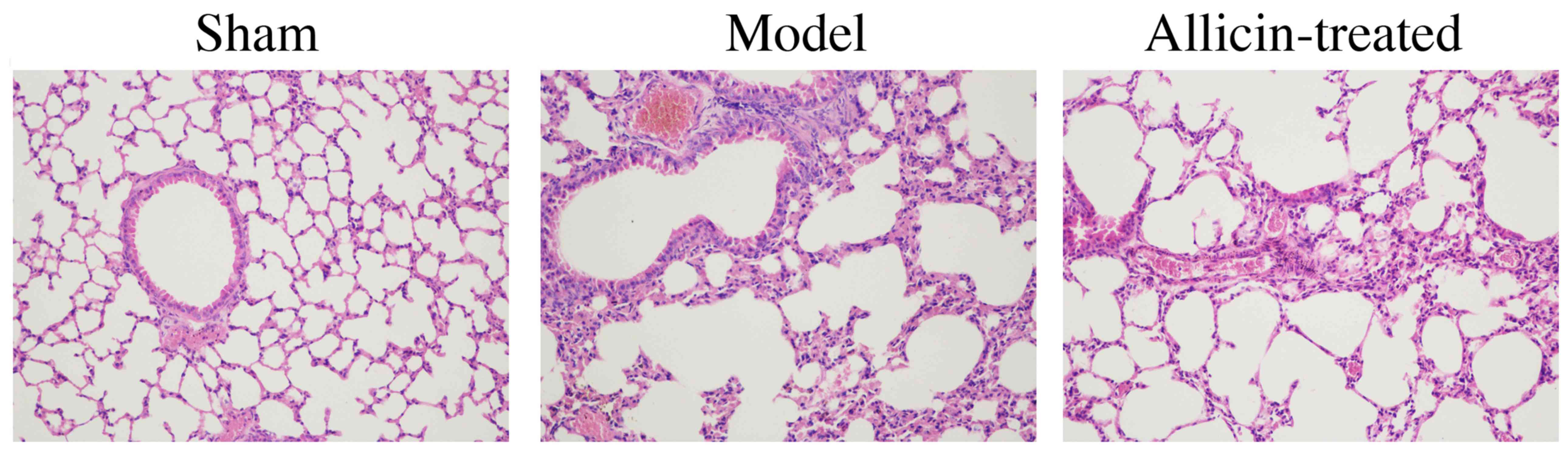
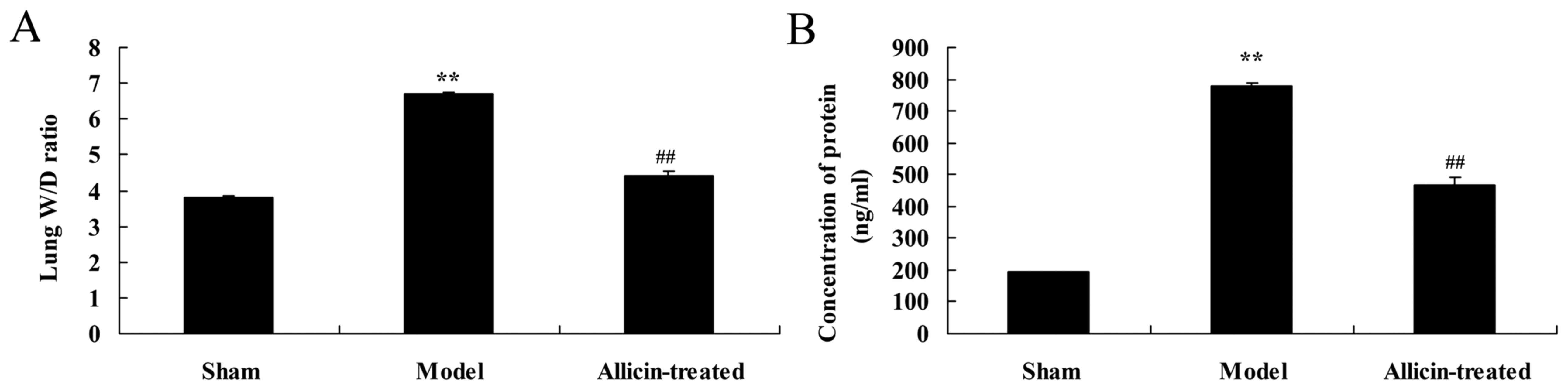
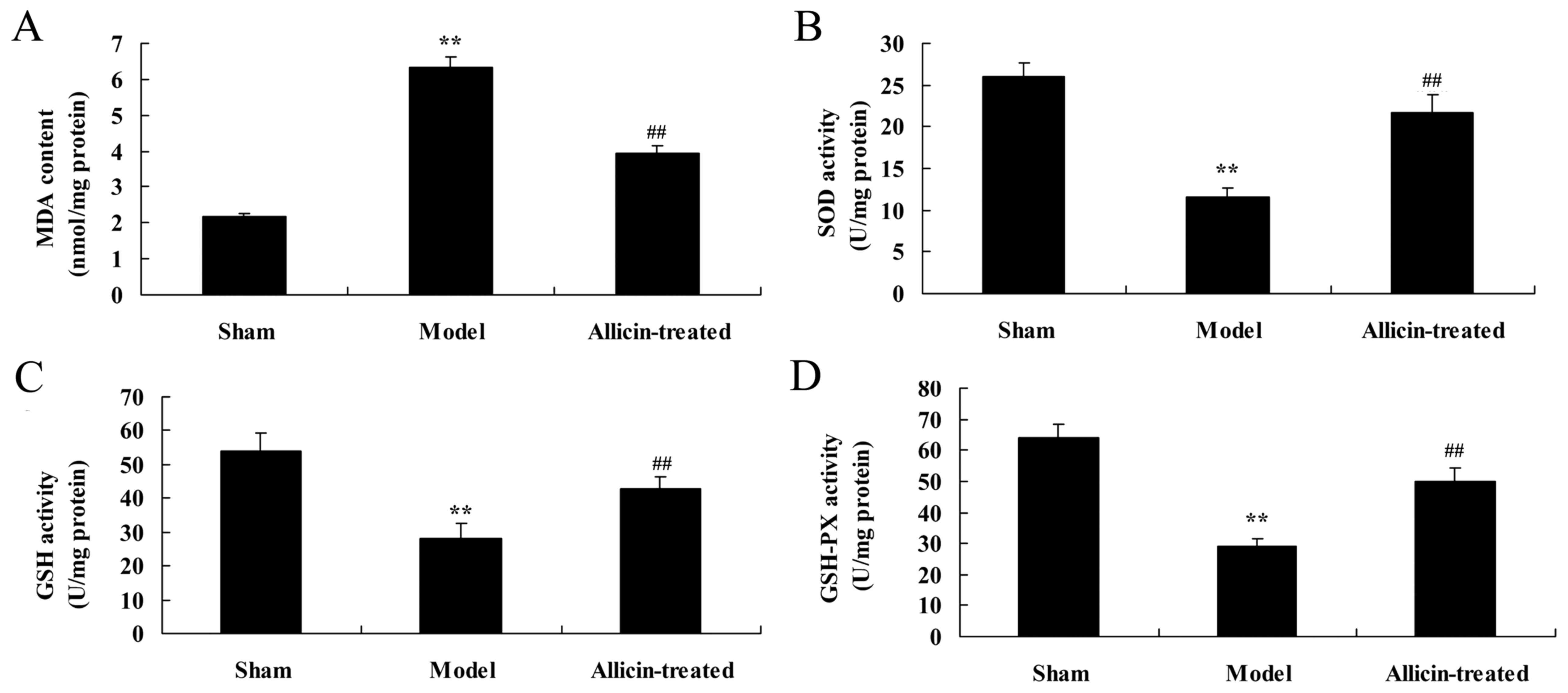
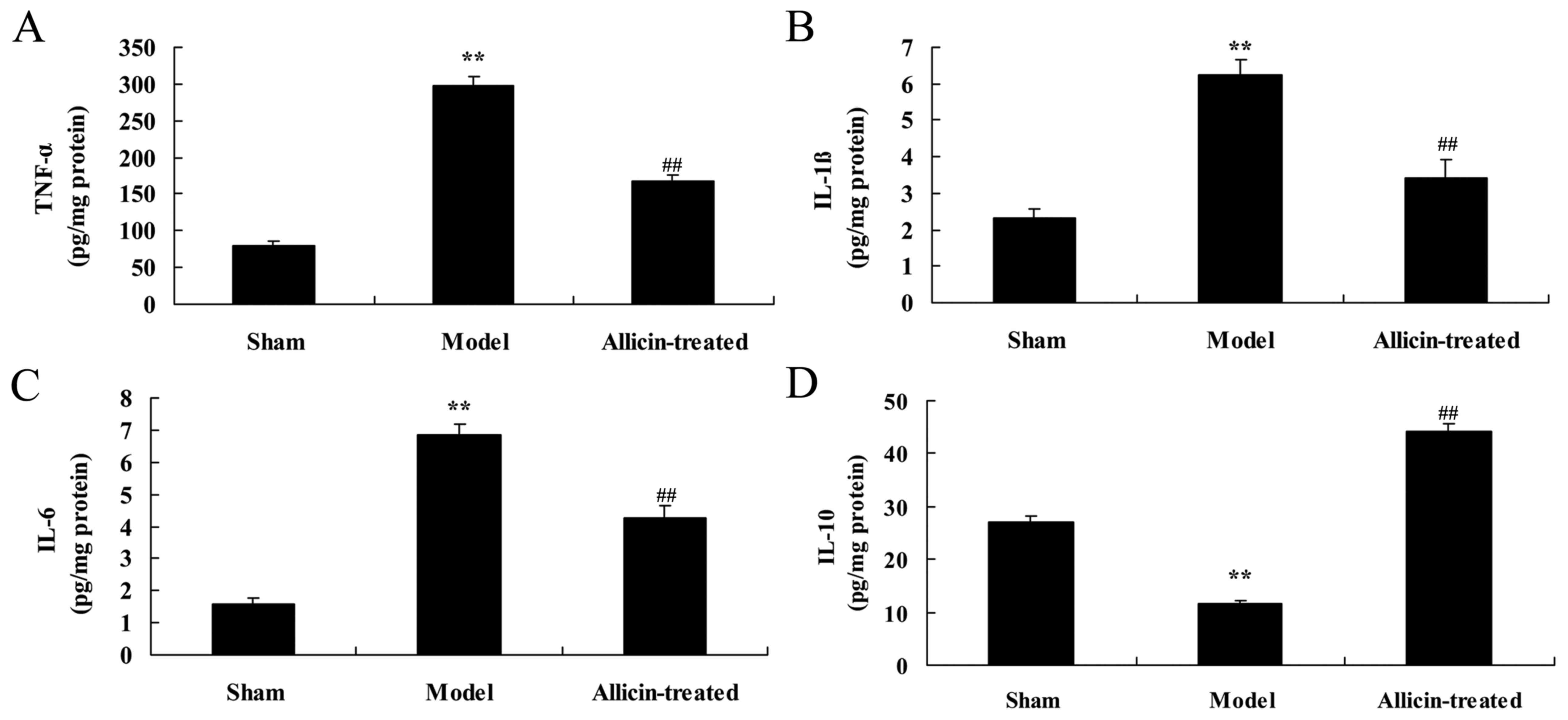
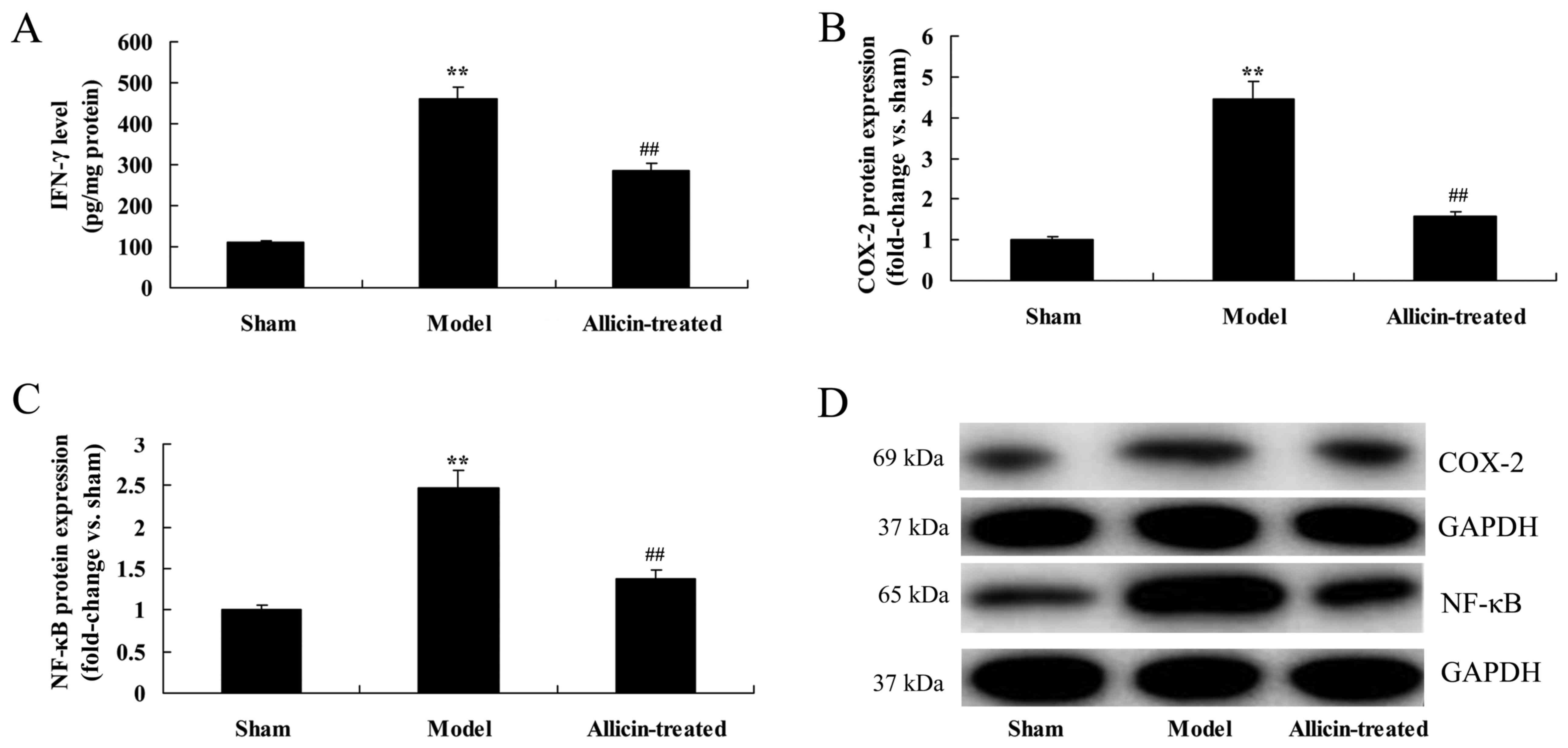
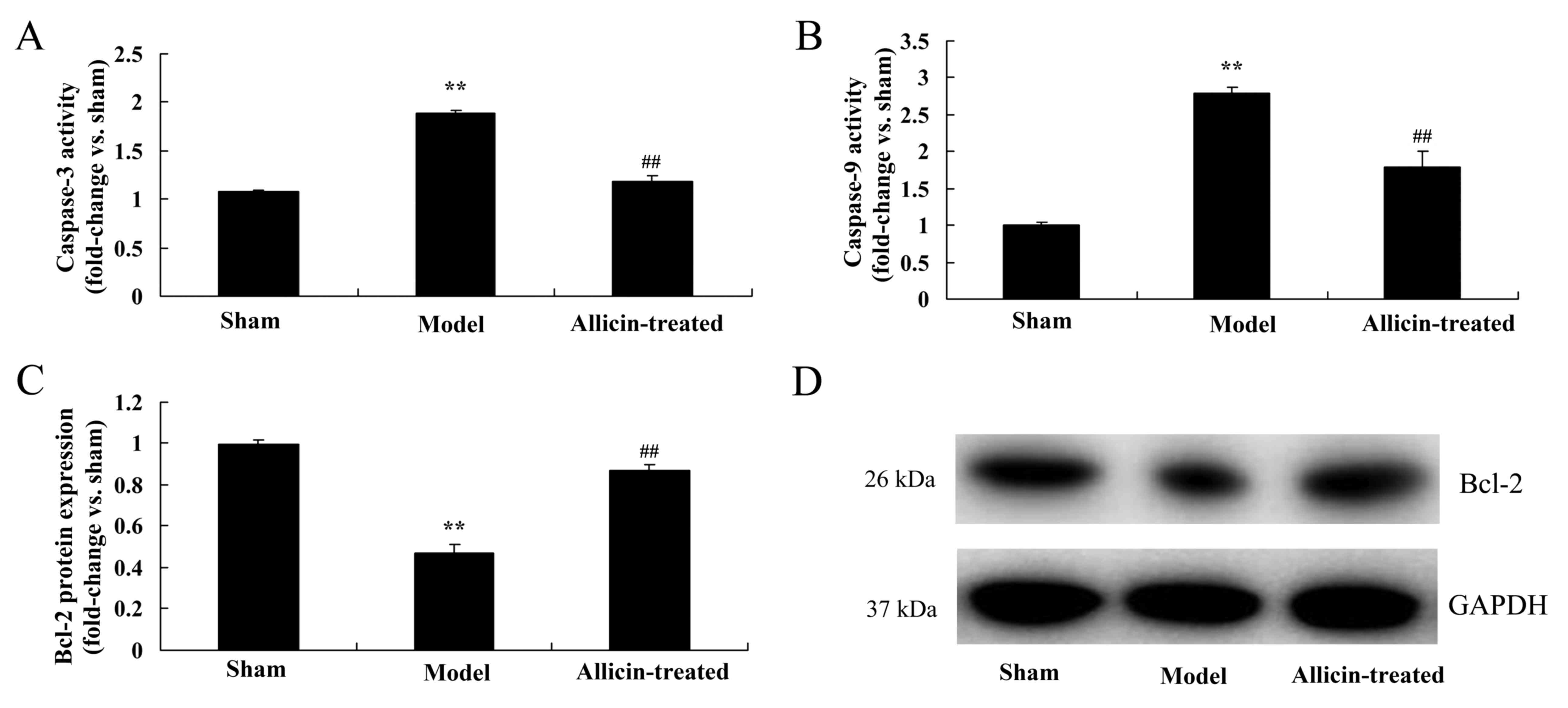
|
1
|
Reisinger MW, Moss M and Clark BJ:
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Acute Respiratory
Distress Syndrome Network Investigators: Brief versus full alcohol
