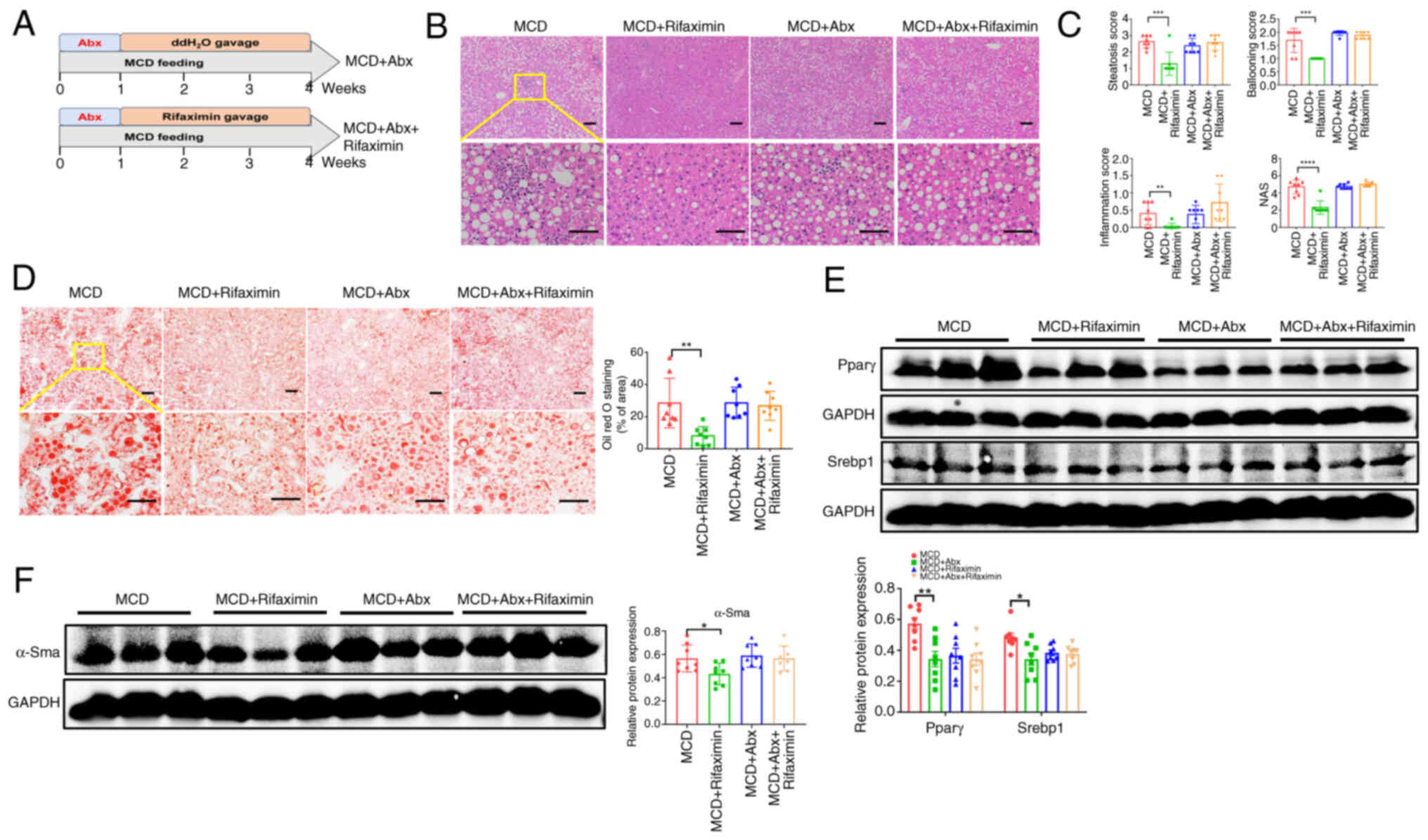
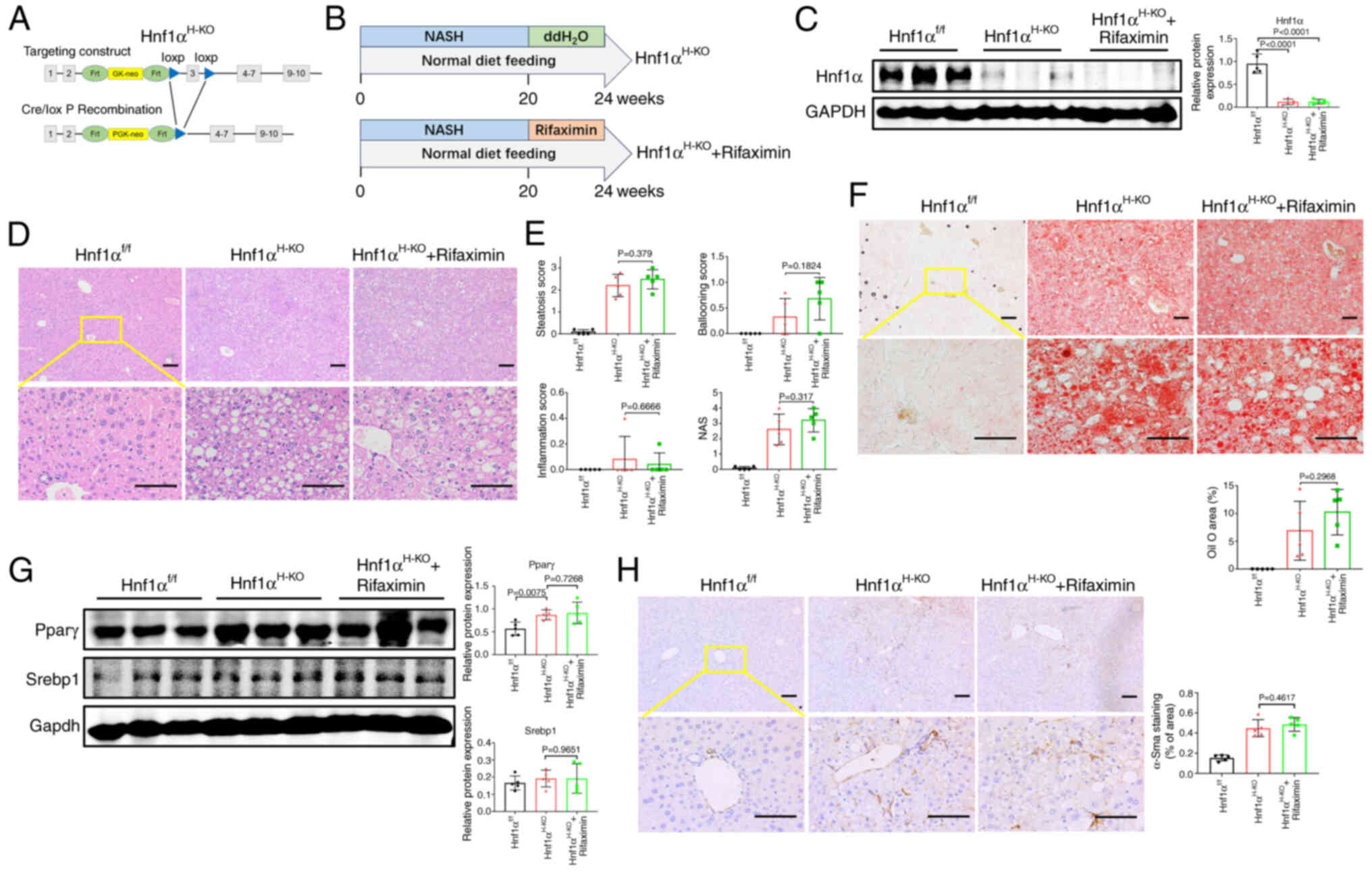
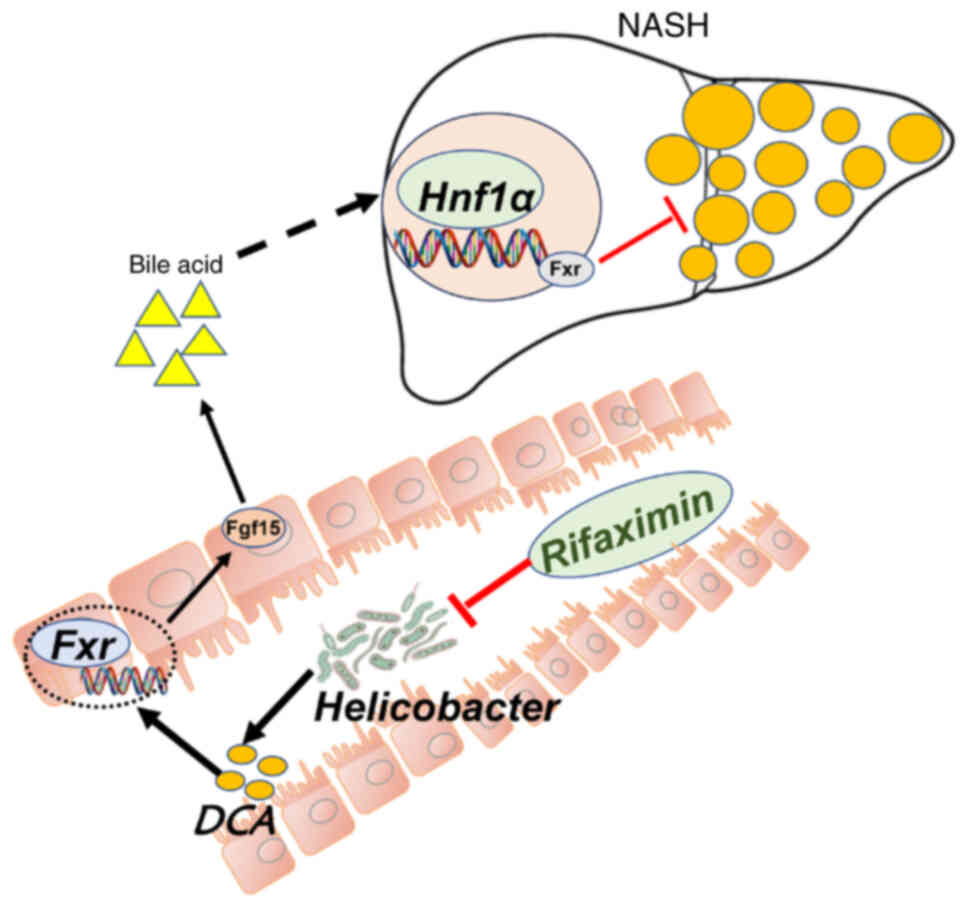
|
1
|
Younossi Z, Tacke F, Arrese M, Chander
Sharma B, Mostafa I, Bugianesi E, Wai-Sun Wong V, Yilmaz Y, George
J, Fan J and Vos MB: Global perspectives on nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease and nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Hepatology.
69:2672–2682. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Friedman SL, Neuschwander-Tetri BA,
Rinella M and Sanyal AJ: Mechanisms of NAFLD development and
therapeutic strategies. Nat Med. 24:908–922. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Schuster S, Cabrera D, Arrese M and
Feldstein AE: Triggering and resolution of inflammation in NASH.
Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 15:349–364. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang X, Coker OO, Chu ES, Fu K, Lau HCH,
Wang YX, Chan AWH, Wei H, Yang X, Sung JJY and Yu J: Dietary
cholesterol drives fatty liver-associated liver cancer by
modulating gut microbiota and metabolites. Gut. 70:761–774. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dr De Sousa SM and Prof Norman RJ :
Metabolic syndrome, diet and exercise. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet
Gynaecol. 37:140–151. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim D, Touros A and Kim WR: Nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease and metabolic syndrome. Clin Liver Dis.
22:133–140. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sharpton SR, Ajmera V and Loomba R:
Emerging role of the gut microbiome in nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease: From composition to function. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol.
