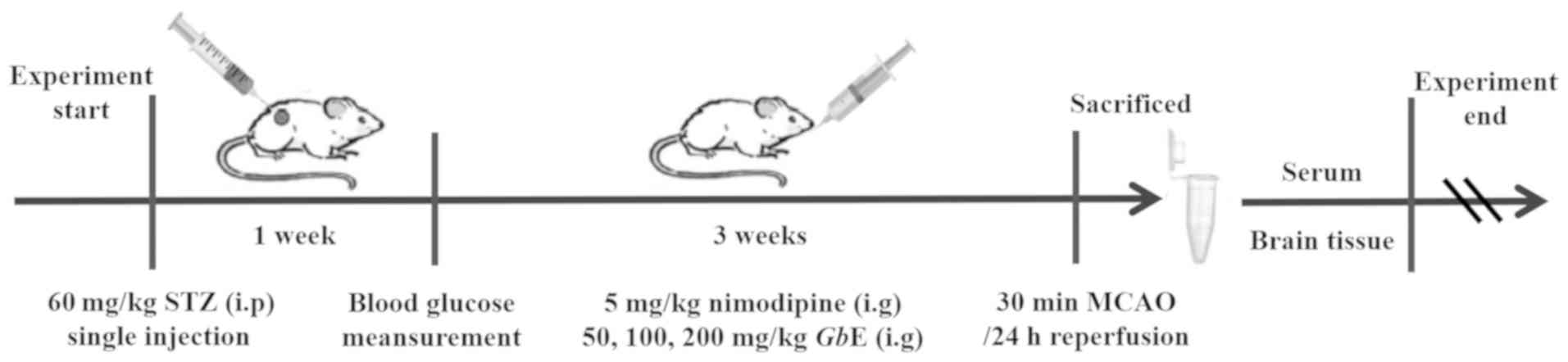
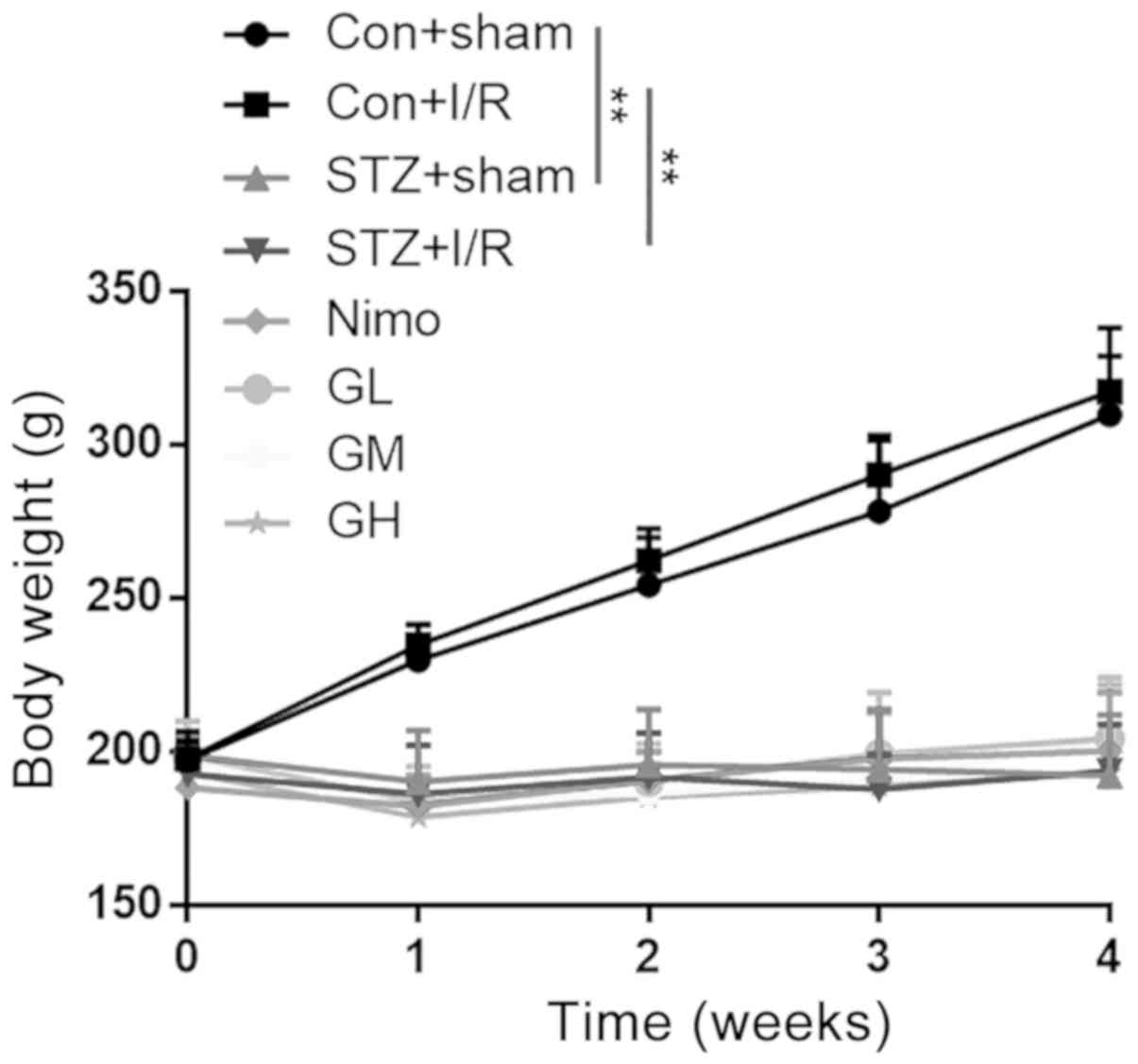
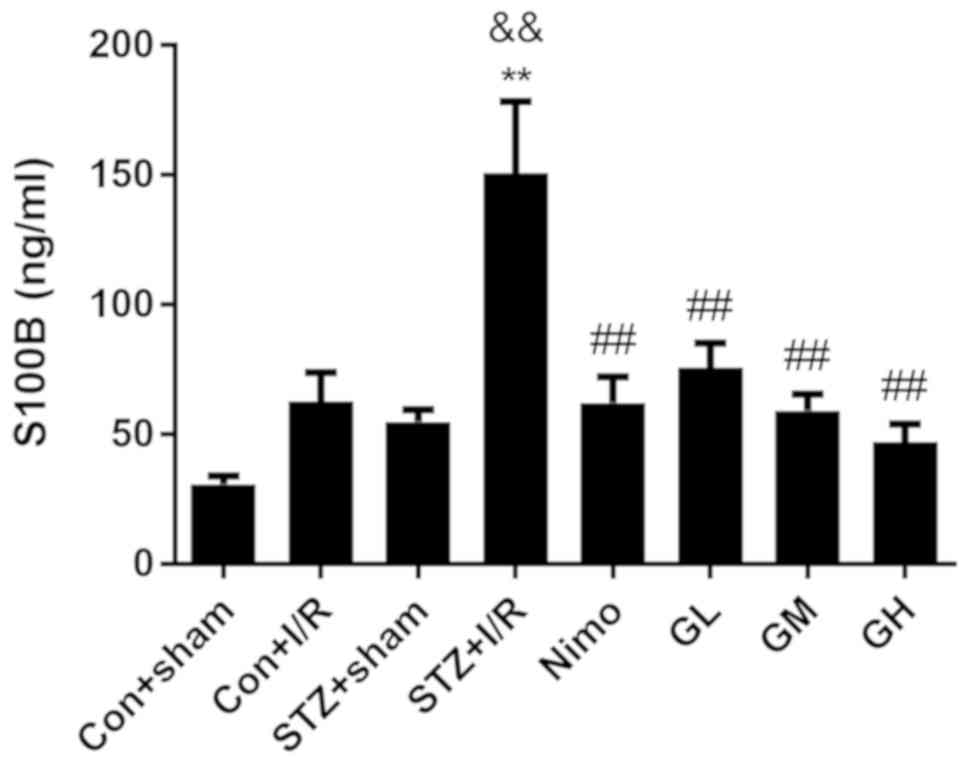
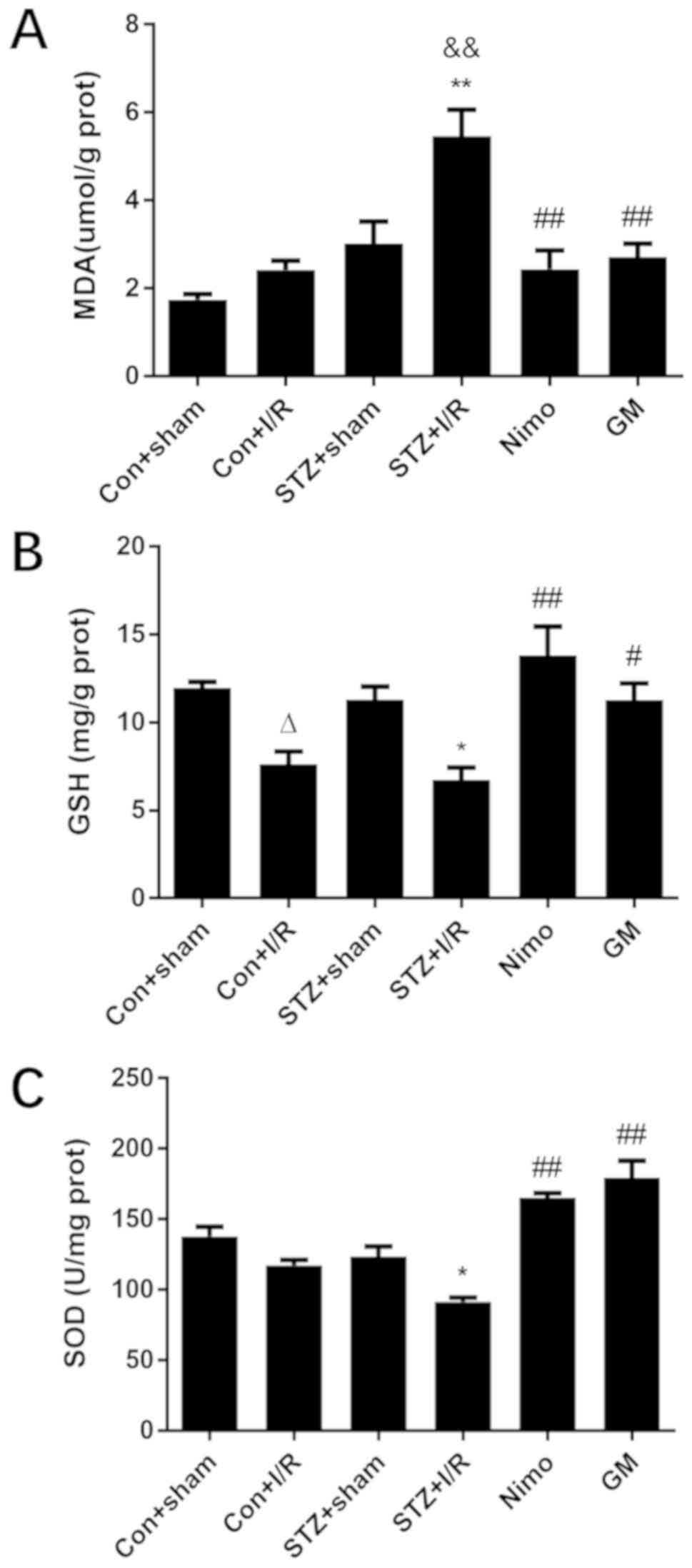
|
1
|
Luitse MJ, Biessels GJ, Rutten GE and
Kappelle LJ: Diabetes, hyperglycaemia, and acute ischaemic stroke.
Lancet Neurol. 11:261–271. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Barrett-Connor E and Khaw KT: Diabetes
mellitus: An independent risk factor for stroke? Am J Epidemiol.
128:116–123. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Muranyi M, Fujioka M, He Q, Han A, Yong G,
Csiszar K and Li PA: Diabetes activates cell death pathway after
transient focal cerebral ischemia. Diabetes. 52:481–486. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rizk NN, Rafols J and Dunbar JC: Cerebral
ischemia induced apoptosis and necrosis in normal and diabetic
rats. Brain Res. 1053:1–9. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Els T, Klisch J, Orszagh M, Hetzel A,
Schulte-Mönting J, Schumacher M and Lucking CH: Hyperglycemia in
patients with focal cerebral ischemia after intravenous
thrombolysis: Influence on clinical outcome and infarct size.
Cerebrovasc Dis. 13:89–94. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration, ;
Sarwar N, Gao P, Seshasai SR, Gobin R, Kaptoge S, Di Angelantonio
E, Ingelsson E, Lawlor DA, Selvin E, et al: Diabetes mellitus,
fasting blood glucose concentration, and risk of vascular disease:
A collaborative meta-analysis of 102 prospective studies. Lancet.
