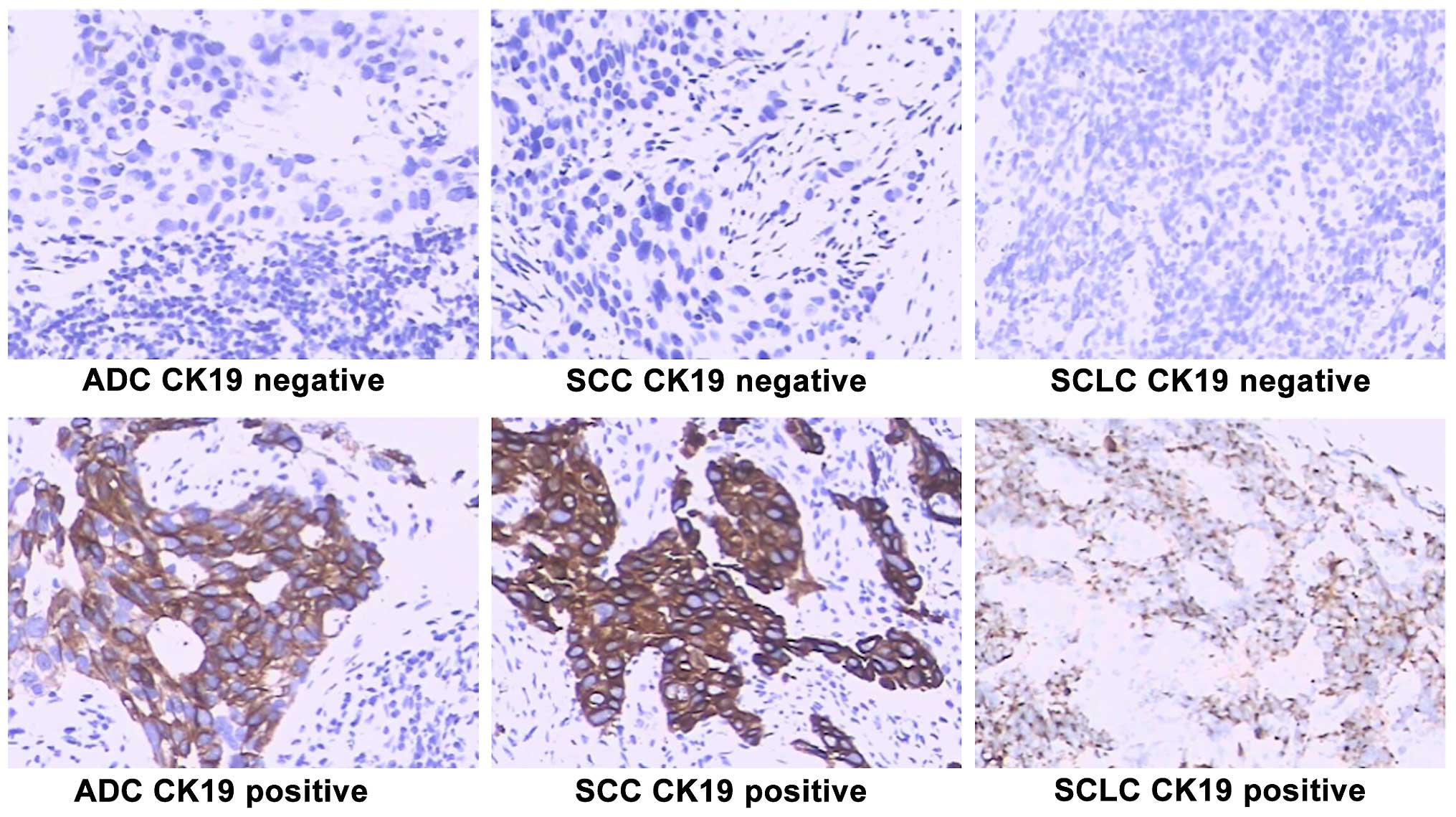
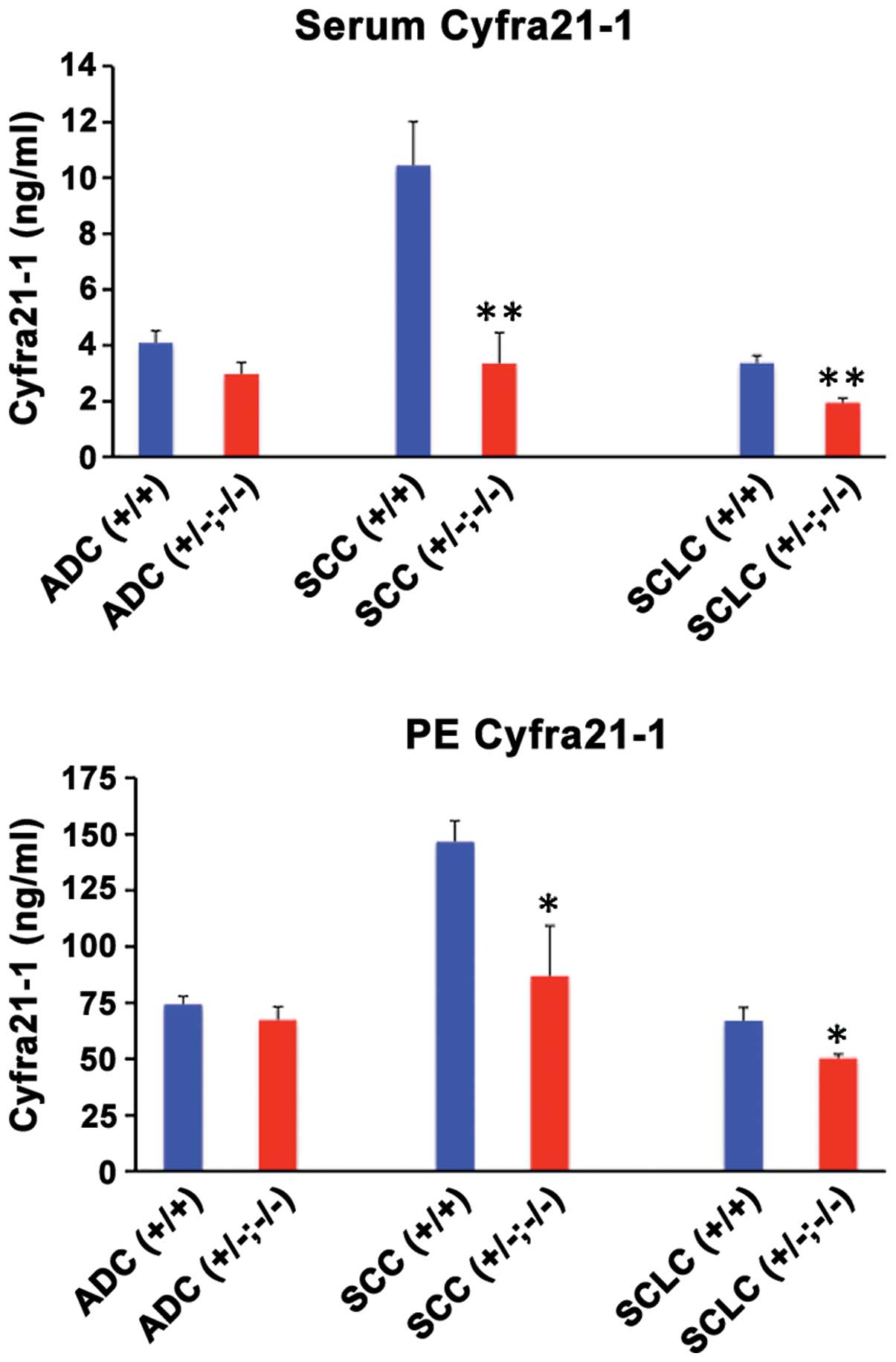
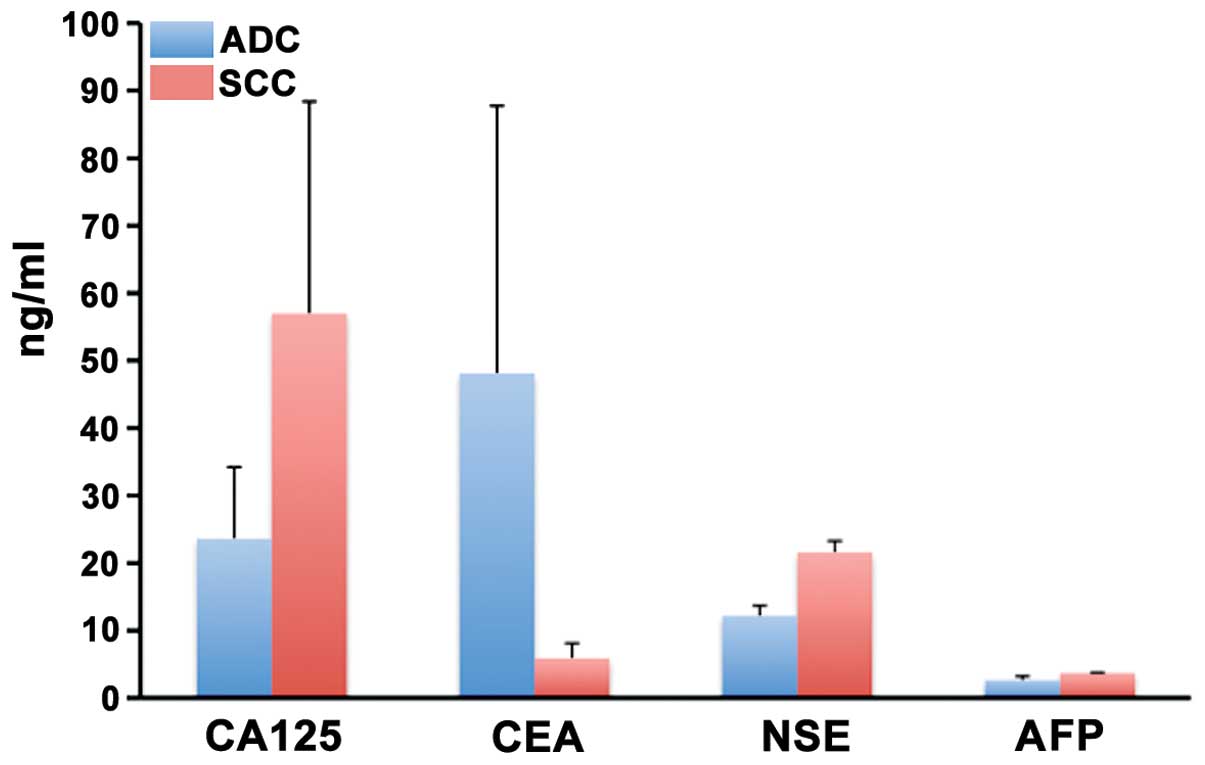
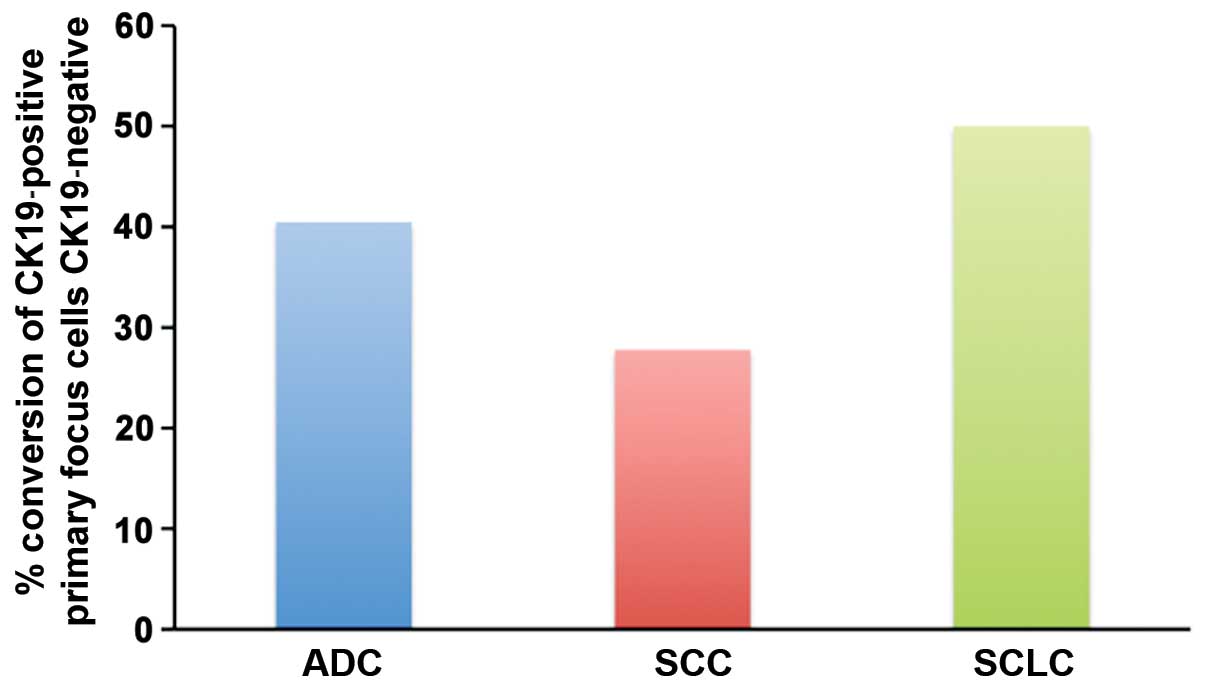
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Haghgoo SM, Allameh A, Mortaz E, Garssen
J, Folkerts G, Barnes PJ and Adcock IM: Pharmacogenomics and
targeted therapy of cancer: Focusing on non-small cell lung cancer.
Eur J Pharmacol. 754:82–91. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Morales-Oyarvide V and Mino-Kenudson M:
High-grade lung adenocarcinomas with micropapillary and/or solid
patterns: A review. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 20:317–323. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Burdett S, Stewart LA and Rydzewska L: A
systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature: Chemotherapy
and surgery versus surgery alone in non-small cell lung cancer. J
Thorac Oncol. 1:611–621. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Travis WD: Pathology of lung cancer. Clin
Chest Med. 2365–81. (viii)2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bastawisy AE, Azzouny ME, Mohammed G,
Allah AA and Behiry E: Serum cytokeratin 19 fragment in advanced
lung cancer: Could we eventually have a serum tumor marker?