use disorders identification test in national heart, lung, and
blood institute acute respiratory distress syndrome network
clinical trials. Crit Care Med. 43:e382–e385. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bernard GR: Potential of N-acetylcysteine
as treatment for the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Eur
Respir J Suppl. 11:496s–498s. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Braunschweig CA, Sheean PM, Peterson SJ,
Gomez Perez S, Freels S, Lateef O, Gurka D and Fantuzzi G:
Intensive nutrition in acute lung injury: A clinical trial
(INTACT). JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 39:13–20. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schwameis R, Eder S, Pietschmann H,
Fischer B, Mascher H, Tzotzos S, Fischer H, Lucas R, Zeitlinger M
and Hermann R: A FIM study to assess safety and exposure of inhaled
single doses of AP301-A specific ENaC channel activator for the
treatment of acute lung injury. J Clin Pharmacol. 54:341–350. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Piva JP, Garcia PC and Fiori H: Mechanical
ventilation in children with acute respiratory distress syndrome: A
huge gap between what we know and our practice!*. Pediatr Crit Care
Med. 14:732–733. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mulder HD, Augustijn QJ, van Woensel JB,
Bos AP, Juffermans NP and Wösten-van Asperen RM: Incidence, risk
factors, and outcome of transfusion-related acute lung injury in
critically ill children: A retrospective study. J Crit Care.
