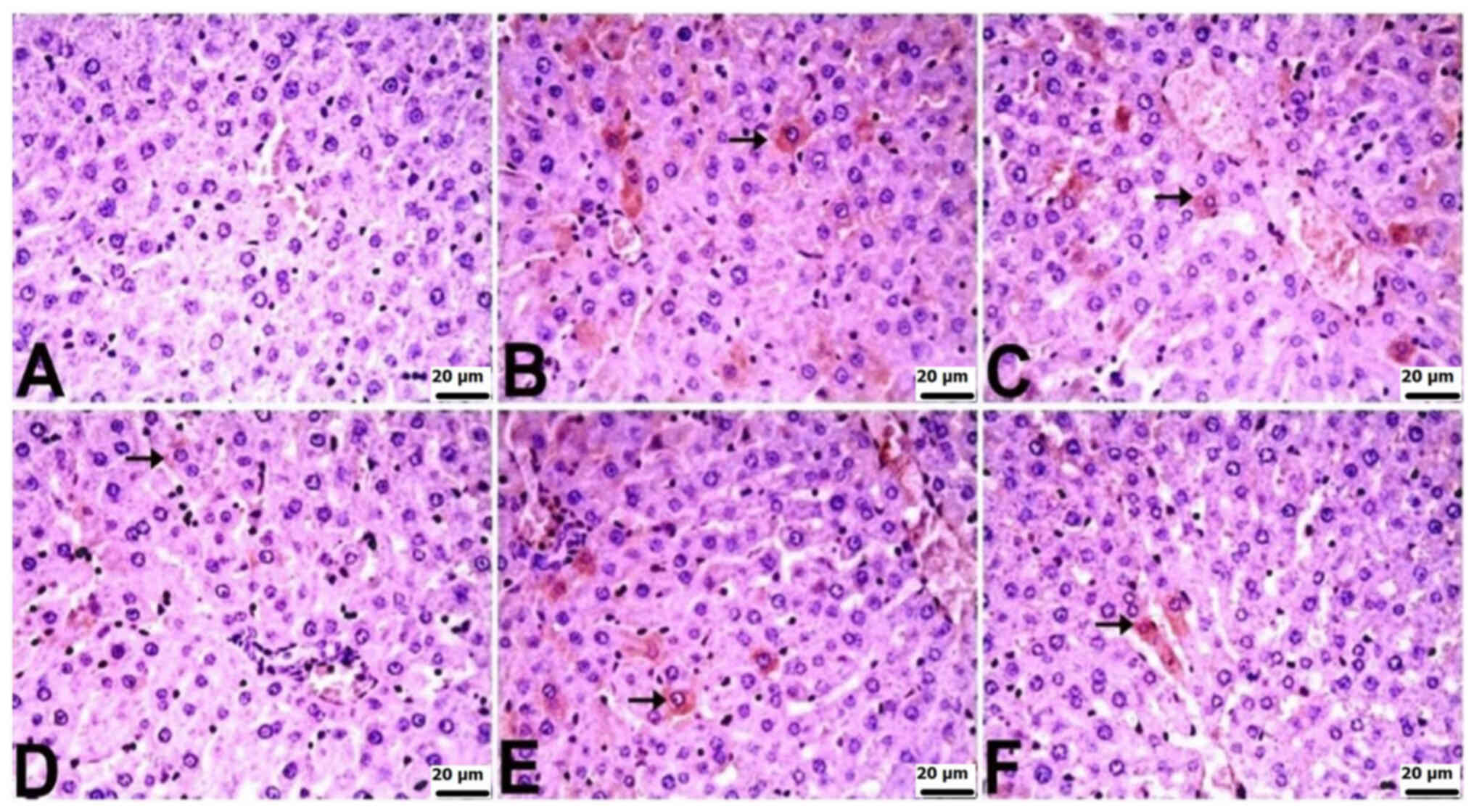
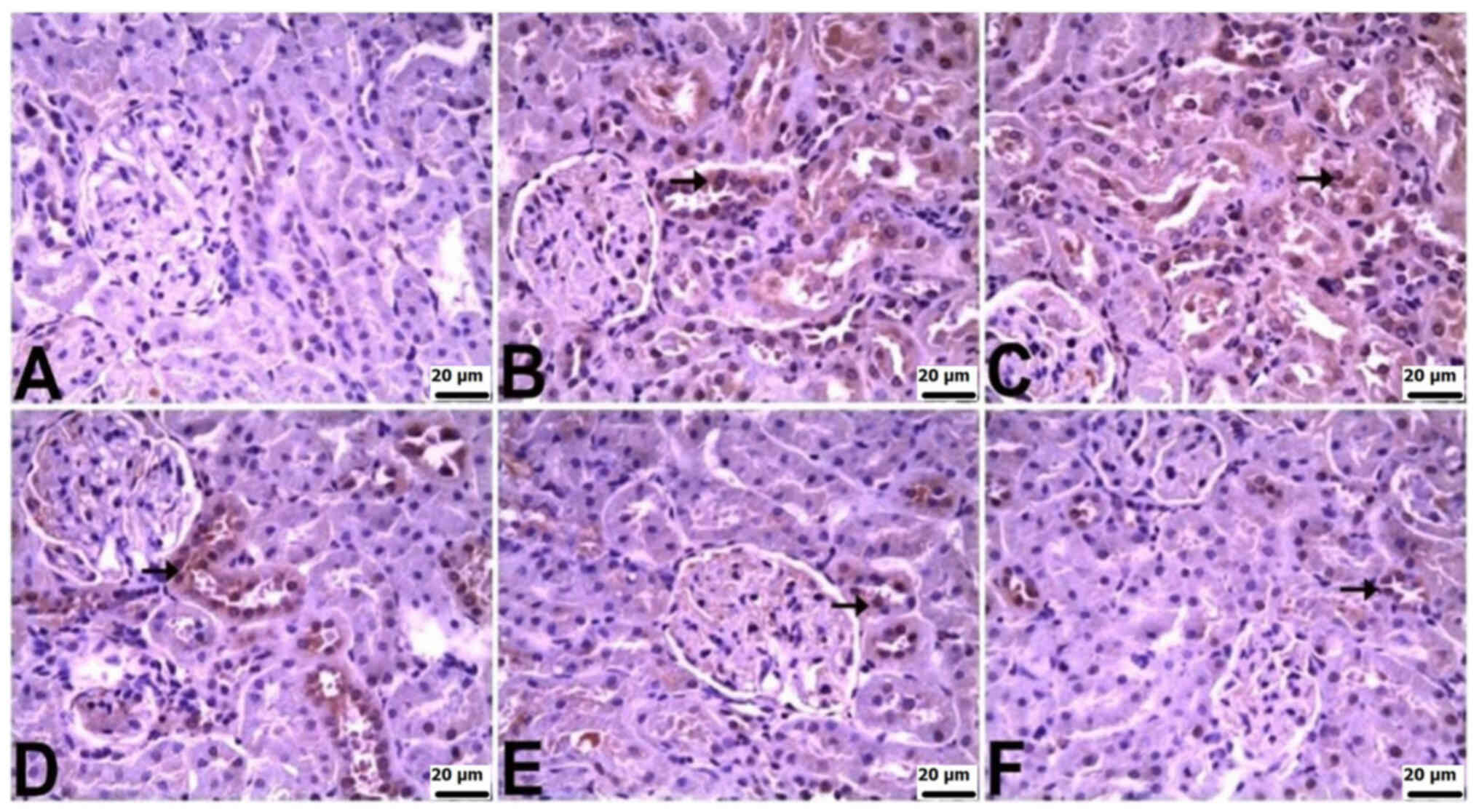
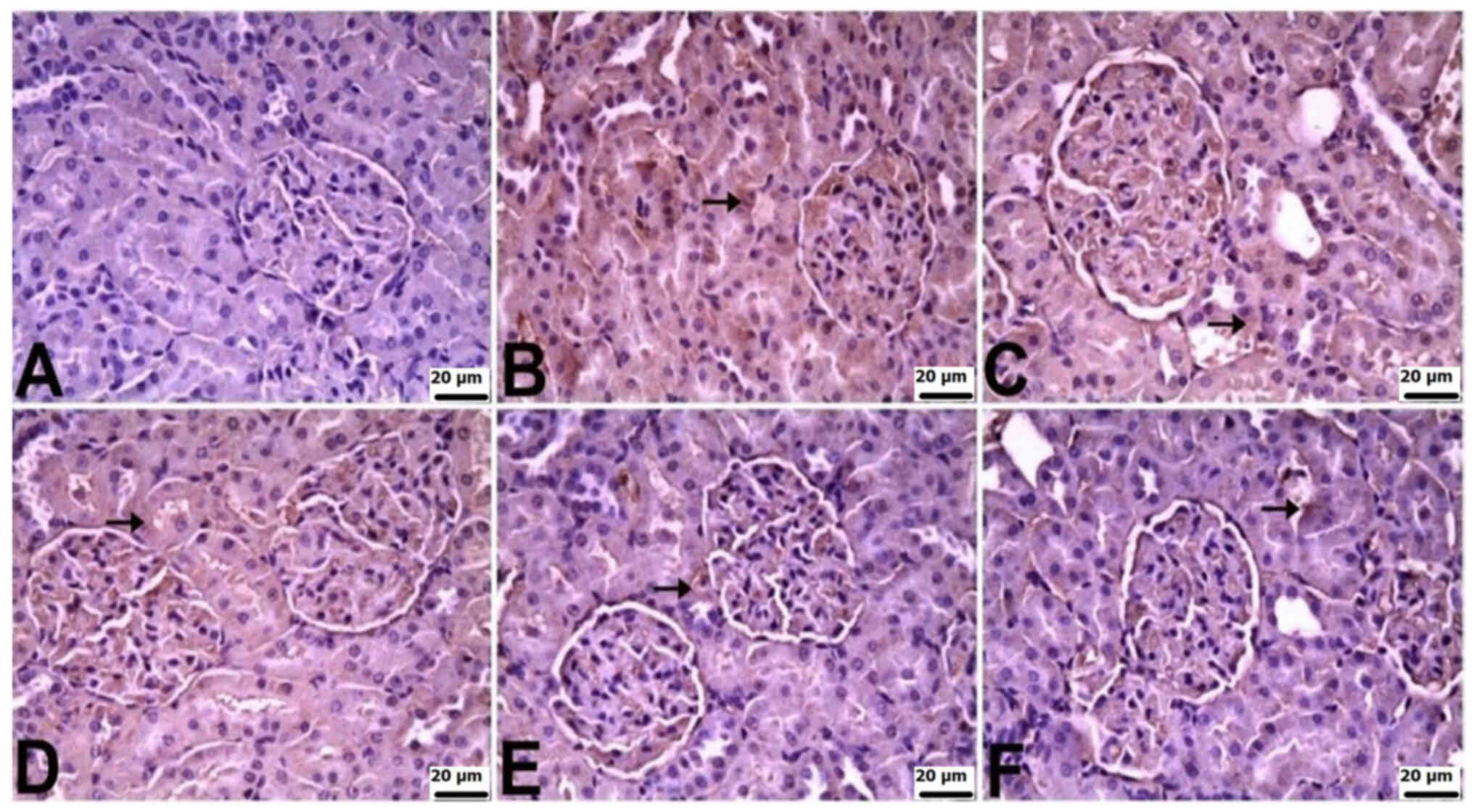
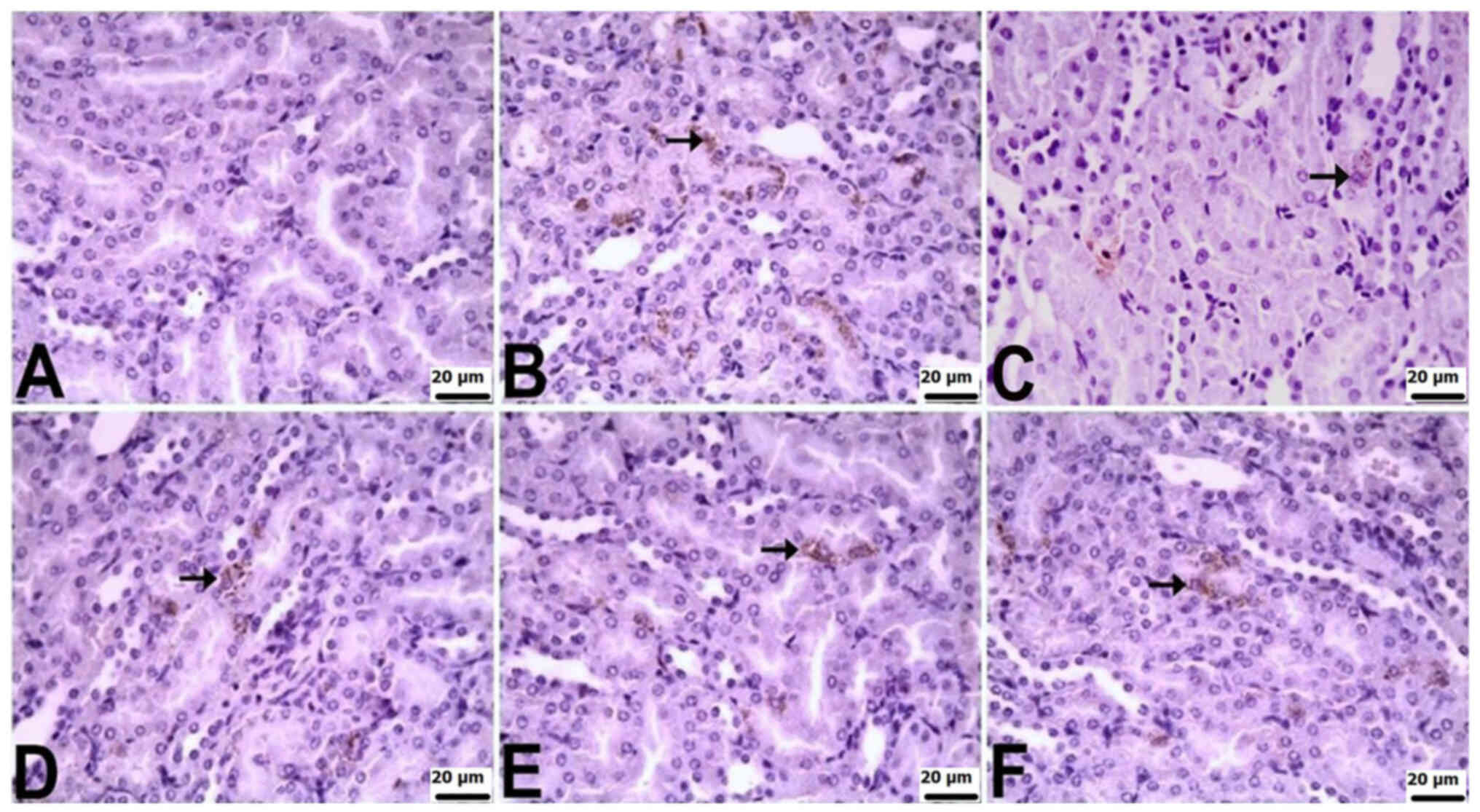
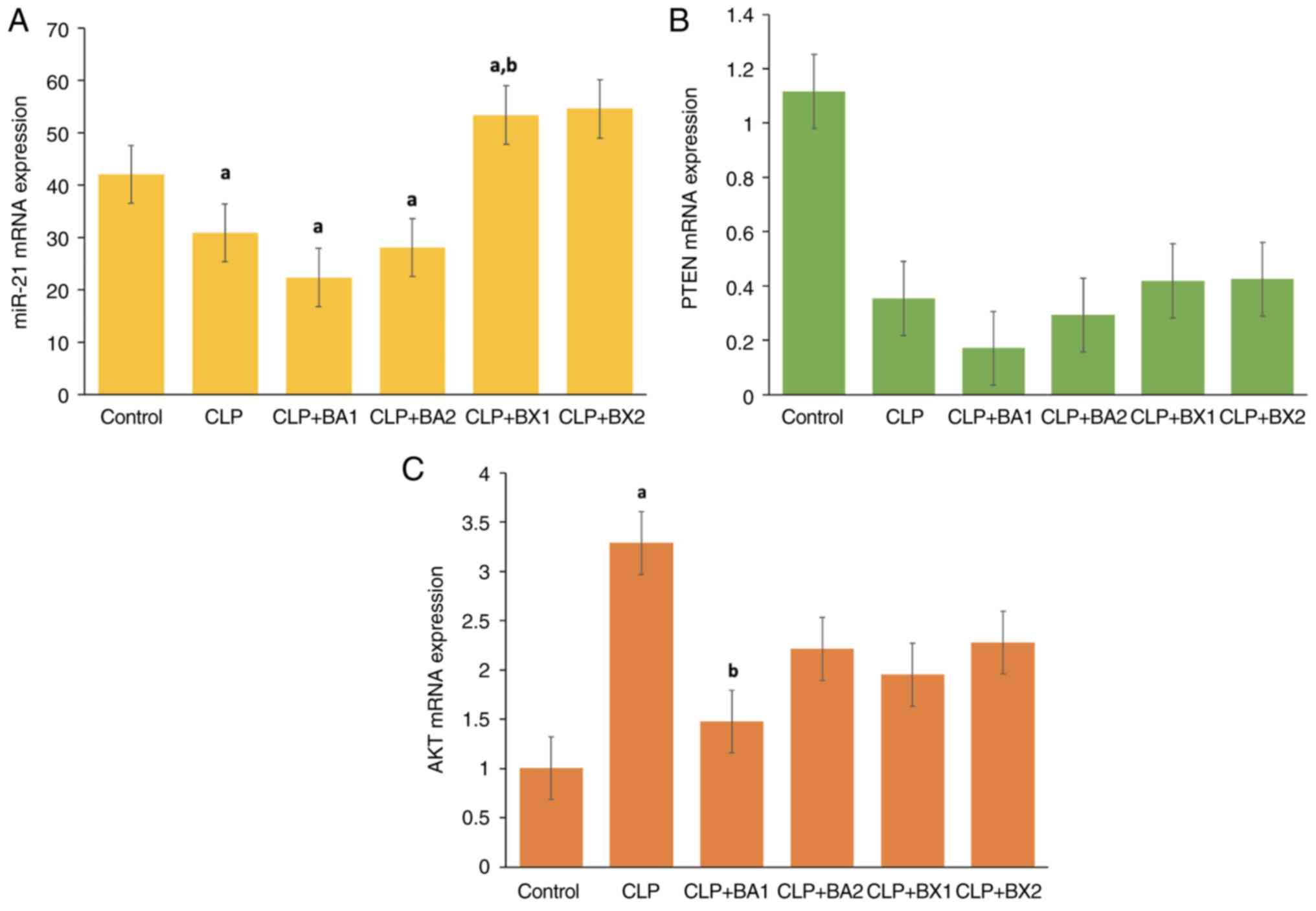
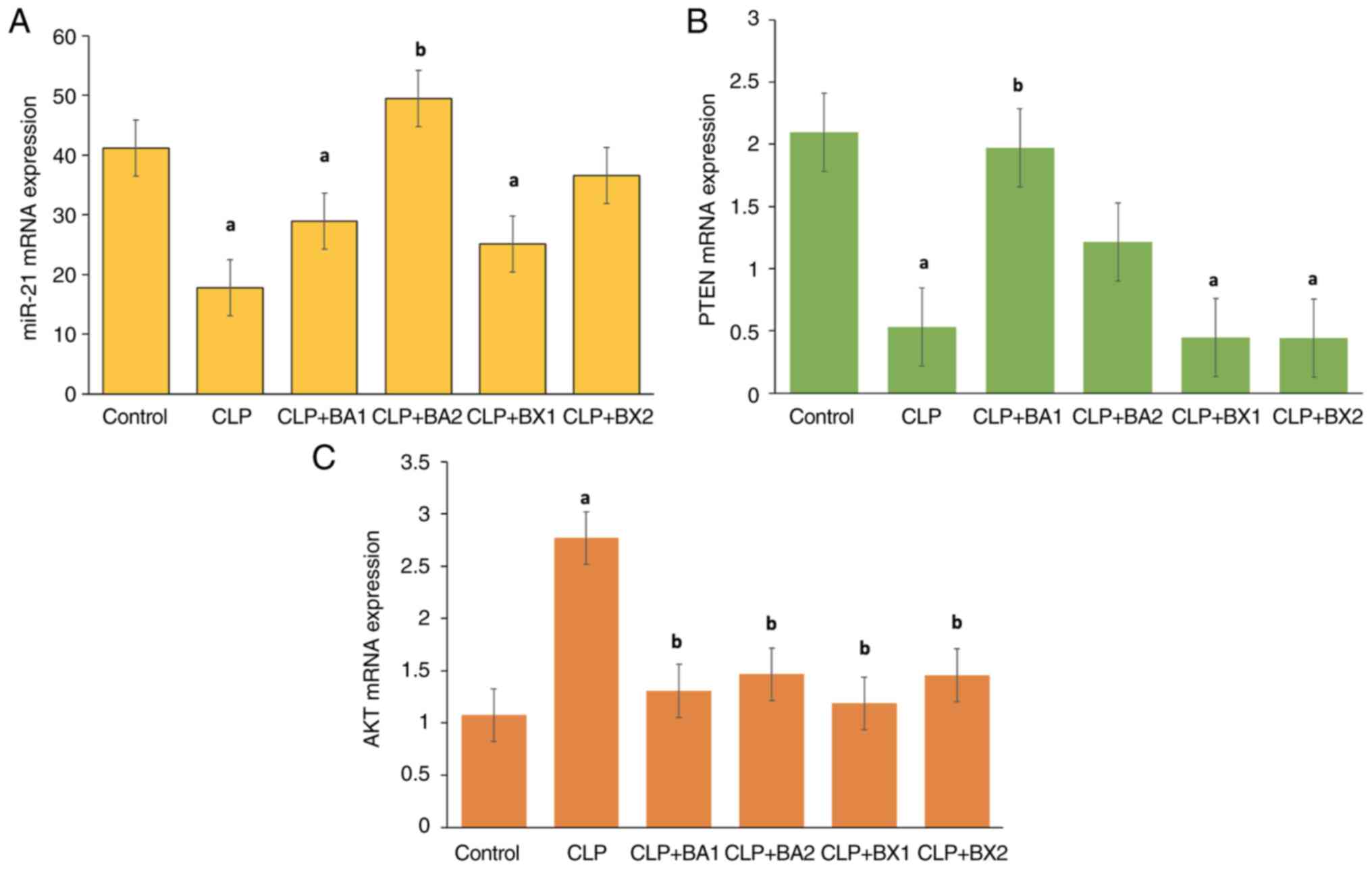
|
1
|
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour C,
Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche
JD, Coopersmith CM, et al: The third international consensus
definitions for sepsis and septic shock (sepsis-3). JAMA.
315:801–810. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rubulotta FM, Ramsay G, Parker MM,
