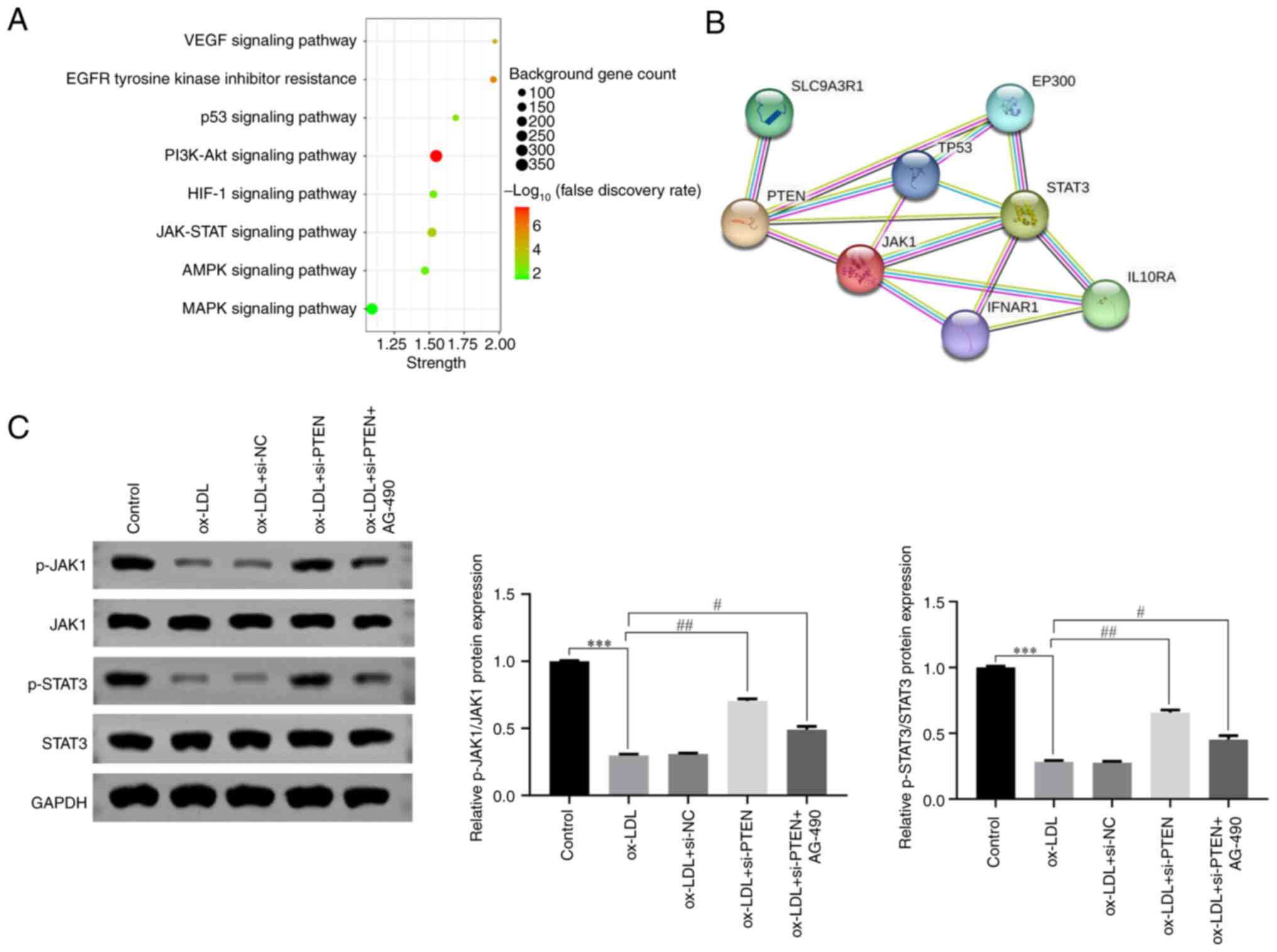
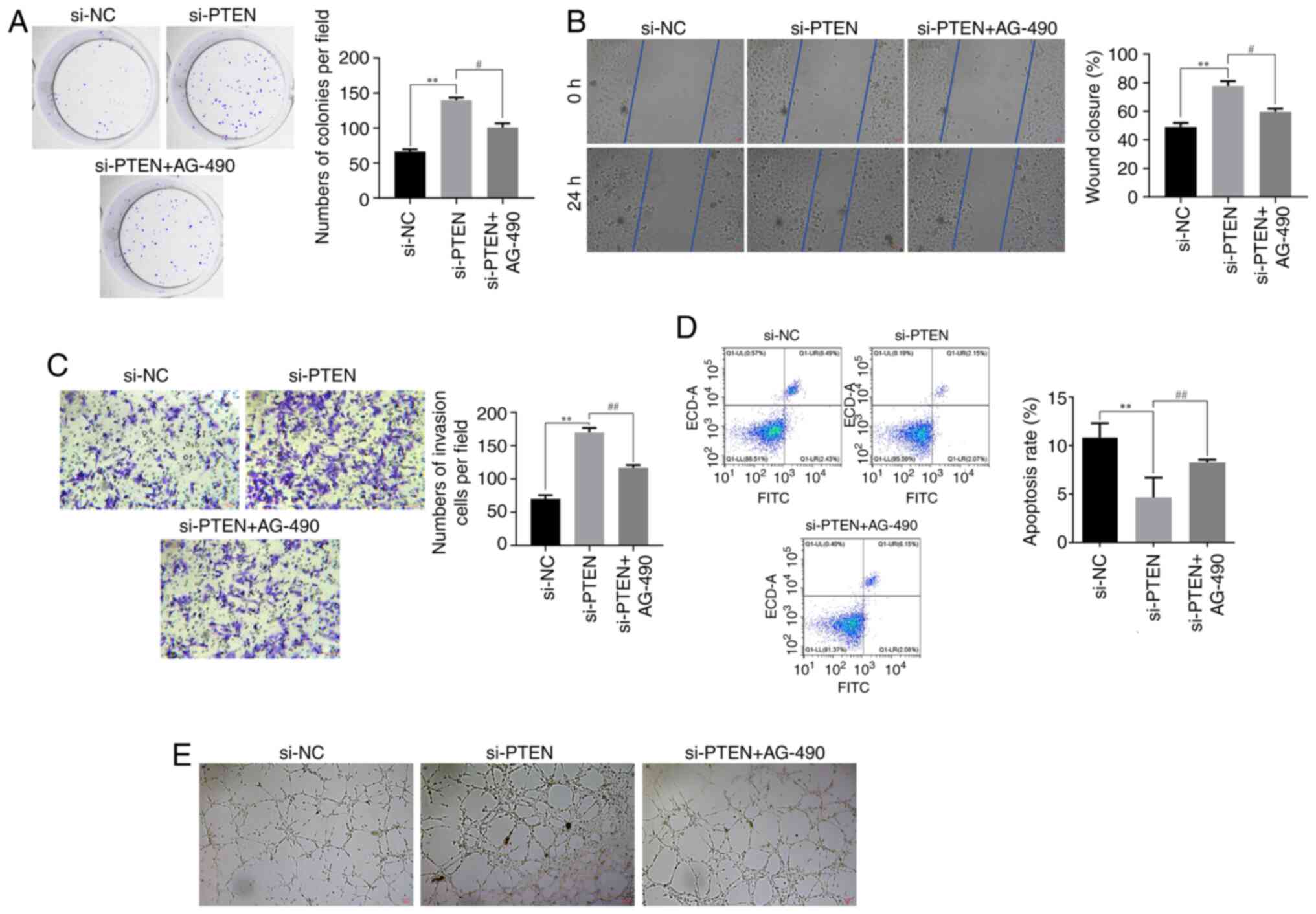
|
1
|
Bartholomew JR: Update on the management
of venous thromboembolism. Cleve Clin J Med. 84 (Suppl 3):S39–S46.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Lutsey PL and Zakai NA: Epidemiology and
prevention of venous thromboembolism. Nat Rev Cardiol. 20:248–262.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Giordano NJ, Jansson PS, Young MN, Hagan
KA and Kabrhel C: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, stratification,
and natural history of pulmonary embolism. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol.
20:135–140. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Boon G, Van Dam LF, Klok FA and Huisman
MV: Management and treatment of deep vein thrombosis in special
populations. Exp Rev Hematol. 11:685–695. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kim KA, Choi SY and Kim R: Endovascular
treatment for lower extremity deep vein thrombosis: An overview.
