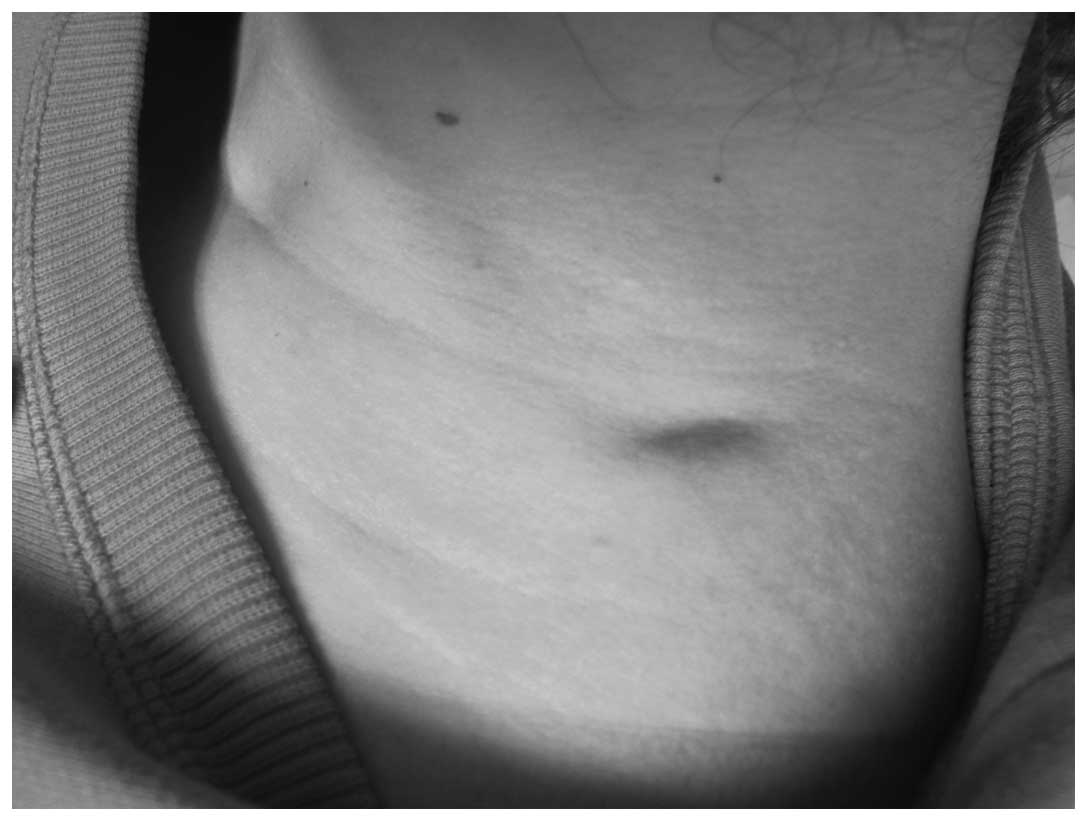
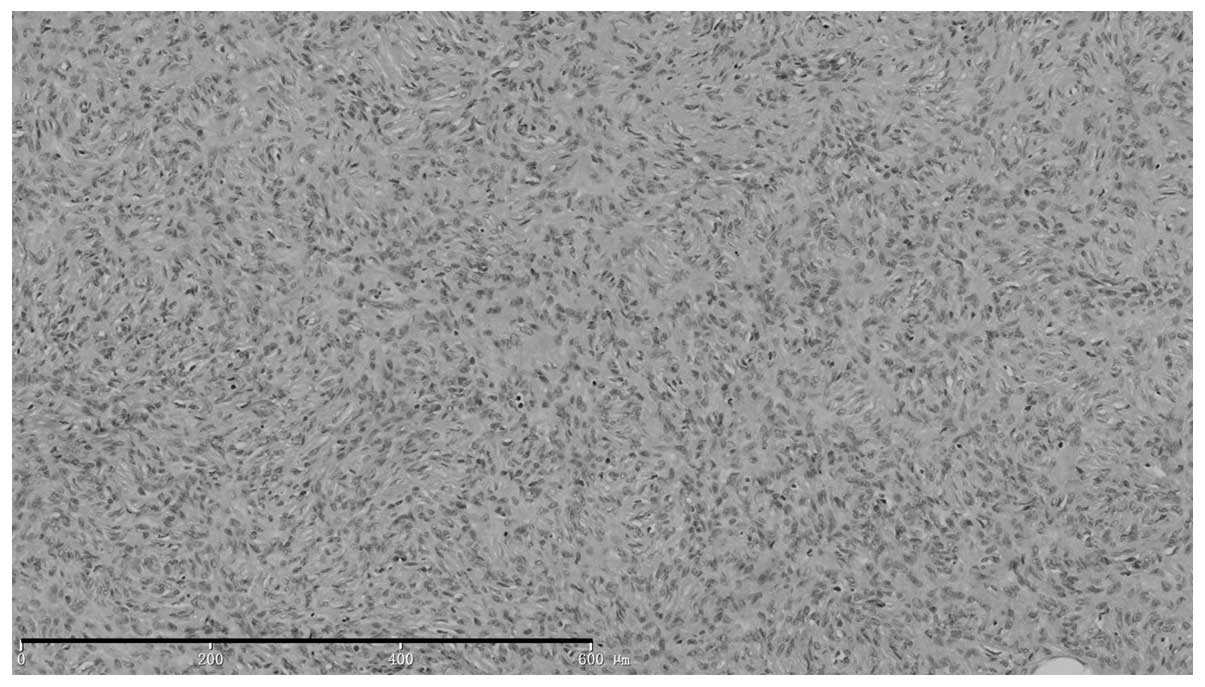
|
1
|
Hegde U, Shetty SK, Sreeshyla HS and
Doddawada VG: Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans - a recurrent lesion
with unusual presentation in the parotid region. J Clin Diag Res.
8:130–131. 2014.
|
|
2
|
Zheng Z, Piao J, Lee JH, Kim SE, Kim SC,
Chung KY and Roh MR: Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: A study of
clinical, pathologic, genetic, and therapeutic features in Korean
patients. Yonsei Med J. 56:440–446. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Saiag P, Grob JJ, Lebbe C, et al:
Diagnosis and treatment of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans.
European consensus-based interdisciplinary guideline. Eur J Cancer.
Jul 16–2015.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Erdem O, Wyatt AJ, Lin E, Wang X and
Prieto VG: Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans treated with wide local
excision and followed at a cancer hospital: Prognostic significance
of clinicopathologic variables. Am J Dermatopathol. 34:24–34. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kim M, Huh CH, Cho KH and Cho S: A study
on the prognostic value of clinical and surgical features of
dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans in Korean patients. J Eur Acad
Dermatol Venereol. 26:964–971. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Suit H, Spiro I, Mankin HJ, Efird J and
Rosenberg AE: Radiation in management of patients with
dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. J Clin Oncol. 14:2365–2369.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Llombart B, Serra-Guillén C, Monteagudo C,
López Guerrero JA and Sanmartíin O: Dermatofibrosarcoma
protuberans: A comprehensive review and update on diagnosis and
management. Semin Diagn Pathol. 30:13–28. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
McArthur G: Molecularly targeted treatment
for dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Semin Oncol. 31:30–36. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sjöblom T, Shimizu A, O'Brien KP, Pietras
K, Dal Cin P, Buchdunger E, Dumanski JP, Ostman A and Heldin CH:
Growth inhibition of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans tumors by the
platelet-derived growth factor receptor antagonist STI571 through
induction of apoptosis. Cancer Res. 61:5778–5783. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kiuru-Kuhlefelt S, El-Rifai W,
Fanburg-Smith J, Kere J, Miettinen M and Knuutila S: Concomitant
DNA copy number amplification at 17q and 22q in dermatofibrosarcoma
protuberans. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 92:192–195. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Qiao J, Patel KU, López-Terrada D and Fang
H: Atrophic dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: Report of a case
demonstrated by detecting COL1A1-PDGFB rearrangement. Diagn Pathol.