9733:2215–2222. 2010.
|
|
7
|
Almdal T, Scharling H, Jensen JS and
Vestergaard H: The independent effect of type 2 diabetes mellitus
on ischemic heart disease, stroke and death: A population-based
study of 13,000 men and women with 20 years of follow-up. Arch
Intern Med. 164:1422–1426. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Giacco F and Brownlee M: Oxidative stress
and diabetic complications. Circ Res. 107:1058–1070. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Brownlee M: Biochemistry and molecular
cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature. 6865:813–820. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Adibhatla RM and Hatcher JF: Lipid
oxidation and peroxidation in CNS health and disease: from
molecular mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 12:125–169. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ran Z, Zhang Y, Wen X and Ma J: Curcumin
inhibits high glucose-induced inflammatory injury in human retinal
pigment epithelial cells through the ROSPI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling
pathway. Mol Med Rep. 19:1024–1031. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pan Y, Wang N, Xia P, Wang E, Guo Q and Ye
Z: Inhibition of Rac1 ameliorates neuronal oxidative stress damage
via reducing Bcl-2/Rac1 complex formation in mitochondria through
PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Exp Neurol. 300:149–166. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Maiese K, Chong ZZ, Wang S and Shang YC:
Oxidant stress and signal transduction in the nervous system with
the PI3-K, Akt and mTOR cascade. Int J Mol Sci. 13:13830–13866.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dong L, Zhou S, Yang X, Chen Q, He Y and
Huang W: Magnolol protects against oxidative stress-mediated neural
cell damage by modulating mitochondrial dysfunction and PI3K/Akt
signaling. J Mol Neurosci. 50:469–481. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Koh PO: Melatonin prevents ischemic brain
injury through activation of the mTOR/p70S6 kinase signaling
pathway. Neurosci Lett. 444:74–78. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yan BC, Wang J, Rui Y, Cao J, Xu P, Jiang
D, Zhu X, Won MH, Bo P and Su P: Neuroprotective effects of
gabapentin against cerebral ischemia reperfusion-induced neuronal
autophagic injury via regulation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling
pathways. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 78:157–171. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xie R, Cheng M, Li M, Xiong X, Daadi M,
Sapolsky RM and Zhao H: Akt isoforms differentially protect against
stroke-induced neuronal injury by regulating mTOR activities. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 33:1875–1885. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tymianski M: Emerging mechanisms of
disrupted cellular signaling in brain ischemia. Nat Neurosci.
14:1369–1373. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Danbolt NC: Glutamate uptake. Prog
Neurobiol. 65:1–105. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Camacho A and Massieu L: Role of glutamate
transporters in the clearance and release of glutamate during
ischemia and its relation to neuronal death. Arch Med Res.
37:11–18. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rao VL, Dogan A, Todd KG, Bowen KK, Kim
BT, Rothstein JD and Dempsey RJ: Antisense knockdown of the glial
glutamate transporter GLT-1, but not the neuronal glutamate
transporter EAAC1, exacerbates transient focal cerebral
ischemia-induced neuronal damage in rat brain. J Neurosci.
21:1876–1883. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wu X, Kihara T, Akaike A, Niidome T and
Sugimoto H: PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling regulates glutamate transporter
1 in astrocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 393:514–518. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ji YF, Zhou L, Xie YJ, Xu SM, Zhu J, Teng
P, Shao CY, Wang Y, Luo JH and Shen Y: Upregulation of glutamate
transporter GLT-1 by mTOR-Akt-NF-κB cascade in astrocytic
oxygen-glucose deprivation. Glia. 61:1959–1975. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Trotti D, Danbolt NC and Volterra A:
Glutamate transporters are oxidant-vulnerable: A molecular link
between oxidative and excitotoxic neurodegeneration? Trends
Pharmacol Sci. 19:328–334. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen MJ, Ng JM, Peng ZF, Manikandan J, Yap
YW, Llanos RM, Beart PM and Cheung NS: Gene profiling identifies
commonalities in neuronal pathways in excitotoxicity: Evidence
favouring cell cycle re-activation in concert with oxidative
stress. Neurochem Int. 62:719–730. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chan PC, Xia Q and Fu PP: Ginkgo
biloba leave extract: Biological, medicinal, and toxicological
effects. J Environ Sci Health C Environ Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev.
25:211–244. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ross R: Atherosclerosis-an inflammatory
disease. N Engl J Med. 340:115–126. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Springer TA: Traffic signals for
lymphocyte recirculation and leukocyte emigration: The multistep
paradigm. Cell. 76:301–314. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Akisu M, Kultursay N, Coker I and
Huseyinov A: Platelet-activating factor is an important mediator in
hypoxic ischemic brain injury in the newborn rat. Flunarizine and
Ginkgo biloba extract reduce PAF concentration in the brain.
