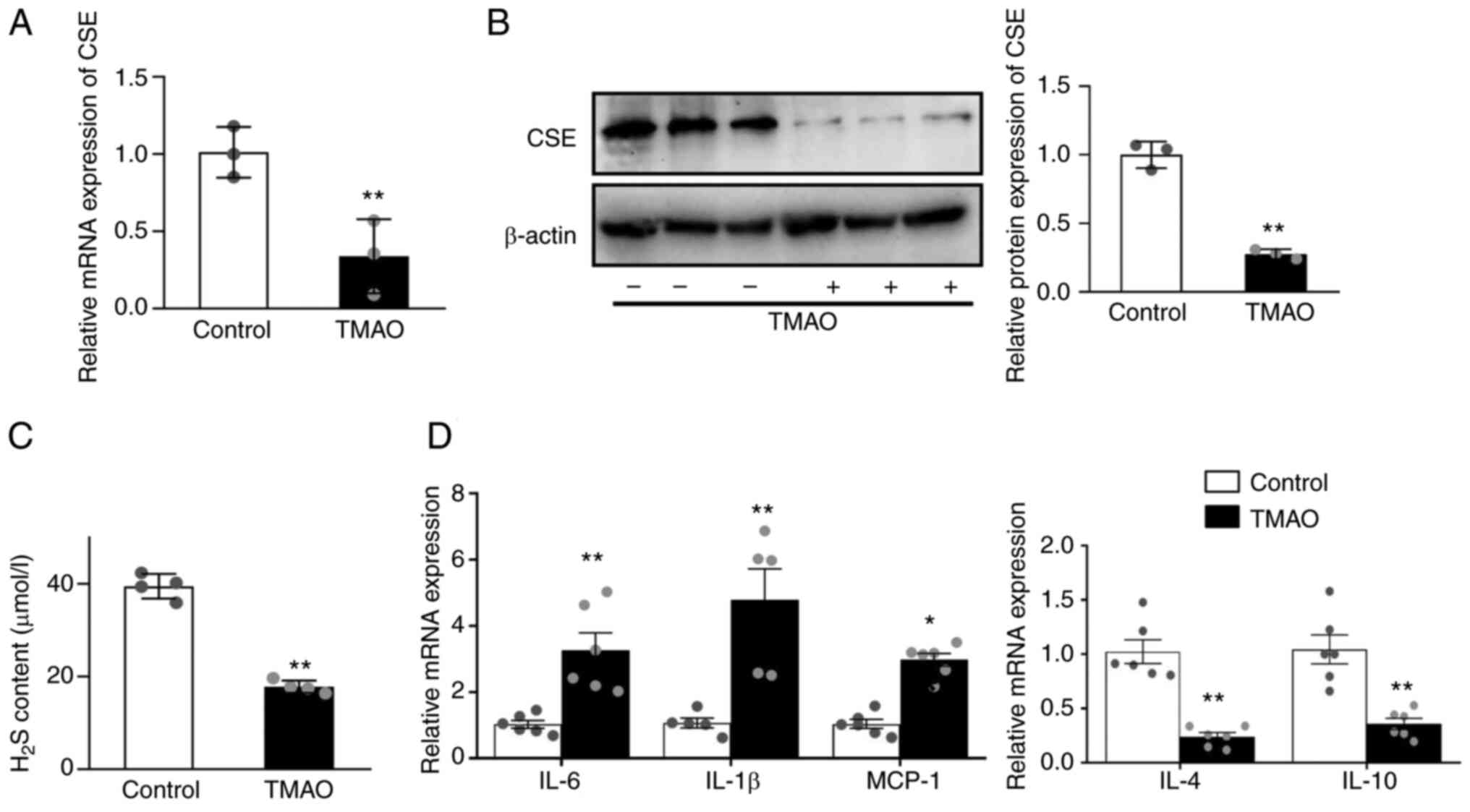
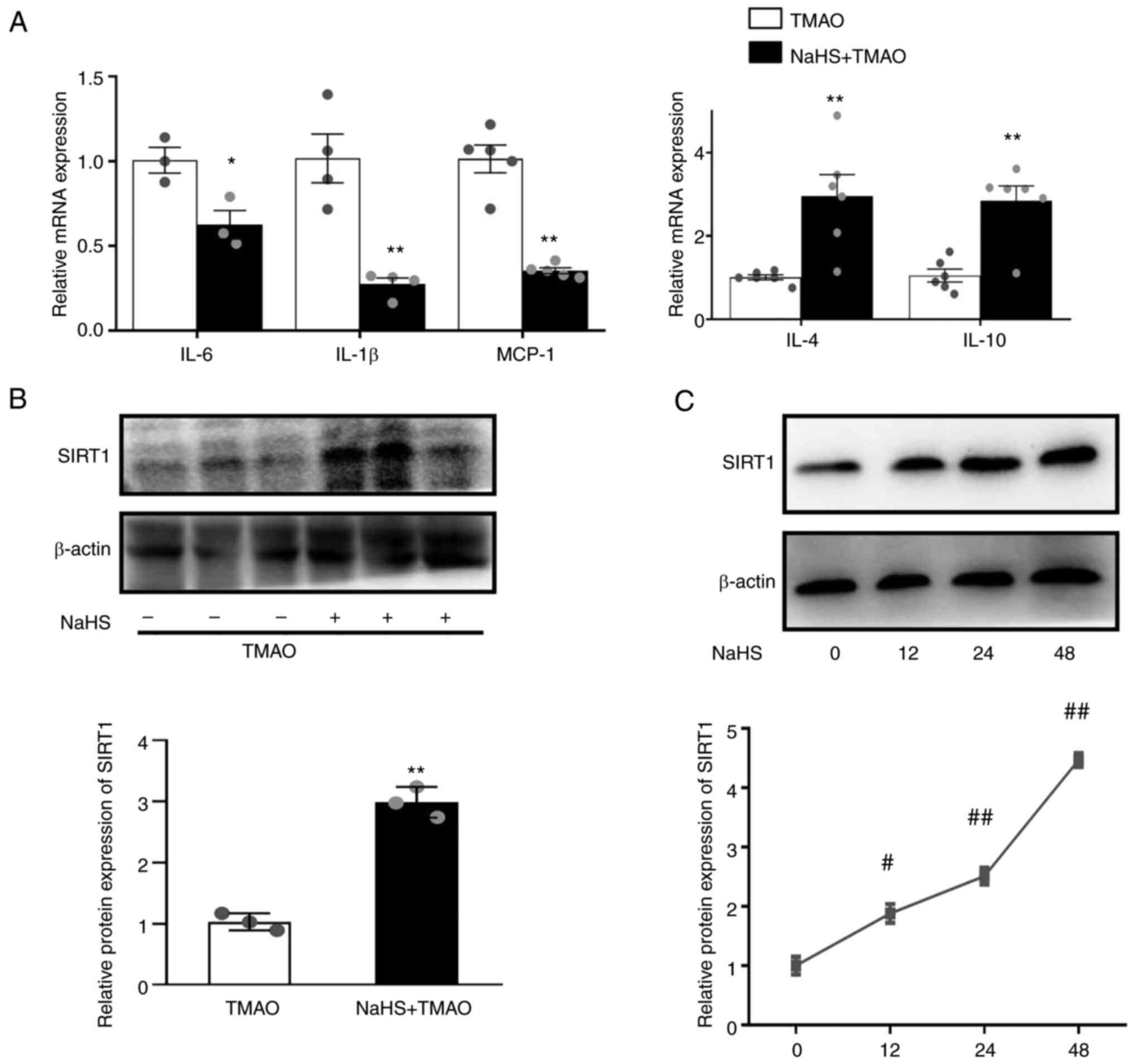
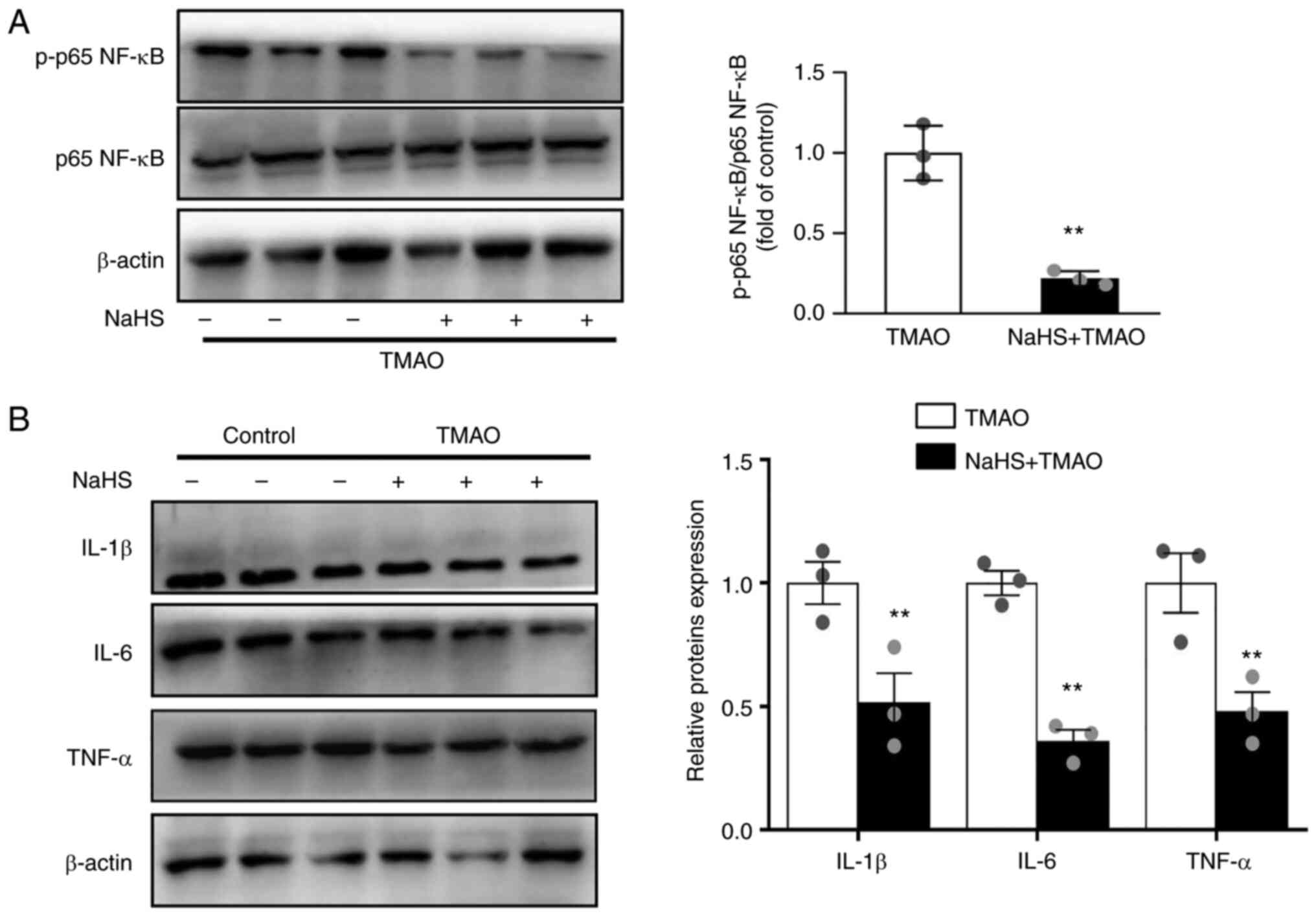
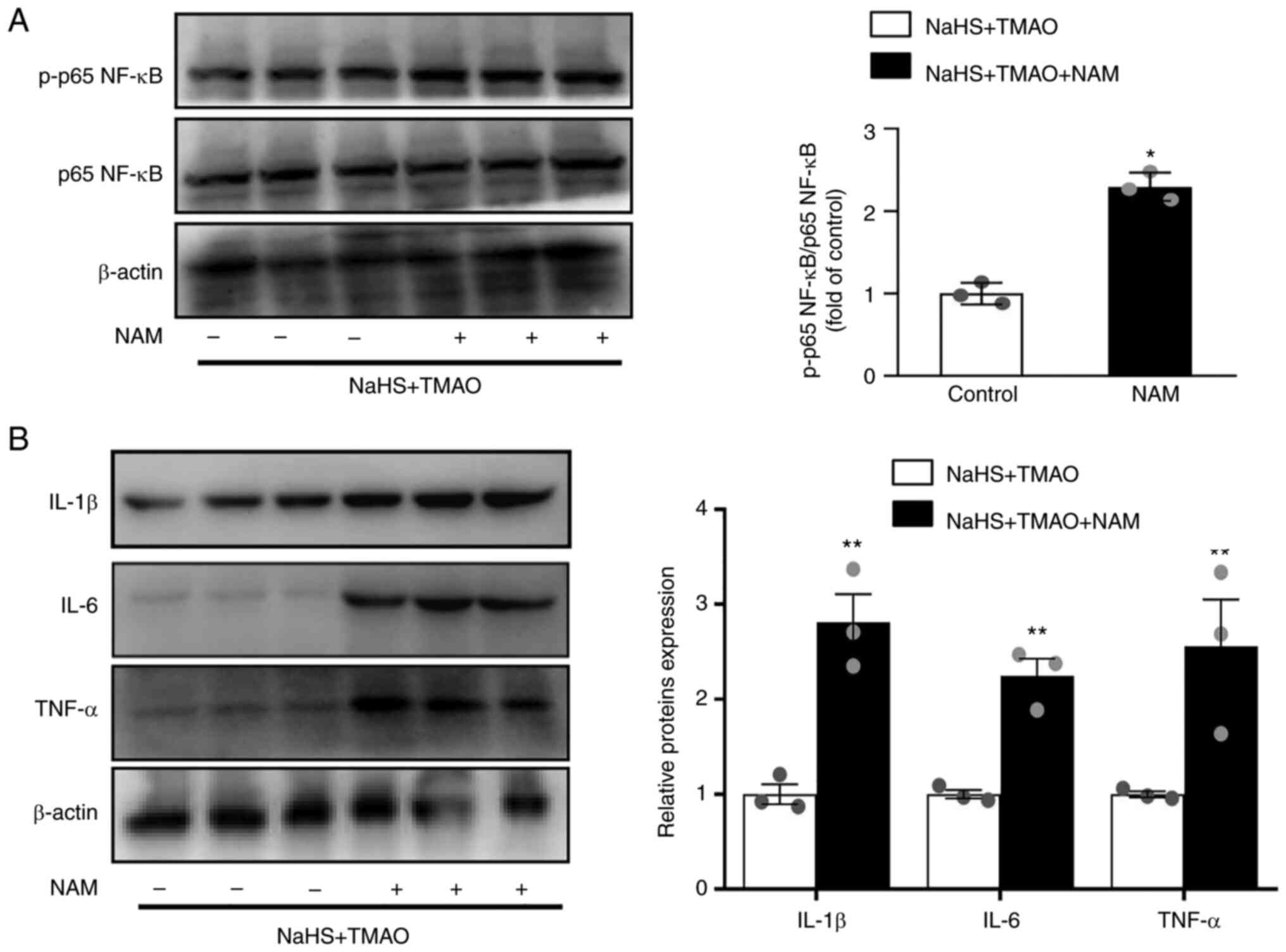
|
1
|
Zhang H, Du J, Huang Y, Tang C and Jin H:
Hydrogen sulfide regulates macrophage function in cardiovascular
diseases. Antioxid Redox Signal. 38:45–56. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Susser LI and Rayner KJ: Through the
layers: How macrophages drive atherosclerosis across the vessel
wall. J Clin Invest. 132:e1570112022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tang WH and Hazen SL: The contributory
role of gut microbiota in cardiovascular disease. J Clin Invest.