Korean J Radiol. 22:931–943. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Goldhaber SZ and Bounameaux H: Pulmonary
embolism and deep vein thrombosis. Lancet. 379:1835–1846. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ghosh N, Garg I, Srivastava S and Kumar B:
Influence of integrins on thrombus formation: A road leading to the
unravelling of DVT. Mol Cell Biochem. 476:1489–1504. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jin J, Wang C, Ouyang Y and Zhang D:
Elevated miR-195-5p expression in deep vein thrombosis and
mechanism of action in the regulation of vascular endothelial cell
physiology. Exp Ther Med. 18:4617–4624. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang W, Qin JJ, Rajaei M, Li X, Yu X, Hunt
C and Zhang R: Targeting MDM2 for novel molecular therapy: Beyond
oncology. Med Res Rev. 40:856–880. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lam B and Roudier E: Considering the role
of murine double minute 2 in the cardiovascular system? Front Cell
Dev Biol. 7:3202019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rodríguez C, Ramos-Araque ME,
Domínguez-Martínez M, Sobrino T, Sánchez-Morán I, Agulla J,
Delgado-Esteban M, Gómez-Sánchez JC, Bolaños JP, Castillo J and
Almeida A: Single-Nucleotide polymorphism 309T>G in the MDM2
promoter determines functional outcome after stroke. Stroke.
49:2437–2444. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hashimoto T, Ichiki T, Ikeda J,
Narabayashi E, Matsuura H, Miyazaki R, Inanaga K, Takeda K and
Sunagawa K: Inhibition of MDM2 attenuates neointimal hyperplasia
via suppression of vascular proliferation and inflammation.
Cardiovasc Res. 91:711–719. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kwon DH, Eom GH, Ko JH, Shin S, Joung H,
Choe N, Nam YS, Min HK, Kook T, Yoon S, et al: MDM2 E3
ligase-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of HDAC1 in vascular
calcification. Nat Commun. 7:104922016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zeng Y, Xu J, Hua YQ, Peng Y and Xu XL:
MDM2 contributes to oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced
inflammation through modulation of mitochondrial damage in
endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis. 305:1–9. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhou S, Gu L, He J, Zhang H and Zhou M:
MDM2 regulates vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA
stabilization in hypoxia. Mol Cell Biol. 31:4928–4937. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lou Z, Ma H, Li X, Zhang F, Du K and Wang
B: Hsa_circ_0001020 accelerates the lower extremity deep vein
thrombosis via sponging miR-29c-3p to promote MDM2 expression.
Thromb Res. 211:38–48. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hu WN, Duan ZY, Wang Q and Zhou DH: The
suppression of ox-LDL-induced inflammatory response and apoptosis
of HUVECs by lncRNA XIAT knockdown via regulating miR-30c-5p/PTEN
axis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:7628–7638. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhu J, Liu B, Wang Z, Wang D, Ni H, Zhang
L and Wang Y: Exosomes from nicotine-stimulated macrophages
accelerate atherosclerosis through miR-21-3p/PTEN-mediated VSMC
migration and proliferation. Theranostics. 9:6901–6919. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wei L, Zhou Q, Tian H, Su Y, Fu GH and Sun
T: Integrin b3 promotes cardiomyocyte proliferation and attenuates
hypoxia-induced apoptosis via regulating the PTEN/Akt/mTOR and
ERK1/2 pathways. Int J Biol Sci. 16:644–654. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tahtasakal R, Sener EF, Delibasi N,
Hamurcu Z, Mehmetbeyoglu E, Bayram KK, Gunes I, Goksuluk D and
Emirogullari ON: Overexpression of the PTEN gene in myocardial
tissues of coronary bypass surgery patients. Arq Bras Cardiol.
120:e202201692023.(In English, Portuguese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chetram MA and Hinton CV: PTEN regulation
of ERK1/2 signaling in cancer. J Recept Signal Transduct Res.
32:190–195. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang J, Feng Q, Liang D and Shi J:
MiRNA-26a inhibits myocardial infarction-induced apoptosis by
targeting PTEN via JAK/STAT pathways. Cells Dev. 165:2036612021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Roger I, Milara J, Montero P and Cortijo
J: The role of JAK/STAT molecular pathway in vascular remodeling
associated with pulmonary hypertension. Int J Mol Sci. 22:49802021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu Y, Shen Y, Li J, Liu J, Liu S and Song
H: Viral infection related venous thromboembolism: Potential
mechanism and therapeutic targets. Ann Palliat Med. 9:1257–1263.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pang Q, You L, Meng X, Li Y, Deng T, Li D
and Zhu B: Regulation of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway: The
promising targets for cardiovascular disease. Biochem Pharmacol.
