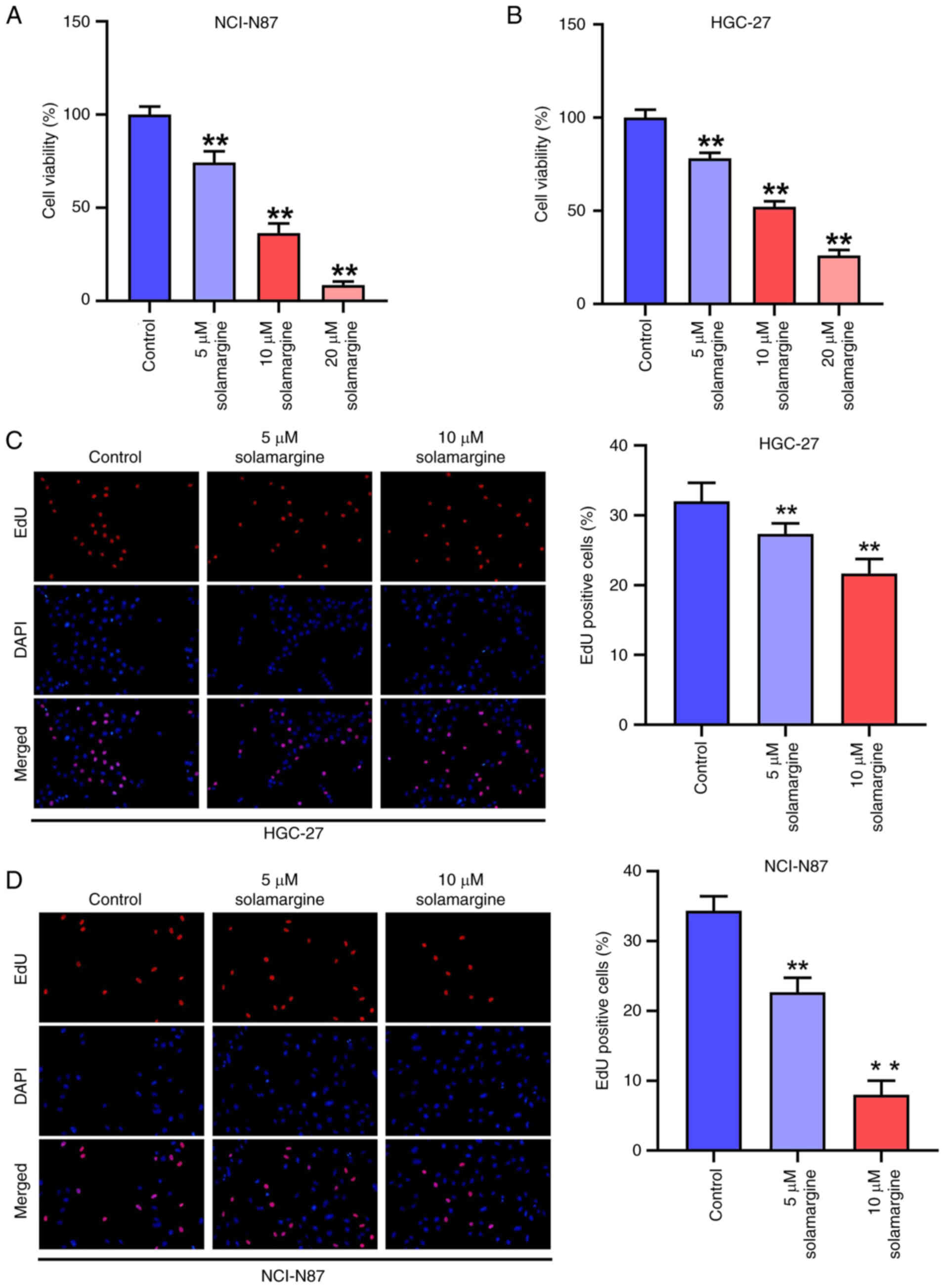
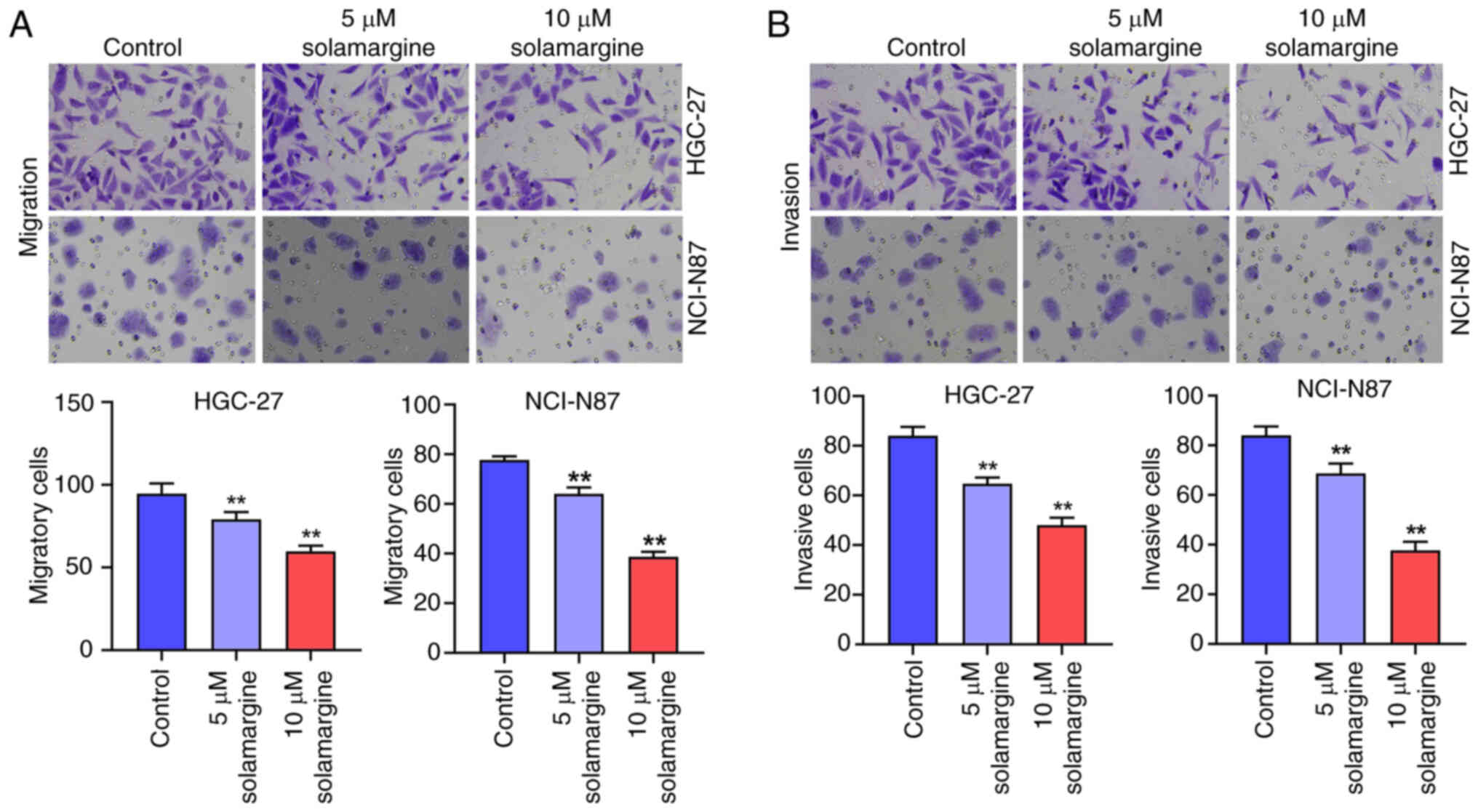
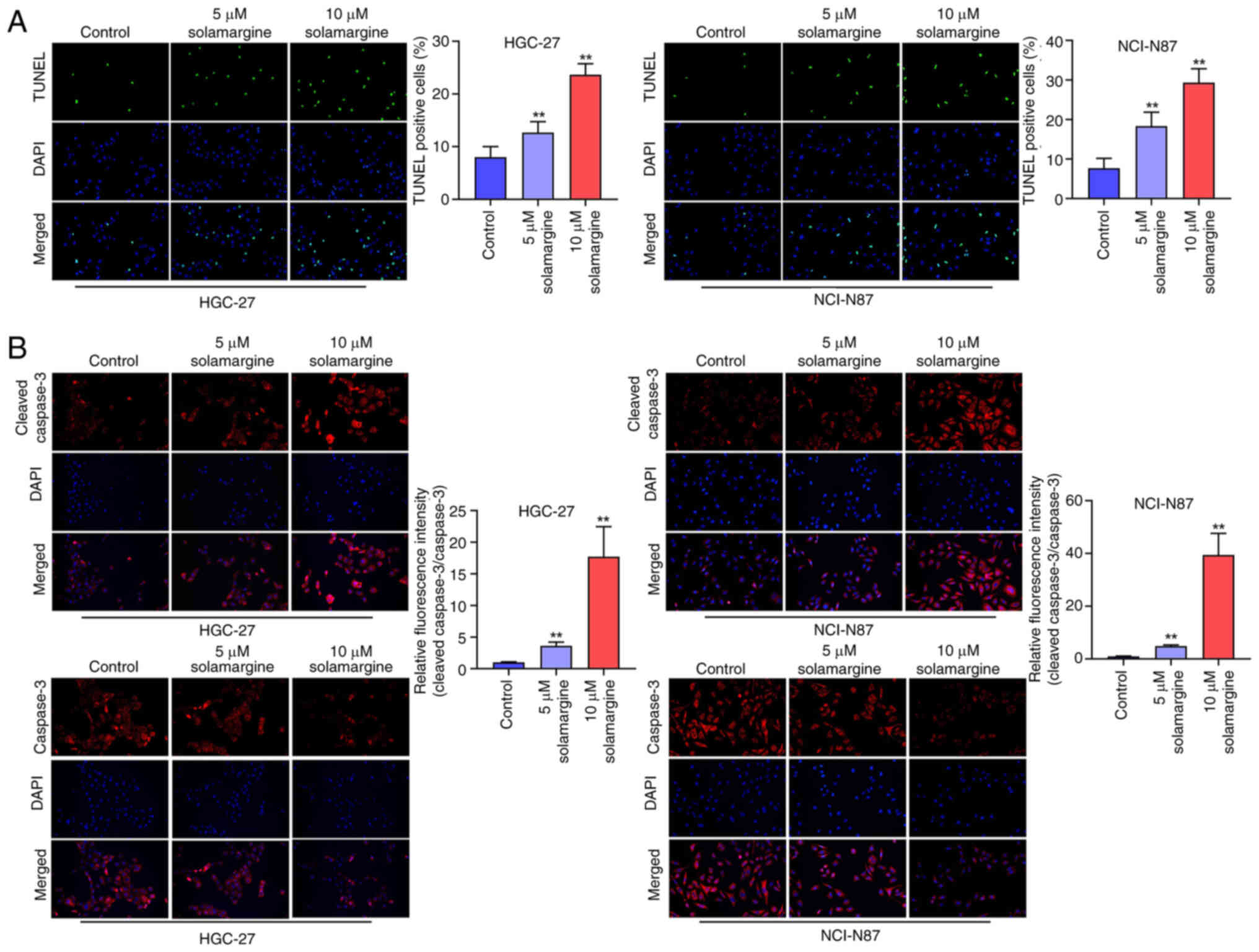
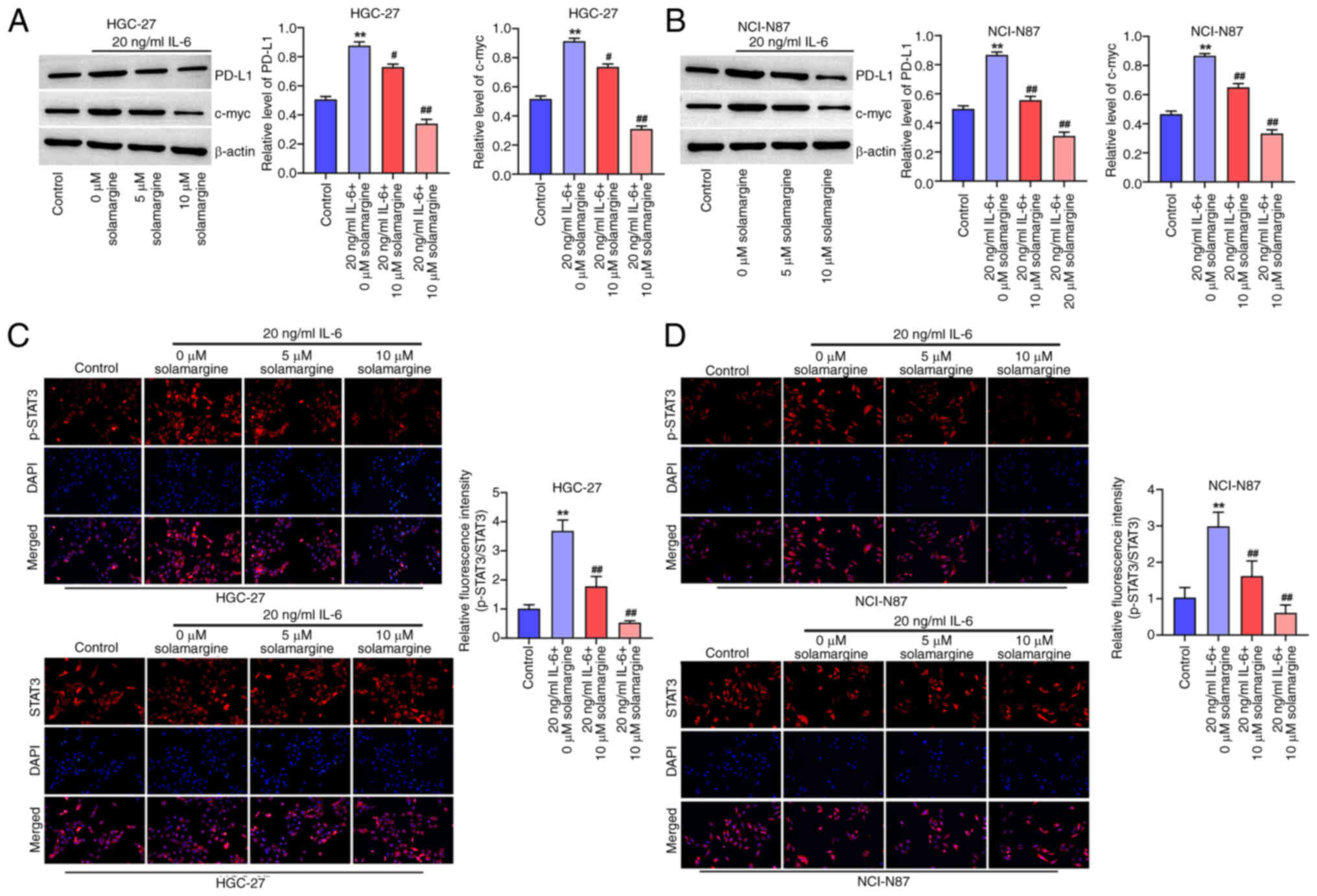
|
1
|
Jeon M, Jang H, Jeon H, Park CG and Kim S:
Long-term late effects in older gastric cancer survivors: Survival
analysis using Cox hazard regression model by retrospective
electronic health records. Support Care Cancer. 32:292023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sun Z, Liu Y, Deng H, Wang S, Zhang J,
Xing C and Xu C: Modified Chaishao Liujunzi Decoction inhibits bile
acid-induced gastric intestinal metaplasia: From network prediction
to experimental verification. Aging (Albany NY). 15:13998–14018.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fang S, Liu Z, Qiu Q, Tang Z, Yang Y,