17:296–306. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ponziani FR, Bhoori S, Castelli C,
Putignani L, Rivoltini L, Del Chierico F, Sanguinetti M, Morelli D,
Paroni Sterbini F, Petito V, et al: Hepatocellular carcinoma is
associated with gut microbiota profile and inflammation in
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 69:107–120. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Grabherr F, Grander C, Effenberger M,
Adolph TE and Tilg H: Gut dysfunction and non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 10:6112019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sun L, Pang Y, Wang X, Wu Q, Liu H, Liu B,
Liu G, Ye M, Kong W and Jiang C: Ablation of gut microbiota
alleviates obesity-induced hepatic steatosis and glucose
intolerance by modulating bile acid metabolism in hamsters. Acta
Pharm Sin B. 9:702–710. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jasirwan COM, Lesmana CRA, Hasan I,
Sulaiman AS and Gani RA: The role of gut microbiota in
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: pathways of mechanisms. Biosci
Microbiota Food Health. 38:81–88. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chávez-Talavera O, Tailleux A, Lefebvre P
and Staels B: Bile acid control of metabolism and inflammation in
obesity, type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia, and nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease. Gastroenterology. 152:1679–1694.e3. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Corbin KD and Zeisel SH: Choline
metabolism provides novel insights into nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease and its progression. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 28:159–165.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu HY, Walden TB, Cai D, Ahl D,
Bertilsson S, Phillipson M, Nyman M and Holm L: Dietary fiber in
bilberry ameliorates pre-obesity events in rats by regulating lipid
depot, cecal short-chain fatty acid formation and microbiota
composition. Nutrients. 11:13502019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhu L, Baker SS, Gill C, Liu W, Alkhouri
R, Baker RD and Gill SR: Characterization of gut microbiomes in
nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) patients: A connection between
endogenous alcohol and NASH. Hepatology. 57:601–609. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Coronel-Castillo CE, Contreras-Carmona J,
Frati-Munari AC, Uribe M and Méndez-Sánchez N: Efficacy of
rifaximin in the different clinical scenarios of hepatic
encephalopathy. Rev Gastroenterol Mex (Engl Ed). 85:56–68. 2020.(In
English, Spanish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chautant F, Guillaume M, Robic MA,
Cadranel JF, Peron JM, Lison H, Cool C, Bureau C and Duhalde V:
Lessons from ‘real life experience’ of rifaximin use in the
management of recurrent hepatic encephalopathy. World J Hepatol.
12:10–20. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fodor AA, Pimentel M, Chey WD, Lembo A,
Golden PL, Israel RJ and Carroll IM: Rifaximin is associated with
modest, transient decreases in multiple taxa in the gut microbiota
of patients with diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome.
Gut Microbes. 10:22–33. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shah ED, Saini SD and Chey WD: Value-based
pricing for rifaximin increases access of patients with irritable
bowel syndrome with diarrhea to therapy. Clin Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 17:2687–2695.e11. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Abdel-Razik A, Mousa N, Shabana W, Refaey
M, Elzehery R, Elhelaly R, Zalata K, Abdelsalam M, Eldeeb AA, Awad
M, et al: Rifaximin in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Hit
multiple targets with a single shot. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
30:1237–1246. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gangarapu V, Ince AT, Baysal B, Kayar Y,
Kılıç U, Gök Ö, Uysal Ö and Şenturk H: Efficacy of rifaximin on
circulating endotoxins and cytokines in patients with nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 27:840–845. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang L, Liu B, Zheng J, Huang J, Zhao Q,
Liu J, Su Z, Wang M, Cui Z, Wang T, et al: Rifaximin alters
intestinal microbiota and prevents progression of ankylosing
spondylitis in mice. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 9:442019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhu Y, He C, Li X, Cai Y, Hu J, Liao Y,
Zhao J, Xia L, He W, Liu L, et al: Gut microbiota dysbiosis worsens
the severity of acute pancreatitis in patients and mice. J
Gastroenterol. 54:347–358. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ni Q, Ding K, Wang KQ, He J, Yin C, Shi J,
Zhang X, Xie WF and Shi YQ: Deletion of HNF1α in hepatocytes
results in fatty liver-related hepatocellular carcinoma in mice.
FEBS Lett. 591:1947–1957. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, Van Natta M, Behling
C, Contos MJ, Cummings OW, Ferrell LD, Liu YC, Torbenson MS,
Unalp-Arida A, et al: Design and validation of a histological
scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology.
