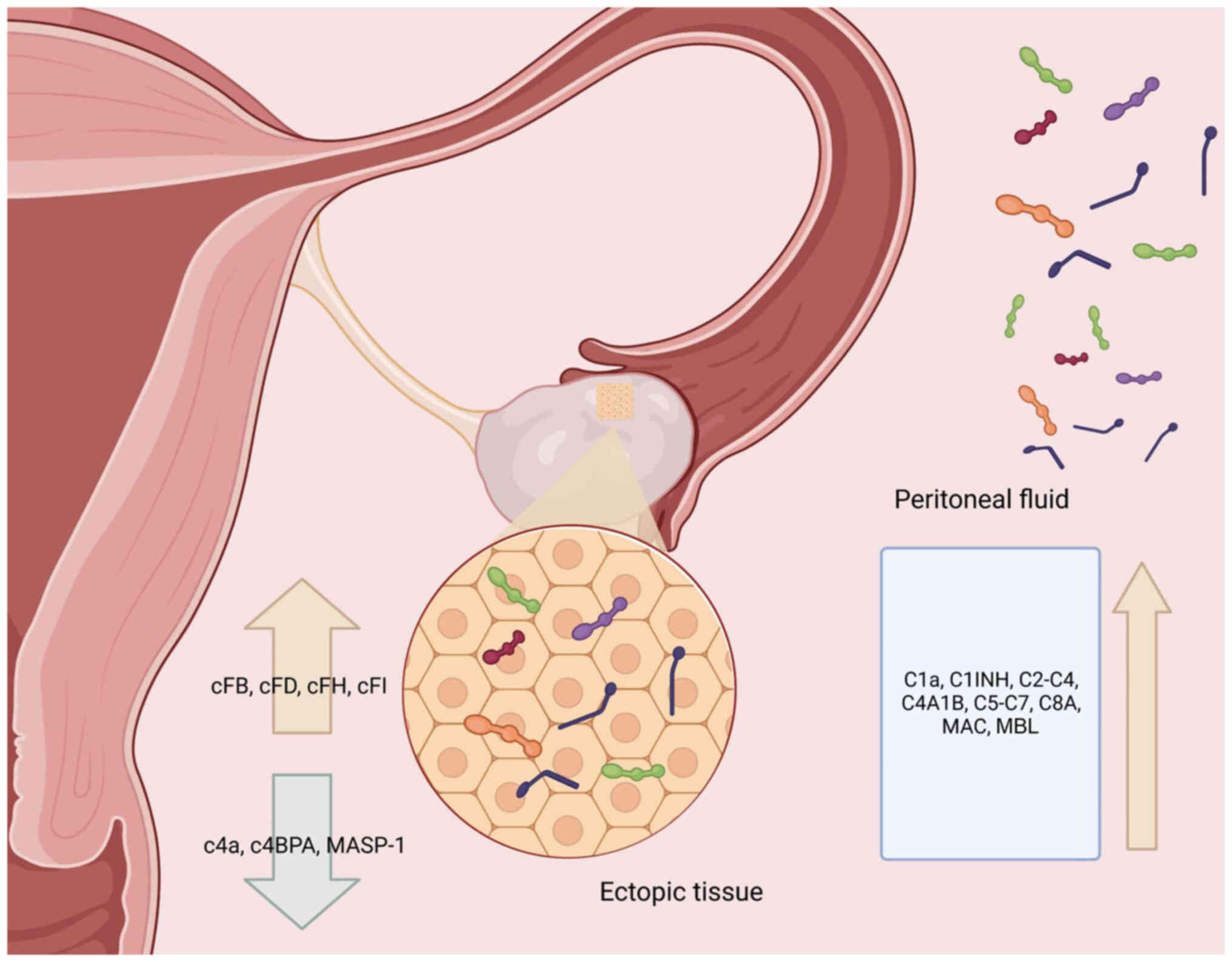
|
1
|
Zondervan KT, Becker CM and Missmer SA:
Endometriosis. N Engl J Med. 382:1244–1256. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Taylor HS, Kotlyar AM and Flores VA:
Endometriosis is a chronic systemic disease: Clinical challenges
and novel innovations. Lancet. 397:839–582. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Williams EA: Endometriosis in
Clinical-practice-surgical aspects. Irish J Med Sci. 152:14–17.
1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Van Gorp T, Amant F, Neven P, Vergote I
and Moerman P: Endometriosis and the development of malignant
tumours of the pelvis. A review of literature. Best Pract Res Clin
Obstet Gynaecol. 18:349–371. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Indrielle-Kelly T, Fruhauf F, Burgetova A,
Fanta M and Fischerova D: Diagnosis of endometriosis 3rd
Part-ultrasound diagnosis of deep endometriosis. Ceska Gynekol.
84:269–275. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fukunaga M, Nomura K, Ishikawa E and
Ushigome S: Ovarian atypical endometriosis: Its close association
with malignant epithelial tumours. Histopathology. 30:249–255.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pearce CL, Templeman C, Rossing MA, Lee A,
Near AM, Webb PM, Nagle CM, Doherty JA, Cushing-Haugen KL, Wicklund
KG, et al: Association between endometriosis and risk of
histological subtypes of ovarian cancer: A pooled analysis of
case-control studies. Lancet Oncol. 13:385–394. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
He Y, Cao B and Huang Y: Effect of
endometriosis on prognosis of ovarian clear cell carcinoma: A
10-year retrospective study. Front Oncol. 14:14383092024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Anglesio MS, Bashashati A, Wang YK, Senz
J, Ha G, Yang W, Aniba MR, Prentice LM, Farahani H, Li Chang H, et
al: Multifocal endometriotic lesions associated with cancer are
clonal and carry a high mutation burden. J Pathol. 236:201–209.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Czernobilsky B and Morris WJ: A histologic
study of ovarian endometriosis with emphasis on hyperplastic and
atypical changes. Obstet Gynecol. 53:318–323. 1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
LaGrenade A and Silverberg SG: Ovarian
tumors associated with atypical endometriosis. Hum Pathol.
19:1080–1084. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nouri B, Hashemi SH, J Ghadimi D,
Roshandel S and Akhlaghdoust M: Machine Learning-based detection of
endometriosis: A retrospective study in a population of iranian
female patients. Int J Fertil Steril. 18:362–366. 2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Moradi Y, Shams-Beyranvand M, Khateri S,
Gharahjeh S, Tehrani S, Varse F, Tiyuri A and Najmi Z: A systematic
review on the prevalence of endometriosis in women. Indian J Med
Res. 154:446–454. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mafra F, Catto M, Bianco B, Barbosa CP and
Christofolini D: Association of Wnt4 polymorphisms with
endometriosis in infertile patients. J Assist Reprod Genet.
32:1359–1364. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Santulli P, Bourdon M, Presse M, Gayet V,
Marcellin L, Prunet C, de Ziegler D and Chapron C:
Endometriosis-Related infertility: Assisted reproductive technology
has no adverse impact on pain or quality-of-life scores. Fertil
Steril. 105:978–987.e4. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ferrero S, Stabilini C, Barra F, Clarizia
R, Roviglione G and Ceccaroni M: Bowel resection for intestinal
endometriosis. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 71:114–128.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chapron C, Marcellin L, Borghese B and
Santulli P: Rethinking mechanisms, diagnosis and management of
endometriosis. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 15:666–682. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ferrero S, Barra F, Scala C and Condous G:
Ultrasonography for bowel endometriosis. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet
Gynaecol. 71:38–50. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Geng JH and Lee YC: Bladder endometriosis.
N Engl J Med. 381:e432019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Santulli P, Marcellin L, Tosti C,
Chouzenoux S, Cerles O, Borghese B, Batteux F and Chapron C: MAP
kinases and the inflammatory signaling cascade as targets for the
treatment of endometriosis? Expert Opin Ther Targets. 19:1465–1483.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Brown J, Crawford TJ, Allen C, Hopewell S
and Prentice A: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for pain in
women with endometriosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
1:CD0047532017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Streuli I, de Ziegler D, Santulli P,
Marcellin L, Borghese B, Batteux F and Chapron C: An update on the
pharmacological management of endometriosis. Expert Opin
Pharmacother. 14:291–305. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu Y, Liu Y, Jia H, Luo C and Chen H:
Treatment of endometriosis with dienogest in combination with
traditional Chinese medicine: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Front Surg. 9:9924902022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chinese Medical Association Obstetrics,
Gynecology Branch, Endometriosis Professional Committee and Chinese
Medical Association Obstetrics and Gynecology Branch Endometriosis
Collaborative Group, . Long-term management of endometriosis:
Chinese expert consensus. Chin J Obstet Gynecol. 53:836–841.
