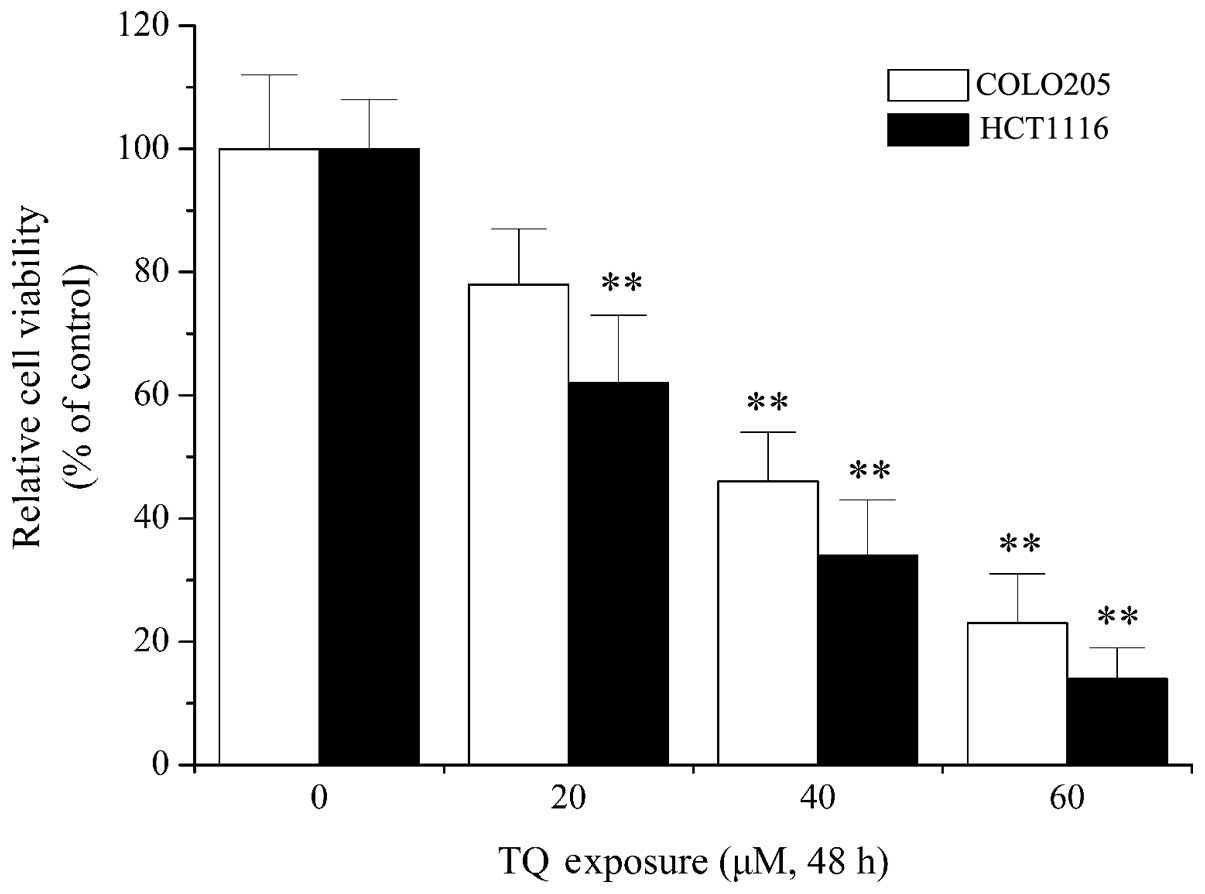
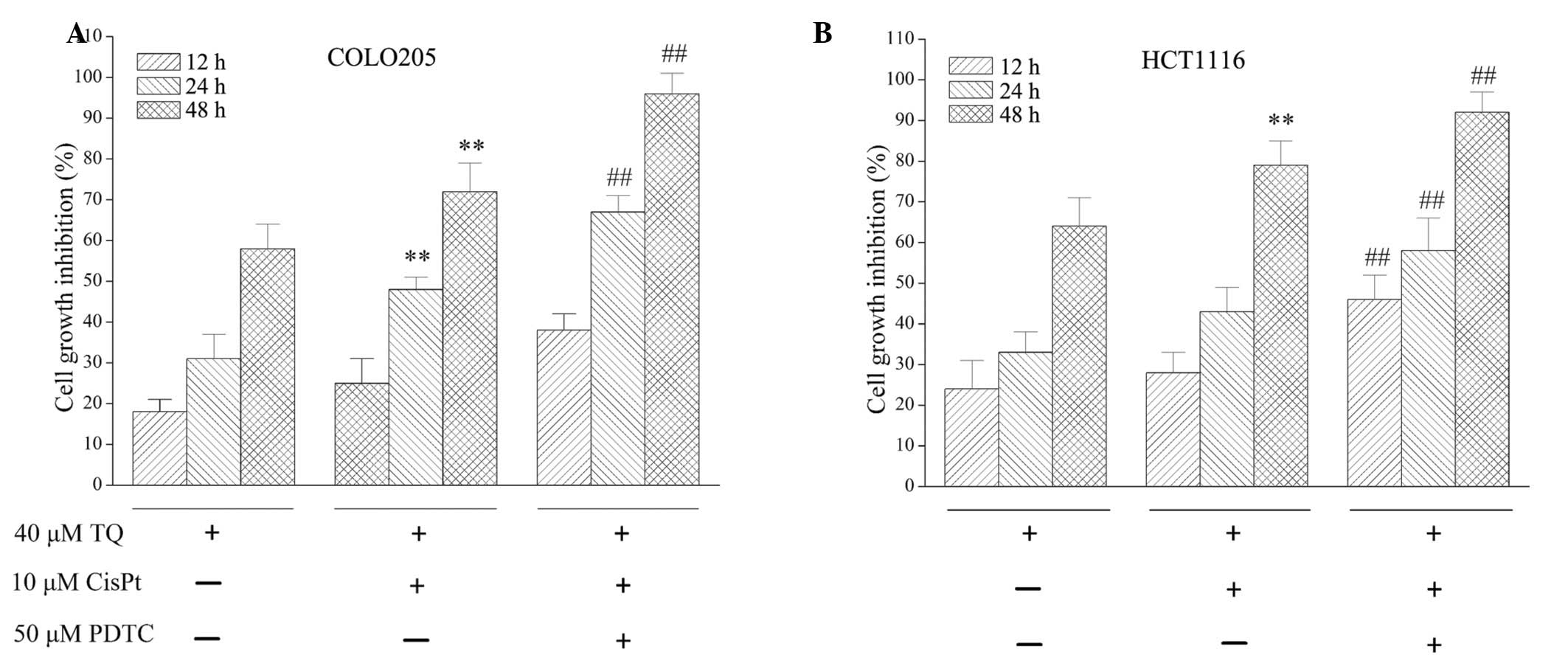
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jin P, Wu ZT, Li SR, Li SJ, Wang JH, Wang
ZH, Lu JG, Cui XJ, Han Y, Rao J and Sheng JQ: Colorectal cancer
screening with fecal occult blood test: A 22-year cohort study.
Oncol Lett. 6:576–582. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kim B and Giardiello FM: Chemoprevention
in familial adenomatous polyposis. Best Pract Res Clin
Gastroenterol. 25:607–622. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fini L, Piazzi G, Daoud Y, Selgrad M,
Maegawa S, Garcia M, Fogliano V, Romano M, Graziani G, Vitaglione
P, et al: Chemoprevention of intestinal polyps in ApcMin/+ mice fed
with western or balanced diets by drinking annurca apple polyphenol
extract. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 4:907–915. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rajput S and Mandal M: Antitumor promoting
potential of selected phytochemicals derived from spices: A review.
Eur J Cancer Prev. 21:205–215. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Woo CC, Kumar AP, Sethi G and Tan KH:
Thymoquinone: Potential cure for inflammatory disorders and cancer.