41:1313–1321. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yue HY, Yin C, Hou JL, Zeng X, Chen YX,
Zhong W, Hu PF, Deng X, Tan YX, Zhang JP, et al: Hepatocyte nuclear
factor 4alpha attenuates hepatic fibrosis in rats. Gut. 59:236–246.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nie Y, Liu Q, Zhang W, Wan Y, Huang C and
Zhu X: Ursolic acid reverses liver fibrosis by inhibiting
NOX4/NLRP3 inflammasome pathways and bacterial dysbiosis. Gut
Microbes. 13:19727462021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
R Core Team, . R: A language and
environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical
Computing; Vienna, Austria: 2021
|
|
30
|
Quan T, Zhou F, Chen H, Jian L, Yang Y,
Xia F, Xiang S, Zhou B and Li S: Ficus hirta Vahl. Ameliorates
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease through regulating lipid
metabolism and gut microbiota. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2022:34747232022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mukherjee S, Zhelnin L, Sanfiz A, Pan J,
Li Z, Yarde M, McCarty J and Jarai G: Development and validation of
an in vitro 3D model of NASH with severe fibrotic phenotype. Am J
Transl Res. 11:1531–1540. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kumar S, Duan Q, Wu R, Harris EN and Su Q:
Pathophysiological communication between hepatocytes and
non-parenchymal cells in liver injury from NAFLD to liver fibrosis.
Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 176:1138692021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Huang R, Guo F, Li Y, Liang Y, Li G, Fu P
and Ma L: Activation of AMPK by triptolide alleviates nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease by improving hepatic lipid metabolism,
inflammation and fibrosis. Phytomedicine. 92:1537392021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Begley M, Gahan CGM and Hill C: The
interaction between bacteria and bile. FEMS Microbiol Rev.
29:625–651. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
de Aguiar Vallim TQ, Tarling EJ and
Edwards PA: Pleiotropic roles of bile acids in metabolism. Cell
Metab. 17:657–669. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Honda T, Ishigami M, Luo F, Lingyun M,
Ishizu Y, Kuzuya T, Hayashi K, Nakano I, Ishikawa T, Feng GG, et
al: Branched-chain amino acids alleviate hepatic steatosis and
liver injury in choline-deficient high-fat diet induced NASH mice.
Metabolism. 69:177–187. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang L, Li HX, Pan WS, Khan FU, Qian C,
Qi-Li FR and Xu X: Novel hepatoprotective role of Leonurine
hydrochloride against experimental non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
mediated via AMPK/SREBP1 signallinging pathway. Biomed
Pharmacother. 110:571–581. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cheng S, Qian K, Wang Y, Wang G, Liu X,
Xiao Y and Wang X: PPARγ inhibition regulates the cell cycle,
proliferation and motility of bladder cancer cells. J Cell Mol Med.
23:3724–3736. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Voigt RM, Summa KC, Forsyth CB, Green SJ,
Engen P, Naqib A, Vitaterna MH, Turek FW and Keshavarzian A: The
circadian clock mutation promotes intestinal dysbiosis. Alcohol
Clin Exp Res. 40:335–347. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Canfora EE, Meex RCR, Venema K and Blaak
EE: Gut microbial metabolites in obesity, NAFLD and T2DM. Nat Rev
Endocrinol. 15:261–273. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Swennes AG, Sheh A, Parry NMA, Muthupalani
S, Lertpiriyapong K, García A and Fox JG: Helicobacter
hepaticus infection promotes hepatitis and preneoplastic foci
in farnesoid X receptor (FXR) deficient mice. PLoS One.
9:e1067642014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Qadri I, Hu LJ, Iwahashi M, Al-Zuabi S,
Quattrochi LC and Simon FR: Interaction of hepatocyte nuclear
factors in transcriptional regulation of tissue specific hormonal
expression of human multidrug resistance-associated protein 2
(abcc2). Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 234:281–292. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Xiong X, Wang X, Lu Y, Wang E, Zhang Z,
Yang J, Zhang H and Li X: Hepatic steatosis exacerbated by
endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated downregulation of FXR in
aging mice. J Hepatol. 60:847–854. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Purushotham A, Xu Q, Lu J, Foley JF, Yan
X, Kim DH, Kemper JK and Li X: Hepatic deletion of SIRT1 decreases
hepatocyte nuclear factor 1α/farnesoid X receptor signaling and
induces formation of cholesterol gallstones in mice. Mol Cell Biol.
32:1226–1236. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|