2018.(In Chinese).
|
|
25
|
Endometriosis Collaborative Group of the
Obstetrics and Gynecology Branch of the Chinese Medical
Association, . Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of
endometriosis. Chin J Obstet Gynecol. 3:161–169. 2015.
|
|
26
|
Vercellini P, Viganò P, Somigliana E and
Fedele L: Endometriosis: Pathogenesis and treatment. Nat Rev
Endocrinol. 10:261–275. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Barbieri RL: Stenosis of the external
cervical os: An association with endometriosis in women with
chronic pelvic pain. Fertil Steril. 70:571–573. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sanfilippo JS, Wakim NG, Schikler KN and
Yussman MA: Endometriosis in Association with Uterine Anomaly. Am J
Obstet Gynecol. 154:39–43. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Halme J, Hammond MG, Hulka JF, Raj SG and
Talbert LM: Retrograde menstruation in healthy women and in
patients with endometriosis. Obstet Gynecol. 64:151–154.
1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Herington JL, Bruner-Tran KL, Lucas JA and
Osteen KG: Immune interactions in endometriosis. Expert Rev Clin
Immunol. 7:611–626. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kyama CM, Debrock S, Mwenda JM and
D'Hooghe TM: Potential involvement of the immune system in the
development of endometriosis. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 1:1232003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Christodoulakos G, Augoulea A,
Lambrinoudaki I, Sioulas V and Creatsas G: Pathogenesis of
endometriosis: The role of defective ‘immunosurveillance’. Eur J
Contracept Reprod Health Care. 12:194–202. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Koninckx PR, Ussia A, Adamyan L, Wattiez
A, Gomel V and Martin DC: Pathogenesis of endometriosis: The
Genetic/Epigenetic theory. Fertil Steril. 111:327–340. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Foster WG: Hypoxia-induced autophagy,
epithelial to mesenchymal transition, and invasion in the
pathophysiology of endometriosis: A perspective. Biol Reprod.
99:905–906. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tanbo T and Fedorcsak P:
Endometriosis-associated infertility: Aspects of pathophysiological
mechanisms and treatment options. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand.
96:659–667. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gibson DA, Simitsidellis I, Collins F and
Saunders PTK: Androgens, oestrogens and endometrium: A fine balance
between perfection and pathology. J Endocrinol. 246:R75–R93. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mohammed Rasheed HA and Hamid P:
Inflammation to infertility: Panoramic view on endometriosis.
Cureus. 12:e115162020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Halis G and Arici A: Endometriosis and
Inflammation in Infertility. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1034:300–315. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kang YJ, Jeung IC, Park A, Park YJ, Jung
H, Kim TD, Lee HG, Choi I and Yoon SR: An increased level of IL-6
suppresses NK cell activity in peritoneal fluid of patients with
endometriosis via regulation of SHP-2 expression. Hum Reprod.
29:2176–2189. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bedaiwy MA, Falcone T, Sharma RK, Goldberg
JM, Attaran M, Nelson DR and Agarwal A: Prediction of endometriosis
with serum and peritoneal fluid markers: A prospective controlled
trial. Hum Reprod. 17:426–431. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Vilas Boas L, Bezerra Sobrinho C, Rahal D,
Augusto Capellari C, Skare T and Nisihara R: Antinuclear antibodies
in patients with endometriosis: A cross-sectional study in 94
patients. Hum Immunol. 83:70–73. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Dias JA Jr, de Oliveira RM and Abrao MS:
Antinuclear antibodies and endometriosis. Int J Gynaecol Obstet.
93:262–263. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Malinowski A, Szpakowski M, Wilczynski J,
Banasik M and Puchala B: Occurrence of antinuclear antibodies in
women with endometriosis and unexplained infertility. Ginekol Pol.
66:420–424. 1995.(In Polish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Swann JB and Smyth MJ: Immune surveillance
of tumors. J Clin Invest. 117:1137–1146. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Vallve-Juanico J, Houshdaran S and Giudice
LC: The endometrial immune environment of women with endometriosis.
Hum Reprod Update. 25:564–591. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Podgaec S, Abrao MS, Dias JA Jr, Rizzo LV,
de Oliveira RM and Baracat EC: Endometriosis: An inflammatory
disease with a Th2 immune response component. Hum Reprod.
22:1373–1379. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Olkowska-Truchanowicz J, Bocian K, Maksym
RB, Bialoszewska A, Wlodarczyk D, Baranowski W, Ząbek J,
Korczak-Kowalska G and Malejczyk J: CD4+
CD25+ FOXP3+ regulatory T cells in peripheral
blood and peritoneal fluid of patients with endometriosis. Hum
Reprod. 28:119–124. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Tanaka E, Sendo F, Kawagoe S and Hiroi M:
Decreased natural killer cell activity in women with endometriosis.
Gynecol Obstet Invest. 34:27–30. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Thiruchelvam U, Wingfield M and O'Farrelly
C: Natural killer cells: Key players in endometriosis. Am J Reprod
Immunol. 74:291–301. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sciezynska A, Komorowski M, Soszynska M
and Malejczyk J: Nk cells as potential targets for immunotherapy in
endometriosis. J Clin Med. 8:172019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Artemova D, Vishnyakova P, Khashchenko E,
Elchaninov A, Sukhikh G and Fatkhudinov T: Endometriosis and
cancer: Exploring the role of macrophages. Int J Mol Sci.
22:51962021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wu MH, Chen KF, Lin SC, Lgu CW and Tsai
SJ: Aberrant expression of leptin in human endometriotic stromal
cells is induced by elevated levels of hypoxia inducible
factor-1alpha. Am J Pathol. 170:590–598. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Semenza GL: Hif-1 and mechanisms of
hypoxia sensing. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 13:167–171. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Becker CM, Rohwer N, Funakoshi T, Cramer
T, Bernhardt W, Birsner A, Folkman J and D'Amato RJ:
2-Methoxyestradiol inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor-1{alpha} and
suppresses growth of lesions in a mouse model of endometriosis. Am
J Pathol. 172:534–544. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Hsiao KY, Chang N, Lin SC, Li YH and Wu
MH: Inhibition of dual specificity Phosphatase-2 by hypoxia
promotes interleukin-8-mediated angiogenesis in endometriosis. Hum
Reprod. 29:2747–2755. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Hsiao KY, Chang N, Tsai JL, Lin SC, Tsai
SJ and Wu MH: Hypoxia-inhibited DUSP2 expression promotes
IL-6/STAT3 signaling in endometriosis. Am J Reprod Immunol.
78:2017.doi: 10.1111/aji.12690. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Sharkey AM, Day K, McPherson A, Malik S,
Licence D, Smith SK and Charnock-Jones DS: Vascular endothelial
growth factor expression in human endometrium is regulated by
hypoxia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 85:402–409. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Kupker W, Schultze-Mosgau A and Diedrich
K: Paracrine changes in the peritoneal environment of women with
endometriosis. Hum Reprod Update. 4:719–723. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Yang HL, Zhou WJ, Chang KK, Mei J, Huang
LQ, Wang MY, Meng Y, Ha SY, Li DJ and Li MQ: The crosstalk between
endometrial stromal cells and macrophages impairs cytotoxicity of
NK cells in endometriosis by secreting IL-10 and TGF-β.
Reproduction. 154:815–825. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
El Hafny-Rahbi B, Brodaczewska K, Collet
G, Majewska A, Klimkiewicz K, Delalande A, Grillon C and Kieda C:
Tumour angiogenesis normalized by Myo-inositol trispyrophosphate
alleviates hypoxia in the microenvironment and promotes antitumor
immune response. J Cell Mol Med. 25:3284–3299. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Thiruchelvam U, Dransfield I, Saunders PT
and Critchley HO: The importance of the macrophage within the human
endometrium. J Leukoc Biol. 93:217–225. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Mehedintu C, Plotogea MN, Ionescu S and
Antonovici M: Endometriosis still a challenge. J Med Life.