Biol Neonate. 74:439–444. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lu Q, Hao M, Wu W, Zhang N, Isaac AT, Yin
J, Zhu X, Du L and Yin X: Antidiabetic cataract effects of GbE,
rutin and quercetin are mediated by the inhibition of oxidative
stress and polyol pathway. Acta Biochim Pol. 65:35–41. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lu Q, Zuo WZ, Ji XJ, Zhou YX, Liu YQ, Yao
XQ, Zhou XY, Liu YW, Zhang F and Yin XX: Ethanolic Ginkgo
biloba leaf extract prevents renal fibrosis through Akt/mTOR
signaling in diabetic nephropathy. Phytomedicine. 22:1071–1078.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Saini AS, Taliyan R and Sharma PL:
Protective effect and mechanism of Ginkgo biloba extract-EGb
761 on STZ-induced diabetic cardiomyopathy in rats. Pharmacogn Mag.
10:172–178. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang J, Wang A, He H, She X, He Y, Li S,
Liu L, Luo T, Huang N, Luo H and Zou K: Trametenolic acid B
protects against cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury through
modulation of microRNA-10a and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways.
Biomed Pharmacother. 112:1086922019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Guan T, Qian Y, Tang X, Huang M, Huang L,
Li Y and Sun H: Maslinic acid, a natural inhibitor of glycogen
phosphorylase, reduces cerebral ischemic injury in hyperglycemic
rats by GLT-1 up-regulation. J Neurosci Res. 89:1829–1839. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yang Y, Shuaib A and Li Q: Quantification
of infarct size on focal cerebral ischemia model of rats using a
simple and economical method. J Neurosci Methods. 84:9–16. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pilz J, Meineke I and Gleiter CH:
Measurement of free and bound malondialdehyde in plasma by
high-performance liquid chromatography as the
2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine derivative. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci
Appl. 742:315–325. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu YW, Zhu X, Li W, Lu Q, Wang JY, Wei YQ
and Yin XX: Ginsenoside Re attenuates diabetes-associated cognitive
deficits in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 101:93–98. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sun Y, Oberley LW and Li Y: A simple
method for clinical assay of superoxide dismutase. Clin Chem.
34:497–500. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Metting Z, Wilczak N, Rodiger LA, Schaaf
JM and van der Naalt J: GFAP and S100B in the acute phase of mild
traumatic brain injury. Neurology. 78:1428–1433. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Rothermundt M, Peters M, Prehn JH and
Arolt V: S100B in brain damage and neurodegeneration. Microsc Res
Tech. 60:614–632. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Foerch C, Wunderlich MT, Dvorak F, Humpich
M, Kahles T, Goertler M, Alvarez-Sabin J, Wallesch CW, Molina CA,
Steinmetz H, et al: Elevated serum S100B levels indicate a higher
risk of hemorrhagic transformation after thrombolytic therapy in
acute stroke. Stroke. 38:2491–2495. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Stadler K: Oxidative stress in diabetes.
Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012:272–287. 2012.
|
|
44
|
Ouyang YB, Voloboueva LA, Xu LJ and
Giffard RG: Selective dysfunction of hippocampal CA1 astrocytes
contributes to delayed neuronal damage after transient forebrain
ischemia. J Neurosci. 27:4253–4260. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kaarisalo MM, Räihä I, Sivenius J,
Immonen-Räihä P, Lehtonen A, Sarti C, Mähönen M, Torppa J,
Tuomilehto J and Salomaa V: Diabetes worsens the outcome of acute
ischemic stroke. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 69:293–298. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kidwell CS, Alger JR and Saver JL:
Evolving paradigms in neuroimaging of the ischemic penumbra.