Ecancermedicalscience. 8:3942014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hsieh TC, Huang WW, Lai CL, Tsao SM and Su
CC: Diagnostic value of tumor markers in lung
adenocarcinoma-associated cytologically negative pleural effusions.
Cancer Cytopathol. 121:483–488. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liang QL, Shi HZ, Qin XJ, Liang XD, Jiang
J and Yang HB: Diagnostic accuracy of tumour markers for malignant
pleural effusion: A meta-analysis. Thorax. 63:35–41. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Miedouge M, Rouzaud P, Salama G, et al:
Evaluation of seven tumour markers in pleural fluid for the
diagnosis of malignant effusions. Br J Cancer. 81:1059–1065. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Huang WW, Tsao SM, Lai CL, Su CC and Tseng
CE: Diagnostic value of Her-2/neu, Cyfra 21–1, and carcinoembryonic
antigen levels in malignant pleural effusions of lung
adenocarcinoma. Pathology. 42:224–228. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Riantawan P, Sangsayan P, Bangpattanasiri
K and Rojanaraweewong P: Limited additive value of pleural fluid
carcinoembryonic antigen level in malignant pleural effusion.
Respiration. 67:24–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hay ED: The mesenchymal cell, its role in
the embryo, and the remarkable signaling mechanisms that create it.
Dev Dyn. 233:706–720. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Guarino M, Micheli P, Pallotti F and
Giordano F: Pathological relevance of epithelial and mesenchymal
phenotype plasticity. Pathol Res Pract. 195:379–389. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Guarino M, Rubino B and Ballabio G: The
role of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer pathology.
Pathology. 39:305–318. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chunhacha P, Sriuranpong V and
Chanvorachote P: Epithelial- mesenchymal transition mediates
anoikis resistance and enhances invasion in pleural
effusion-derived human lung cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 5:1043–1047.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kosacka M and Jankowska R: Comparison of
cytokeratin 19 expression in tumor tissue and serum CYFRA 21–1
levels in non-small cell lung cancer. Pol Arch Med Wewn. 119:33–37.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xu GP, Li QQ, Cao XX, Chen Q, Zhao ZH,
Diao ZQ and Xu ZD: The effect of TGF-β1 and Smad7 gene transfer on
the phenotypic changes of rat alveolar epithelial cells. Cell Mol
Biol Lett. 12:457–472. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Romero S, Fernández C, Arriero JM, Espasa
A, Candela A, Martín C and Sánchez-Payá J: CEA, CA 15–3 and CYFRA
21–1 in serum and pleural fluid of patients with pleural effusions.
Eur Respir J. 9:17–23. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fujisue M, Nishimura R, Okumura Y, Tashima
R, Nishiyama Y, Osako T, Toyozumi Y and Arima N: Clinical
significance of ck19 negative breast cancer. Cancers (Basel).
5:1–11. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pietanza MC, Byers LA, Minna JD and Rudin
CM: Small cell lung cancer: Will recent progress lead to improved
outcomes? Clin Cancer Res. 21:2244–2255. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ono A, Takahashi T, Mori K, Akamatsu H,
Shukuya T, Taira T, Kenmotsu H, Naito T, Murakami H, Nakajima T, et
al: Prognostic impact of serum CYFRA 21–1 in patients with advanced
lung adenocarcinoma: A retrospective study. BMC Cancer. 13:3542013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bachman KE and Park BH: Duel nature of
TGF-beta signaling: Tumor suppressor vs. tumor promoter. Curr Opin
Oncol. 17:49–54. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wakefield LM and Roberts AB: TGF-β
signaling: positive and negative effects on tumorigenesis. Curr
Opin Genet Dev. 12:22–29. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Akhurst RJ and Derynck R: TGF-β signaling
in cancer - a double-edged sword. Trends Cell Biol. 11:S44–S51.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jakowlew SB: Transforming growth
factor-beta in cancer and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
25:435–457. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gold LI: The role for transforming growth
factor-beta (TGF-beta) in human cancer. Crit Rev Oncog. 10:303–360.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Guadamillas MC, Cerezo A and Del Pozo MA:
Overcoming anoikis-pathways to anchorage-independent growth in
cancer. J Cell Sci. 124:3189–3197. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ko H, Kim S, Jin CH, Lee E, Ham S, Yook JI
and Kim K: Protein kinase casein kinase 2-mediated upregulation of
N-cadherin confers anoikis resistance on esophageal carcinoma
cells. Mol Cancer Res. 10:1032–1038. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|