7:349–357. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Matarese G, De Placido G, Nikas Y and
Alviggi C: Pathogenesis of endometriosis: Natural immunity
dysfunction or autoimmune disease? Trends Mol Med. 9:223–228. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Hogg C, Horne AW and Greaves E:
Endometriosis-associated macrophages: Origin, phenotype, and
function. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 11:72020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Capobianco A and Rovere-Querini P:
Endometriosis, a disease of the macrophage. Front Immunol. 4:92013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Colette S and Donnez J: Are aromatase
inhibitors effective in endometriosis treatment? Expert Opin
Investig Drugs. 20:917–931. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Check JH: Chronic pelvic pain
syndromes-Traditional and novel therapies: Part I surgical therapy.
Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol. 38:10–13. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Sivori S, Vitale M, Morelli L, Sanseverino
L, Augugliaro R, Bottino C, Moretta L and Moretta A: P46, a novel
natural killer cell-specific surface molecule that mediates cell
activation. J Exp Med. 186:1129–1136. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Freud AG, Zhao S, Wei S, Gitana GM,
Molina-Kirsch HF, Atwater SK and Natkunam Y: Expression of the
activating receptor, NKp46 (CD335), in human natural killer and
T-cell neoplasia. Am J Clin Pathol. 140:853–866. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Cooper MA, Fehniger TA and Caligiuri MA:
The biology of human natural killer-cell subsets. Trends Immunol.
22:633–640. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Cooper MA, Fehniger TA, Turner SC, Chen
KS, Ghaheri BA, Ghayur T, Carson WE and Caligiuri MA: Human natural
killer cells: A unique innate immunoregulatory role for the
CD56(bright) subset. Blood. 97:3146–3151. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Hamerman JA, Ogasawara K and Lanier LL: NK
cells in innate immunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 17:29–35. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Vivier E, Tomasello E, Baratin M, Walzer T
and Ugolini S: Functions of natural killer cells. Nat Immunol.
9:503–510. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Freud AG, Mundy-Bosse BL, Yu J and
Caligiuri MA: The broad spectrum of human natural killer cell
diversity. Immunity. 47:820–833. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Reeves RK, Li H, Jost S, Blass E, Li H,
Schafer JL, Varner V, Manickam C, Eslamizar L, Altfeld M, et al:
Antigen-specific NK cell memory in rhesus macaques. Nat Immunol.
16:927–932. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Hammer Q, Ruckert T and Romagnani C:
Natural killer cell specificity for viral infections. Nat Immunol.
19:800–808. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Nikzad R, Angelo LS, Aviles-Padilla K, Le
DT, Singh VK, Bimler L, Vukmanovic-Stejic M, Vendrame E, Ranganath
T, Simpson L, et al: Human natural killer cells mediate adaptive
immunity to viral antigens. Sci Immunol. 4:eaat81162019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Morvan MG and Lanier LL: Nk cells and
cancer: You can teach innate cells new tricks. Nat Rev Cancer.
16:7–19. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Chiossone L, Dumas PY, Vienne M and Vivier
E: Natural killer cells and other innate lymphoid cells in cancer.
Nat Rev Immunol. 18:671–688. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Raulet DH and Vance RE: Self-tolerance of
natural killer cells. Nat Rev Immunol. 6:520–531. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Karre K, Ljunggren HG, Piontek G and
Kiessling R: Selective rejection of H-2-deficient lymphoma variants
suggests alternative immune defence strategy. Nature. 319:675–678.
1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Viant C, Fenis A, Chicanne G, Payrastre B,
Ugolini S and Vivier E: SHP-1-mediated inhibitory signals promote
responsiveness and anti-Tumour functions of natural killer cells.
Nat Commun. 5:51082014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
van der Touw W, Chen HM, Pan PY and Chen
SH: LILRB Receptor-mediated regulation of myeloid cell maturation
and function. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 66:1079–1087. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Stojanovic A, Correia MP and Cerwenka A:
The NKG2D/NKG2DL axis in the crosstalk between lymphoid and myeloid
cells in health and disease. Front Immunol. 9:8272018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Zingoni A, Molfetta R, Fionda C, Soriani
A, Paolini R, Cippitelli M, Cerboni C and Santoni A: NKG2D and its
ligands: ‘One for all, all for one’. Front Immunol. 9:4762018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Ferlazzo G, Thomas D, Lin SL, Goodman K,
Morandi B, Muller WA, Moretta A and Münz C: The abundant NK cells
in human secondary lymphoid tissues require activation to express
killer cell Ig-like receptors and become cytolytic. J Immunol.
172:1455–1462. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Bryceson YT, March ME, Ljunggren HG and
Long EO: Synergy among receptors on resting NK cells for the
activation of natural cytotoxicity and cytokine secretion. Blood.
107:159–166. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Masztalerz A, Van Rooijen N, Den Otter W
and Everse LA: Mechanisms of Macrophage cytotoxicity in IL-2 and
IL-12 mediated tumour regression. Cancer Immunol Immunother.
52:235–242. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Mukherjee S, Jensen H, Stewart W, Stewart
D, Ray WC, Chen SY, Nolan GP, Lanier LL and Das J: In silico
modeling identifies CD45 as a regulator of IL-2 synergy in the
NKG2D-mediated activation of immature human NK cells. Sci Signal.
10:eaai90622017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Fehniger TA and Caligiuri MA: Interleukin
15: Biology and relevance to human disease. Blood. 97:14–32. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Kasaian MT, Whitters MJ, Carter LL, Lowe
LD, Jussif JM, Deng B, Johnson KA, Witek JS, Senices M, Konz RF, et
al: Il-21 limits NK cell responses and promotes Antigen-specific T
cell activation: A mediator of the transition from innate to
adaptive immunity. Immunity. 16:559–569. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Tarannum M and Romee R: Cytokine-induced
memory-like natural killer cells for cancer immunotherapy. Stem
Cell Res Ther. 12:5922021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Marcus A, Mao AJ, Lensink-Vasan M, Wang L,
Vance RE and Raulet DH: Tumor-derived cGAMP triggers a
STING-mediated interferon response in non-tumor cells to activate
the NK cell response. Immunity. 49:754–763.e4. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Lettau M, Paulsen M, Schmidt H and Janssen
O: Insights into the molecular regulation of fasl (CD178) biology.
Eur J Cell Biol. 90:456–466. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Prager I and Watzl C: Mechanisms of
natural killer Cell-mediated cellular cytotoxicity. J Leukoc Biol.
105:1319–1329. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Gazvani R and Templeton A: Peritoneal
environment, cytokines and angiogenesis in the pathophysiology of
endometriosis. Reproduction. 123:217–226. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Ulukus M and Arici A: Immunology of
endometriosis. Minerva Ginecol. 57:237–248. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Symons LK, Miller JE, Kay VR, Marks RM,
Liblik K, Koti M and Tayade C: The immunopathophysiology of
endometriosis. Trends Mol Med. 24:748–762. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Oosterlynck DJ, Meuleman C, Waer M,
Vandeputte M and Koninckx PR: The natural killer activity of
peritoneal fluid lymphocytes is decreased in women with
endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 58:290–295. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Maeda N, Izumiya C, Kusum T, Masumoto T,
Yamashita C, Yamamoto Y, Oguri H and Fukaya T: Killer inhibitory
receptor CD158a overexpression among natural killer cells in women
with endometriosis is undiminished by laparoscopic surgery and
gonadotropin releasing hormone agonist treatment. Am J Reprod
Immunol. 51:364–372. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Vigano P, Vercellini P, Di Blasio AM,
Colombo A, Candiani GB and Vignali M: Deficient antiendometrium
Lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity in patients with endometriosis.