Biochem Pharmacol. 83:443–451. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Abukhader MM: Thymoquinone in the clinical
treatment of cancer: Fact or fiction? Pharmacogn Rev. 7:117–120.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Schneider-Stock R, Fakhoury IH, Zaki AM,
El-Baba CO and Gali-Muhtasib HU: Thymoquinone: Fifty years of
success in the battle against cancer models. Drug Discov Today.
19:18–30. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sutton KM, Greenshields AL and Hoskin DW:
Thymoquinone, a bioactive component of black caraway seeds, causes
G1 phase cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in triple-negative breast
cancer cells with mutant p53. Nutr Cancer. 66:408–418. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang J, Kuang XR, Lv PT and Yan XX:
Thymoquinone inhibits proliferation and invasion of human
nonsmall-cell lung cancer cells via ERK pathway. Tumour Biol.
36:259–269. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Siveen KS, Mustafa N, Li F, Kannaiyan R,
Ahn KS, Kumar AP, Chng WJ and Sethi G: Thymoquinone overcomes
chemoresistance and enhances the anticancer effects of bortezomib
through abrogation of NF-κB regulated gene products in multiple
myeloma xenograft mouse model. Oncotarget. 5:634–648. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mu GG, Zhang LL, Li HY, Liao Y and Yu HG:
Thymoquinone pretreatment overcomes the insensitivity and
potentiates the antitumor effect of gemcitabine through abrogation
of Notch1, PI3K/Akt/mTOR regulated signaling pathways in pancreatic
cancer. Dig Dis Sci. 60:1067–1080. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ichwan SJ, Al-Ani IM, Bilal HG, Suriyah
WH, Taher M and Ikeda MA: Apoptotic activities of thymoquinone, an
active ingredient of black seed (Nigella sativa), in cervical
cancer cell lines. Chin J Physiol. 57:249–255. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
El-Baba C, Mahadevan V, Fahlbusch FB, S
SM, Rau TT, Gali-Muhtasib H and Schneider-Stock R:
Thymoquinone-induced conformational changes of PAK1 interrupt
prosurvival MEK-ERK signaling in colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer.
13:2012014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dirican A, Atmaca H, Bozkurt E, Erten C,
Karaca B and Uslu R: Novel combination of docetaxel and
thymoquinone induces synergistic cytotoxicity and apoptosis in
DU-145 human prostate cancer cells by modulating PI3K-AKT pathway.
Clin Transl Oncol. 17:145–151. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chu SC, Hsieh YS, Yu CC, Lai YY and Chen
PN: Thymoquinone induces cell death in human squamous carcinoma
cells via caspase activation-dependent apoptosis and LC3-II
activation-dependent autophagy. PLoS One. 9:e1015792014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ashour AE, Abd-Allah AR, Korashy HM, Attia
SM, Alzahrani AZ, Saquib Q, Bakheet SA, Abdel-Hamied HE, Jamal S
and Rishi AK: Thymoquinone suppression of the human hepatocellular
carcinoma cell growth involves inhibition of IL-8 expression,
elevated levels of TRAIL receptors, oxidative stress and apoptosis.
Mol Cell Biochem. 389:85–98. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Salim LZ, Mohan S, Othman R, Abdelwahab
SI, Kamalidehghan B, Sheikh BY and Ibrahim MY: Thymoquinone induces
mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in
vitro. Molecules. 18:11219–11240. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Racoma IO, Meisen WH, Wang QE, Kaur B and
Wani AA: Thymoquinone inhibits autophagy and induces
cathepsin-mediated, caspase-independent cell death in glioblastoma
cells. PLoS One. 8:e728822013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Peng L, Liu A, Shen Y, Xu HZ, Yang SZ,
Ying XZ, Liao W, Liu HX, Lin ZQ, Chen QY, et al: Antitumor and
anti-angiogenesis effects of thymoquinone on osteosarcoma through
the NF-κB pathway. Oncol Rep. 29:571–578. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Paramasivam A, Sambantham S, Shabnam J, et
al: Anti-cancer effects of thymoquinone in mouse neuroblastoma
(Neuro-2a) cells through caspase-3 activation with down-regulation
of XIAP. Toxicol Lett. 213:151–159. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mu HQ, Yang S, Wang YJ and Chen YH: Role
of NF-κB in the anti-tumor effect of thymoquinone on bladder
cancer. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 92:392–396. 2012.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lei X, Lv X, Liu M, Yang Z, Ji M, Guo X
and Dong W: Thymoquinone inhibits growth and augments
5-fluorouracil-induced apoptosis in gastric cancer cells both in
vitro and in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 417:864–868. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nessa MU, Beale P, Chan C, Yu JQ and Huq
F: Synergism from combinations of cisplatin and oxaliplatin with
quercetin and thymoquinone in human ovarian tumour models.