Stroke. 35 (11 Suppl 1):S2662–S2665. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Tanaka N, Ikeda Y, Ohta Y, Deguchi K, Tian
F, Shang J, Matsuura T and Abe K: Expression of Keap1-Nrf2 system
and antioxidative proteins in mouse brain after transient middle
cerebral artery occlusion. Brain Res. 1370:246–253. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Manickam DS, Brynskikh AM, Kopanic JL,
Sorgen PL, Klyachko NL, Batrakova EV, Bronich TK and Kabanov AV:
Well-defined cross-linked antioxidant nanozymes for treatment of
ischemic brain injury. J Control Release. 162:636–645. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Weismann D, Hartvigsen K, Lauer N, Bennett
KL, Scholl HP, Charbel Issa P, Cano M, Brandstatter H, Tsimikas S,
Skerka C, et al: Complement factor H binds malondialdehyde epitopes
and protects from oxidative stress. Nature. 478:76–81. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Martinic-Popovic I, Lovrencic-Huzjan A and
Demarin V: Assessment of subtle cognitive impairment in stroke-free
patients with carotid disease. Acta Clin Croat. 48:231–240.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Lee K, Kim EH, Song D, Kim YD, Nam HS, Lee
HS and Heo JH: Lenticulostriate artery involvement is predictive of
poor outcomes in superficial middle cerebral artery territory
infarction. Yonsei Med J. 58:123–130. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Cahill SP, Yu RQ, Green D, Todorova EV and
Snyder JS: Early survival and delayed death of developmentally-born
dentate gyrus neurons. Hippocampus. 27:1155–1167. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wegener S, Weber R, Ramos-Cabrer P,
Uhlenkueken U, Sprenger C, Wiedermann D, Villringer A and Hoehn M:
Temporal profile of T2-weighted MRI distinguishes between
pannecrosis and selective neuronal death after transient focal
cerebral ischemia in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 26:38–47.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Echeverry R, Wu J, Haile WB, Guzman J and
Yepes M: Tissue-type plasminogen activator is a neuroprotectant in
the mouse hippocampus. J Clin Invest. 120:2194–2205. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Miyawaki T, Ofengeim D, Noh KM,
Latuszek-Barrantes A, Hemmings BA, Follenzi A and Zukin RS: The
endogenous inhibitor of Akt, CTMP, is critical to ischemia-induced
neuronal death. Nat Neurosci. 12:618–626. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Liu Y, Wang H, Liu N, Du J, Lan X, Qi X,
Zhuang C, Sun T, Li Y and Yu J: Oxymatrine protects neonatal rat
against hypoxic-ischemic brain damage via PI3K/Akt/GSK3β pathway.
Life Sci. May 16–2019, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.04.070
|
|
57
|
Cheng SM, Ho TJ, Yang AL, Chen IJ, Kao CL,
Wu FN, Lin JA, Kuo CH, Ou HC, Huang CY and Lee SD: Exercise
training enhances cardiac IGFI-R/PI3K/Akt and Bcl-2 family
associated pro-survival pathways in streptozotocin-induced diabetic
rats. Int J Cardiol. 167:478–485. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Kim GD, Oh J, Park HJ, Bae K and Lee SK:
Magnolol inhibits angiogenesis by regulating ROS-mediated apoptosis
and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in mES/EB-derived
endothelial-like cells. Int J Oncol. 43:600–610. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Qi S, Xin Y, Guo Y, Diao Y, Kou X, Luo L
and Yin Z: Ampelopsin reduces endotoxic inflammation via repressing
ROS-mediated activation of PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathways. Int
Immunopharmacol. 12:278–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Wang J, Li G, Wang Z, Zhang X, Yao L, Wang
F, Liu S, Yin J, Ling EA, Wang L and Hao A: High glucose-induced
expression of inflammatory cytokines and reactive oxygen species in
cultured astrocytes. Neuroscience. 202:58–68. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Yang Y, Gozen O, Watkins A, Lorenzini I,
Lepore A, Gao Y, Vidensky S, Brennan J, Poulsen D, Won Park J, et
al: Presynaptic regulation of astroglial excitatory
neurotransmitter transporter GLT1. Neuron. 61:880–894. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Mdzinarishvili A, Sumbria R, Lang D and
Klein J: Ginkgo extract EGb761 confers neuroprotection by reduction
of glutamate release in ischemic brain. J Pharm Pharm Sci.
15:94–102. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Ghosh M, Yang Y, Rothstein JD and Robinson
MB: Nuclear factor-κB contributes to neuron-dependent induction of
glutamate transporter-1 expression in astrocytes. J Neurosci.
31:9159–9169. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Mitra R, Dube SK and Jain V: Isolated
diastolic hypotension: A unique complication of intra-arterial
nimodipine infusion!! J Clin Anesth. 59(1)2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Rhee KJ, Lee CG, Kim SW, Gim DH, Kim HC
and Jung BD: Extract of Ginkgo biloba ameliorates
Streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes mellitus and High-fat
diet-induced type 2 diabetes mellitus in mice. Int J Med Sci.
12:987–994. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Aziz TA, Hussain SA, Mahwi TO, Ahmed ZA,
Rahman HS and Rasedee A: The efficacy and safety of Ginkgo
biloba extract as an adjuvant in type 2 diabetes mellitus
patients ineffectively managed with metformin: A double-blind,
randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Drug Des Devel Ther.
12:735–742. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|