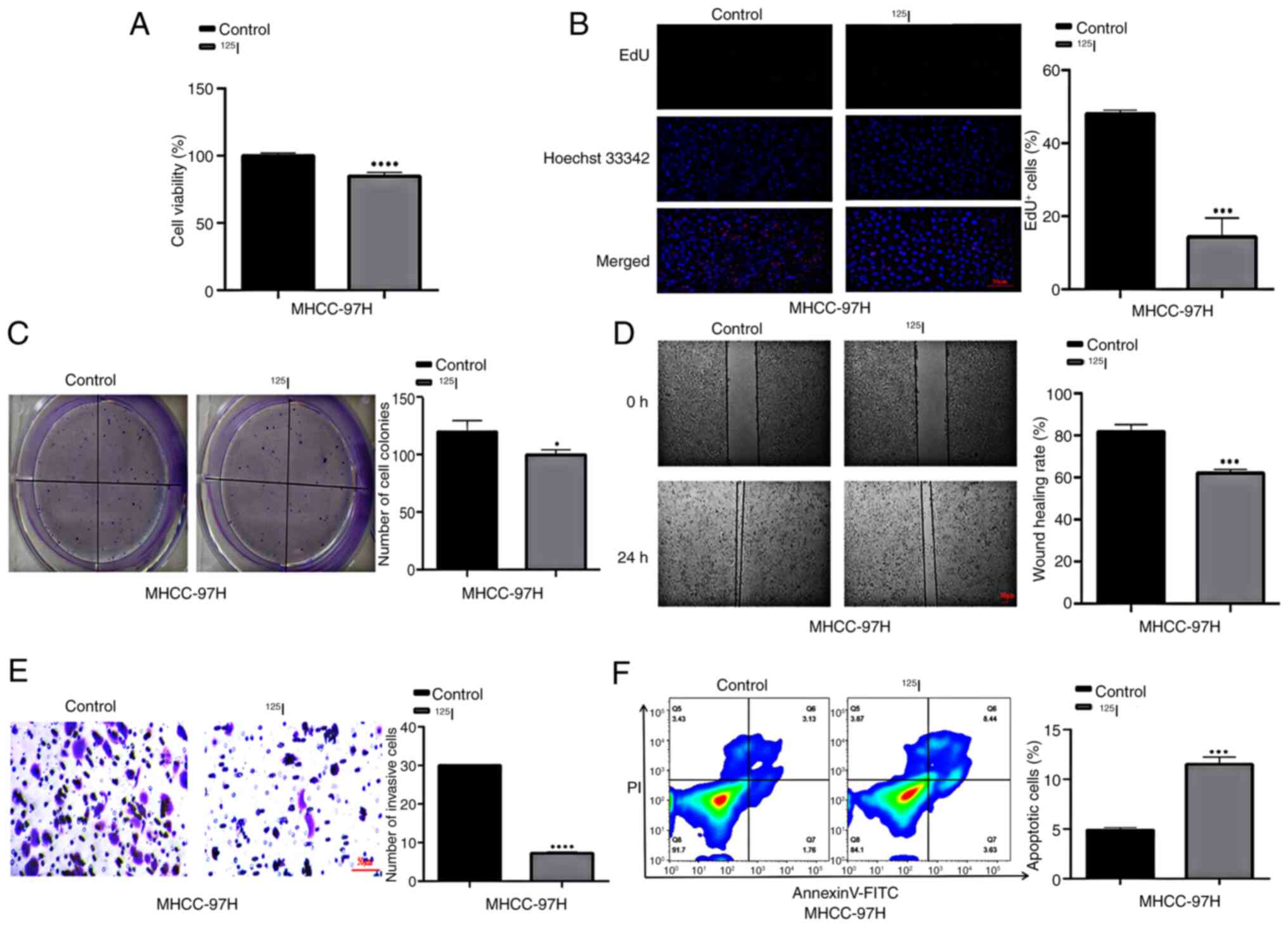
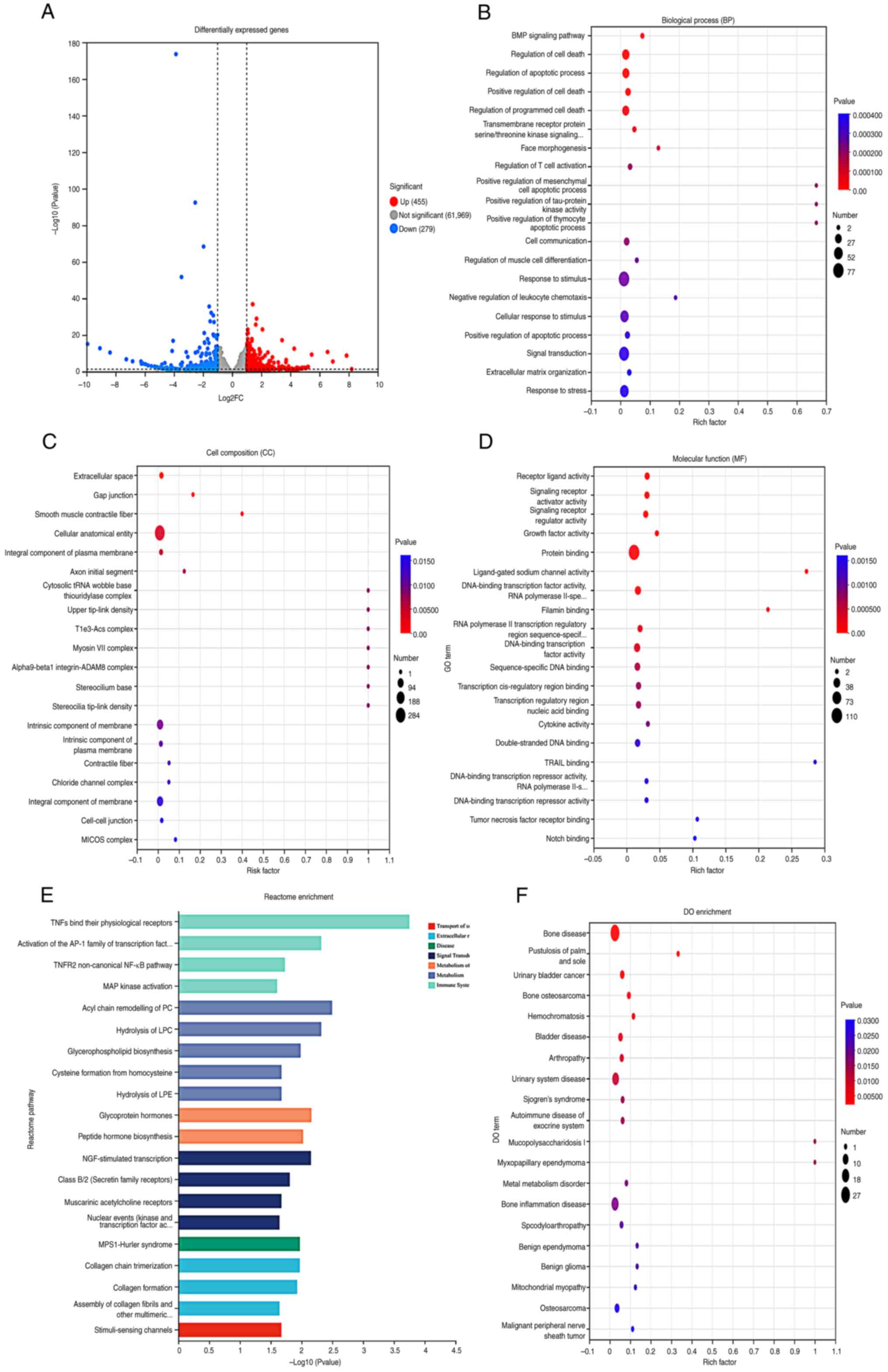
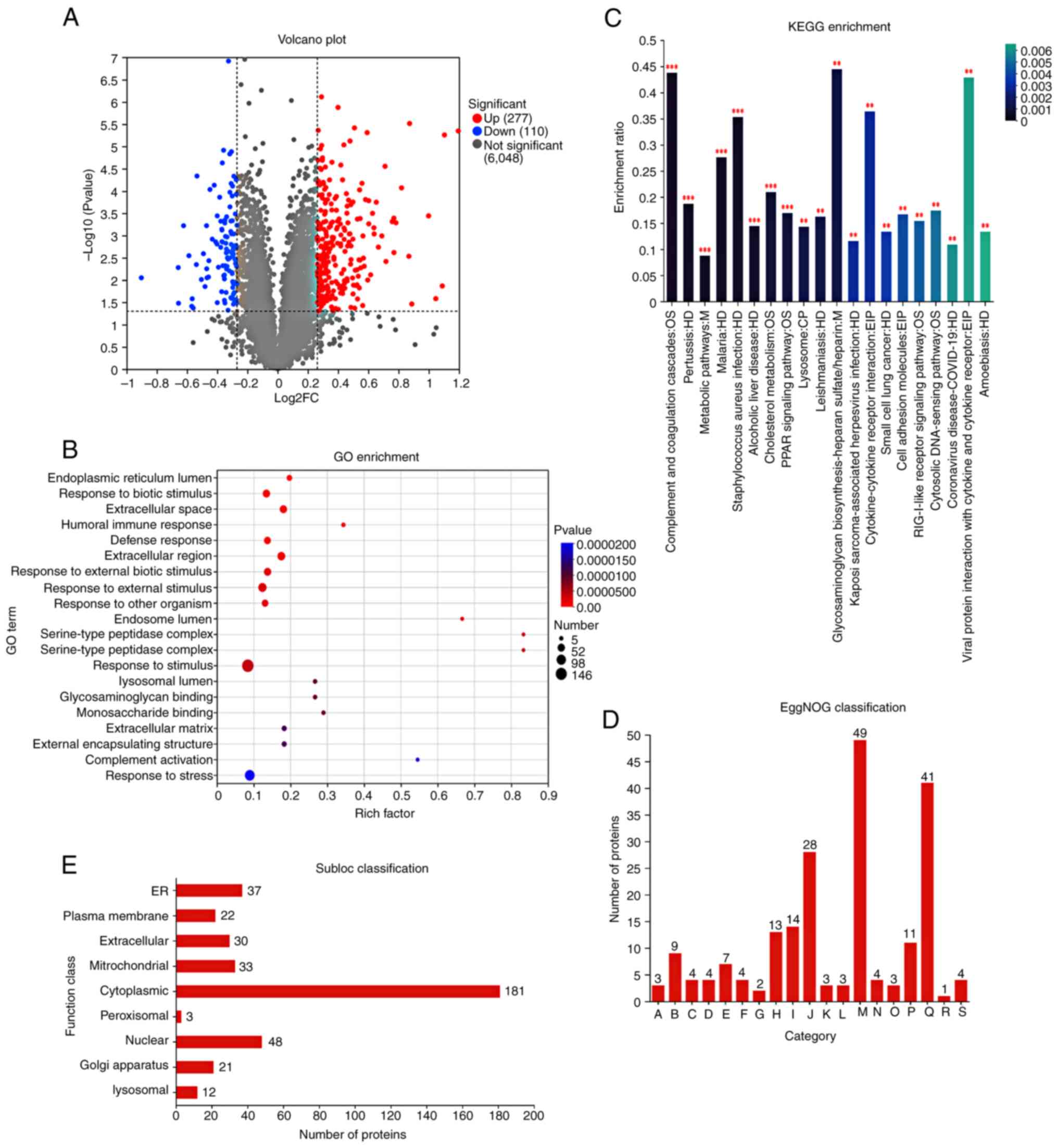
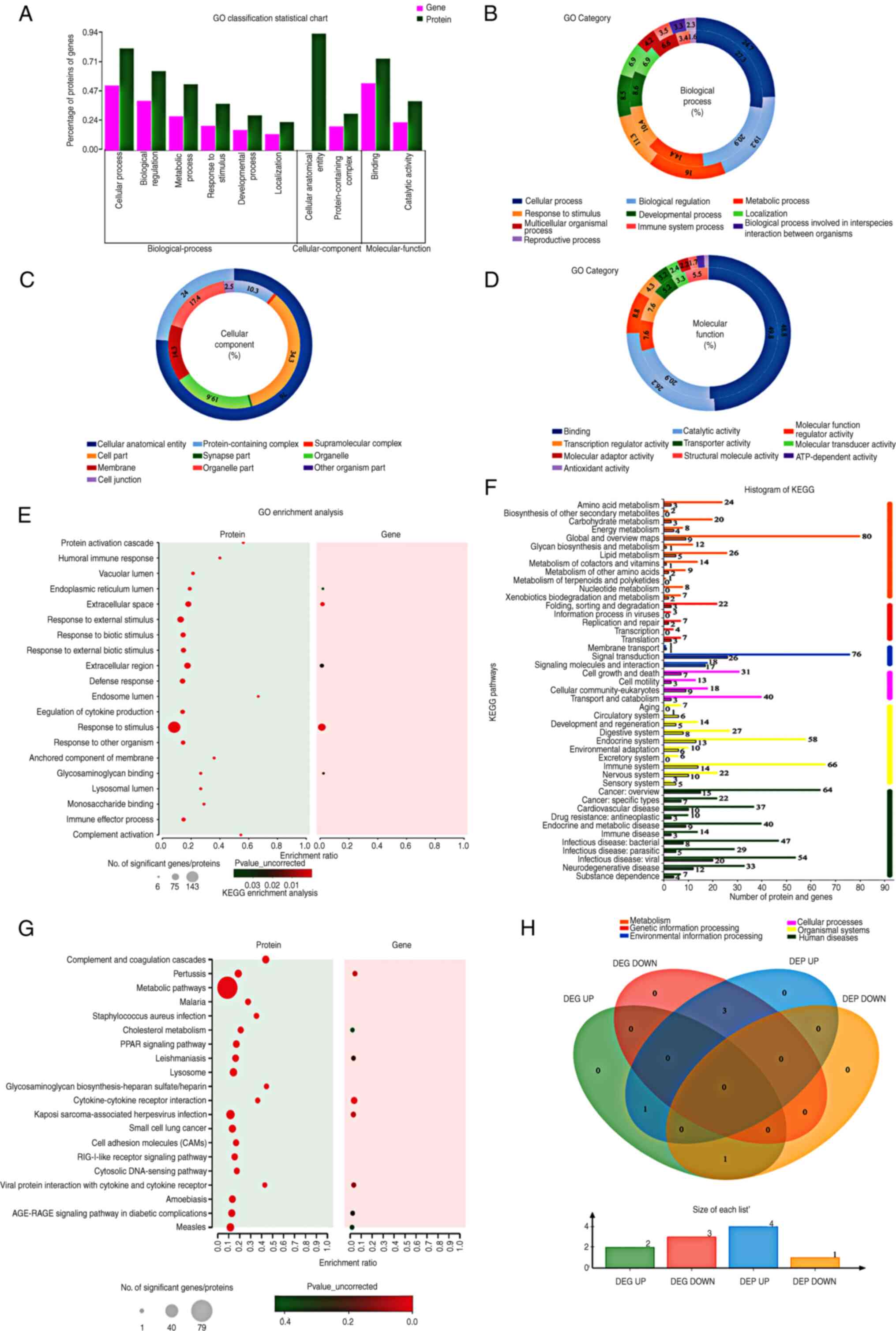
|
1
|
Tsuchiya N, Sawada Y, Endo I, Saito K,
Uemura Y and Nakatsura T: Biomarkers for the early diagnosis of
hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 21:10573–10583.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang W and Wei C: Advances in the early
diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Genes Dis. 7:308–319. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Huang S, Cao Y, Wang R, Liu H, Wang T and