Dellinger RP, Levy MM and Poeze M; Surviving Sepsis Campaign
Steering Committee; European Society of Intensive Care Medicine;
Society of Critical Care Medicine, : An international survey:
Public awareness and perception of sepsis. Crit Care Med.
37:167–170. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Guarino M, Perna B, Cesaro AE, Maritati M,
Spampinato MD, Contini C and De Giorgio R: 2023 Update on sepsis
and septic shock in adult patients: Management in the emergency
department. J Clin Med. 12:31882023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
WHO, . Global report on the epidemiology
and burden of sepsis: Current evidence identifying gaps and future
directions. World Health Organization; Geneva: 2020
|
|
5
|
Chiu C and Legrand M: Epidemiology of
sepsis and septic shock. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 34:71–76. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vakkalanka JP, Harland KK, Swanson MB and
Mohr NM: Clinical and epidemiological variability in severe sepsis:
An ecological study. J Epidemiol Community Health. 72:741–745.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Caraballo C and Jaimes F: Organ
dysfunction in sepsis: An ominous trajectory from infection to
death. Yale J Biol Med. 92:629–640. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Canabal JM and Kramer DJ: Management of
sepsis in patients with liver failure. Curr Opin Crit Care.
14:189–197. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jarrar D, Wang P and Chaudry IH:
Hepatocellular dysfunction-basic considerations. Holzheimer RG and
Mannick JA: Surgical Treatment: Evidence-Based and Problem-Oriented
Munich, Zuckschwerdt: 2001, PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yan J and Li S and Li S: The role of the
liver in sepsis. Int Rev Immunol. 33:498–510. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bagshaw SM, Uchino S, Bellomo R, Morimatsu
H, Morgera S, Schetz M, Tan I, Bouman C, Macedo E, Gibney N, et al:
Septic acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: Clinical
characteristics and outcomes. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2:431–439.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Khwaja A: KDIGO clinical practice
guidelines for acute kidney injury. Nephron Clin Pract.
120:c179–c184. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ma S, Evans RG, Iguchi N, Tare M,
Parkington HC, Bellomo R, May CN and Lankadeva YR: Sepsis-induced
acute kidney injury: A disease of the microcirculation.
Microcirculation. 26:e124832019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nedeva C, Menassa J and Puthalakath H:
Sepsis: Inflammation is a necessary evil. Front Cell Dev Biol.