Fertil Steril. 56:894–899. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Lotze MT and Rosenberg SA: Results of
clinical trials with the administration of interleukin 2 and
adoptive immunotherapy with activated cells in patients with
cancer. Immunobiology. 172:420–437. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Sikora J, Smycz-Kubanska M,
Mielczarek-Palacz A, Bednarek I and Kondera-Anasz Z: The
involvement of multifunctional TGF-β and related cytokines in
pathogenesis of endometriosis. Immunol Lett. 201:31–37. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Dias JA Jr, Podgaec S, de Oliveira RM,
Carnevale Marin ML, Baracat EC and Abrao MS: Patients with
endometriosis of the rectosigmoid have a higher percentage of
natural killer cells in peripheral blood. J Minim Invasive Gynecol.
19:317–324. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Oosterlynck DJ, Meuleman C, Lacquet FA,
Waer M and Koninckx PR: Flow cytometry analysis of lymphocyte
subpopulations in peritoneal fluid of women with endometriosis. Am
J Reprod Immunol. 31:25–31. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Vernet-Tomas Mdel M, Perez-Ares CT, Verdu
N, Molinero JL, Fernandez-Figueras MT and Carreras R: The
endometria of patients with endometriosis show higher expression of
Class I human leukocyte antigen than the endometria of healthy
women. Fertil Steril. 85:78–83. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Wu MY, Yang JH, Chao KH, Hwang JL, Yang YS
and Ho HN: Increase in the expression of killer cell inhibitory
receptors on peritoneal natural killer cells in women with
endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 74:1187–1191. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Matsuoka S, Maeda N, Izumiya C, Yamashita
C, Nishimori Y and Fukaya T: Expression of inhibitory-motif killer
immunoglobulin-like receptor, KIR2DL1, is increased in natural
killer cells from women with pelvic endometriosis. Am J Reprod
Immunol. 53:249–254. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Maeda N, Izumiya C, Oguri H, Kusume T,
Yamamoto Y and Fukaya T: Aberrant expression of intercellular
adhesion Molecule-1 and killer inhibitory receptors induces immune
tolerance in women with pelvic endometriosis. Fertil Steril.
77:679–683. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Galandrini R, Porpora MG, Stoppacciaro A,
Micucci F, Capuano C, Tassi I, Di Felice A, Benedetti-Panici P and
Santoni A: Increased frequency of human leukocyte Antigen-E
inhibitory receptor Cd94/Nkg2a-Expressing peritoneal natural killer
cells in patients with endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 89 (5
Suppl):S1490–S1496. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Nowak I, Ploski R, Barcz E, Dziunycz P,
Kaminski P, Kostrzewa G, Milewski Ł, Roszkowski PI, Senitzer D,
Malejczyk J and Kuśnierczyk P: KIR2DS5 in the presence of HLA-C C2
protects against endometriosis. Immunogenetics. 67:203–209. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Guo SW, Du Y and Liu X: Platelet-derived
Tgf-Beta1 mediates the Down-modulation of Nkg2d expression and may
be responsible for impaired natural Killer (Nk) cytotoxicity in
women with endometriosis. Hum Reprod. 31:1462–1474. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Bellelis P, Frediani Barbeiro D,
Gueuvoghlanian-Silva BY, Kalil J, Abrao MS and Podgaec S:
Interleukin-15 and Interleukin-7 Are the major cytokines to
maintain endometriosis. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 84:435–444. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Yu JJ, Sun HT, Zhang ZF, Shi RX, Liu LB,
Shang WQ, Wei CY, Chang KK, Shao J, Wang MY and Li MQ: Il15
promotes growth and invasion of endometrial stromal cells and
inhibits killing activity of NK cells in endometriosis.
Reproduction. 152:151–160. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Gonzalez-Foruria I, Santulli P, Chouzenoux
S, Carmona F, Batteux F and Chapron C: Soluble ligands for the
NKG2D receptor are released during endometriosis and correlate with
disease Severity. PLoS One. 10:e01199612015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Salih HR, Rammensee HG and Steinle A:
Cutting edge: Down-regulation of mica on human tumors by
proteolytic shedding. J Immunol. 169:4098–4102. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Salih HR, Goehlsdorf D and Steinle A:
Release of micb molecules by tumor cells: Mechanism and soluble
micb in sera of cancer patients. Hum Immunol. 67:188–195. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Mazzeo D, Vigano P, Di Blasio AM,
Sinigaglia F, Vignali M and Panina-Bordignon P: Interleukin-12 and
Its Free P40 subunit regulate immune recognition of endometrial
cells: Potential role in endometriosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
83:911–916. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Mei J, Zhou WJ, Zhu XY, Lu H, Wu K, Yang
HL, Fu Q, Wei CY, Chang KK, Jin LP, et al: Suppression of Autophagy
and HCK Signaling Promotes PTGS2high FCGR3−
NK cell differentiation triggered by ectopic endometrial stromal
cells. Autophagy. 14:1376–1397. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Palumbo JS, Talmage KE, Massari JV, La
Jeunesse CM, Flick MJ, Kombrinck KW, Hu Z, Barney KA and Degen JL:
Tumor cell-associated tissue factor and circulating hemostatic
factors cooperate to increase metastatic potential through natural
killer cell-dependent and-independent mechanisms. Blood.
110:133–141. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Nieswandt B, Hafner M, Echtenacher B and
Mannel DN: Lysis of tumor cells by natural killer cells in mice is
impeded by platelets. Cancer Res. 59:1295–1300. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Kopp HG, Placke T and Salih HR:
Platelet-derived transforming growth factor-beta down-regulates
NKG2D thereby inhibiting natural killer cell antitumor reactivity.
Cancer Res. 69:7775–7783. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Zhang Q, Ding D, Liu X and Guo SW:
Activated platelets induce estrogen receptor beta expression in
endometriotic stromal cells. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 80:187–192.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Binyamin L, Alpaugh RK, Hughes TL, Lutz
CT, Campbell KS and Weiner LM: Blocking NK cell inhibitory
self-recognition promotes antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity
in a model of anti-lymphoma therapy. J Immunol. 180:6392–6401.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Andre P, Denis C, Soulas C,
Bourbon-Caillet C, Lopez J, Arnoux T, Bléry M, Bonnafous C,
Gauthier L, Morel A, et al: Anti-NKG2A mAb is a checkpoint
inhibitor that promotes anti-tumor immunity by unleashing both T
and NK cells. Cell. 175:1731–1743.e13. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Chan EY, Yap DY, Colucci M, Ma AL, Parekh
RS and Tullus K: Use of rituximab in childhood idiopathic nephrotic
syndrome. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 18:533–548. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Sivori S, Della Chiesa M, Carlomagno S,
Quatrini L, Munari E, Vacca P, Tumino N, Mariotti FR, Mingari MC,
Pende D and Moretta L: Inhibitory receptors and checkpoints in
human NK cells, implications for the immunotherapy of cancer. Front
Immunol. 11:21562020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Velasco I, Quereda F, Bermejo R, Campos A
and Acien P: Intraperitoneal recombinant Interleukin-2 activates
leukocytes in rat endometriosis. J Reprod Immunol. 74:124–132.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Quereda F, Bermejo R, Velasco I, Campos A
and Acien P: The effect of intraperitoneal Interleukin-2 on
surgically induced endometriosis in rats. Eur J Obstet Gynecol
Reprod Biol. 136:243–248. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Dicitore A, Castiglioni S, Saronni D,
Gentilini D, Borghi MO, Stabile S, Vignali M, Di Blasio AM, Persani
L and Vitale G: Effects of human recombinant type I IFNs (IFN-α2b
and IFN-β1a) on growth and migration of primary endometrial stromal
cells from women with deeply infiltrating endometriosis: A
preliminary study. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 230:192–198.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Wu MY, Chao KH, Chen SU, Chen HF, Yang YS,
Huang SC and Ho HN: The suppression of peritoneal cellular immunity
in women with endometriosis could be restored after gonadotropin
releasing hormone agonist treatment. Am J Reprod Immunol.
35:510–516. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Regis S, Dondero A, Caliendo F, Bottino C
and Castriconi R: NK cell function regulation by TGF-β-induced
epigenetic mechanisms. Front Immunol. 11:3112020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Yoshimura A, Wakabayashi Y and Mori T:
Cellular and molecular basis for the regulation of inflammation by
TGF-beta. J Biochem. 147:781–792. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Young VJ, Brown JK, Saunders PT, Duncan WC
and Horne AW: The peritoneum is both a source and target of TGF-β
in women with endometriosis. PLoS One. 9:e1067732014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Zhang M, Xu T, Tong D, Li S, Yu X, Liu B,
Jiang L and Liu K: Research advances in endometriosis-related
signaling pathways: A review. Biomed Pharmacother. 164:1149092023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Hawinkels LJ and Ten Dijke P: Exploring
Anti-TGF-β therapies in cancer and fibrosis. Growth Factors.