30:55–59. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lorenz RT and Cysewski GR: Commercial
potential for Haematococcus microalgae as a natural source
of astaxanthin. Trends Biotechnol. 18:160–167. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fitzgerald JC, Topjian AA, McInnes AD,
Mattei P, McCloskey JJ, Friess SH and Kilbaugh TJ: Bi-caval dual
lumen venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and
high-frequency percussive ventilatory support for postintubation
tracheal injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome. J Pediatr
Surg. 46:e11–e15. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wallock-Richards D, Doherty CJ, Doherty L,
Clarke DJ, Place M, Govan JR and Campopiano DJ: Garlic revisited:
Antimicrobial activity of allicin-containing garlic extracts
against Burkholderia cepacia complex. PLoS One.
9:e1127262014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Huang S, Dai Y, Zhang Z, Hao W and Chen H:
Docosahexaenoic acid intake ameliorates ketamine-induced impairment
of spatial cognition and learning ability in ICR mice. Neurosci
Lett. 580:125–129. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen S, Tang Y, Qian Y, Chen R, Zhang L,
Wo L and Chai H: Allicin prevents
H2O2-induced apoptosis of HUVECs by
inhibiting an oxidative stress pathway. BMC Complement Altern Med.
14:3212014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chu YL, Ho CT, Chung JG, Raghu R, Lo YC
and Sheen LY: Allicin induces anti-human liver cancer cells through
the p53 gene modulating apoptosis and autophagy. J Agric Food Chem.
61:9839–9848. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Feldberg RS, Chang SC, Kotik AN, Nadler M,
Neuwirth Z, Sundstrom DC and Thompson NH: In vitro mechanism of
inhibition of bacterial cell growth by allicin. Antimicrob Agents
Chemother. 32:1763–1768. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Khodavandi A, Harmal NS, Alizadeh F,
Scully OJ, Sidik SM, Othman F, Sekawi Z, Ng KP and Chong PP:
Comparison between allicin and fluconazole in Candida
albicans biofilm inhibition and in suppression of HWP1
gene expression. Phytomedicine. 19:56–63. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Elkayam A, Peleg E, Grossman E, Shabtay Z
and Sharabi Y: Effects of allicin on cardiovascular risk factors in
spontaneously hypertensive rats. Isr Med Assoc J. 15:170–173.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rice TW, Wheeler AP, Thompson BT,
deBoisblanc BP, Steingrub J and Rock P: NIH NHLBI Acute Respiratory
Distress Syndrome Network of Investigators: Enteral omega-3 fatty
acid, gamma-linolenic acid, and antioxidant supplementation in
acute lung injury. JAMA. 306:1574–1581. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huang TY, Tsai PS, Wang TY, Huang CL and
Huang CJ: Hyperbaric oxygen attenuation of
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury involves heme
oxygenase-1. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 49:1293–1301. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang C, Wang HY, Liu ZW, Fu Y and Zhao B:
Effect of endogenous hydrogen sulfide on oxidative stress in oleic
acid-induced acute lung injury in rats. Chin Med J. 124:3476–3480.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yamaoka S, Kim HS, Ogihara T, Oue S,
Takitani K, Yoshida Y and Tamai H: Severe Vitamin E deficiency
exacerbates acute hyperoxic lung injury associated with increased
oxidative stress and inflammation. Free Radic Res. 42:602–612.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Balyasnikova IV, Visintine DJ, Gunnerson
HB, Paisansathan C, Baughman VL, Minshall RD and Danilov SM:
Propofol attenuates lung endothelial injury induced by
ischemia-reperfusion and oxidative stress. Anesth Analg.