Anticancer Res. 31:3789–3797. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Luo P, Tan Z, Zhang Z, Li H and Mo Z:
Inhibitory effects of salvianolic acid B on the high
glucose-induced mesangial proliferation via NF-κB-dependent
pathway. Biol Pharm Bull. 31:1381–1386. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lui VW, Boehm AL, Koppikar P, Leeman RJ,
Johnson D, Ogagan M, Childs E, Freilino M and Grandis JR:
Antiproliferative mechanisms of a transcription factor decoy
targeting signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)
3: The role of STAT1. Mol Pharmacol. 71:1435–1443. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rajput S, Kumar BN, Sarkar S, Das S, Azab
B, Santhekadur PK, Das SK, Emdad L, Sarkar D, Fisher PB and Mandal
M: Targeted apoptotic effects of thymoquinone and tamoxifen on XIAP
mediated Akt regulation in breast cancer. PLoS One. 8:e613422013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kolli-Bouhafs K, Boukhari A, Abusnina A,
Velot E, Gies JP, Lugnier C and Rondé P: Thymoquinone reduces
migration and invasion of human glioblastoma cells associated with
FAK, MMP-2 and MMP-9 down-regulation. Invest New Drugs.
30:2121–2131. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hussain AR, Ahmed M, Ahmed S, Manogaran P,
Platanias LC, Alvi SN, Al-Kuraya KS and Uddin S: Thymoquinone
suppresses growth and induces apoptosis via generation of reactive
oxygen species in primary effusion lymphoma. Free Radic Biol Med.
50:978–987. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gali-Muhtasib H, Ocker M, Kuester D,
Krueger S, El-Hajj Z, Diestel A, Evert M, El-Najjar N, Peters B,
Jurjus A, et al: Thymoquinone reduces mouse colon tumor cell
invasion and inhibits tumor growth in murine colon cancer models. J
Cell Mol Med. 12:330–342. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gali-Muhtasib H, Kuester D, Mawrin C,
Bajbouj K, Diestel A, Ocker M, Habold C, Foltzer-Jourdainne C,
Schoenfeld P, Peters B, et al: Thymoquinone triggers inactivation
of the stress response pathway sensor CHEK1 and contributes to
apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Res. 68:5609–5618.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shoieb AM, Elgayyar M, Dudrick PS, Bell JL
and Tithof PK: In vitro inhibition of growth and induction of
apoptosis in cancer cell lines by thymoquinone. Int J Oncol.
22:107–113. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Woo CC, Hsu A, Kumar AP, Sethi G and Tan
KH: Thymoquinone inhibits tumor growth and induces apoptosis in a
breast cancer xenograft mouse model: The role of p38 MAPK and ROS.
PLoS One. 8:e753562013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
El-Mahdy MA, Zhu Q, Wang QE, Wani G and
Wani AA: Thymoquinone induces apoptosis through activation of
caspase-8 and mitochondrial events in p53-null myeloblastic
leukemia HL-60 cells. Int J Cancer. 117:409–417. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li F, Rajendran P and Sethi G:
Thymoquinone inhibits proliferation, induces apoptosis and
chemosensitizes human multiple myeloma cells through suppression of
signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 activation
pathway. Br J Pharmacol. 161:541–554. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Badr G, Mohany M and Abu-Tarboush F:
Thymoquinone decreases F-actin polymerization and the proliferation
of human multiple myeloma cells by suppressing STAT3
phosphorylation and Bcl2/Bcl-XL expression. Lipids Health Dis.