124:4204–4211. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sun X, Jiao X, Ma Y, Liu Y, Zhang L, He Y
and Chen Y: Trimethylamine N-oxide induces inflammation and
endothelial dysfunction in human umbilical vein endothelial cells
via activating ROS-TXNIP-NLRP3 inflammasome. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 481:63–70. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang X, Li Y, Yang P, Liu X, Lu L, Chen
Y, Zhong X, Li Z, Liu H, Ou C, et al: Trimethylamine-N-oxide
promotes vascular calcification through activation of NLRP3
(nucleotide-binding domain, leucine-rich-containing family, pyrin
domain-containing-3) inflammasome and NF-κB (nuclear factor κB)
signals. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 40:751–765. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang W, Miikeda A, Zuckerman J, Jia X,
Charugundla S, Zhou Z, Kaczor-Urbanowicz KE, Magyar C, Guo F, Wang
Z, et al: Inhibition of microbiota-dependent TMAO production
attenuates chronic kidney disease in mice. Sci Rep. 11:5182021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Casin KM and Calvert JW: Harnessing the
benefits of endogenous hydrogen sulfide to reduce cardiovascular
disease. Antioxidants (Basel). 10:3832021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lv B, Chen S, Tang C, Jin H, Du J and
Huang Y: Hydrogen sulfide and vascular regulation-an update. J Adv
Res. 27:85–97. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu HT, Zhou ZX, Ren Z, Yang S, Liu LS,
Wang Z, Wei DH, Ma XF, Ma Y and Jiang ZS: EndMT: Potential target
of H2S against atherosclerosis. Curr Med Chem.
28:3666–3680. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mani S, Li H, Untereiner A, Wu L, Yang G,
Austin RC, Dickhout JG, Lhoták Š, Meng QH and Wang R: Decreased
endogenous production of hydrogen sulfide accelerates
atherosclerosis. Circulation. 127:2523–2534. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cheung SH, Kwok WK, To KF and Lau JYW:
Anti-atherogenic effect of hydrogen sulfide by over-expression of
cystathionine gamma-lyase (CSE) gene. PLoS One. 9:e1130382014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liao M, Liu Y, Yuan J, Wen Y, Xu G, Zhao
J, Cheng L, Li J, Wang X, Wang F, et al: Single-cell landscape of
bronchoalveolar immune cells in patients with COVID-19. Nat Med.
26:842–844. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Winnik S, Auwerx J, Sinclair DA and Matter
CM: Protective effects of sirtuins in cardiovascular diseases: From
bench to bedside. Eur Heart J. 36:3404–3412. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lin XL, Liu Y, Liu M, Hu H, Pan Y, Fan XJ,
Hu XM and Zou WW: Inhibition of hydrogen peroxide-induced human
umbilical vein endothelial cells aging by allicin depends on
sirtuin1 activation. Med Sci Monit. 23:563–570. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Luo XY, Qu SL, Tang ZH, Zhang Y, Liu MH,
Peng J, Tang H, Yu KL, Zhang C, Ren Z and Jiang ZS: SIRT1 in
cardiovascular aging. Clin Chim Acta. 437:106–114. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang Y, Tang ZH, Ren Z, Qu SL, Liu MH,
Liu LS and Jiang ZS: Hydrogen sulfide, the next potent preventive
and therapeutic agent in aging and age-associated diseases. Mol
Cell Biol. 33:1104–1113. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Suo R, Zhao ZZ, Tang ZH, Ren Z, Liu X, Liu
LS, Wang Z, Tang CK, Wei DH and Jiang ZS: Hydrogen sulfide prevents
H2O2 induced senescence in human umbilical
vein endothelial cells through SIRT1 activation. Mol Med Rep.