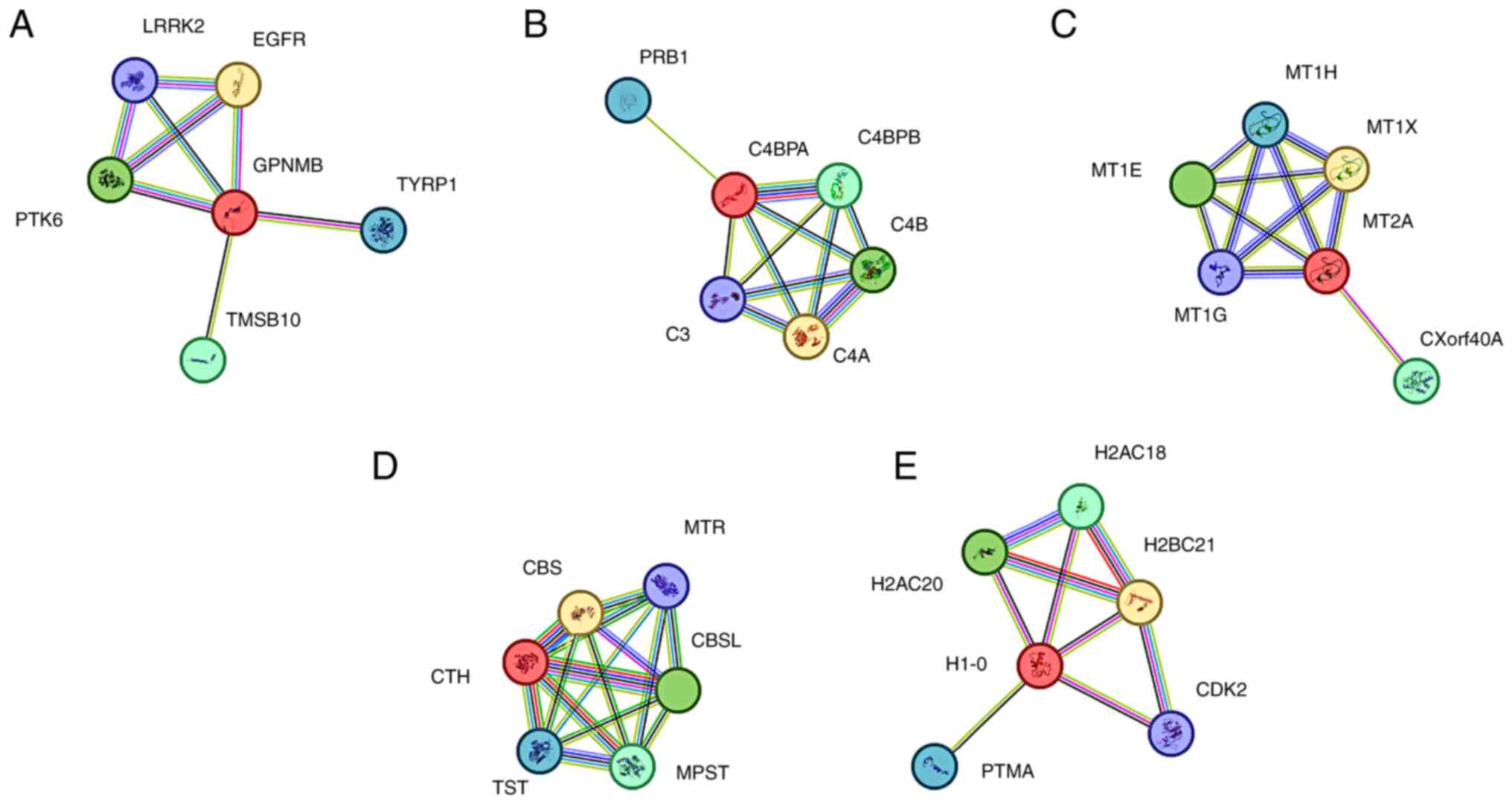
Yang S: Feasibility of 125I brachytherapy combined with
arterial infusion chemotherapy in patients with advanced pancreatic
cancer. Medicine (Baltimore). 102:e350332023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang X and Wang D: Clinical analysis of
125I seed implantation combined with epidermal growth
factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in advanced non-small
cell lung cancer. J BUON. 26:1879–1886. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Peng S, Yang QX, Zhang T, Lu MJ, Yang G,
Liu ZY, Zhang R and Zhang FJ: Lobaplatin-TACE combined with