7:1082019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sprague AH and Khalil RA: Inflammatory
cytokines in vascular dysfunction and vascular disease. Biochem
Pharmacol. 78:539–552. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Simmons J and Pittet JF: The coagulopathy
of acute sepsis. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 28:227–236. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang YY and Ning BT: Signaling pathways
and intervention therapies in sepsis. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
6:4072021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhou S, Sun Y, Zhao K, Gao Y, Cui J, Qi L
and Huang L: miR-21/PTEN pathway mediates the cardioprotection of
geniposide against oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced
endothelial injury via suppressing oxidative stress and
inflammatory response. Int J Mol Med. 45:1305–1316. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Das K and Rao LVM: The role of microRNAs
in inflammation. Int J Mol Sci. 23:154792022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ge J, Yao Y, Jia H, Li P and Sun W:
Inhibition of miR-21 ameliorates LPS-induced acute lung injury
through increasing B cell lymphoma-2 expression. Innate Immun.
26:693–702. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Formosa A, Turgeon P and Dos Santos CC:
Role of miRNA dysregulation in sepsis. Mol Med. 28:992022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
De Melo P, Pineros Alvarez AR, Ye X,
Blackman A, Alves-Filho JC, Medeiros AI, Rathmell J, Pua H and
Serezani CH: Macrophage-derived MicroRNA-21 drives overwhelming
glycolytic and inflammatory response during sepsis via repression
of the PGE2/IL-10 axis. J Immunol. 207:902–912. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fu D, Dong J, Li P, Tang C, Cheng W, Xu Z,
Zhou W, Ge J, Xia C and Zhang Z: MiRNA-21 has effects to protect
kidney injury induced by sepsis. Biomed Pharmacother. 94:1138–1144.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Acosta-Martinez M and Cabail MZ: The
PI3K/Akt pathway in meta-inflammation. Int J Mol Sci. 23:153302022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Vidotto T, Melo CM, Castelli E, Koti M,
Dos Reis RB and Squire JA: Emerging role of PTEN loss in evasion of
the immune response to tumours. Br J Cancer. 122:1732–1743. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Turkez H, Arslan ME, Tatar A and
Mardinoglu A: Promising potential of boron compounds against
Glioblastoma: In vitro antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and
anticancer studies. Neurochem Int. 149:1051372021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yıldız K, Makav M, Adalı Y and Bulut M:
Therapeutic effects of boric acid in a septic arthritis model
induced by escherichia coli in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res.
200:4762–4770. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bolt HM, Başaran N and Duydu Y: Effects of
boron compounds on human reproduction. Arch Toxicol. 94:717–724.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hadrup N, Frederiksen M and Sharma AK:
Toxicity of boric acid, borax and other boron containing compounds:
A review. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 121:1048732021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Richold M: Boron exposure from consumer
products. Biol Trace Elem Res. 66:121–129. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nielsen FH and Meacham SL: Growing
evidence for human health benefits of boron. J Evid Based
Complement Altern Med. 16:169–180. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Chen S, Huang J, Liu T, Zhang F, Zhao C,
Jin E and Li S: PI3K/Akt signaling pathway mediates the effect of
low-dose boron on barrier function, proliferation and apoptosis in
rat intestinal epithelial cells. Sci Rep. 14:3932024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang C, Jin E, Deng J, Pei Y, Ren M, Hu Q,
Gu Y and Li S: GPR30 mediated effects of boron on rat spleen
lymphocyte proliferation, apoptosis, and immune function. Food Chem
Toxicol. 146:1118382020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wen H: Sepsis induced by cecal ligation
and puncture. Methods Mol Biol. 1031:117–124. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hubbard WJ, Choudhry M, Schwacha MG, Kerby
JD, Rue LW III, Bland KI and Chaudry IH: Cecal ligation and
puncture. Shock. 24 (Suppl 1):S52–S57. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Solbach P, Potthoff A, Raatschen HJ,
Soudah B, Lehmann U, Schneider A, Gebel MJ, Manns MP and Vogel A:
Testosterone-receptor positive hepatocellular carcinoma in a
29-year old bodybuilder with a history of anabolic androgenic
steroid abuse: A case report. BMC Gastroenterol. 15:602015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sygitowicz G and Sitkiewicz D: Molecular
mechanisms of organ damage in sepsis: An overview. Braz J Infect
Dis. 24:552–560. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ince C: The microcirculation is the motor
of sepsis. Crit Care. 9 (Suppl 4):S13–S19. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Legrand M, Klijn E, Payen D and Ince C:
The response of the host microcirculation to bacterial sepsis: Does
the pathogen matter? J Mol Med (Berl). 88:127–133. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Blackwell TS and Christman JW: Sepsis and
cytokines: Current status. Br J Anaesth. 77:110–117. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Oppenheim JJ: Cytokines: Past, present,
and future. Int J Hematol. 74:3–8. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ono S, Tsujimoto H, Hiraki S and Aosasa S:
Mechanisms of sepsis-induced immunosuppression and immunological
modification therapies for sepsis. Ann Gastroenterol Surg.
