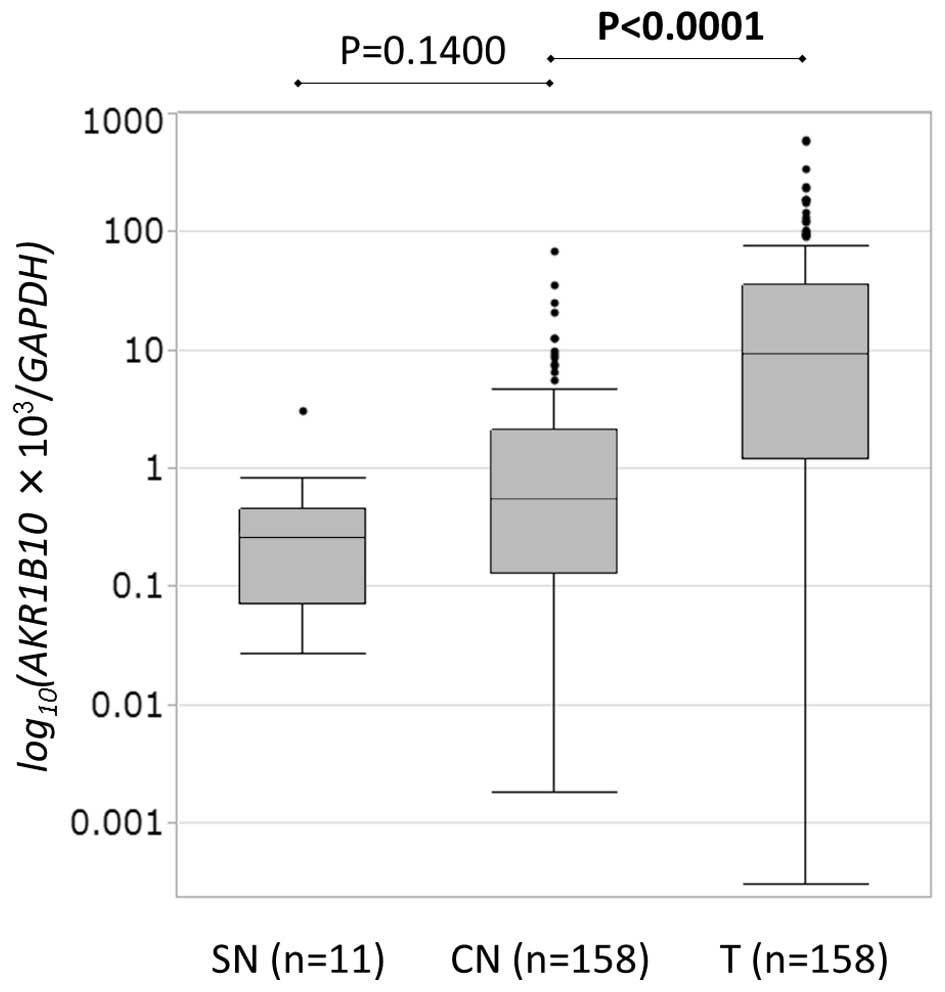
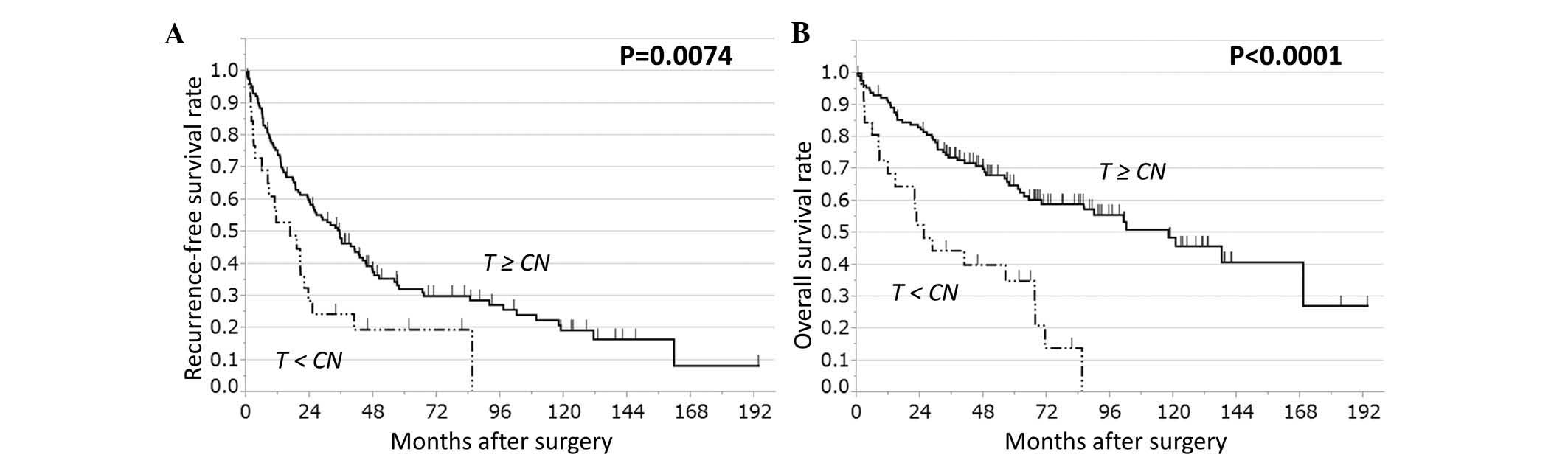
|
1
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rahbari NN, Mehrabi A, Mollberg NM, Müller
SA, Koch M, Büchler MW and Weitz J: Hepatocellular carcinoma:
Current management and perspectives for the future. Ann Surg.
253:453–469. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kobayashi A, Kawasaki S, Miyagawa S, Miwa
S, Noike T, Takagi S, Iijima S and Miyagawa Y: Results of 404
hepatic resections including 80 repeat hepatectomies for
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology. 53:736–741.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen MS, Li JQ, Zheng Y, Guo RP, Liang HH,
Zhang YQ, Lin XJ and Lau WY: A prospective randomized trial
comparing percutaneous local ablative therapy and partial
hepatectomy for small hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg.
243:321–328. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Taura K, Ikai I, Hatano E, Fujii H, Uyama
N and Shimahara Y: Implication of frequent local ablation therapy
for intrahepatic recurrence in prolonged survival of patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing hepatic resection: An analysis
of 610 patients over 16 years old. Ann Surg. 244:265–273. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen PJ, Chen DS, Lai MY, Chang MH, Huang
GT, Yang PM, Sheu JC, Lee SC, Hsu HC and Sung JL: Clonal origin of
recurrent hepatocellular carcinomas. Gastroenterology. 96:527–529.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Imamura H, Matsuyama Y, Tanaka E, Ohkubo