radioactive 125I seed implantation for treatment of
primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
15:5155–5160. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sun H, Zhang M, Liu R, Liu Y, Hou Y and Wu
C: Endovascular implantation of 125I seed combined with
transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for unresectable
hepatocellular carcinoma. Future Oncol. 14:1165–1176. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Brown ZJ, Tsilimigras DI, Ruff SM, Mohseni
A, Kamel IR, Cloyd JM and Pawlik TM: Management of hepatocellular
carcinoma: A review. JAMA Surg. 158:410–420. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Juaid N, Amin A, Abdalla A, Reese K,
Alamri Z, Moulay M, Abdu S and Miled N: Anti-hepatocellular
carcinoma biomolecules: molecular targets insights. Int J Mol.
22:107742021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Li D, Wang WJ, Wang YZ, Wang YB and Li YL:
Lobaplatin promotes 125I-induced apoptosis and inhibition of
proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma by upregulating
PERK-eIF2α-ATF4-CHOP pathway. Cell Death Dis. 10:7442019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chelakkot C, Chelakkot VS, Shin Y and Song
K: Modulating glycolysis to improve cancer therapy. Int J Mol Sci.
24:26062023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu LX, Heng JH, Deng DX, Zhao H, Zheng
ZY, Liao LD, Lin W, Xu XE, Li EM and Xu LY: Sulconazole induces
panoptosis by triggering oxidative stress and inhibiting glycolysis
to increase radiosensitivity in esophageal cancer. Mol Cell
Proteomics. 22:1005512023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zheng J, Luo J, Zeng H, Guo L and Shao G:
125I suppressed the Warburg effect viaregulating
miR-338/PFKL axis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed Pharmacother.