29:140–152. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Voelker J, Berg PH, Sheetz M, Duffin K,
Shen T, Moser B, Greene T, Blumenthal SS, Rychlik I, Yagil Y, et
al: Anti-TGF-β1 antibody therapy in patients with diabetic
nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 28:953–962. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Clayton RD, Duffy SR, Wilkinson N, Garry R
and Jackson AM: Increase in peripheral blood mononuclear cell
(PBMC)- and CD56+ cell-mediated killing of endometrial stromal
cells by mycobacteria; a possible role in endometriosis
immunotherapy? Hum Reprod. 19:1886–1893. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Oksasoglu B, Hepokur C, Misir S, Yildiz C,
Sonmez G and Yanik A: Determination of PD-1 expression in
peripheral blood cells in patients with endometriosis. Gynecol
Endocrinol. 37:157–161. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Wu L, Lv C, Su Y, Li C, Zhang H, Zhao X
and Li M: Expression of programmed death-1 (PD-1) and Its Ligand
PD-L1 is upregulated in endometriosis and promoted by
17beta-estradiol. Gynecol Endocrinol. 35:251–256. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Chen Z, Yang Y, Liu LL and Lundqvist A:
Strategies to augment natural killer (NK) cell activity against
solid tumors. Cancers (Basel). 11:10402019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Memon H and Patel BM: Immune checkpoint
inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer: A Bird's eye view. Life
Sci. 233:1167132019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Giannopoulos K: Targeting immune signaling
checkpoints in acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Med. 8:2362019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Hofmann L, Forschner A, Loquai C,
Goldinger SM, Zimmer L, Ugurel S, Schmidgen MI, Gutzmer R, Utikal
JS, Göppner D, et al: Cutaneous, gastrointestinal, hepatic,
endocrine, and renal side-effects of Anti-PD-1 therapy. Eur J
Cancer. 60:190–209. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Sosa A, Lopez Cadena E, Simon Olive C,
Karachaliou N and Rosell R: Clinical assessment of immune-related
adverse events. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 10:17588359187646282018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Afolabi LO, Adeshakin AO, Sani MM, Bi J
and Wan X: Genetic reprogramming for NK cell cancer immunotherapy
with CRISPR/Cas9. Immunology. 158:63–69. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Wang L, Dou M, Ma Q, Yao R and Liu J:
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-modified NK cells against cancer:
Opportunities and challenges. Int Immunopharmacol. 74:1056952019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Kloess S, Kretschmer A, Stahl L, Fricke S
and Koehl U: CAR-expressing natural killer cells for cancer
retargeting. Transfus Med Hemother. 46:4–13. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Seshadri S and Sunkara SK: Natural killer
cells in female infertility and recurrent miscarriage: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Hum Reprod Update. 20:429–438. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Hadinedoushan H, Mirahmadian M and
Aflatounian A: Increased natural killer cell cytotoxicity and Il-2
production in recurrent spontaneous abortion. Am J Reprod Immunol.
58:409–414. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Hashimoto D, Chow A, Noizat C, Teo P,
Beasley MB, Leboeuf M, Becker CD, See P, Price J, Lucas D, et al:
Tissue-resident macrophages self-maintain locally throughout adult
life with minimal contribution from circulating monocytes.
Immunity. 38:792–804. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Gomez Perdiguero E, Klapproth K, Schulz C,
Busch K, Azzoni E, Crozet L, Garner H, Trouillet C, de Bruijn MF,
Geissmann F and Rodewald HR: Tissue-resident macrophages originate
from yolk-sac-derived erythro-myeloid progenitors. Nature.
518:547–551. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Gordon S and Martinez FO: Alternative
activation of macrophages: Mechanism and functions. Immunity.
32:593–604. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Verreck FA, de Boer T, Langenberg DM,
Hoeve MA, Kramer M, Vaisberg E, Kastelein R, Kolk A, de
Waal-Malefyt R and Ottenhoff TH: Human IL-23-producing type 1
macrophages promote but IL-10-producing type 2 macrophages subvert
immunity to (myco)bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:4560–4565.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Bonatz G, Hansmann ML, Buchholz F, Mettler
L, Radzun HJ and Semm K: Macrophage- and lymphocyte-subtypes in the
endometrium during different phases of the ovarian cycle. Int J
Gynaecol Obstet. 37:29–36. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Vallve-Juanico J, Santamaria X, Vo KC,
Houshdaran S and Giudice LC: Macrophages display proinflammatory
phenotypes in the eutopic endometrium of women with endometriosis
with relevance to an infectious etiology of the disease. Fertil
Steril. 112:1118–1128. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Maybin JA and Critchley HO: Menstrual
physiology: Implications for endometrial pathology and beyond. Hum
Reprod Update. 21:748–761. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Bain CC and Jenkins SJ: The biology of
serous cavity macrophages. Cell Immunol. 330:126–135. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Hudson QJ, Ashjaei K, Perricos A, Kuessel
L, Husslein H, Wenzl R and Yotova I: Endometriosis patients show an
increased M2 response in the peritoneal CD14+low/CD68+low
macrophage subpopulation coupled with an increase in the T-helper 2
and T-regulatory cells. Reprod Sci. 27:1920–1931. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Roszer T: Understanding the mysterious M2
macrophage through activation markers and effector mechanisms.
Mediators Inflamm. 2015:8164602015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Mantovani A, Sica A, Sozzani S, Allavena
P, Vecchi A and Locati M: The Chemokine system in diverse forms of
macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol. 25:677–686.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Bardi GT, Smith MA and Hood JL: Melanoma
exosomes promote mixed M1 and M2 macrophage polarization. Cytokine.
105:63–72. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Simpson JL, Elias S, Malinak LR and
Buttram VC Jr: Heritable aspects of Endometriosis. I. Genetic
studies. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 137:327–331. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Dmowski WP, Gebel H and Braun DP:
Decreased apoptosis and sensitivity to macrophage mediated
cytolysis of endometrial cells in endometriosis. Hum Reprod Update.
4:696–701. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Wu MH, Shoji Y, Wu MC, Chuang PC, Lin CC,
Huang MF and Tsai SJ: Suppression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 by
prostaglandin E(2) in peritoneal macrophage is associated with
severity of endometriosis. Am J Pathol. 167:1061–1069. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Gou Y, Li X, Li P, Zhang H, Xu T, Wang H,
Wang B, Ma X, Jiang X and Zhang Z: Estrogen receptor β upregulates
CCL2 via NF-κB signaling in endometriotic stromal cells and
recruits macrophages to promote the pathogenesis of endometriosis.
Hum Reprod. 34:646–658. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Kwon MJ, Shin HY, Cui Y, Kim H, Thi AH,
Choi JY, Kim EY, Hwang DH and Kim BG: CCL2 mediates
neuron-macrophage interactions to drive proregenerative macrophage
activation following preconditioning injury. J Neurosci.
35:15934–15947. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Johan MZ, Ingman WV, Robertson SA and Hull
ML: Macrophages infiltrating endometriosis-like lesions exhibit
progressive phenotype Changes in a heterologous mouse model. J
Reprod Immunol. 132:1–8. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Bacci M, Capobianco A, Monno A, Cottone L,
Di Puppo F, Camisa B, Mariani M, Brignole C, Ponzoni M, Ferrari S,
et al: Macrophages are alternatively activated in patients with
endometriosis and required for growth and vascularization of
lesions in a mouse model of disease. Am J Pathol. 175:547–556.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Huang YJ, Yang CK, Wei PL, Huynh TT,
Whang-Peng J, Meng TC, Hsiao M, Tzeng YM, Wu AT and Yen Y:
Ovatodiolide suppresses colon tumorigenesis and prevents
polarization of M2 Tumor-associated macrophages through YAP
oncogenic pathways. J Hematol Oncol. 10:602017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Monsivais D, Dyson MT, Yin P, Coon JS,
Navarro A, Feng G, Malpani SS, Ono M, Ercan CM, Wei JJ, et al: ERβ-
and prostaglandin E2-regulated pathways integrate cell
proliferation via Ras-like and estrogen-regulated growth inhibitor
in endometriosis. Mol Endocrinol. 28:1304–1315. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Han SJ, Jung SY, Wu SP, Hawkins SM, Park
MJ, Kyo S, Qin J, Lydon JP, Tsai SY, Tsai MJ, et al: Estrogen
receptor β modulates apoptosis complexes and the inflammasome to
drive the pathogenesis of endometriosis. Cell. 163:960–974. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Stanojevic S, Curuvija I, Blagojevic V,
Petrovic R, Prijic I and Vujic V: The involvement of estrogen
receptors α and β in the in vitro effects of 17β-estradiol on
secretory profile of peritoneal macrophages from naturally
menopausal female and middle-aged male rats. Exp Gerontol.