7:1865–1870. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Feng T, Liu P, Wang X, Luo J, Zuo X, Jiang
X, Liu C, Li Y, Li N, Chen M, et al: SIRT1 activator E1231 protects
from experimental atherosclerosis and lowers plasma cholesterol and
triglycerides by enhancing ABCA1 expression. Atherosclerosis.
274:172–181. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nguyen PA, Won JS, Rahman MK, Bae EJ and
Cho MK: Modulation of Sirt1/NF-κB interaction of evogliptin is
attributed to inhibition of vascular inflammatory response leading
to attenuation of atherosclerotic plaque formation. Biochem
Pharmacol. 168:452–464. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li X, Zhang KY, Zhang P, Chen LX, Wang L,
Xie M, Wang CY and Tang XQ: Hydrogen sulfide inhibits
formaldehyde-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress in PC12 cells by
upregulation of SIRT-1. PLoS One. 9:e898562014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Stein S, Lohmann C, Schäfer N, Hofmann J,
Rohrer L, Besler C, Rothgiesser KM, Becher B, Hottiger MO, Borén J,
et al: SIRT1 decreases Lox-1-mediated foam cell formation in
atherogenesis. Eur Heart J. 31:2301–2309. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Du C, Lin X, Xu W, Zheng F, Cai J, Yang J,
Cui Q, Tang C, Cai J, Xu G and Geng B: Sulfhydrated sirtuin-1
increasing its deacetylation activity is an essential epigenetics
mechanism of anti-atherogenesis by hydrogen sulfide. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 30:184–197. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Huang YE, Tang ZH, Xie W, Shen XT, Liu MH,
Peng XP, Zhao ZZ, Nie DB, Liu LS and Jiang ZS: Endogenous hydrogen
sulfide mediates the cardioprotection induced by ischemic
postconditioning in the early reperfusion phase. Exp Ther Med.
4:1117–1123. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen CY, Leu HB, Wang SC, Tsai SH, Chou
RH, Lu YW, Tsai YL, Kuo CS, Huang PH, Chen JW and Lin SJ:
Inhibition of trimethylamine N-oxide attenuates neointimal
formation through reduction of inflammasome and oxidative stress in
a mouse model of carotid artery ligation. Antioxid Redox Signal.
38:215–233. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nallasamy P, Kang ZY, Sun X, Anandh Babu
PV, Liu D and Jia Z: Natural compound resveratrol attenuates
TNF-alpha-induced vascular dysfunction in mice and human
endothelial cells: The Involvement of the NF-κB signaling pathway.
Int J Mol Sci. 22:124862021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gupta R, Sahu M, Tripathi R, Ambasta RK
and Kumar P: Protein S-sulfhydration: Unraveling the prospective of
hydrogen sulfide in the brain, vasculature and neurological
manifestations. Ageing Res Rev. 76:1015792022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sun HJ, Xiong SP, Cao X, Cao L, Zhu MY, Wu
ZY and Bian JS: Polysulfide-mediated sulfhydration of SIRT1
prevents diabetic nephropathy by suppressing phosphorylation and
acetylation of p65 NF-κB and STAT3. Redox Biol. 38:1018132021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fu BC, Hullar MAJ, Randolph TW, Franke AA,
Monroe KR, Cheng I, Wilkens LR, Shepherd JA, Madeleine MM, Le
Marchand L, et al: Associations of plasma trimethylamine N-oxide,
choline, carnitine, and betaine with inflammatory and
cardiometabolic risk biomarkers and the fecal microbiome in the
multiethnic cohort adiposity phenotype study. Am J Clin Nutr.
111:1226–1234. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tang WHW and Hazen SL: Microbiome,
trimethylamine N-oxide, and cardiometabolic disease. Transl Res.