10:2362011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
El-Najjar N, Chatila M, Moukadem H,
Vuorela H, Ocker M, Gandesiri M, Schneider-Stock R and
Gali-Muhtasib H: Reactive oxygen species mediate
thymoquinone-induced apoptosis and activate ERK and JNK signaling.
Apoptosis. 15:183–195. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gali-Muhtasib H, Diab-Assaf M, Boltze C,
Al-Hmaira J, Hartig R, Roessner A and Schneider-Stock R:
Thymoquinone extracted from black seed triggers apoptotic cell
death in human colorectal cancer cells via a p53-dependent
mechanism. Int J Oncol. 25:857–866. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lang M, Borgmann M, Oberhuber G, Evstatiev
R, Jimenez K, Dammann KW, Jambrich M, Khare V, Campregher C, Ristl
R and Gasche C: Thymoquinone attenuates tumor growth in ApcMin mice
by interference with Wnt-signaling. Mol Cancer. 12:412013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Jrah-Harzallah H, Ben-Hadj-Khalifa S,
Almawi WY, Maaloul A, Houas Z and Mahjoub T: Effect of Thymoquinone
on 1,2-dimethyl-hydrazine-induced oxidative stress during
initiation and promotion of colon carcinogenesis. Eur J Cancer.
49:1127–1135. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Asfour W, Almadi S and Haffar L:
Thymoquinone suppresses cellular proliferation, inhibits VEGF
production and obstructs tumor progression and invasion in the rat
model of DMH-induced colon carcinogenesis. Pharmacol Pharm. 4:7–17.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Velho-Pereira R, Kumar A, Pandey BN,
Jagtap AG and Mishra KP: Radiosensitization in human breast
carcinoma cells by thymoquinone: Role of cell cycle and apoptosis.
Cell Biol Int. 35:1025–1029. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jafri SH, Glass J, Shi R, Zhang S, Prince
M and Kleiner-Hancock H: Thymoquinone and cisplatin as a
therapeutic combination in lung cancer: In vitro and in vivo. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 29:872010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Banerjee S, Kaseb AO, Wang Z, Kong D,
Mohammad M, Padhye S, Sarkar FH and Mohammad RM: Antitumor activity
of gemcitabine and oxaliplatin is augmented by thymoquinone in
pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 69:5575–5583. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Housman G, Byler S, Heerboth S, Lapinska
K, Longacre M, Snyder N and Sarkar S: Drug resistance in cancer: An
overview. Cancers (Basel). 6:1769–1792. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Aggarwal BB: Nuclear factor-kappaB: The
enemy within. Cancer Cell. 6:203–208. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Shishodia S and Aggarwal BB: Nuclear
factor-kappaB activation mediates cellular transformation,
proliferation, invasion angiogenesis and metastasis of cancer.
Cancer Treat Res. 119:139–173. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ahn KS and Aggarwal BB: Transcription
factor NF-kappaB: A sensor for smoke and stress signals. Ann NY
Acad Sci. 1056:218–233. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Nair A, Venkatraman M, Maliekal TT, Nair B
and Karunagaran D: NF-kappaB is constitutively activated in
high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions and squamous cell
carcinomas of the human uterine cervix. Oncogene. 22:50–58. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Li W, Tan D, Zenali MJ and Brown RE:
Constitutive activation of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB) signaling
pathway in fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 3:238–243. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Nagel D, Vincendeau M, Eitelhuber AC and
Krappmann D: Mechanisms and consequences of constitutive NF-κB
activation in B-cell lymphoid malignancies. Oncogene. 33:5655–5665.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Baldwin AS: Control of oncogenesis and
cancer therapy resistance by the transcription factor NF-kappaB. J
Clin Invest. 107:241–246. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Shen HM and Tergaonkar V: NFkappaB
signaling in carcinogenesis and as a potential molecular target for
cancer therapy. Apoptosis. 14:348–363. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wang S, Liu Z, Wang L and Zhang X:
NF-kappaB signaling pathway, inflammation and colorectal cancer.
Cell Mol Immunol. 6:327–334. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|