7:1662012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Loss L and Zeitouni NC: Management of
scalp dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Dermatol Surg. 31:1428–1433.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Garcia C, Clark RE and Buchanan M:
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Int J Dermatol. 35:867–871. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Llombart B, Monteagudo C, Sanmartin O,
López-Guerrero JA, Serra-Guillén C, Poveda A, Jorda E,
Fernandez-Serra A, Pellíin A, Guillén C and Llombart-Bosch A:
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: A clinicopathological,
immunohistochemical, genetic (COL1A1-PDGFB) and therapeutic study
of low-grade versus high-grade (fibrosarcomatous) tumors. J Am Acad
Dermatol. 65:564–575. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Maki RG, Awan RA, Dixon RH, Jhanwar S and
Antonescu CR: Differential sensitivity to imatinib of 2 patients
with metastatic sarcoma arising from dermatofibrosarcoma
protuberans. Int J Cancer. 100:623–626. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hanabusa M, Kamo R, Harada T and Ishii M:
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans with atrophic appearance at early
stage of the tumor. J Dermatol. 34:336–339. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Martin L, Piette F, Blanc P, Mortier L,
Avril MF, Delaunay MM, Dréno B, Granel F, Mantoux F, Aubin F, et
al: Clinical variants of the preprotuberant stage of
dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Br J Dermatol. 153:932–936. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Haycox CL, Odland PB, Olbricht SM and
Piepkorn M: Immunohistochemical characterization of
dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans with practical applications for
diagnosis and treatment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 37:438–444. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dominguez-Malagón HR, Ordóňez NG and
Mackay B: Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: Ultrastructural and
immunocytochemical observations. Ultrastruct Pathol. 19:281–289.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sachdev R and Sundram U: Expression of
CD163 in dermatofibroma, cellular fibrous histiocytoma and
dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: Comparison with CD68, CD34 and
Factor XIIIa. J Cutan Pathol. 33:353–360. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bakry O and Attia A: Atrophic
dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. J Dermatol Case Rep. 6:14–17.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Marque M, Bessis D, Pedeutour F, Viseux V,
Guillot B and Fraitag-Spinner S: Medallion-like dermal dendrocyte
hamartoma: The main diagnostic pitfall is congenital atrophic
dermatofibrosarcoma. Br J Dermatol. 160:190–193. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bowne WB, Antonescu CR, Leung DH, Katz SC,
Hawkins WG, Woodruff JM, Brennan MF and Lewis JJ:
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: A clinicopathologic analysis of
patients treated and followed at a single institution. Cancer.
88:2711–2720. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wu JK, Malik MM and Egan CA: Atrophic
dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: An uncommon and misleading
variant. Australas J Dermatol. 45:175–177. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Labropoulos SV, Fletcher JA, Oliveira AM,
Papadopoulos S and Razis ED: Sustained complete remission of
metastatic dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans with imatinib mesylate.
Anticancer Drugs. 16:461–466. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rutkowski P, Debiec-Rychter M, Nowecki Z,
Michej W, Symonides M, Ptaszynski K and Ruka W: Treatment of
advanced dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans with imatinib mesylate
with or without surgical resection. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol.
25:264–270. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Price VE, Fletcher JA, Zielenska M, Cole
W, Viero S, Manson DE, Stuart M and Pappo AS: Imatinib mesylate: An
attractive alternative in young children with large, surgically
challenging dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Pediatr Blood Cancer.
44:511–515. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kohli N and Srivastava D:
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Dermatology Atlas for Skin of
Color. Jackson-Richards D and Pandya AG: (Berlin). Springer.
269–272. 2014.
|