179:108–115. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Stubbs JR, House JA, Ocque AJ, Zhang S,
Johnson C, Kimber C, Schmidt K, Gupta A, Wetmore JB, Nolin TD, et
al: Serum trimethylamine-N-oxide is elevated in CKD and correlates
with coronary atherosclerosis burden. J Am Soc Nephrol. 27:305–313.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen ML, Zhu XH, Ran L, Lang HD, Yi L and
Mi MT: Trimethylamine-N-oxide induces vascular inflammation by
activating the NLRP3 inflammasome through the SIRT3-SOD2-mtROS
signaling pathway. J Am Heart Assoc. 6:e0063472017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu MH, Lin XL, Zhang Y, He J, Tan TP, Wu
SJ, Liu J, Tian W, Chen L, Yu S, et al: Hydrogen sulfide attenuates
doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by inhibiting reactive oxygen
species-activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 in H9c2
cardiac myocytes. Mol Med Rep. 12:6841–6848. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu MH, Zhang Y, He J, Tan TP, Wu SJ, Guo
DM, He H, Peng J, Tang ZH and Jiang ZS: Hydrogen sulfide protects
H9c2 cardiac cells against doxorubicin-induced cytotoxicity through
the PI3K/Akt/FoxO3a pathway. Int J Mol Med. 37:1661–1668. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Luo ZL, Ren JD, Huang Z, Wang T, Xiang K,
Cheng L and Tang LJ: The role of exogenous hydrogen sulfide in free
fatty acids induced inflammation in macrophages. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 42:1635–1644. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang D, Wu C, Ba D, Wang N, Wang Y, Li X,
Li Q and Zhao G: Ferroptosis contribute to neonicotinoid
imidacloprid-evoked pyroptosis by activating the
HMGB1-RAGE/TLR4-NF-κB signaling pathway. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf.
253:1146552023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Olas B: Hydrogen sulfide as a
‘double-faced’ compound: One with Pro- and antioxidant effect. Adv
Clin Chem. 78:187–196. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang Y, Yu R, Wu L and Yang G: Hydrogen
sulfide guards myoblasts from ferroptosis by inhibiting ALOX12
acetylation. Cell Signal. 78:1098702021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhao X, Zhang L, Liu X, Zhao Z, Zhong X
and Wang Y: Exogenous hydrogen sulfide inhibits neutrophils
extracellular traps formation via the HMGB1/TLR4/p-38 MAPK/ROS axis
in hyperhomocysteinemia rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 537:7–14.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bai L, Dai J, Xia Y, He K, Xue H, Guo Q,
Tian D, Xiao L, Zhang X, Teng X, et al: Hydrogen sulfide
ameliorated high choline-induced cardiac dysfunction by inhibiting
cGAS-STING-NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2022:13928962022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Qin M, Long F, Wu W, Yang D, Huang M, Xiao
C, Chen X, Liu X and Zhu YZ: Hydrogen sulfide protects against
DSS-induced colitis by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome. Free Radic
Biol Med. 137:99–109. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang Y, Liao S, Pan Z, Jiang S, Fan J, Yu
S, Xue L, Yang J, Ma S, Liu T, et al: Hydrogen sulfide alleviates
particulate matter-induced emphysema and airway inflammation by
suppressing ferroptosis. Free Radic Biol Med. 186:1–16. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhao Z, Li G, Wang Y, Li Y, Xu H, Liu W,
Hao W, Yao Y and Zeng R: Cytoplasmic HMGB1 induces renal tubular
ferroptosis after ischemia/reperfusion. Int Immunopharmacol.
116:1097572023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Castelblanco M, Lugrin J, Ehirchiou D,
Nasi S, Ishii I, So A, Martinon F and Busso N: Hydrogen sulfide
inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation and reduces cytokine
production both in vitro and in a mouse model of inflammation. J
Biol Chem. 293:2546–2557. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Koeth RA, Lam-Galvez BR, Kirsop J, Wang Z,
Levison BS, Gu X, Copeland MF, Bartlett D, Cody DB, Dai HJ, et al:
l-Carnitine in omnivorous diets induces an atherogenic gut
microbial pathway in humans. J Clin Invest. 129:373–387. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Feng S, Chen S, Yu W, Zhang D, Zhang C,
Tang C, Du J and Jin H: H2S inhibits pulmonary arterial
endothelial cell inflammation in rats with monocrotaline-induced
pulmonary hypertension. Lab Invest. 97:268–278. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhang QJ, Wang Z, Chen HZ, Zhou S, Zheng
W, Liu G, Wei YS, Cai H, Liu DP and Liang CC: Endothelium-specific
overexpression of class III deacetylase SIRT1 decreases
atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Cardiovasc Res.