T, Hasegawa K, Miyagawa S, Sugawara Y, Minagawa M, Takayama T,
Kawasaki S and Makuuchi M: Risk factors contributing to early and
late phase intrahepatic recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma
after hepatectomy. J Hepatol. 38:200–207. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Portolani N, Coniglio A, Ghidoni S,
Giovanelli M, Benetti A, Tiberio GA and Giulini SM: Early and late
recurrence after liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma:
Prognostic and therapeutic implications. Ann Surg. 243:229–235.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cucchetti A, Piscaglia F, Caturelli E,
Benvegnù L, Vivarelli M, Ercolani G, Cescon M, Ravaioli M, Grazi
GL, Bolondi L and Pinna AD: Comparison of recurrence of
hepatocellular carcinoma after resection in patients with cirrhosis
to its occurrence in a surveilled cirrhotic population. Ann Surg
Oncol. 16:413–422. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Matsuda M, Fujii H, Kono H and Matsumoto
Y: Surgical treatment of recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma based
on the mode of recurrence: Repeat hepatic resection or ablation are
good choices for patients with recurrent multicentric cancer. J
Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 8:353–359. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Morimoto O, Nagano H, Sakon M, Fujiwara Y,
Yamada T, Nakagawa H, Miyamoto A, Kondo M, Arai I, Yamamoto T, et
al: Diagnosis of intrahepatic metastasis and multicentric
carcinogenesis by microsatellite loss of heterozygosity in patients
with multiple and recurrent hepatocellular carcinomas. J Hepatol.