2:351–358. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Matsuda N and Hattori Y: Systemic
inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS): Molecular pathophysiology
and gene therapy. J Pharmacol Sci. 101:189–198. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Tekeli H, Ekren Asıcı GS and Bildik A:
Anti-inflammatory effect of boric acid on cytokines in
ovariectomy-induced rats. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand).
67:313–320. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Oberholzer A, Oberholzer C and Moldawer
LL: Interleukin-10: A complex role in the pathogenesis of sepsis
syndromes and its potential as an anti-inflammatory drug. Crit Care
Med. 30 (1 Suppl):S58–S63. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Baker SJ, Ding CZ, Akama T, Zhang YK,
Hernandez V and Xia Y: Therapeutic potential of boron-containing
compounds. Future Med Chem. 1:1275–1288. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Romero-Aguilar KS, Arciniega-Martínez IM,
Farfán-García ED, Campos-Rodríguez R, Reséndiz-Albor AA and
Soriano-Ursúa MA: Effects of boron-containing compounds on immune
responses: Review and patenting trends. Expert Opin Ther Pat.
29:339–351. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Bolat I, Kapakin KAT, Kirman EM, Gundogdu
G, Gundogdu K, Miloglu FD and Tasci SY: Investigation of the
effects of boric acid used in the treatment of rat models with knee
osteoarthritis induced by monosodium iodoacetate on liver tissue.
Harran Üniv Vet Fak Derg. 12:202–208. 2023.
|
|
50
|
Soriano-Ursúa MA, Das BC and
Trujillo-Ferrara JG: Boron-containing compounds: Chemico-biological
properties and expanding medicinal potential in prevention,
diagnosis and therapy. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 24:485–500. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ince S, Keles H, Erdogan M, Hazman O and
Kucukkurt I: Protective effect of boric acid against carbon
tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Drug Chem Toxicol.
35:285–292. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Ince S, Kucukkurt I, Demirel HH, Acaroz
DA, Akbel E and Cigerci IH: Protective effects of boron on
cyclophosphamide induced lipid peroxidation and genotoxicity in
rats. Chemosphere. 108:197–204. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Nara K, Kawashima N, Noda S, Fujii M,
Hashimoto K, Tazawa K and Okiji T: Anti-inflammatory roles of
microRNA 21 in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human dental pulp
cells. J Cell Physiol. 234:21331–21341. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Feng J, Li A, Deng J, Yang Y, Dang L, Ye
Y, Li Y and Zhang W: miR-21 attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced
lipid accumulation and inflammatory response: Potential role in
cerebrovascular disease. Lipids Health Dis. 13:272014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Guo D and Donner DB: Tumor necrosis factor
promotes phosphorylation and binding of insulin receptor substrate
1 to phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol
Chem. 271:615–618. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kim S, Domon-Dell C, Kang J, Chung DH,
Freund JN and Evers BM: Down-regulation of the tumor suppressor
PTEN by the tumor necrosis factor-alpha/nuclear factor-kappaB
(NF-kappaB)-inducing kinase/NF-kappaB pathway is linked to a
default IkappaB-alpha autoregulatory loop. J Biol Chem.
279:4285–4291. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Puri KD, Doggett TA, Huang CY, Douangpanya
J, Hayflick JS, Turner M, Penninger J and Diacovo TG: The role of
endothelial PI3Kgamma activity in neutrophil trafficking. Blood.
106:150–157. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Yasuda T: Hyaluronan inhibits Akt, leading
to nuclear factor-κB down-regulation in
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated U937 macrophages. J Pharmacol Sci.
115:509–515. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Huang JB, Ding Y, Huang DS, Liang AJ, Zeng
WK, Zeng ZP, Qin CQ and Barden B: Inhibition of the PI3K/AKT
pathway reduces tumor necrosis factor-alpha production in the
cellular response to wear particles in vitro. Artif Organs.
37:298–307. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Scientific Committee on Consumer Safety
(SCCS), . Opinion of the boron compounds. SCCS, 2010. https://ec.europa.eu/health/scientific_committees/consumer_safety/docs/sccs_o_027.pdf
|