100:929–936. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lingappan K, Jiang W, Wang L, Wang G,
Couroucli XI, Shivanna B, Welty SE, Barrios R, Khan MF, Nebert DW,
et al: Mice deficient in the gene for cytochrome P450 (CYP)1A1 are
more susceptible than wild-type to hyperoxic lung injury: Evidence
for protective role of CYP1A1 against oxidative stress. Toxicol
Sci. 141:68–77. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sunil VR, Vayas KN, Massa CB, Gow AJ,
Laskin JD and Laskin DL: Ozone-induced injury and oxidative stress
in bronchiolar epithelium are associated with altered pulmonary
mechanics. Toxicol Sci. 133:309–319. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Saini Y, Greenwood KK, Merrill C, Kim KY,
Patial S, Parameswaran N, Harkema JR and LaPres JJ: Acute
cobalt-induced lung injury and the role of hypoxia-inducible factor
1alpha in modulating inflammation. Toxicol Sci. 116:673–681. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lo Re S, Dumoutier L, Couillin I, Van Vyve
C, Yakoub Y, Uwambayinema F, Marien B, van den Brûle S, Van Snick
J, Uyttenhove C, et al: IL-17A-producing gammadelta T and Th17
lymphocytes mediate lung inflammation but not fibrosis in
experimental silicosis. J Immunol. 184:6367–6377. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Misumi T, Tanaka T, Mikawa K, Nishina K,
Morikawa O and Obara H: Effects of sivelestat, a new elastase
inhibitor, on IL-8 and MCP-1 production from stimulated human
alveolar epithelial type II cells. J Anesth. 20:159–165. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li J, Zhao L, He X, Zeng YJ and Dai SS:
Sinomenine protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung
injury in mice via adenosine A2A receptor signaling.
PLoS One. 8:e592572013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu W, Dong M, Bo L, Li C, Liu Q, Li Z and
Jin F: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate suppresses alveolar epithelial
cell apoptosis in seawater aspiration-induced acute lung injury via
inhibiting STAT1-caspase-3/p21 associated pathway. Mol Med Rep.
13:829–836. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Damarla M, Parniani AR, Johnston L,
Maredia H, Serebreni L, Hamdan O, Sidhaye VK, Shimoda LA, Myers AC,
Crow MT, et al: Mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein
kinase 2 mediates apoptosis during lung vascular permeability by
regulating movement of cleaved caspase 3. Am J Respir Cell Mol
Biol. 50:932–941. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Halimah E, Diantini A, Destiani DP,
Pradipta IS, Sastramihardja HS, Lestari K, Subarnas A, Abdulah R
and Koyama H: Induction of caspase cascade pathway by
kaempferol-3-rhamnoside in LNCaP prostate cancer cell lines. Biomed
Rep. 3:115–117. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Guo Q, Jin J, Yuan JX, Zeifman A, Chen J,
Shen B and Huang J: VEGF, Bcl-2 and Bad regulated by angiopoietin-1
in oleic acid induced acute lung injury. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 413:630–636. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Qiu X, Li H, Tang H, Jin Y, Li W, Yu Sun,
Ping Feng, Sun X and Xia Z: Hydrogen inhalation ameliorates
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. Int
Immunopharmacol. 11:2130–2137. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mangiacapra F, Colaiori I, Ricottini E,
Balducci F, Creta A, Demartini C, Minotti G and Di Sciascio G:
Heart Rate reduction by IVabradine for improvement of ENDothELial
function in patients with coronary artery disease: The RIVENDEL
study. Clin Res Cardiol. 106:69–75. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|