119:1094022019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang H, Ma D, Wang C, Zhao S and Liu C:
Triptolide Inhibits Invasion and Tumorigenesis of Hepatocellular
Carcinoma MHCC-97H Cells Through NF-κB Signaling. Med Sci Monit.
22:1827–1836. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and
the 2 (−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fujita M, Chen MM, Siwak DR, Sasagawa S,
Oosawa-Tatsuguchi A, Arihiro K, Ono A, Miura R, Maejima K, Aikata
H, et al: Proteo-genomic characterization of virus-associated liver
cancers reveals potential subtypes and therapeutic targets. Nat
Commun. 13:64812022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang W, Yang C, Hu Y, Yi K, Xiao W, Xu X
and Chen Z: Comprehensive analysis of the correlation of the
pan-cancer gene HAUS5 with prognosis and immune infiltration in
liver cancer. Sci Rep. 13:24092023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhou PY, Zhou C, Gan W, Tang Z, Sun BY,
Huang JL, Liu G, Liu WR, Tian MX, Jiang XF, et al: Single-cell and
spatial architecture of primary liver cancer. Commun Biol.
6:11812023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Qiu Z, Yu C, Qiu X, Li Q, Li J, Chen Z,
Chang S, Zhang S, Fan G and Wang S: Safety and Efficacy of
CT-Guided Iodine-125 Brachytherapy for Portal Vein Tumor Thrombus
in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Acad Radiol. 30 (Suppl 1):S53–S60.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
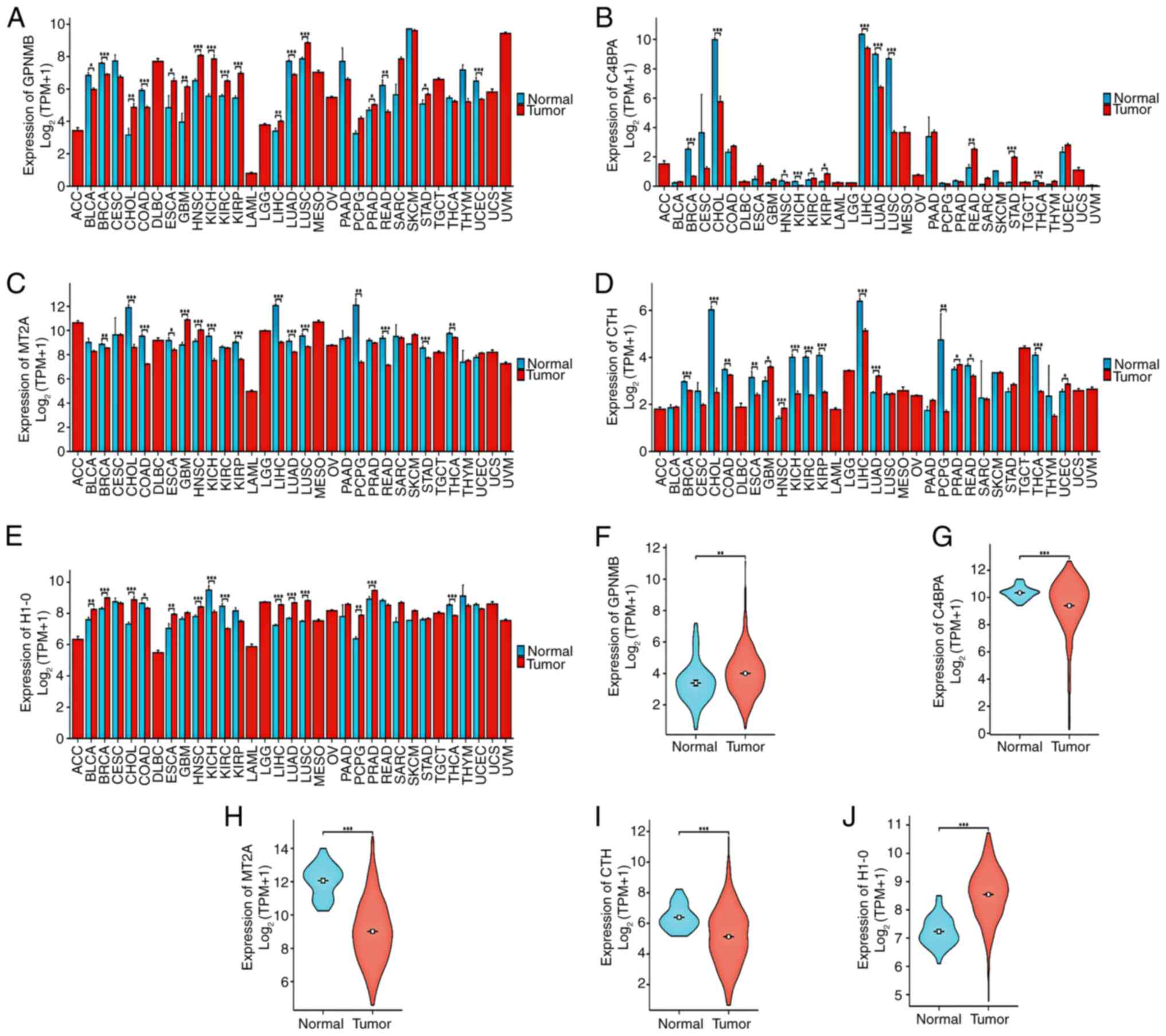
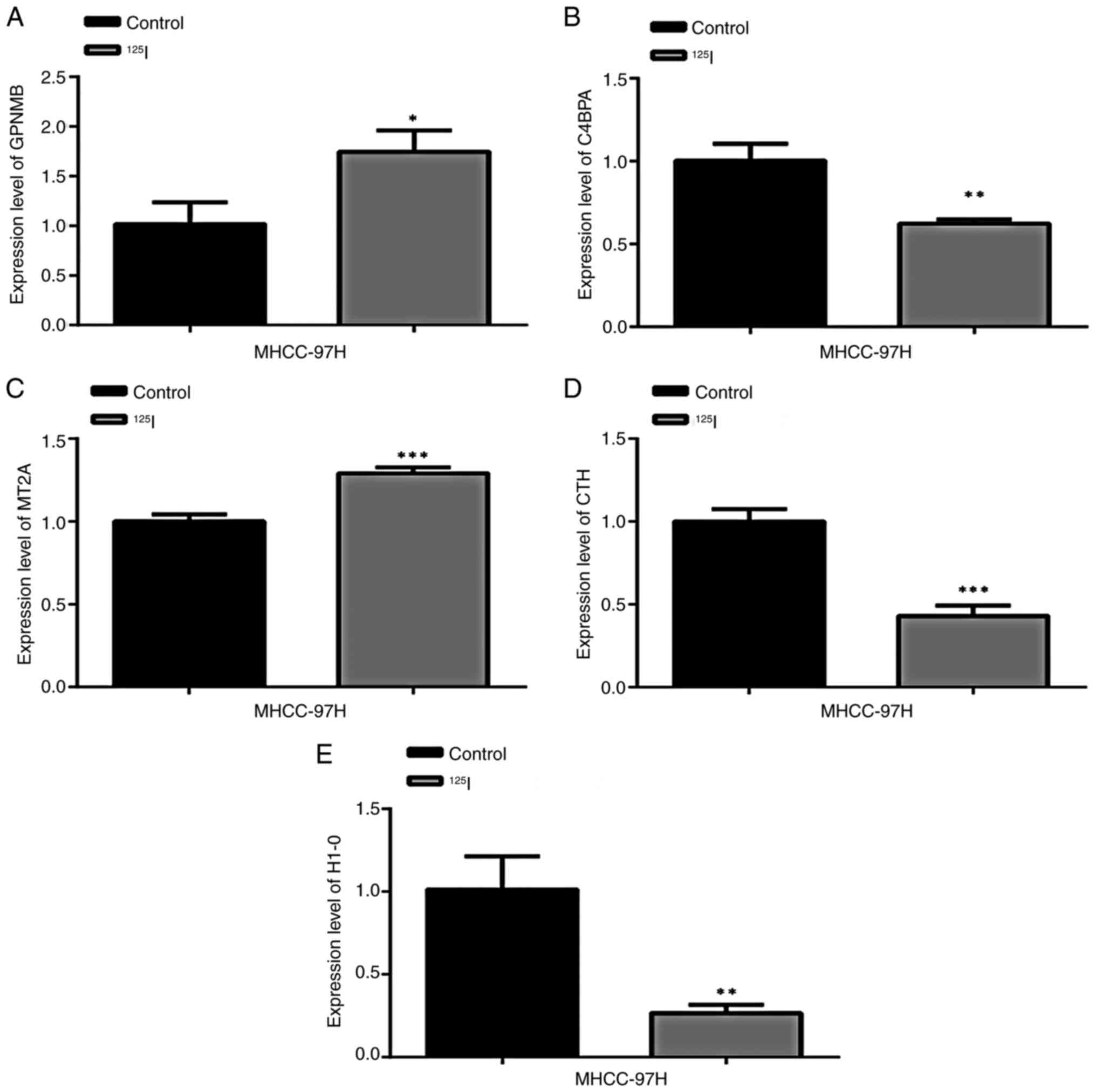
Saade M, Araujo de Souza G, Scavone C and
Kinoshita PF: The Role of GPNMB in Inflammation. Front Immunol.