113:86–94. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Zhao Y, Gong P, Chen Y, Nwachukwu JC,
Srinivasan S, Ko C, Bagchi MK, Taylor RN, Korach KS, Nettles KW, et
al: Dual suppression of estrogenic and inflammatory activities for
targeting of endometriosis. Sci Transl Med. 7:271ra92015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Panchanathan R, Shen H, Zhang X, Ho SM and
Choubey D: Mutually positive regulatory feedback loop between
interferons and estrogen receptor-alpha in mice: Implications for
sex bias in autoimmunity. PLoS One. 5:e108682010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Smith S, Ni Gabhann J, McCarthy E, Coffey
B, Mahony R, Byrne JC, Stacey K, Ball E, Bell A, Cunnane G, et al:
Estrogen receptor α regulates tripartite motif-containing protein
21 expression, contributing to dysregulated cytokine production in
systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 66:163–172.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Feldman I, Feldman GM, Mobarak C,
Dunkelberg JC and Leslie KK: Identification of proteins within the
nuclear factor-kappa B transcriptional complex including estrogen
receptor-alpha. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 196:394.e1–13. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Kalaitzidis D and Gilmore TD:
Transcription factor cross-talk: The estrogen receptor and
NF-kappaB. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 16:46–52. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Greaves E, Temp J, Esnal-Zufiurre A,
Mechsner S, Horne AW and Saunders PT: Estradiol is a critical
mediator of macrophage-nerve cross talk in peritoneal
endometriosis. Am J Pathol. 185:2286–2297. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Gaudet HM, Cheng SB, Christensen EM and
Filardo EJ: The G-protein coupled estrogen receptor, gper: The
inside and inside-out story. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 418:207–219.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Revankar CM, Cimino DF, Sklar LA,
Arterburn JB and Prossnitz ER: A Transmembrane intracellular
estrogen receptor mediates rapid cell signaling. Science.
307:1625–1630. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Heublein S, Lenhard M, Vrekoussis T,
Schoepfer J, Kuhn C, Friese K, Makrigiannakis A, Mayr D and Jeschke
U: The G-protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER) is expressed in
normal human ovaries and is upregulated in ovarian endometriosis
and pelvic inflammatory disease involving the ovary. Reprod Sci.
19:1197–1204. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Okamoto M, Suzuki T, Mizukami Y and Ikeda
T: The Membrane-type estrogen receptor G-protein-coupled estrogen
receptor suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced interleukin 6 via
inhibition of nuclear factor-kappa B pathway in murine macrophage
cells. Anim Sci J. 88:1870–1879. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Calippe B, Douin-Echinard V, Delpy L,
Laffargue M, Lelu K, Krust A, Pipy B, Bayard F, Arnal JF, Guéry JC
and Gourdy P: 17Beta-estradiol promotes TLR4-triggered
proinflammatory mediator production through direct estrogen
receptor alpha signaling in macrophages in vivo. J Immunol.
185:1169–1176. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Zhang YH, He M, Wang Y and Liao AH:
Modulators of the balance between M1 and M2 macrophages during
pregnancy. Front Immunol. 8:1202017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Chen S, Liu Y, Zhong Z, Wei C, Liu Y and
Zhu X: Peritoneal immune microenvironment of endometriosis: Role
and therapeutic perspectives. Front Immunol. 14:11346632023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
187
|
Hirata T, Osuga Y, Takamura M, Kodama A,
Hirota Y, Koga K, Yoshino O, Harada M, Takemura Y, Yano T and
Taketani Y: Recruitment of CCR6-expressing Th17 cells by CCL 20
secreted from IL-1 beta-, TNF-alpha-, and IL-17A-stimulated
endometriotic stromal cells. Endocrinology. 151:5468–5476. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Buerger C, Shirsath N, Lang V, Berard A,
Diehl S, Kaufmann R, Boehncke WH and Wolf P: Inflammation dependent
mTORC1 signaling interferes with the switch from keratinocyte
proliferation to differentiation. PLoS One. 12:e01808532017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Schenken RS, Johnson JV and Riehl RM:
C-myc protooncogene polypeptide expression in endometriosis. Am J
Obstet Gynecol. 164:1031–1037. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Selam B, Kayisli UA, Garcia-Velasco JA,
Akbas GE and Arici A: Regulation of Fas ligand expression by IL-8
in human endometrium. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 87:3921–3927. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
Gazvani MR, Christmas S, Quenby S, Kirwan
J, Johnson PM and Kingsland CR: Peritoneal fluid concentrations of
interleukin-8 in women with endometriosis: Relationship to stage of
disease. Human Reproduction. 13:1957–1961. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
Borrelli GM, Abrao MS and Mechsner S: Can
chemokines be used as biomarkers for endometriosis? A systematic
review. Hum Reprod. 29:253–266. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Schneider J, Jimenez E, Rodriguez F and
del Tanago JG: c-myc, c-erb-B2, nm23 and p53 expression in human
endometriosis. Oncol Rep. 5:49–52. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Capobianco A, Monno A, Cottone L, Venneri
MA, Biziato D, Di Puppo F, Ferrari S, De Palma M, Manfredi AA and
Rovere-Querini P: Proangiogenic Tie2(+) macrophages infiltrate
human and murine endometriotic lesions and dictate their growth in
a mouse model of the disease. Am J Pathol. 179:2651–2659. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Kats R, Collette T, Metz CN and Akoum A:
Marked elevation of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in the
peritoneal fluid of women with endometriosis. Fertil Steril.
78:69–76. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Akoum A, Metz CN, Al-Akoum M and Kats R:
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor expression in the
intrauterine endometrium of women with endometriosis varies with
disease stage, infertility status, and pelvic pain. Fertil Steril.
85:1379–1385. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
197
|
Morin M, Bellehumeur C, Therriault MJ,
Metz C, Maheux R and Akoum A: Elevated levels of macrophage
migration inhibitory factor in the peripheral blood of women with
endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 83:865–872. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
198
|
Kats R, Metz CN and Akoum A: Macrophage
migration inhibitory factor is markedly expressed in active and
early-stage endometriotic lesions. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
87:883–889. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
199
|
Seeber B, Sammel MD, Fan X, Gerton GL,
Shaunik A, Chittams J and Barnhart KT: Panel of markers can
accurately predict endometriosis in a subset of patients. Fertil
Steril. 89:1073–1081. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
200
|
Zinovkin DA, Pranjol MZI, Bilsky IA and
Zmushko VA: Tumor-associated T-lymphocytes and macrophages are
decreased in endometrioid endometrial carcinoma with melf-pattern
stromal changes. Cancer Microenviron. 11:107–114. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
201
|
Jha P, Farooq A, Agarwal N and Buckshee K:
In vitro sperm phagocytosis by human peritoneal macrophages in
endometriosis-associated infertility. Am J Reprod Immunol.