Kuang Z, Du X, Xiao S, Liu Y, Luo Y, et al: Diagnosing and grading
gastric atrophy and intestinal metaplasia using semi-supervised
deep learning on pathological images: Development and validation
study. Gastric Cancer. 27:343–354. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhu Y, Huang C, Zhang C, Zhou Y, Zhao E,
Zhang Y, Pan X, Huang H, Liao W and Wang X: LncRNA MIR200CHG
inhibits EMT in gastric cancer by stabilizing miR-200c from
target-directed miRNA degradation. Nat Commun. 14:81412023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pei H, Yang J, Li W, Luo X, Xu Y, Sun X,
Chen Q, Zhao Q, Hou L, Tan G and Ji D: Solanum nigrum Linn:
Advances in anti-cancer activity and mechanism in digestive system
tumors. Med Oncol. 40:3112023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Long K, Zhou H, Li Y, Liu L and Cai J: The
value of chest computed tomography in evaluating lung cancer in a
lobe affected by stable pulmonary tuberculosis in middle-aged and
elderly patients: A preliminary study. Front Oncol. 12:8681072022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Han Y, Shi J, Xu Z, Zhang Y, Cao X, Yu J,
Li J and Xu S: Identification of solamargine as a cisplatin
sensitizer through phenotypical screening in cisplatin-resistant
NSCLC organoids. Front Pharmacol. 13:8021682022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Qu X, Xie J, Zhang Y and Wang Z:
Solamargine alleviates proliferation and metastasis of cervical
cancer cells by blocking the CXCL3-Mediated Erk signaling pathway.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022:76347542022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ge J, Wang P, Ma H and Zhang J:
Solamargine inhibits prostate cancer cell growth and enhances the
therapeutic efficacy of docetaxel via Akt Signaling. J Oncol.
2022:90559542022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Huang S, Sun M, Ren Y, Luo T, Wang X, Weng
G and Cen D: Solamargine induces apoptosis of human renal carcinoma
cells via downregulating phosphorylated STAT3 expression. Oncol
Lett. 26:4932023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cha JH, Chan LC, Li CW, Hsu JL and Hung
MC: Mechanisms Controlling PD-L1 expression in cancer. Mol Cell.
76:359–370. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ai L, Xu A and Xu J: Roles of PD-1/PD-L1
Pathway: Signaling, cancer, and beyond. Adv Exp Med Biol.
1248:33–59. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Civriz AH, Teke K, Akdas EM, Dillioglugil
O, Vural C and Yaprak Bayrak B: The prognostic value of expressions
of STAT3, PD-L1, and PD-L2 in Ta/T1 urothelial carcinoma before and
after BCG treatment. Ural Oncol. 41:486.e1–486.e13. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wen J, Peng H, Wang D, Wen ZM, Liu YT, Qu
J, Cui HX, Wang YY, DU YL, Wang T, et al: Lipopolysaccharides
protect mesenchymal stem cell against cardiac ischemia-reperfusion
injury by HMGB1/STAT3 signaling. J Geriatr Cardiol. 20:801–812.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Erlichman N, Meshel T, Baram T, Abu Raiya
A, Horvitz T, Ben-Yaakov H and Ben-Baruch A: The Cell-Autonomous
Pro-Metastatic Activities of PD-L1 in Breast Cancer Are Regulated
by N-Linked Glycosylation-Dependent Activation of STAT3 and STAT1.