80:191–199. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Liu Z, Han Y, Li L, Lu H, Meng G, Li X,
Shirhan M, Peh MT, Xie L, Zhou S, et al: The hydrogen sulfide
donor, GYY4137, exhibits anti-atherosclerotic activity in high fat
fed apolipoprotein E(−/-) mice. Br J Pharmacol. 169:1795–1809.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Miranda MX, van Tits LJ, Lohmann C,
Arsiwala T, Winnik S, Tailleux A, Stein S, Gomes AP, Suri V, Ellis
JL, et al: The Sirt1 activator SRT3025 provides atheroprotection in
Apoe-/- mice by reducing hepatic Pcsk9 secretion and enhancing Ldlr
expression. Eur Heart J. 36:51–59. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wen L, Chen Z, Zhang F, Cui X, Sun W,
Geary GG, Wang Y, Johnson DA, Zhu Y, Chien S and Shyy JY:
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase β phosphorylation
of sirtuin 1 in endothelium is atheroprotective. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 110:E2420–E2427. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Gorenne I, Kumar S, Gray K, Figg N, Yu H,
Mercer J and Bennett M: Vascular smooth muscle cell sirtuin 1
protects against DNA damage and inhibits atherosclerosis.
Circulation. 127:386–396. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
He S, Wang Y, Liu J, Li P, Luo X and Zhang
B: Activating SIRT1 deacetylates NF-κB p65 to alleviate liver
inflammation and fibrosis via inhibiting NLRP3 pathway in
macrophages. Int J Med Sci. 20:505–519. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Chen H, Lin X, Yi X, Liu X, Yu R, Fan W,
Ling Y, Liu Y and Xie W: SIRT1-mediated p53 deacetylation inhibits
ferroptosis and alleviates heat stress-induced lung epithelial
cells injury. Int J Hyperthermia. 39:977–986. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Breitenstein A, Stein S, Holy EW, Camici
GG, Lohmann C, Akhmedov A, Spescha R, Elliott PJ, Westphal CH,
Matter CM, et al: Sirt1 inhibition promotes in vivo arterial
thrombosis and tissue factor expression in stimulated cells.
Cardiovasc Res. 89:464–472. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Fiordelisi A, Iaccarino G, Morisco C,
Coscioni E and Sorriento D: NFkappaB is a key player in the
crosstalk between inflammation and cardiovascular diseases. Int J
Mol Sci. 20:15992019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Yuan Q, Zhang D, Liu C, Zhang C and Yuan
D: Chikusetsusaponin V inhibits LPS-activated inflammatory
responses via SIRT1/NF-κB signaling pathway in RAW264.7 cells.
Inflammation. 41:2149–2159. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Adjei-Mosi J, Sun Q, Smithson SB, Shealy
GL, Amerineni KD, Liang Z, Chen H, Wang M, Ping Q, Han J, et al:
Age-dependent loss of hepatic SIRT1 enhances NLRP3 inflammasome
signaling and impairs capacity for liver fibrosis resolution. Aging
Cell. e138112023.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Li D, Liu X, Pi W, Zhang Y, Yu L, Xu C,
Sun Z and Jiang J: Fisetin attenuates doxorubicin-induced
cardiomyopathy in vivo and in vitro by inhibiting ferroptosis
through SIRT1/Nrf2 signaling pathway activation. Front Pharmacol.
12:8084802022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Guo C, Zhang Y, Ling T, Zhao C, Li Y, Geng
M, Gai S, Qi W, Luo X, Chen L, et al: Chitosan oligosaccharides
alleviate colitis by regulating intestinal microbiota and
PPARγ/SIRT1-mediated NF-κB pathway. Mar Drugs. 20:962022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|