36:235–237. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
202
|
Forster R, Sarginson A, Velichkova A, Hogg
C, Dorning A, Horne AW, Saunders PTK and Greaves E:
Macrophage-derived insulin-like growth Factor-1 is a key
neurotrophic and nerve-sensitizing factor in pain associated with
endometriosis. FASEB J. 33:11210–11222. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
203
|
Bushnell LF: Endometriosis and estrogen
therapy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 55:9151948. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
204
|
Barbieri RL: Endometriosis and the
estrogen threshold theory. Relation to surgical and medical
treatment. J Reprod Med. 43 (3 Suppl):S287–S292. 1998.
|
|
205
|
Howell R, Dowsett M, King N and Edmonds
DK: Endocrine effects of gnrh analogue with low-dose hormone
replacement therapy in women with endometriosis. Clin Endocrinol
(Oxf). 43:609–615. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
206
|
Chang CY, Chiang AJ, Yan MJ, Lai MT, Su
YY, Huang HY, Chang CY, Li YH, Li PF, Chen CM, et al: Ribosome
biogenesis serves as a therapeutic target for treating
endometriosis and the associated complications. Biomedicines.
10:1852022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
207
|
Khoufache K, Bazin S, Girard K,
Guillemette J, Roy MC, Verreault JP, Al-Abed Y, Foster W and Akoum
A: Macrophage migration inhibitory factor antagonist blocks the
development of endometriosis in vivo. PLoS One. 7:e372642012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
208
|
Daha MR: Role of complement in innate
immunity and infections. Crit Rev Immunol. 30:47–52. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
209
|
Conigliaro P, Triggianese P, Ballanti E,
Perricone C, Perricone R and Chimenti MS: Complement, infection,
and autoimmunity. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 31:532–541. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
210
|
Trouw LA, Blom AM and Gasque P: Role of
complement and complement regulators in the removal of apoptotic
cells. Mol Immunol. 45:1199–1207. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
211
|
Hajishengallis G, Reis ES, Mastellos DC,
Ricklin D and Lambris JD: Novel mechanisms and functions of
complement. Nat Immunol. 18:1288–1298. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
212
|
Lubbers R, van Essen MF, van Kooten C and
Trouw LA: Production of complement components by cells of the
immune system. Clin Exp Immunol. 188:183–194. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
213
|
Merle NS, Church SE, Fremeaux-Bacchi V and
Roumenina LT: Complement system part I-molecular mechanisms of
activation and regulation. Front Immunol. 6:2622015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
214
|
Merle NS, Noe R, Halbwachs-Mecarelli L,
Fremeaux-Bacchi V and Roumenina LT: Complement system part II: Role
in immunity. Front Immunol. 6:2572015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
215
|
Ricklin D, Reis ES and Lambris JD:
Complement in disease: A defence system turning offensive. Nat Rev
Nephrol. 12:383–401. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
216
|
Zhang T, De Carolis C, Man GCW and Wang
CC: The Link between Immunity, autoimmunity and endometriosis: A
literature update. Autoimmunity Revi. 17:945–955. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
217
|
Aslan C, Ak H, Askar N, Ozkaya AB,
Ergenoglu AM, Yeniel AO, Akdemir A and Aydin HH: Overexpression of
complement C5 in endometriosis. Clin Biochem. 47:496–498. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
218
|
Rahal D, Andrade F and Nisihara R:
Insights into the role of complement system in the pathophysiology
of endometriosis. Immunol Lett. 231:43–48. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
219
|
Kabut J, Kondera-Anasz Z, Sikora J and
Mielczarek-Palacz A: Levels of complement components iC3b, C3c, C4,
and SC5b-9 in peritoneal fluid and serum of infertile women with
endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 88:1298–1303. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
220
|
Sikora J, Wroblewska-Czech A,
Smycz-Kubanska M, Mielczarek-Palacz A, Cygal A, Witek A and
Kondera-Anasz Z: The role of complement components C1q, MBL and C1
inhibitor in pathogenesis of endometriosis. Arch Gynecol Obstet.
297:1495–1501. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
221
|
Ahn SH, Khalaj K, Young SL, Lessey BA,
Koti M and Tayade C: Immune-inflammation gene signatures in
endometriosis patients. Fertil Steril. 106:1420–1431.e7. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
222
|
Weed JC and Arquembourg PC: Endometriosis:
Can it produce an autoimmune response resulting in infertility?
Clin Obstet Gynecol. 23:885–893. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
223
|
Isaacson KB, Coutifaris C, Garcia CR and
Lyttle CR: Production and secretion of complement component-3 by
endometriotic tissue. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 69:1003–1009. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
224
|
Badawy SZA, Cuenca V, Stitzel A, Jacobs
RDB and Tomar RH: Autoimmune phenomena in infertile patients with
endometriosis. Obstet Gynecol. 63:271–275. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
225
|
Badawy SZA, Cuenca V, Marshall L,
Munchback R, Rinas AC and Coble DA: Cellular-components in
peritoneal-fluid in infertile patients with and without
endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 42:704–708. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
226
|
Tao XJ, Sayegh RA and Isaacson KB:
Increased expression of complement component 3 in human ectopic
endometrium compared with the matched eutopic endometrium. Fertil
Steril. 68:460–467. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
227
|
Sayegh RA, Tao XJ, Awwad JT and Isaacson
KB: Localization of the expression of complement component 3 in the
human endometrium by in situ hybridization. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 81:1641–1649. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
228
|
Steele RW, Dmowski WP and Marmer DJ:
Immunological aspects of human endometriosis. Am J Reprod Immunol
(1980). 6:33–36. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
229
|
Meek SC, Hodge DD and Musich JR:
Autoimmunity in infertile patients with endometriosis. Am J Obstet
Gynecol. 158:1365–1373. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
230
|
Isaacson KB, Galman M, Coutifaris C and
Lyttle CR: Endometrial synthesis and secretion of complement
component-3 by patients with and without endometriosis. Fertil
Steril. 53:836–841. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
231
|
Hasan A, Rahim A, Afzal M, Naveed AK, Ayub
S and Jahan S: Serum albumin and C3 complement levels in
endometriosis. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 29:702–705. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
232
|
Bischof P, Planasbasset D, Campana A and
Meisser A: Investigations on the cell type responsible for the
endometrial secretion of complement component-3 (C3). Human Reprod.
9:1652–1659. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
233
|
Liu CF, Min XY, Wang N, Wang JX, Ma N,
Dong X, Zhang B, Wu W, Li ZF, Zhou W and Li K: Complement receptor
3 Has negative impact on tumor surveillance through suppression of
natural killer cell function. Front Immunol. 8:16022017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
234
|
Suryawanshi S, Huang X, Elishaev E, Budiu
RA, Zhang L, Kim S, Donnellan N, Mantia-Smaldone G, Ma T, Tseng G,
et al: Complement pathway is frequently altered in endometriosis
and endometriosis-associated ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
20:6163–6174. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
235
|
Woelfler MM, Meinhold-Heerlein IM,
Soehngen L, Rath W, Knuechel R, Neulen J, Maass N and Henkel C:
Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis in peritoneal fluid samples
identifies differential protein regulation in patients suffering
from peritoneal or ovarian endometriosis. Fertil Steril.
95:2764–2768. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
236
|
Riley CF, Moen MH and Videm V:
Inflammatory markers in endometriosis: Reduced peritoneal
neutrophil response in minimal endometriosis. Acta Obstet Gynecol
Scand. 86:877–881. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
237
|
Kruse C, Steffensen R, Nielsen HJ and
Jensenius JC: Mannan-binding lectin polymorphisms and serum levels
in patients with endometriosis. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol.
181:256–258. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
238
|
Kruse C, Steffensen R, Nielsen HJ and
Jensenius JC: Mannan-binding lectin polymorphisms and serum levels
in patients with endometriosis. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol.
181:256–258. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
239
|
Kavoussi SK, Mueller MD and Lebovic DI:
Expression of mannose-binding lectin in the peritoneal fluid of
women with and without endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 85:1526–1528.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
240
|
Ozerkan K, Oral B and Uncu G:
Mannose-binding lectin levels in endometriosis. Fertil Steril.
94:775–776. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
241
|
Karadadas E, Hortu I, Ak H, Ergenoglu AM,
Karadadas N and Aydin HH: Evaluation of complement system proteins
C3a, C5a and C6 in patients of endometriosis. Clin Biochem.