213:1155872023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Baldini C, Moriconi FR, Galimberti S,
Libby P and De Caterina R: The JAK-STAT pathway: An emerging target
for cardiovascular disease in rheumatoid arthritis and
myeloproliferative neoplasms. Eur Heart J. 42:4389–4400. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fu X, Sun Z, Long Q, Tan W, Ding H, Liu X,
Wu L, Wang Y and Zhang W: Glycosides from Buyang Huanwu Decoction
inhibit atherosclerotic inflammation via JAK/STAT signaling
pathway. Phytomedicine. 105:1543852022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xu M, Li X and Song L: Baicalin regulates
macrophages polarization and alleviates myocardial
ischaemia/reperfusion injury via inhibiting JAK/STAT pathway. Pharm
Biol. 58:655–663. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xue W and Deng L: EP300 improves
endothelial injury and mitochondrial dysfunction in coronary artery
disease by regulating histone acetylation of SOCS1 promoter via
inhibiting JAK/STAT pathway. Cytokine. 176:1565072024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ma Y, Tan F and Yu S: Diosmin inhibits
apoptosis of vascular endothelial cells in rats with traumatic deep
vein thrombosis through JAK-STAT signaling pathway. Panminerva Med.
24:10.23736/S0031–0808.19.03718-2. 2019.
|
|
31
|
Ren G, Yang EJ, Tao S, Mou PK, Pu Y, Chen
LJ and Shim JS: MDM2 inhibition is synthetic lethal with PTEN loss
in colorectal cancer cells via the p53-dependent mechanism. Int J
Biol Sci. 19:3544–3557. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Szklarczyk D, Gable AL, Nastou KC, Lyon D,
Kirsch R, Pyysalo S, Doncheva NT, Legeay M, Fang T, Bork P, et al:
The STRING database in 2021: Customizable protein-protein networks,
and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement
sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 49((D1)): D605–D612. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen L, Zhang YH, Wang S, Zhang Y, Huang T
and Cai YD: Prediction and analysis of essential genes using the
enrichments of gene ontology and KEGG pathways. PLoS One.
12:e01841292017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sun LL, Xiao L, Du XL, Hong L, Li CL, Jiao
J, Li WD and Li XQ: MiR-205 promotes endothelial progenitor cell
angiogenesis and deep vein thrombosis recanalization and resolution
by targeting PTEN to regulate Akt/autophagy pathway and MMP2
expression. J Cell Mol Med. 23:8493–8504. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang Y, Liu J, Jia W, Tian X, Jiang P,
Cheng Z and Li J: AGEs/RAGE blockade downregulates Endothenin-1
(ET-1), mitigating Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVEC)
injury in deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Bioengineered. 12:1360–1368.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Athanasios A, Charalampos V, Vasileios T
and Ashraf GM: Protein-Protein interaction (PPI) network: Recent
advances in drug discovery. Curr Drug Metab. 18:5–10. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chang CJ, Freeman DJ and Wu H: PTEN
regulates Mdm2 expression through the P1 promoter. J Biol Chem.
279:29841–29848. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang T, Guan R, Xia F, Du J and Xu L:
Curcumin promotes venous thrombi resolve process in a mouse deep
venous thrombosis model via regulating miR-499. Microvasc Res.
136:1041482021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Maeshima T, Aisu S, Ohkura N, Watanabe M
and Itagaki F: The association between deep vein thrombosis,
pulmonary embolism, and janus kinase inhibitors: Reporting status
and signal detection in the Japanese adverse drug event report
database. Drugs Real World Outcomes. 11:369–375. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Orozco-García E, van Meurs DJ, Calderón
JC, Narvaez-Sanchez R and Harmsen MC: Endothelial plasticity across
PTEN and Hippo pathways: A complex hormetic rheostat modulated by
extracellular vesicles. Transl Oncol. 31:1016332023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chu C, Wang B, Zhang Z, Liu W, Sun S,
Liang G, Zhang X, An H, Wei R, Zhu X, et al: miR-513c-5p
suppression aggravates pyroptosis of endothelial cell in deep
venous thrombosis by promoting caspase-1. Front Cell Dev Biol.
10:8387852022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Obermayer G, Afonyushkin T and Binder CJ:
Oxidized low-density lipoprotein in inflammation-driven thrombosis.
J Thromb Haemost. 16:418–428. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|