Cells. 12:23382023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang R, Ye H, Yang B, Ao M, Yu X, Wu Y, Xi
M and Hou M: m6A-modified circNFIX promotes ovarian cancer
progression and immune escape via activating IL-6R/JAK1/STAT3
signaling by sponging miR-647. Int Immunopharmacol. 124((Pt A)):
1108792023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ye H, Yu W, Li Y, Bao X, Ni Y, Chen X, Sun
Y, Chen A, Zhou W and Li J: AIM2 fosters lung adenocarcinoma immune
escape by modulating PD-L1 expression in tumor-associated
macrophages via JAK/STAT3. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 19:22697902023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
de Carvalho T, Lara P, Jorquera-Cordero C,
Aragão CFS, de Santana Oliveira A, Garcia VB, de Paiva Souza SV,
Schomann T, Soares LAL, da Matta Guedes PM and de Araújo Júnior RF:
Inhibition of murine colorectal cancer metastasis by targeting
M2-TAM through STAT3/NF-kB/AKT signaling using macrophage 1-derived
extracellular vesicles loaded with oxaliplatin, retinoic acid, and
Libidibia ferrea. Biomed Pharmacother. 168:1156632023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Han Y, Liu D and Li L: PD-1/PD-L1 pathway:
Current researches in cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 10:727–742.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dermani FK, Samadi P, Rahmani G, Kohlan AK
and Najafi R: PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint: Potential target for
cancer therapy. J Cell Physiol. 234:1313–1325. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fan J, Fan F, He J and Sun Y: Agaricus
blazei Murill extract FA-2-b-β inhibits gastric cancer cell
proliferation by apoptosis by the mitochondrial pathway and
blocking the cell cycle. Asian J Surg. 47:1560–1561. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Han EK, Woo JW, Suh KJ, Kim SH, Kim JH and
Park SY: PD-L1 (SP142) expression in primary and
recurrent/metastatic triple-negative breast cancers and its
clinicopathological significance. Cancer Res Treat. 56:557–566.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Anderson HG, Takacs GP, Harris DC, Kuang
Y, Harrison JK and Stepien TL: Global stability and parameter
analysis reinforce therapeutic targets of PD-L1-PD-1 and MDSCs for
glioblastoma. J Math Biol. 88:102023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu P, Wei H, Li K, Zhu S, Li J, Chen C,
Zhang D, Li Y, Zhu L, Yi X, et al: The traditional chinese medicine
monomer Ailanthone improves the therapeutic efficacy of anti-PD-L1
in melanoma cells by targeting c-Jun. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
41:3462022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu Y, Liu X, Zhang N, Yin M, Dong J, Zeng
Q, Mao G, Song D, Liu L and Deng H: Berberine diminishes cancer
cell PD-L1 expression and facilitates antitumor immunity inhibiting
the deubiquitination activity of CSN5. Acta Pharm Sin B.
10:2299–2312. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang J, He X, Jia Z, Yan A, Xiao K, Liu S,
Hou M, Long Y and Ding X: Shenqi Fuzheng injection restores the
sensitivity to gefitinib in non-small cell lung cancer by
inhibiting the IL-22/STAT3/AKT pathway. Pharm Biol. 62:33–41. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li XH, Huang GZ, Xu ZL, Zhao CY, Dong XY,
Cui BK and Lin XJ: IL20RB signaling enhances stemness and
chemotherapy resistance in pancreatic cancer. J Transl Med.
21:9112023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu C, Shen A, Song J, Cheng L, Zhang M,
Wang Y and Liu X: LncRNA-CCAT5-mediated crosstalk between
Wnt/β-Catenin and STAT3 signaling suggests novel therapeutic
approaches for metastatic gastric cancer with high Wnt activity.
Cancer Commun (Lond). 44:76–100. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jiang T, Xia Y, Li Y, Lu C, Lin J, Shen Y,
Lv J, Xie L, Gu C, Xu Z and Wang L: TRIM29 promotes antitumor
immunity through enhancing IGF2BP1 ubiquitination and subsequent
PD-L1 downregulation in gastric cancer. Cancer Lett.
581:2165102024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang H, Zhou Z, Zhang J, Hao T, Wang P, Wu
P, Su R, Yang H, Deng G, Chen S, et al: Pumilio1 regulates
NPM3/NPM1 axis to promote PD-L1-mediated immune escape in gastric
cancer. Cancer Lett. 581:2164982024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|