39:215–221. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nomoto S, Yamashita K, Koshikawa K, Nakao
A and Sidransky D: Mitochondrial D-loop mutations as clonal markers
in multicentric hepatocellular carcinoma and plasma. Clin Cancer
Res. 8:481–487. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nomoto S, Kinoshita T, Kato K, Otani S,
Kasuya H, Takeda S, Kanazumi N, Sugimoto H and Nakao A:
Hypermethylation of multiple genes as clonal markers in
multicentric hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 97:1260–1265.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kumada T, Nakano S, Takeda I, Sugiyama K,
Osada T, Kiriyama S, Sone Y, Toyoda H, Shimada S, Takahashi M and
Sassa T: Patterns of recurrence after initial treatment in patients
with small hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 25:87–92. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Stangegaard M: Gene expression analysis
using agilent DNA microarrays. Methods Mol Biol. 529:133–145. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tsai SJ and Wiltbank MC: Quantification of
mRNA using competitive RT-PCR with standard-curve methodology.
Biotechniques. 21:862–866. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang Z, Zhang G, Wu J and Jia M: Adjuvant
therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: Current situation and
prospect. Drug Discov Ther. 7:137–143. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Takenaka K, Adachi E, Nishizaki T,
Hiroshige K, Ikeda T, Tsuneyoshi M and Sugimachi K: Possible
multicentric occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma: A
clinicopathological study. Hepatology. 19:889–894. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cao D, Fan ST and Chung SS: Identification
and characterization of a novel human aldose reductase-like gene. J
Biol Chem. 273:11429–11435. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Endo H, Shiroki T, Nakagawa T, Yokoyama M,
Tamai K, Yamanami H, Fujiya T, Sato I, Yamaguchi K, Tanaka N, et
al: Enhanced expression of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR is associated
with the development of gastric cancer. PLoS One. 8:e770702013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kang MW, Lee ES, Yoon SY, Jo J, Lee J, Kim
HK, Choi YS, Kim K, Shim YM, Kim J and Kim H: AKR1B10 is associated
with smoking and smoking-related non-small-cell lung cancer. J Int
Med Res. 39:78–85. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang W, Li H, Yang Y, Liao J and Yang GY:
Knockdown or inhibition of aldo-keto reductase 1B10 inhibits
pancreatic carcinoma growth via modulating Kras-E-cadherin pathway.
Cancer Lett. 355:273–280. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Heringlake S, Hofdmann M, Fiebeler A,
Manns MP, Schmiegel W and Tannapfel A: Identification and
expression analysis of the aldo-ketoreductase1-B10 gene in primary
malignant liver tumours. J Hepatol. 52:220–227. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Schmitz KJ, Sotiropoulos GC, Baba HA,
Schmid KW, Müller D, Paul A, Auer T, Gamerith G and Loeffler-Ragg
J: AKR1B10 expression is associated with less aggressive
hepatocellular carcinoma: A clinicopathological study of 168 cases.
Liver Int. 31:810–816. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Matkowskyj KA, Bai H, Liao J, Zhang W, Li
H, Rao S, Omary R and Yang GY: Aldoketoreductase family 1B10
(AKR1B10) as a biomarker to distinguish hepatocellular carcinoma
from benign liver lesions. Hum Pathol. 45:834–843. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tsuzura H, Genda T, Sato S, Murata A,
Kanemitsu Y, Narita Y, Ishikawa S, Kikuchi T, Mori M, Hirano K, et
al: Expression of aldo-keto reductase family 1 member b10 in the
early stages of human hepatocarcinogenesis. Int J Mol Sci.
15:6556–6568. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sato S, Genda T, Hirano K, Tsuzura H,
Narita Y, Kanemitsu Y, Kikuchi T, Iijima K, Wada R and Ichida T:
Up-regulated aldo-keto reductase family 1 member B10 in chronic
hepatitis C: Association with serum alpha-fetoprotein and
hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 32:1382–1390. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kosuge T, Makuuchi M, Takayama T, Yamamoto
J, Shimada K and Yamasaki S: Long-term results after resection of
hepatocellular carcinoma: Experience of 480 cases.
Hepatogastroenterology. 40:328–332. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Izumi R, Shimizu K, Ii T, Yagi M, Matsui
O, Nonomura A and Miyazaki I: Prognostic factors of hepatocellular
carcinoma in patients undergoing hepatic resection.
Gastroenterology. 106:720–727. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hanazaki K, Kajikawa S, Koide N, Adachi W
and Amano J: Prognostic factors after hepatic resection for
hepatocellular carcinoma with hepatitis C viral infection:
Univariate and multivariate analysis. Am J Gastroenterol.
96:1243–1250. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|