12:6747392021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xie R, Okita Y, Ichikawa Y, Fikry MA,
Huynh Dam KT, Tran STP and Kato M: Role of the kringle-like domain
in glycoprotein NMB for its tumorigenic potential. Cancer Sci.
110:2237–2246. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen L, Shan X, Wan X, Zha W and Fan R:
HOMER3 promotes liver hepatocellular carcinoma cancer progression
by -upregulating EZH2 and mediating miR-361/GPNMB axis. Pathol Res
Pract. 254:1551502024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Blom AM: A cluster of positively charged
amino acids in the alpha-chain of C4b-binding protein (C4BP) is
pivotal for the regulation of the complement system and the
interaction with bacteria. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl.
233:37–49. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Blom AM: Structural and functional studies
of complement inhibitor C4b-binding protein. Biochem Soc Trans.
30:978–982. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Feng G, Li J, Zheng M, Yang Z, Liu Y,
Zhang S, Ye L, Zhang W and Zhang X: Hepatitis B virus X protein
up-regulates C4b-binding protein α through activating transcription
factor Sp1 in protection of hepatoma cells from complement attack.
Oncotarget. 7:28013–28026. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dong W, Xia Z, Chai Z, Qiu Z, Wang X, Yang
Z, Wang J, Zhang T, Zhang Q and Jin J: Proteomic analysis of small
extracellular vesicles from the plasma of patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Surg Oncol. 20:3872022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
He X, Wang Y, Zhang W, Li H, Luo R, Zhou
Y, Liao CL, Huang H, Lv X, Xie Z and He M: Screening differential
expression of serum proteins in AFP-negative HBV-related
hepatocellular carcinoma using iTRAQ-MALDI-MS/MS. Neoplasma.
61:17–26. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kanda T, Jiang X and Yokosuka O: Androgen
receptor signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma and pancreatic
cancers. World J Gastroenterol. 20:9229–9236. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kohli A, Huang SL, Chang TC, Chao CC and
Sun NK: H1.0 induces paclitaxel-resistance genes expression in
ovarian cancer cells by recruiting GCN5 and androgen receptor.
Cancer Sci. 113:2616–2626. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pan Y, Ye S, Yuan D, Zhang J, Bai Y and
Shao C: Hydrogen sulfide (H2S)/cystathionine γ-lyase (CSE) pathway
contributes to the proliferation of hepatoma cells. Mutat Res.
763–764. 10–18. 2014.
|
|
30
|
Xiang J, Wu X, Liu W, Wei H, Zhu Z, Liu S,
Song C, Gu Q, Wei S and Zhang Y: Bioinformatic analyzes and
validation of cystathionine gamma-lyase as a prognostic biomarker
and related to immune infiltrates in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Heliyon. 9:e161522023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu F, Li H, Chang H, Wang J and Lu J:
Identification of hepatocellular carcinoma-associated hub genes and
pathways by integrated microarray analysis. Tumori. 101:206–214.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang Y, Jiang T, Li Z, Lu L, Zhang R,
Zhang D, Wang X and Tan J: Analysis of differentially co-expressed
genes based on microarray data of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Neoplasma. 64:216–221. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Datta J, Majumder S, Kutay H, Motiwala T,
Frankel W, Costa R, Cha HC, MacDougald OA, Jacob ST and Ghoshal K:
Metallothionein expression is suppressed in primary human
hepatocellular carcinomas and is mediated through inactivation of
CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha by phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase signaling cascade. Cancer Res. 67:2736–2746. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Park Y and Yu E: Expression of
metallothionein-1 and metallothionein-2 as a prognostic marker in
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 28:1565–1572.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tomasi ML, Cossu C, Spissu Y, Floris A,
Ryoo M, Iglesias-Ara A, Wang Q, Pandol SJ, Bhowmick NA, Seki E, et
al: S-adenosylmethionine and methylthioadenosine inhibit cancer
metastasis by targeting microRNA 34a/b-methionine
adenosyltransferase 2A/2B axis. Oncotarget. 8:78851–78869. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|