81:15–19. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
242
|
Stefkovich ML, Arao Y, Hamilton KJ and
Korach KS: Experimental models for evaluating non-genomic estrogen
signaling. Steroids. 133:34–37. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
243
|
Al-Sabbagh M, Lam EW and Brosens JJ:
Mechanisms of endometrial progesterone resistance. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 358:208–215. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
244
|
Han SJ and O'Malley BW: The dynamics of
nuclear receptors and nuclear receptor coregulators in the
pathogenesis of endometriosis. Hum Reprod Update. 20:467–484. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
245
|
Patel BG, Rudnicki M, Yu J, Shu Y and
Taylor RN: Progesterone resistance in endometriosis: Origins,
consequences and interventions. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand.
96:623–632. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
246
|
Kastner P, Krust A, Turcotte B, Stropp U,
Tora L, Gronemeyer H and Chambon P: Two distinct estrogen-regulated
promoters generate transcripts encoding the two functionally
different human progesterone receptor forms A and B. EMBO J.
9:1603–1614. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
247
|
Patel B, Elguero S, Thakore S, Dahoud W,
Bedaiwy M and Mesiano S: Role of Nuclear progesterone receptor
isoforms in uterine pathophysiology. Hum Reprod Update. 21:155–173.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
248
|
Vasquez YM and DeMayo FJ: Role of nuclear
receptors in blastocyst implantation. Semin Cell Dev Biol.
24:724–735. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
249
|
Chantalat E, Valera MC, Vaysse C, Noirrit
E, Rusidze M, Weyl A, Vergriete K, Buscail E, Lluel P, Fontaine C,
et al: Estrogen receptors and endometriosis. Int J Mol Sci.
21:28152020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
250
|
Wang Y, Zhu L, Kuokkanen S and Pollard JW:
Activation of protein synthesis in mouse uterine epithelial cells
by estradiol-17β is mediated by a PKC-ERK1/2-mTOR signaling
pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:E1382–E1391. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
251
|
Reis FM, Petraglia F and Taylor RN:
Endometriosis: Hormone regulation and clinical consequences of
chemotaxis and apoptosis. Hum Reprod Update. 19:406–418. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
252
|
Yilmaz BD and Bulun SE: Endometriosis and
nuclear receptors. Hum Reprod Update. 25:473–485. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
253
|
Xue Q, Lin Z, Cheng YH, Huang CC, Marsh E,
Yin P, Milad MP, Confino E, Reierstad S, Innes J and Bulun SE:
Promoter methylation regulates estrogen receptor 2 in human
endometrium and endometriosis. Biol Reprod. 77:681–687. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
254
|
Trukhacheva E, Lin Z, Reierstad S, Cheng
YH, Milad M and Bulun SE: Estrogen receptor (ER) beta regulates
eralpha expression in stromal cells derived from ovarian
endometriosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 94:615–622. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
255
|
Bulun SE, Yilmaz BD, Sison C, Miyazaki K,
Bernardi L, Liu S, Kohlmeier A, Yin P, Milad M and Wei J:
Endometriosis. Endocr Rev. 40:1048–1079. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
256
|
Burney RO, Talbi S, Hamilton AE, Vo KC,
Nyegaard M, Nezhat CR, Lessey BA and Giudice LC: Gene expression
analysis of endometrium reveals progesterone resistance and
candidate susceptibility genes in women with endometriosis.
Endocrinology. 148:3814–3826. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
257
|
Flores VA, Vanhie A, Dang T and Taylor HS:
Progesterone receptor status predicts response to progestin therapy
in endometriosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 103:4561–4568. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
258
|
Broi MGD, Rocha CVJ, Meola J, Martins WP,
Carvalho FM, Ferriani RA and Navarro PA: Expression of PGR, HBEGF,
ITGAV, ITGB3 and SPP1 genes in eutopic endometrium of infertile
women with endometriosis during the implantation window: A pilot
study. JBRA Assist Reprod. 21:196–202. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
259
|
Strowitzki T, Marr J, Gerlinger C,
Faustmann T and Seitz C: Dienogest is as effective as leuprolide
acetate in treating the painful symptoms of endometriosis: A
24-Week, randomized, multicentre, open-label trial. Hum Reprod.
25:633–641. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
260
|
Saunders PTK and Horne AW: Endometriosis:
Etiology, pathobiology, and therapeutic prospects. Cell.
184:2807–2824. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
261
|
Ferrero S, Evangelisti G and Barra F:
Current and emerging treatment options for endometriosis. Expert
Opin Pharmacother. 19:1109–1125. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
262
|
Capezzuoli T, Rossi M, La Torre F,
Vannuccini S and Petraglia F: Hormonal drugs for the treatment of
endometriosis. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 67:1023112022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
263
|
Dunselman GA, Vermeulen N, Becker C,
Calhaz-Jorge C, D'Hooghe T, De Bie B, Heikinheimo O, Horne AW,
Kiesel L, Nap A, et al: ESHRE guideline: Management of women with
endometriosis. Hum Reprod. 29:400–412. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
264
|
Crosignani PG, Luciano A, Ray A and
Bergqvist A: Subcutaneous depot medroxyprogesterone acetate versus
leuprolide acetate in the treatment of endometriosis-associated
pain. Hum Reprod. 21:248–256. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
265
|
Selak V, Farquhar C, Prentice A and Singla
A: Danazol for pelvic pain associated with endometriosis. Cochrane
Database Syst Rev. CD0000682007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
266
|
Strowitzki T, Faustmann T, Gerlinger C and
Seitz C: Dienogest in the treatment of endometriosis-associated
pelvic pain: A 12-week, randomized, double-blind,
placebo-controlled study. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol.
151:193–198. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
267
|
Petaja J: Inflammation and coagulation. An
overview. Thromb Res. 127 (Suppl 2):S34–S37. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
268
|
Demetz G and Ott I: The interface between
inflammation and coagulation in cardiovascular disease. Int J
Inflam. 2012:8603012012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
269
|
Lessey BA, Castelbaum AJ, Sawin SW, Buck
CA, Schinnar R, Bilker W and Strom BL: Aberrant integrin expression
in the endometrium of women with endometriosis. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 79:643–649. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
270
|
Regidor PA, Vogel C, Regidor M, Schindler
AE and Winterhager E: Expression pattern of integrin adhesion
molecules in endometriosis and human endometrium. Hum Reprod
Update. 4:710–718. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
271
|
Libersan D and Merhi Y: Platelet
P-selectin expression: Requirement for protein kinase C, but not
protein tyrosine kinase or phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Thromb
Haemost. 89:1016–1023. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
272
|
Guo SW, Ding D, Geng JG, Wang L and Liu X:
P-selectin as a potential therapeutic target for endometriosis.
Fertil Steril. 103:990–1000.e8. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
273
|
Lorant DE, Patel KD, McIntyre TM, McEver
RP, Prescott SM and Zimmerman GA: Coexpression of Gmp-140 and paf
by endothelium stimulated by histamine or thrombin: A juxtacrine
system for adhesion and activation of neutrophils. J Cell Biol.
115:223–234. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
274
|
Lefer DJ: Pharmacology of selectin
inhibitors in ischemia/reperfusion states. Annu Rev Pharmacol
Toxicol. 40:283–294. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
275
|
Kling D, Stucki C, Kronenberg S, Tuerck D,
Rheaume E, Tardif JC, Gaudreault J and Schmitt C: Pharmacological
control of platelet-leukocyte interactions by the human
anti-P-selectin antibody inclacumab-preclinical and clinical
studies. Thromb Res. 131:401–410. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
276
|
Harada T and Taniguchi F: Dienogest: A new
therapeutic agent for the treatment of endometriosis. Womens Health
(Lond). 6:27–35. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
277
|
Kaminski K, Fiegler P, Marr J and Moore C:
Treatment of endometriosis with dienogest: Preliminary report.
Ginekol Pol. 72:299–304. 2001.(In Polish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
278
|
Harada T, Momoeda M, Taketani Y, Aso T,
Fukunaga M, Hagino H and Terakawa N: Dienogest is as effective as
intranasal buserelin acetate for the relief of pain symptoms
associated with endometriosis-a randomized, double-blind,
multicenter, controlled trial. Fertil Steril. 91:675–681. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
279
|
Rother RP, Rollins SA, Mojcik CF, Brodsky
RA and Bell L: Discovery and development of the complement
inhibitor eculizumab for the treatment of paroxysmal nocturnal
hemoglobinuria. Nat Biotechnol. 25:1256–1264. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|